biopsychology
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
what are the 2 divisions of the nervous system and what do they consist off
central nervous system - brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system - somatic and autonomic - has 2 other divisions sympathetic and parasympathetic
role of CNS
receives, processes, interprets, and stores sensory information. - brain
controls reflex activicties - spinal cord
what is the role of cerebrum and cerebellum
The brain has four main areas:
Cerebrum:
-main outer layer of the brain.
-split in two halves.
divided into four main areas; frontal lobe for thought, occipital lobe for vision, motor cortex for movement and auditory cortex for speech.
Cerebellum: motor skills and balance
what is the role of diencephalon - what 2 past of the brain does it consist of and what do they do
what is the role of the brain stem
Diencephalon: comprises the thalamus (relay station sending nerve impulses from
senses to correct area of brain for processing) and the hypothalamus (memory, hunger,
thirst)
Brain Stem: regulates automatic functions e.g. breathing
features of the Peripheral nervous system and their roles
somatic - controls voluntary movement
autonomic system - controls involuntary response these can be sympathetic - fight or flight or parasympathetic rest or digest
what is peripheral nervous system and what’s its main role
it comprises of all nerves located outside the brain and spinal cord.
Its main role is to relay messages between the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the body’s muscles, organs, and senses.
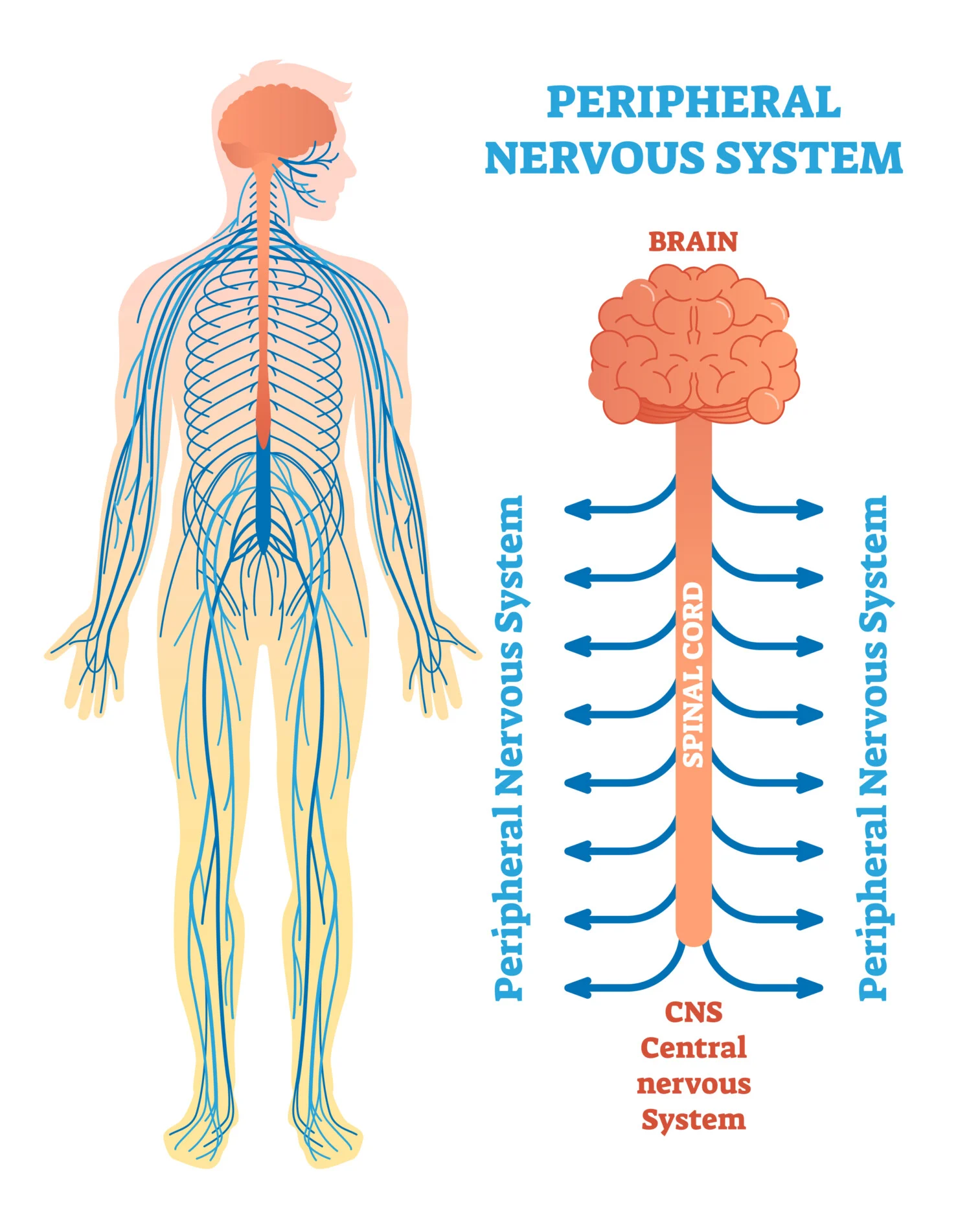
What is the Somatic Nervous System (SNS)?
The Somatic Nervous System is part of the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) and is involved in voluntary control of body movements.
It consists of:
Sensory Receptors: These carry information from sensory organs (skin, eyes, ears) to the spinal cord and brain.
What is the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)?
The Autonomic Nervous System is also part of the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) and regulates involuntary internal processes, ensuring homeostasis (the body's stable internal environment).
Role:
Transmits information to and from internal organs (heart, lungs, stomach, etc.).
Controls unconscious bodily functions, such as heart rate, digestion,and body temperature.
Components:
two branches:
Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS):
Function: Prepares the body for fight or flight in response to stress or danger.
Physiological Responses:
Increased heart rate, blood pressure.
Dilation of pupils.
Increased blood flow to muscles.
Purpose: Helps the body respond quickly to threats.
Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS):
Function: Restores the body to its normal, restful state after the threat is over (i.e., “rest and digest”).
Physiological Responses:
Decreases heart rate and blood pressure.
Stimulates digestive processes (e.g., salivation, digestion).
Encourages relaxation and recovery.
Purpose: Helps the body conserve energy and return to balance.