M5: CLEFT LIP & PALATE ASSESSMENT
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
INCIDENCE
1.94 per 1000 live births for cleft lip and palate | CLEFT LIP: Recurrence rate of 23 per 1000 CLEFT PALATE FOR NON-SYNDROMIC CLEFTS: 14 per 1000 | ||||
SYNDROMIC CONDITIONS WITH OR W/O CLEFT | |||||
CHINESE: 1.30 JAPANESE: 1.34 ASIAN: 1.47 | TOTAL: 1.33 per 1000 live births | ||||
NON-SYNDROMIC CONDITIONS WITH OR W/O CLEFT | |||||
CHINESE: 1.20 JAPANESE: 1.18 OTHER ASIANS: 1.22 | TOTAL: 1.19 per 1000 live births | ||||
SYNDROMIC CONDITIONS WITH OR W/O CLEFT
CHINESE: 1.30 JAPANESE: 1.34 ASIAN: 1.47 | TOTAL: 1.33 per 1000 live births |
NON-SYNDROMIC CONDITIONS WITH OR W/O CLEFT
CHINESE: 1.20 JAPANESE: 1.18 OTHER ASIANS: 1.22 | TOTAL: 1.19 per 1000 live births |
VISUAL EXAMINATION
Normal variations in structure = unusual characteristics; but not abnormal → abnormalities may have no relation in speech | Determine PHYSICAL FACTORS that appear to interfere with ARTICULATION and/or RESONANCE → other anomalies must also be noted |
PHYSICAL FACTORS, ARTICULATION, RESONANCE
Determine _________ that appear to interfere with _______ and/or _______ → other anomalies must also be noted
EYES
→ spaces between the eyes
HYPERTELORISM | HYPOTELORISM | PALPEBRAL FISSURE |
Excessive space between eyes | Too little space between eyes | Narrow palpebral fissure may indicate congenital craniofacial condition |
HYPERTELORISM
Excessive space between eyes
HYPOTELORISM
Too little space between eyes
PALPEBRAL FISSURE
Narrow palpebral fissure may indicate congenital craniofacial condition
EARS
→ shape, position, symmetry
If development interrupted = ears can be found somewhere else
NOSE AND AIRWAY
→ SHAPE: flattened nares
→ FLARING: nasal patency → if nose is wide, so will the flare be
LIPS
→ closure during rest and speech, symmetry, scarring, lip pits, mobility
LIP PITS | MANDIBLE |
→ van der woude syndrome → indentation in the lips → without cleft lip = no implication in speech | → v-shape → indication of craniofacial condition → narrow maxillary/mandibulary arch → placement of tongue (macro/microglossia) |
LIP PITS
→ van der woude syndrome
→ indentation in the lips
→ without cleft lip = no implication in speech
van der woude syndrome
lips pits are also known as ______
MANDIBLE
→ v-shape
→ indication of craniofacial condition
→ narrow maxillary/mandibulary arch
→ placement of tongue (macro/microglossia)
HARD PALATE
MUCOSA | POSITION OF ALVEOLAR RIDGE | PALATAL VAULT | MAXILLARY ARCH | ||||||||
Color, rugae, incisive papilla | Dome shape | ||||||||||
SCARS OF CLEFTING | FISTULAS | SUBMUCOUS CLEFT | |||||||||
Position, size, small opening on palate | Notch in the border of h/s palate | ||||||||||
MUCOSA
Color, rugae, incisive papilla
PALATAL VAULT
Dome shape
FISTULAS
Position, size, small opening on palate
→ Anterior to velar dimple: affect resonance
→ Posterior to velar dimple: no significant effect
→ ORONASAL FISTULA: somewhere between nose and alveolar ridge
SUBMUCOUS CLEFT
Notch in the border of h/s palate
→ Bifid uvula; hypoplastic uvula
→ HYPOPLASTIC: doesn’t move around
→ HYPERNASALITY
Anterior to velar dimple
affect resonance
Posterior to velar dimple
no significant effect
ORONASAL FISTULA
somewhere between nose and alveolar ridge
COMPLETE CLEFT
From outside all the way back
HYPOPLASTIC
doesn’t move around
PALATAL FISTULA
→ Seen immediately
→ nasal emissions present
ALVEOLUS FISTULA
→ underneath the lips
→ most have problem with dentition
POSTERIOR AND LATERAL PHARYNGEAL WALLS
→ movement
→ thorough evaluation of pharyngeal walls require instrumentation
PASSAVANT’S RIDGE | → Help occlude the pharynx → look at the movement of the muscles, both side and back in sync with elevation of the soft palate |
PASSAVANT’S RIDGE
→ Help occlude the pharynx
→ look at the movement of the muscles, both side and back in sync with elevation of the soft palate
TONSILS
→ located between anterior and posterior faucial pillars
→ non-existent among adults but present in children → begin to shrink as child reaches puberty
0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
Absent | Small | Estend beyond edge of faucial pillars | Beyond the pillars | Large, meeting at the midline |
EFFECTS ON VELAR MOVEMENT
→ tonsils → in between → tonsils are enlarged, it will get in the way of your movement
→ forcing out voice without help of palatal elevation
EFFECTS ON VELAR MOVEMENT
→ tonsils → in between → tonsils are enlarged, it will get in the way of your movement
→ forcing out voice without help of palatal elevation
0
Absent
1
Small
2
Extend beyond edge of faucial pillars
3
Beyond the pillars
4
Large, meeting at the midline
DENTAL AND OCCLUSION
→ alignment of mandible vs maxilla
→ molar alignment not frontal incisors
→ no teeth: children with CLAP = prone to poor dental hygiene (90%)
OCCLUSION | ||
CLASS I | CLASS II | CLASS III |
Normal occlusion | Retruded mandible (overbite) | Protruded mandible (underbite) |
+Open bite and cross bite
CLASS I
Normal occlusion
CLASS II
Retruded mandible (overbite)
CLASS III
Protruded mandible (underbite)
MALOCCLUSION
CROSSBITE | ANTERIOR CROSSBITE | LATERAL CROSSBITE |
Maxillary teeth are inside the mandibular teeth | Maxillary incisors | Small maxillary arch |
DEEP BITE | OVERJET | UNDERJET |
Excessive vertical overlap (crowding in oral cavity) | Incisors labioverted | Incisors are linguaverted |
SUPERNUMERARY TEETH | Children with alot of teeth | |
+Clefts, supernumerary teeth
CROSSBITE
Maxillary teeth are inside the mandibular teeth
ANTERIOR CROSSBITE
Maxillary incisors
LATERAL CROSSBITE
Small maxillary arch
DEEP BITE
Excessive vertical overlap (crowding in oral cavity)
OVERJET
Incisors labioverted
UNDERJET
Incisors are linguaverted
SUPERNUMERARY TEETH
Children with alot of teeth
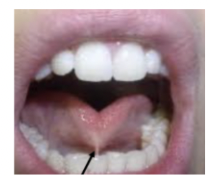
TONGUE
Size in relation to mandibular arch, palatal arch, oral cavity, micro-macroglossia, glossoptosis | GLOSSOPTOSIS | COLOR | LINGUAL FRENULUM | MOBILITY | |||||
Drooping of tongue | Pale-ish reddish pink | → tiny tissue underneath the tongue INSERTION/POSITION: has to be ¾ of the length underneath the tongue | → Elevation, lateral, curling → a lot of children with cleft lip and palate can still move their tongue | ||||||
ANKYLOGLOSSIA tongue-tied , difficulty with vowels, alveolar sounds, some people are born with this even if they don’t have cleft | |||||||||
LINGUAL FRENUM | LINGUAL CLEAVAGE | ||||||||
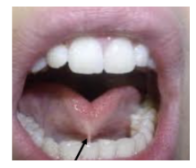 | 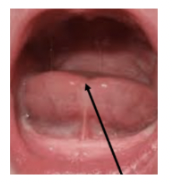 | ||||||||
GLOSSOPTOSIS
Drooping of tongue
TONGUE COLOR
Pale-ish reddish pink
LINGUAL FRENULUM
→ tiny tissue underneath the tongue
INSERTION/POSITION: has to be ¾ of the length underneath the tongue
TONGUE INSERTION/POSITION
has to be ¾ of the length underneath the tongue
TONGUE MOBILITY
→ Elevation, lateral, curling
→ a lot of children with cleft lip and palate can still move their tongue
ANKYLOGLOSSIA
tongue-tied , difficulty with vowels, alveolar sounds, some people are born with this even if they don’t have cleft
LINGUAL FRENUM
LINGUAL CLEAVAGE
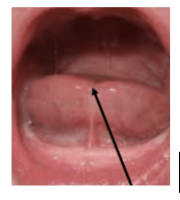
DIRECT EVALUATION
INDIRECT EVALUATION
MANNER OF EVALUATION
DIRECT EVALUATION
→ procedures that give direct information to the examiner such as allowing examination of the anatomical and physiological defects that causes velopharyngeal dysfunction
VIDEOFLUOROSCOPY | NASOPHARYNGOSCOPY/ENDOSCOPY |
→ xray with movement; moving image of the internal part of the mouth → view of the entire length of the pharyngeal wall → helpful in determining surgical and prosthetic options for vp dysfunction treatment → helpful is assessing placement of prosthetic device → evaluate effects of SURGICAL PROCEDURES → has pre- and post-surgical information ADVANTAGES
USES
| ENDOSCOPY → procedure that allows VISUALIZATION of the interior of a canal or hollow organ by means of a special instrument → assess structure and function of the vocal tract → provides the examiner opportunity to observe ARTICULATION, PHONATION, RESONANCE, AND SWALLOWING NASOPHARYNGOSCOPY → commonly used in clinical setting for the evaluation of VP dysfunction → view of all structures of the VP valve and function during speech → clear rationale for design and placement of pharyngoplasty surgery; pharyngeal flaps → INSTRUMENT TO ASSESS EFFECTIVITY OF FLAPS: sphincteroplasty or retropharyngeal implant → examine larynx and vocal folds → used to assess swallowing
ADVANTAGES
|
VIDEOFLUOROSCOPY
→ xray with movement; moving image of the internal part of the mouth
→ view of the entire length of the pharyngeal wall
→ helpful in determining surgical and prosthetic options for vp dysfunction treatment
→ helpful is assessing placement of prosthetic device
→ evaluate effects of SURGICAL PROCEDURES
→ has pre- and post-surgical information
ADVANTAGES
Use of cineradiography and AUDIO RECORDING
Does not require film developing/processing
Reduction in the exposure to RADIATION
USES
Evaluate STRUCTURE and function of the VP MECHANISM
Can confirm VP opening and determine size and relative shape of opening
Helpful in assessing extent and symmetry of lateral pharyngeal wall movement, upward mov’t of velum during speech
VIDEOFLUOROSCOPY ADVANTAGES
Use of cineradiography and AUDIO RECORDING
Does not require film developing/processing
Reduction in the exposure to RADIATION
VIDEOFLUOROSCOPY USES
Evaluate STRUCTURE and function of the VP MECHANISM
Can confirm VP opening and determine size and relative shape of opening
Helpful in assessing extent and symmetry of lateral pharyngeal wall movement, upward mov’t of velum during speech
ENDOSCOPY
→ procedure that allows VISUALIZATION of the interior of a canal or hollow organ by means of a special instrument
→ assess structure and function of the vocal tract
→ provides the examiner opportunity to observe ARTICULATION, PHONATION, RESONANCE, AND SWALLOWING
NASOPHARYNGOSCOPY
→ commonly used in clinical setting for the evaluation of VP dysfunction
→ view of all structures of the VP valve and function during speech
→ clear rationale for design and placement of pharyngoplasty surgery; pharyngeal flaps
→ INSTRUMENT TO ASSESS EFFECTIVITY OF FLAPS: sphincteroplasty or retropharyngeal implant
→ examine larynx and vocal folds
→ used to assess swallowing
FIBEROPTIC ENDOSCOPIC EVALUATION OF SWALLOWING (FEES)
sphincteroplasty or retropharyngeal implant
INSTRUMENT TO ASSESS EFFECTIVITY OF FLAPS:
FIBEROPTIC ENDOSCOPIC EVALUATION OF SWALLOWING
used to assess swallowing
NASOPHARYNGOSCOPY/ENDOSCOPY ADVANTAGES
No radiation exposure
May be repeated frequently
Ease of administration
Generally painless
Easy to record
Accessible
Therapeutic applications
INDIRECT EVALUATION
→ do not allow visualization of the structures. Provide OBJECTIVE DATA regarding the results of velopharyngeal function such as AIRFLOW, AIR PRESSURE, or ACOUSTIC output
NASOMETER | ADVANTAGES | ||||
→ computer based instrument developed by Adams McCutcheon and Fletcher. → measures the relative amount of nasal acoustic energy in an individual’s speech → measure air flow and aerodynamics NASALANCE = N/(N+O) X 100 Nasalance scores = compared with normative data Acoustic energy is captured in both NASAL and ORAL sources. Value is converted → nasalance score → determines hypernasality and hyponasality | → easy, non-invasive procedure → substantiates objective findings → provides a visual display/feedback → can be used for treatment | ||||
GOLD STANDARD FOR CLEFT PALATE EVALUATION | |||||
→ nasopharyngoscopy, nasometry | |||||
NASOMETER
→ computer based instrument developed by Adams McCutcheon and Fletcher.
→ measures the relative amount of nasal acoustic energy in an individual’s speech
→ measure air flow and aerodynamics
NASALANCE = N/(N+O) X 100
Nasalance scores = compared with normative data
Acoustic energy is captured in both NASAL and ORAL sources. Value is converted → nasalance score → determines hypernasality and hyponasality
NASOMETER ADVANTAGES
→ easy, non-invasive procedure
→ substantiates objective findings
→ provides a visual display/feedback
→ can be used for treatment
nasopharyngoscopy, nasometry
GOLD STANDARD FOR CLEFT PALATE EVALUATION
AIR PADDLE
→ use ordinary bond paper not carotolina or tissue
→ most effective to check for NAE
DENTAL MIRROR
check misting
LISTENING TUBE
amplify and monitor nasal airflow and resonance
STRAW
→ same as stethoscope
→ listen to audible NAE
STHETOSCOPE
→ put the tip of the tube at the entrance of a nostril
→ listen for air or sound through the scope
SEE-SCAPE
→ u-tube glass you can buy in stores with a stopper in the end, a nasal olive, and inside there is a floater
FEEDING
Determine child’s feeding menthod | Determine amount of milk intake | Determine how much time the child is able to consume from a 4 OZ BOTTLE | |||||||||||||||
Determine the child’s ability abe to chew and swallow all types of food consistencies | Determine if the child has food allergies | Determine what type of food the child eats If the child is not a certain weight, they can’t be operated on |
4 OZ BOTTLE
Determine how much time the child is able to consume from a ______