Biology 120- Labs: 1 and 2
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Parts of a microscope:
Oculars, Interpupillary distance scale, binocular tube, revolving nosepiece, arm, objective lenses, coarse focus adjustment knob, fine focus adjustment knob, mechanical stage controls, light intensity control, light source, stage, slide holder, condenser and iris diaphragm assembly, iris diaphragm adjustment knob, power switch, power switch
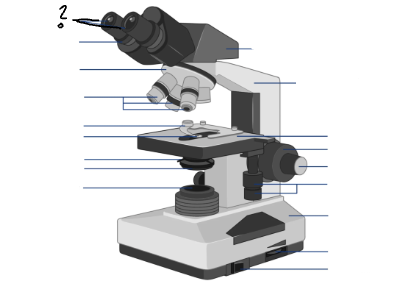
Oculars
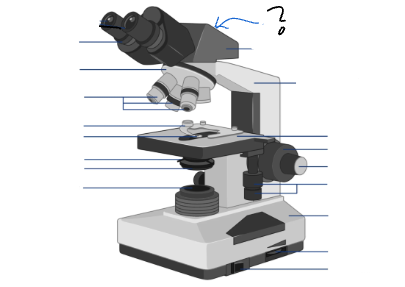
Interpupillary distance scale
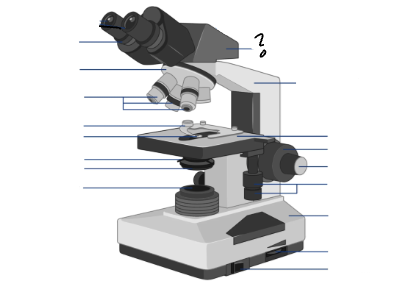
Binocular tube
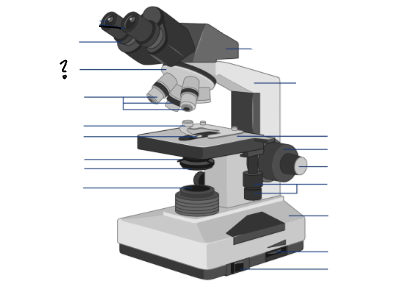
Revolving nosepiece
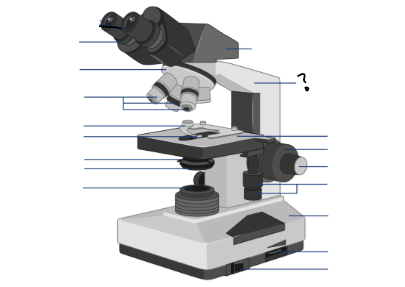
arm
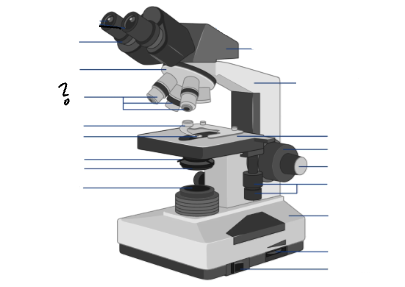
Objective lenses
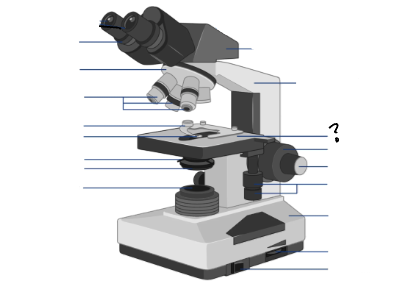
Stage
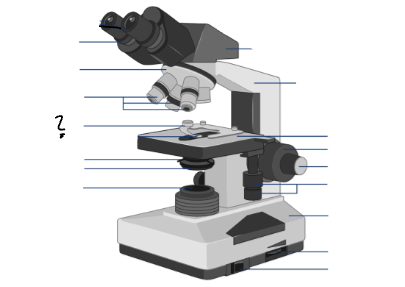
Slide holder
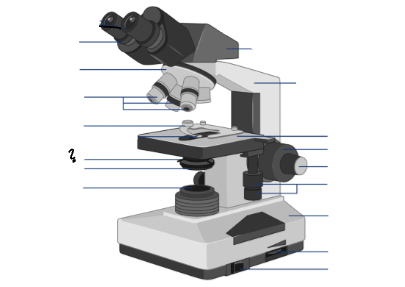
Condenser and iris diaphragm assembly
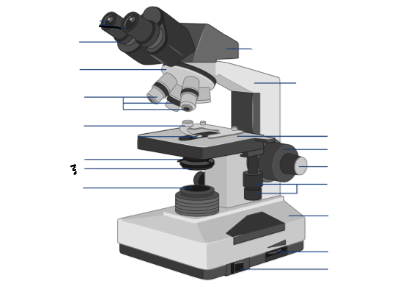
Iris diaphram adjustment lever
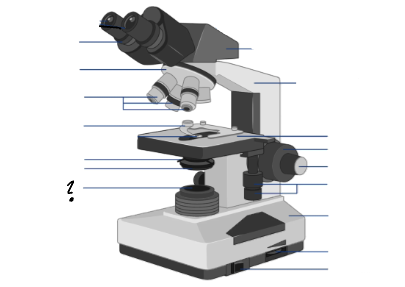
light source
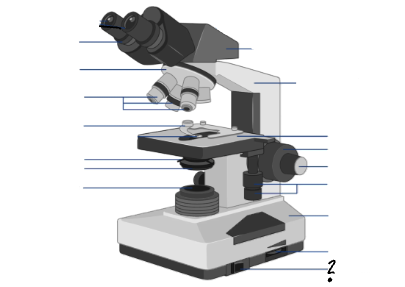
light switch
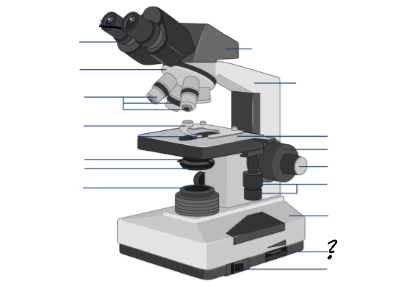
light intensity control
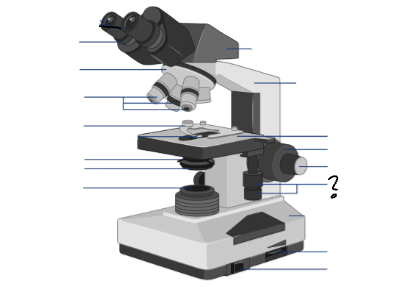
mechanical stage controls
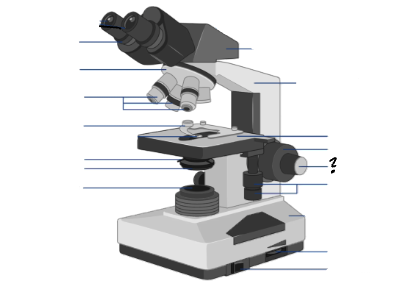
fine focus adjustment knob
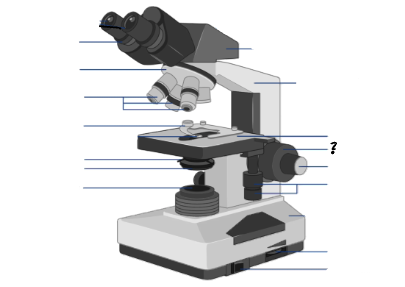
coarse focus adjustment knob
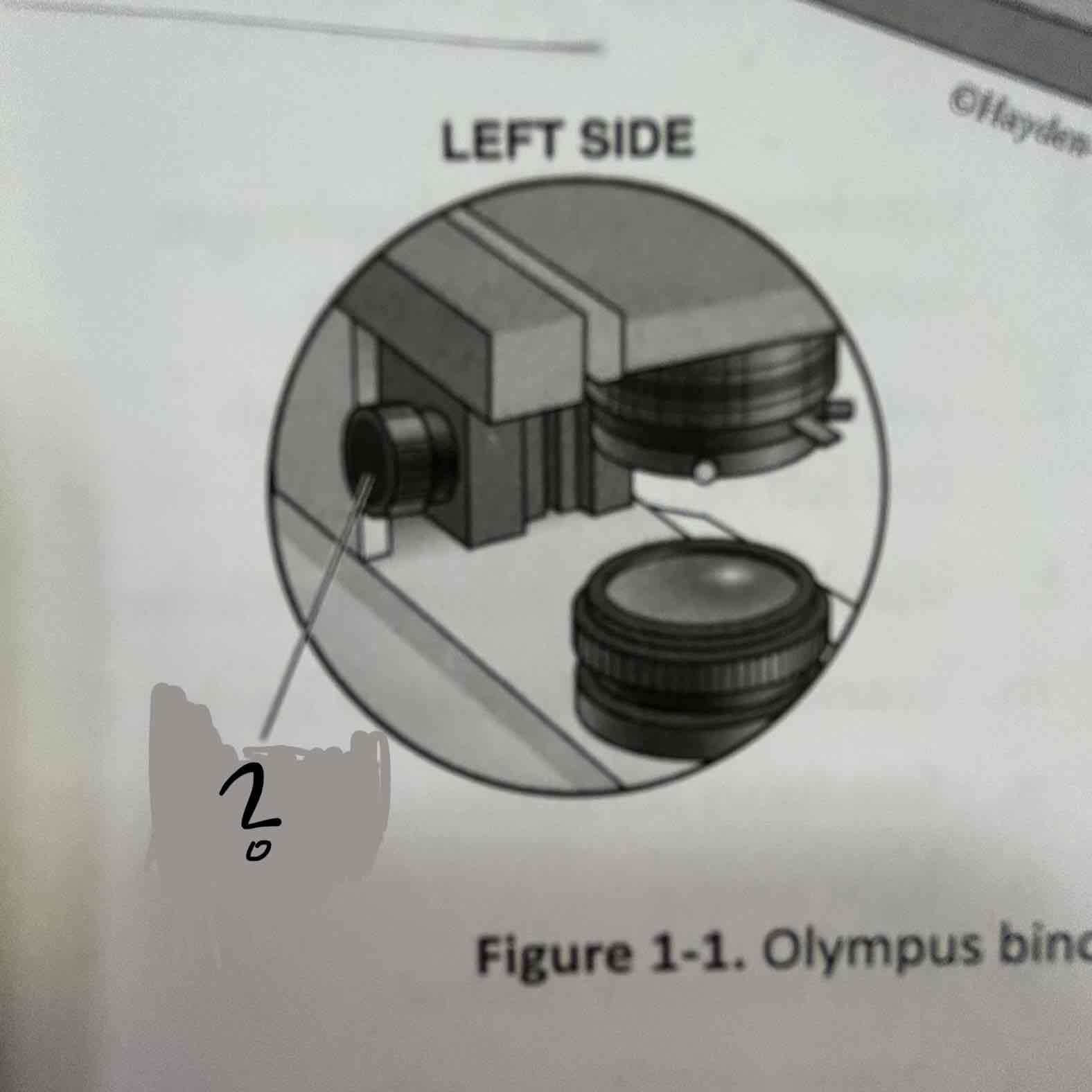
Condenser adjustment knob
Prokaryotes
often unicellular, some may form chains(called filaments)
lack a membrane-bound nucleus instead it contains a nucleoid which contains the DNA.
cell wall is made up of Polysaccarides or amino acids.
DOES NOT contain membrane-bound organelles
Prokaryote types;
Bacteria and Archaea
Eukaryotic
can be unicellular or multicellular
contains a membrane-bound nucleus
cel wall is made up of Cellulose for plants, Chitin for fungi, animals do not have a cell wall.
Contains membrane bound organelles
Eukaryotic types
Animals, protists, fungi, plants
Actual size of cell (or organism) is ‘what’ divided by ‘what’?
diameter of field of view of selected objective, Over, # of times the cell or organism can fit across the field of view.

calculating TPI
Divide the selected genus to the total amount in the water sample. (frequency)
then multiply the pollution index (given) to the frequency(calculating rTPI)
add all the rTPI (relative total pollution index) to get the total polution index
ranges of pollution (TPI); high, probable, lower organic pollution.
high- 4-5
probable- 2-4
low- lower than 2
all living cells have four basic structural features:
plasma membrane, cytoplasm, DNA, and ribosomes
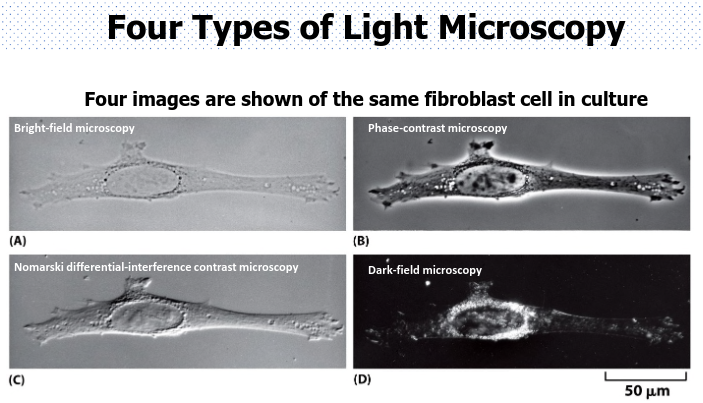
The four different types of light microscopy plus the two special types of light microscopy
fluorescence and confocal laser scanning microscopy
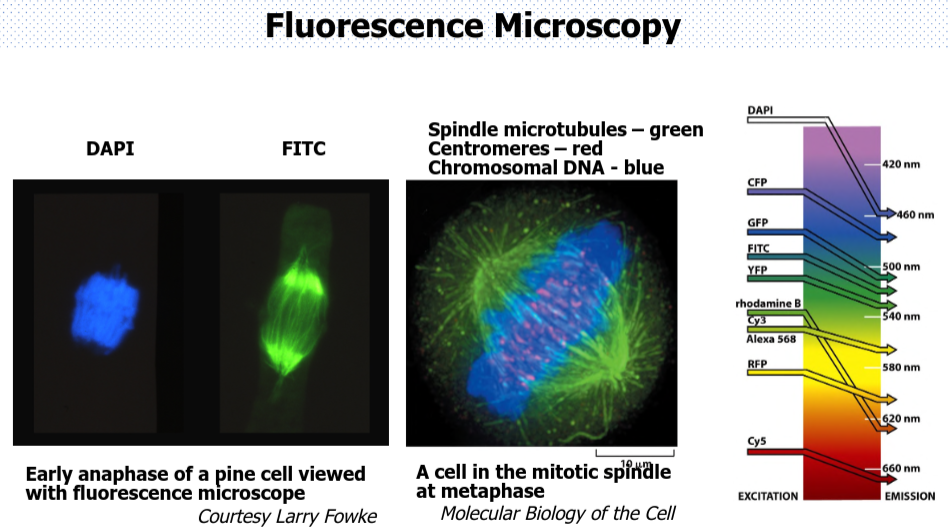
type of microscopy where you can see the image in colour
fluorensence microscopy
can look at live specimens
can create a 3-D image
uses lasers
real time imaging
high resolution
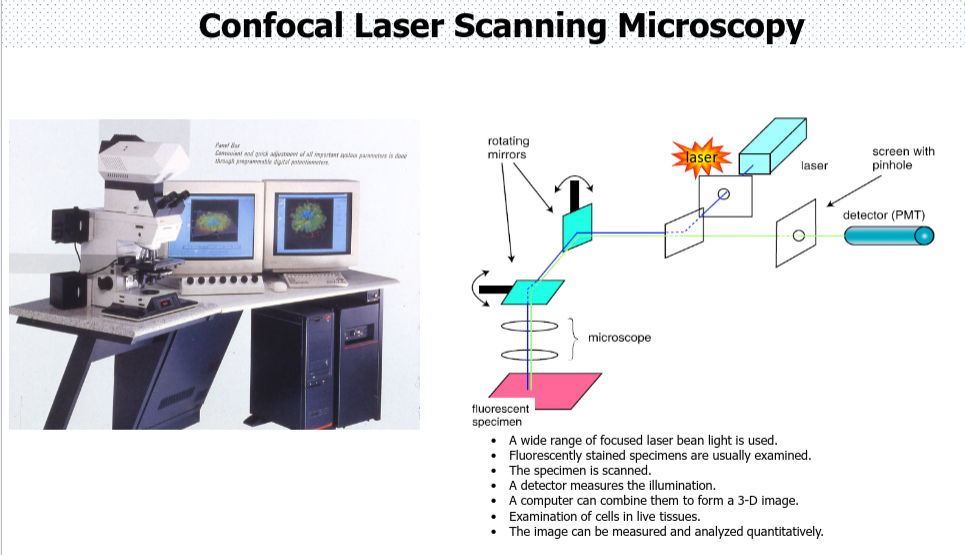
higher resolution
specimen must be dead
specimen is stained with heavy metals
What are the two kinds of electron microscopy?
Election microscopy
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
very thin sections
images are black and white
electrons pass through the specimen (light region)
electrons that do not pass through the specimen (dark regions)
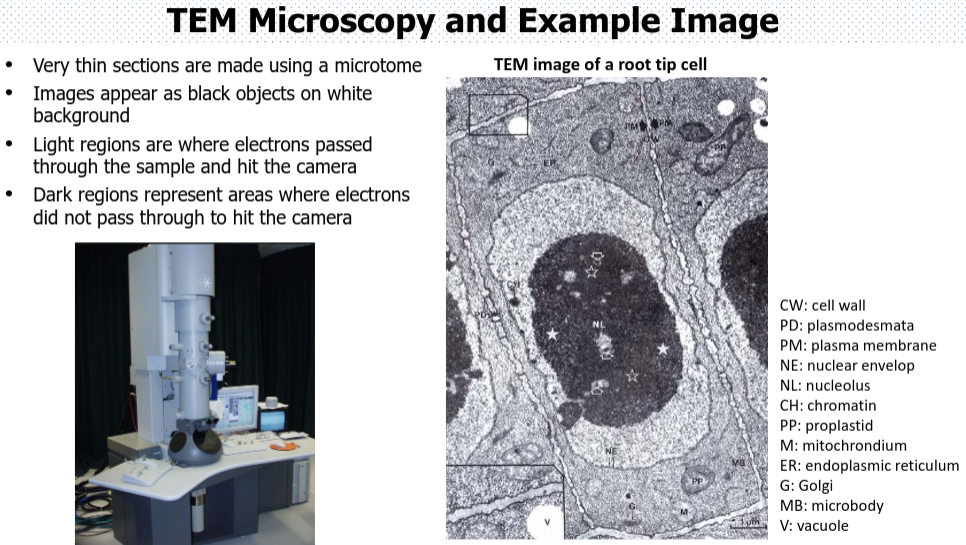
no sectioning needed
3-D image only of the surface
uses electrons

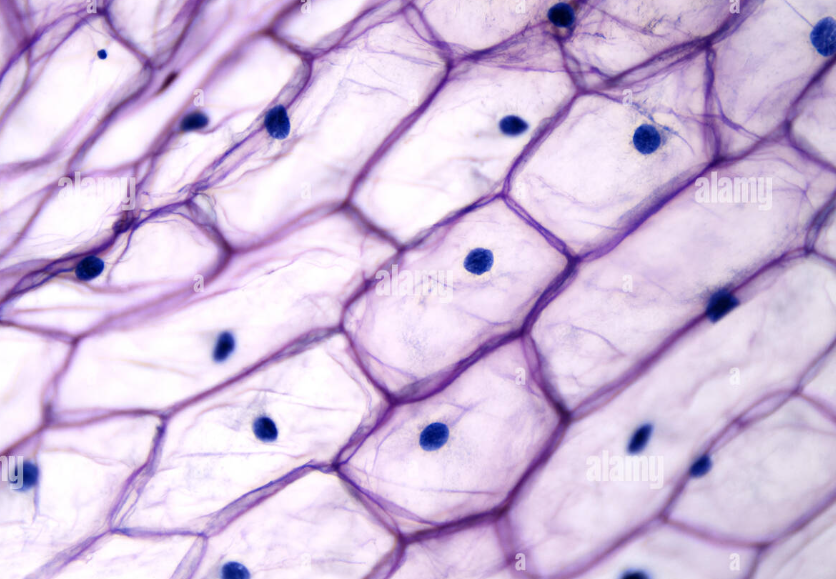
what do onion cells contain?
cell wall
nucleus
nucleolus
central vacuole
cytoplasmic strand
cellular granules
what are the three membrane-bound organelles plastids?
chloroplasts, chromoplasts, and leucoplasts
What colour are chloroplasts? due to what? What are they the site for?
green, chlorophylls, photosynthesis
What colours are chromoplasts? due to what?
yellow, orange, red, or dark purple. carotenoids.
What colour are Leucoplasts? what is their function?
they are non-pigmented plastids that function in the storage of starch, proteins, or fats (lipids)
What do green pepper cells contain?
cell wall
chloroplasts
central vacuole
nucleus
nucleolus
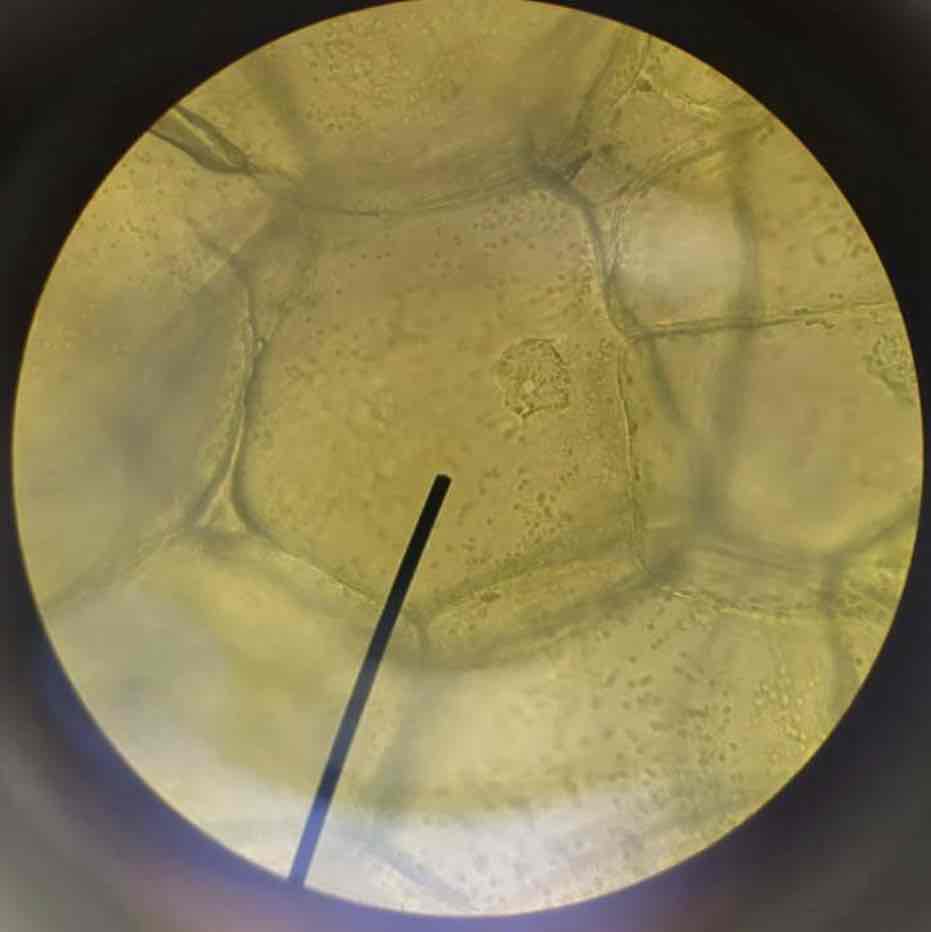
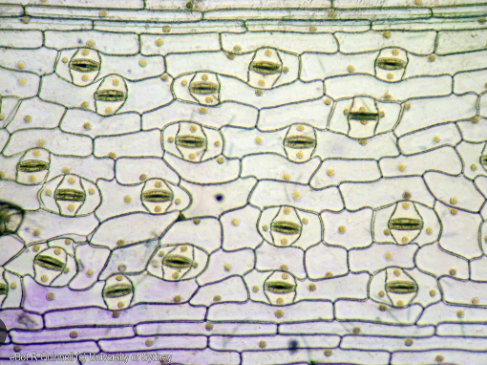
What do red pepper cells contain?
cell wall
plasmodesmata (the little ‘bubbles’ between the of the cell wall)
chromoplasts
central vacuole
nucleus
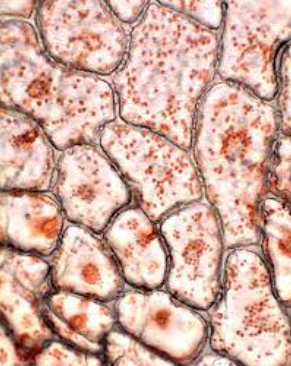
What does Tradescantia contain?
cell wall
leucoplasts
central vacuole
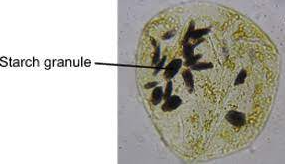
What does bananas contain?
cell wall
starch grains
cytoplasm
striations
Functions of cell structure: cell wall
provides tensile strength and protection against mechanical and osmotic stress
It allows cells to develop turgor pressure
Functions of cell structure: central vacuole
holds materials and waste and also maintains proper pressure
Found in the centre of plant cells
Functions of cell structure: chloroplast
contain chlorophyll that traps sunlight, food for the plant
Found in the leaves of the plant
Functions of cell structure: chromoplasts
synthesis and stores caroteniod pigments in plants
Functions of cell structure: cilia
used for locomotion and found on the outside of Eukaryotic cells
Functions of cell structure: contractile vacuole
controls the intracellular water balance in plant cells
Functions of cell structure: cytoplasm
gel-like fluid in the cell that allows the functions of the organelles to operate
Functions of cell structure: cytoskeleton microtubles and microfilaments
Microtubles- made of tublin
maintains cell shape
can be used for motility
Microfilaments- made of actin and used to support the shape of the cell.
Functions of cell structure: Flagella
used for locomotion
found primarily in Prokaryotes
Functions of cell structure: food vacuole
used to digest food
present in unicellular structures e.g. amoeba
Functions of cell structure: golgi apparatus
sorts and sends proteins to proper places
Functions of cell structure: leucoplast
plastids that are composed of colourless organelles
stores starch, lipids, and proteins
Functions of cell structure: lysosome
responsible for digestion in Eukaryotic cells
Functions of cell structure: mitochondria
located in the cytoplasm
functions as eukaryotic cells digestive system
Functions of cell structure: Nucleolus
found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells
makes ribosomes (made of protein and RNA)
Functions of cell structure: Nucleus
stores the cells DNA
facilitates transcription and replication
Functions of cell structure: plasma membrane
separates the cell from the outside environment
Functions of cell structure: Ribosome
found floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum
In charge of protein synthesis
Functions of cell structure: rough ER
produce proteins for the rest of the cell
Functions of cell structure: smooth ER
lipid synthesis
Functions of cell structure: vesicle
transports material of the cell
Anthocyanins
blue, purple, and red pigments
they are not plastids
occurs in the central vacuole
In the spinach leaf experiment what was observed?
cells that make up the leaves of a plant are specialized to carry out the process of photosynthesis
the process occurs in specialized organelles called chloroplasts
the intercellular spaces between cells carry carbon dioxide which enters through stomata.
the byproduct of oxygen is produce
when we put the discs in a vaccum, sodium bicarbonate solution filled the spaces between the cells, causing them to sink
when we put some of the discs under the light, the process of photosynthesis occured creating oxygen
the oxygen replaced the sodium bicarbonate between the cells, making the leaves float
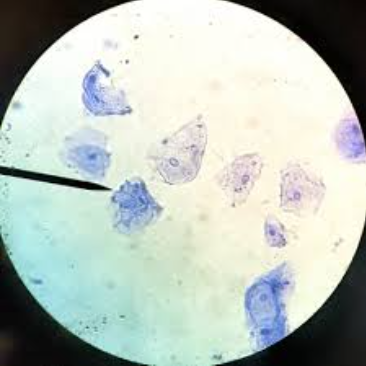
What does a cheek cell contain?
plasma membrane
cytoplasm
nucleus
Animal compared to plant cells
both eukaryotic
animal cells are usually colourless (have to stain them)
plants have a cell wall