x-ray special views
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
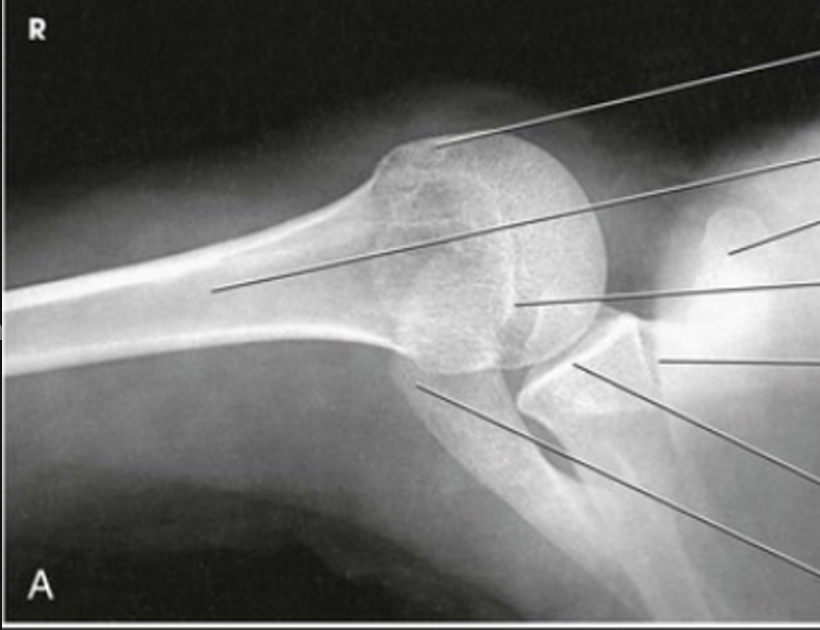
what view is this?
inferosuperior axial shoulder (lawrence method)
inferosuperior axial shoulder (lawrence method)
with patient supine, the humerus is abducted 90 degrees
IR is placed in contact with the superior aspect of the shoulder and rests upright on the table top
CR is directed horizontally through the axilla to the acromioclavicular joint.
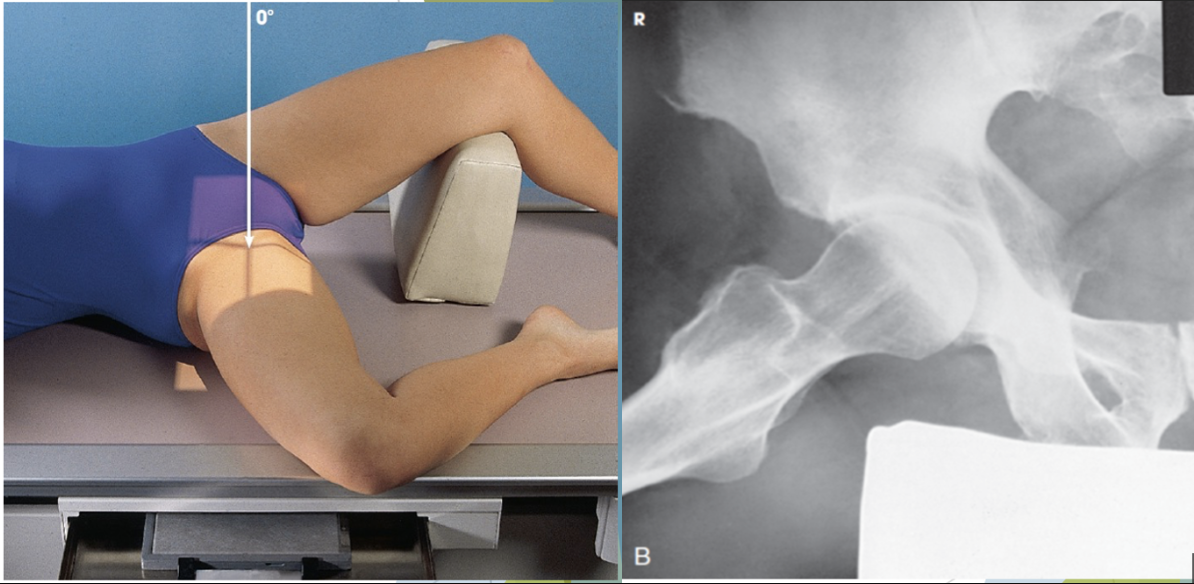
what view is this?
lateral hip - (lauenstein method)
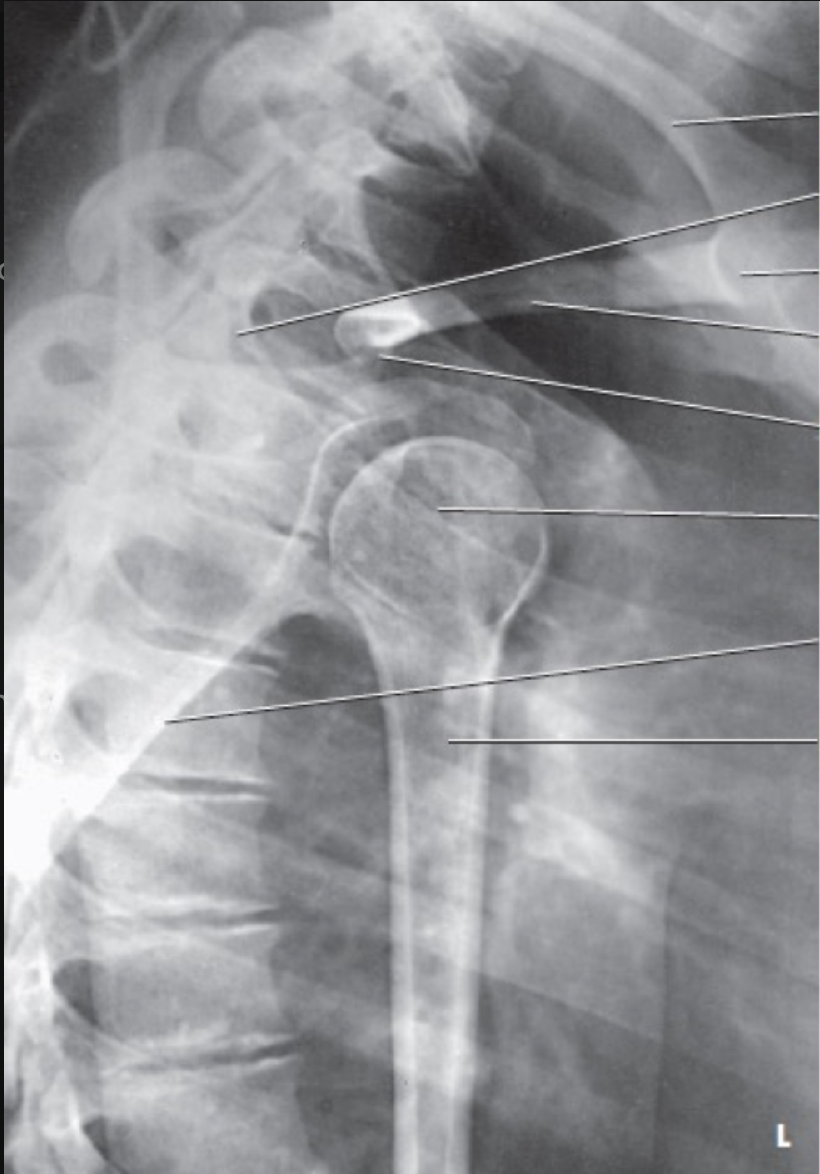
what view is this?
transthoracic lateral shoulder (lawrence method)
transthoracic lateral shoulder (lawrence method)
epicondylar line is positioned perpendicular to the IR
unaffected arm is raised above the patient’s head
CR is directed across the thoracic cavity to the surgical neck of the affected humerus
demonstrates the proximal humerus through the thoracic cavity with the lesser tubercle seen in profile
breathing technique may be used to blur the rib and lung detail
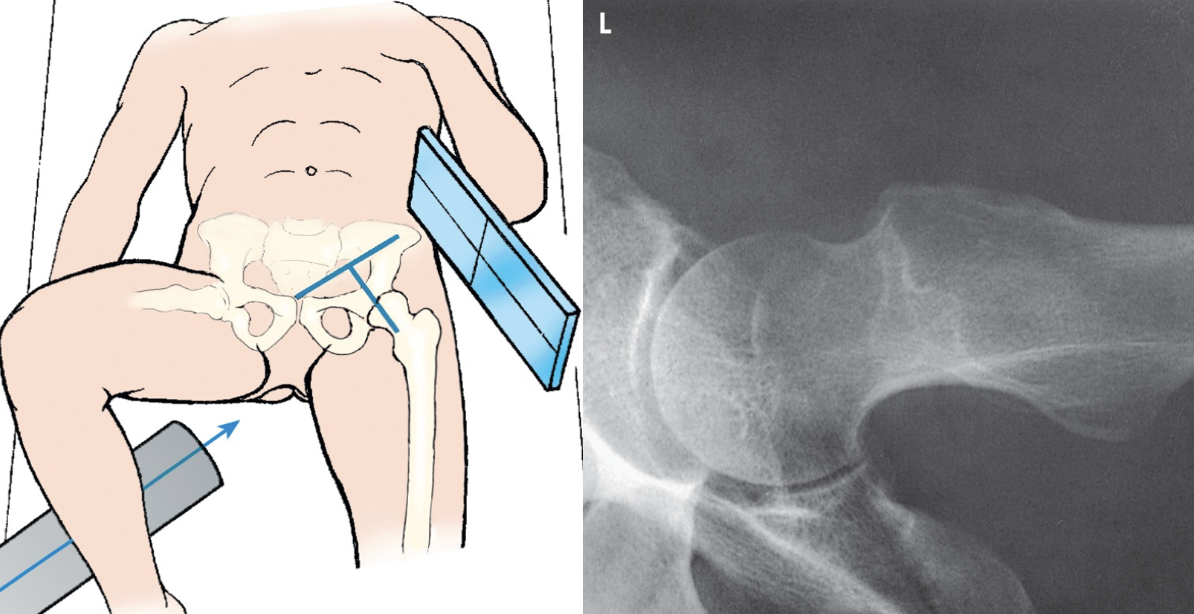
what view is this?
axiolateral hip - danelius - miller
axiolateral hip - danelius - miller
performed on patients with a suspected fracture or dislocated hip who cannot perform a frog leg lateral
top of the grid IR is placed in the crease above the iliac crest
IR is placed paralle to the affected femoral neck
CR is directed perpendicular to the long axis of the. femoral neck
unaffected leg must tbe elevated out of the way
what view is this?
ap axial outlet taylor method
ap axial outlet taylor method
patient lies in the supine position
for males the CR is directed 20 to 35 degrees cephalic and directed to the MSP and 2 inches distal to the superior border of the pubic symphysis
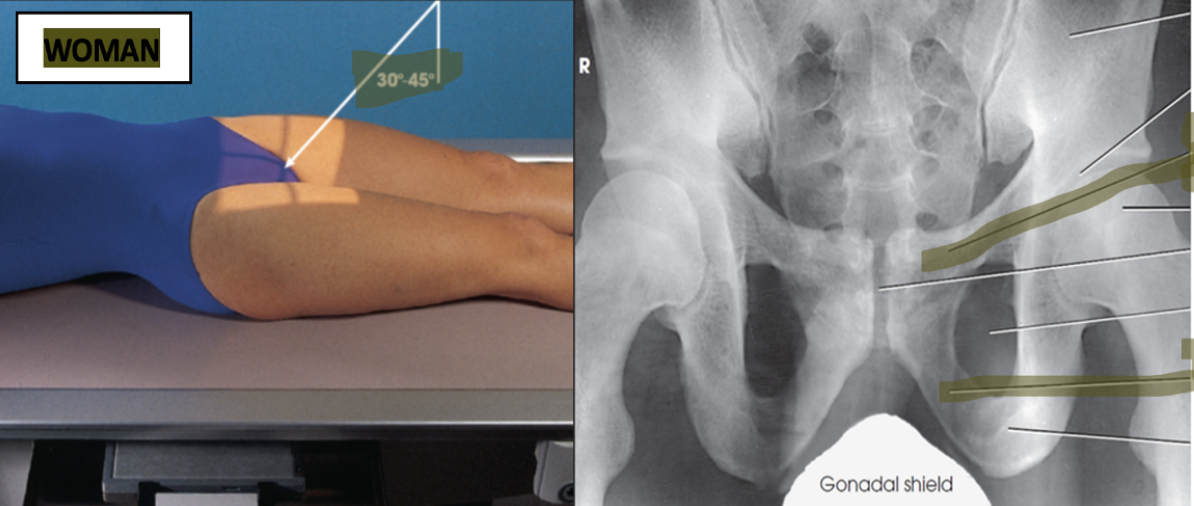
for females the CR is directed 30 to 45 degrees cephalic and directed to the MSP and 2 inches distal to the superior border of the pubic symphysis
demonstrates the pelvic rami without the foreshortening seen on an AP or PA projection
what view is this?
superoinferior axial inlet - (bridgeman method)
superoinferior axial inlet - (bridgeman method)
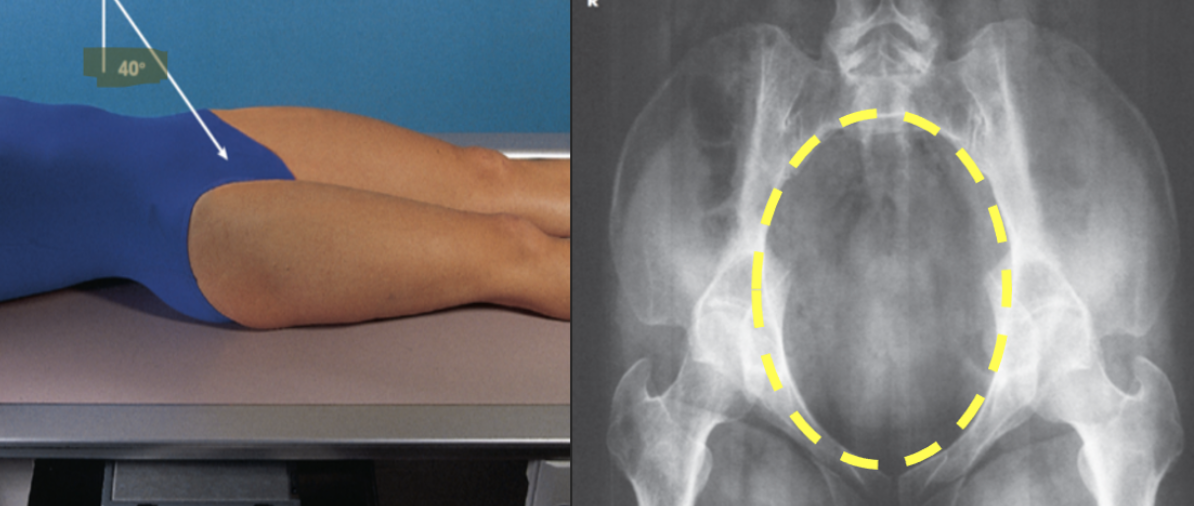
patient lies in the supine position
IR is centered at the level of the greater trochanter
CR is directed 40 degrees caudad to the MSP and entering the body at the level of the ASIS
demonstrates the anterior pubic and ischial bones and the pubic symphysis
what view is this?
AP dens (fuchs)
AP dens (fuchs)
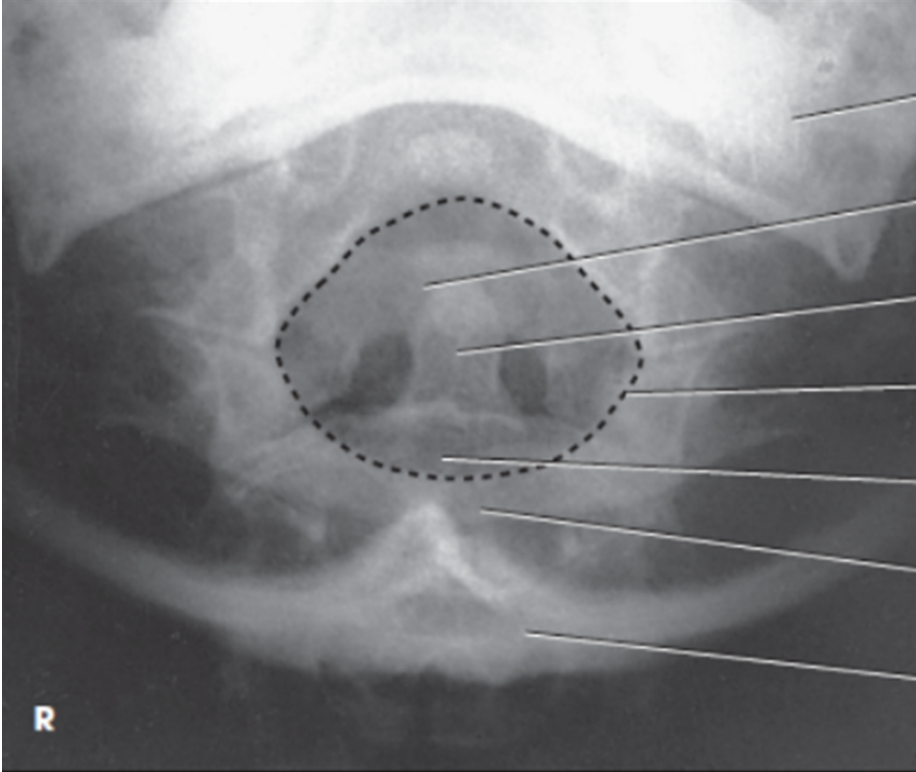
center the midsagittal plane of the body to the midline of the grid
extend the chin until the tip of the chin and the tip of the mastoid process are vertical
direct CR to enter the neck on the midsagittal plane just distal to the tip of the chin
image shows AP projection of the dens lying within the circular foramen magnum
what view is this?
sesamoid, tangential
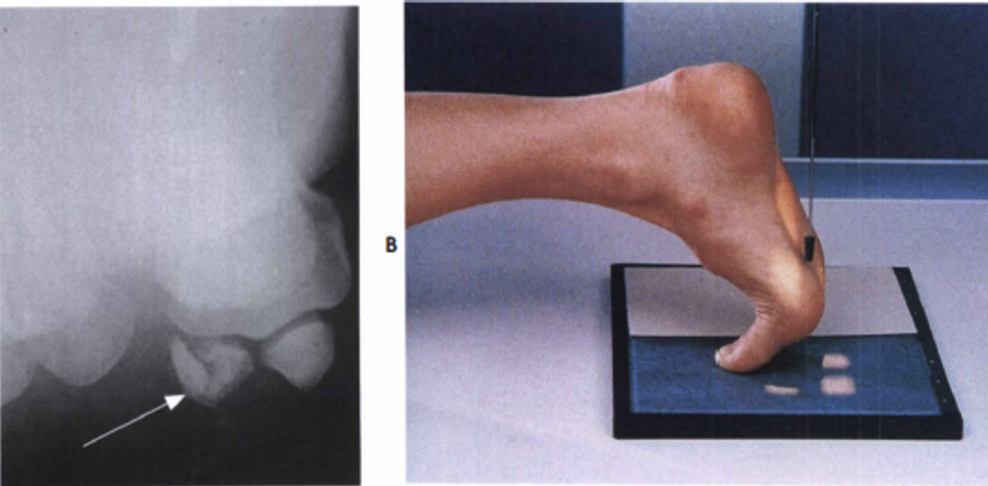
sesamoid, tangential
the great toe is rested on the IR in a dorsiflexed position, plantar surface forms a 15 to 20 degree angle from vertical
CR is directed perpendicular to the first metatarsophalangeal joint
demonstrates a tangential projection of the metatarsal head in profile and the sesamoid bones
what view is this?
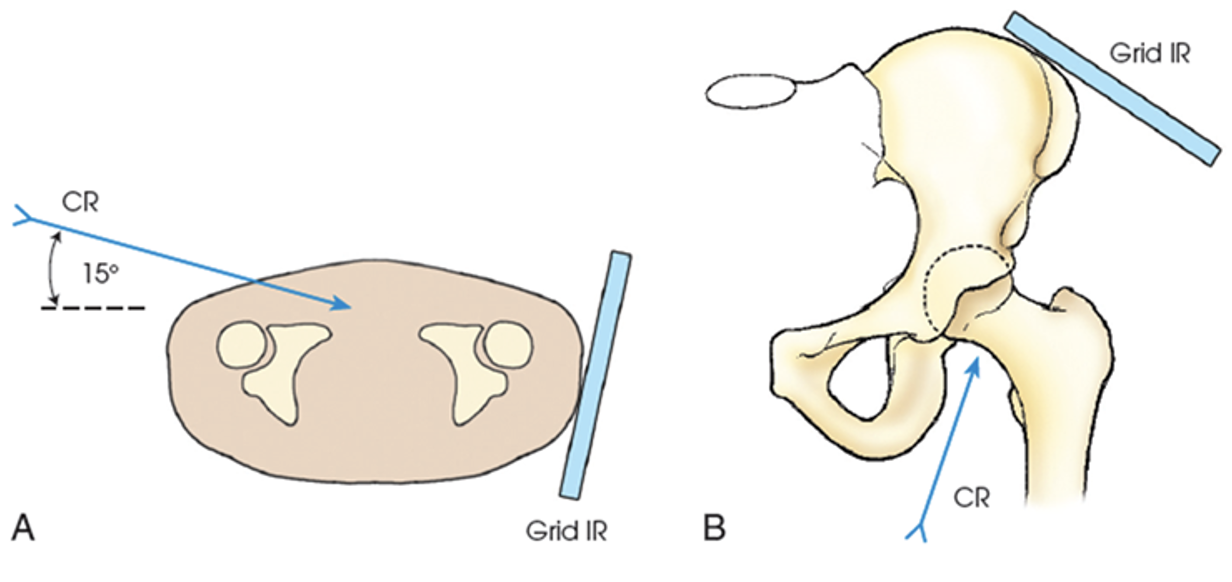
axiolateral inferosuperior (clements-nakayama method)
axiolateral inferosuperior (clements-nakayama method)
performed in cases of possible bilateral hip fractures
patient lies supine with the lower limbs remaining in a neutral position
grid is adjusted parallel to the femoral neck and tilted back approximately 15 degrees
CR is directed 15 degrees posteriorly and perpendicular to the femoral neck and IR
demonstrates a lateral view of the hip, acetabulum, and proximal femur
what view is this?
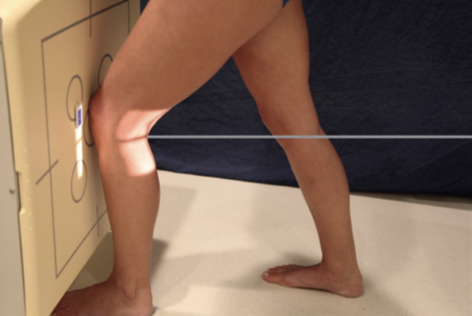
homblad method
homblad method
requires the lower leg to be placed in the same plane (parallel to) as the IR
the long axis of the femur is angled approximately 70 degrees from the surface of the image receptor 20 degrees from the vertical
CR is directed perpendicular to the IR and to the shaft of the lower leg entering at the knee joint
what view is this?
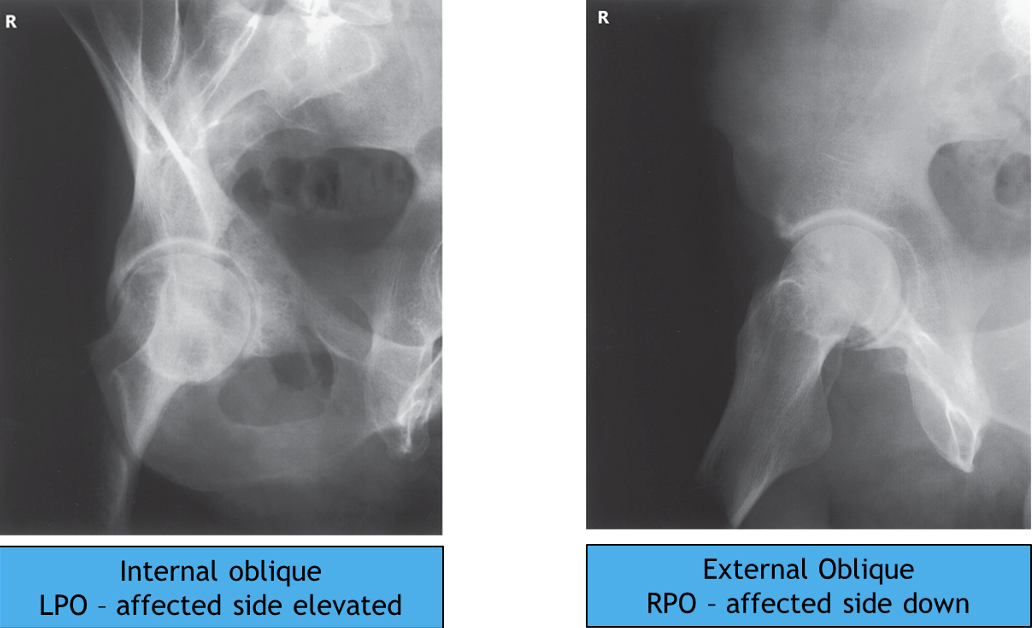
judet
judet
CR is directed perpendicular to the IR and entering the body 2 inches inferior to the ASIS of the affected side
patient’s body is placed in a supine 45 degree oblique position with the affected side up - places the affected hip and acetabulum in the internal oblique position
CR is directed perpendicular to the IR and entering at the pubic symphysis
patient’s body is placed in a supine 45 degree oblique position with the affected side down, this places the affected hip and acetabulum in the external oblique position
BOTH VIEWS DEMONSTRATE POSSIBLE FRACTURES OF THE ACETABULUM
what view is this?
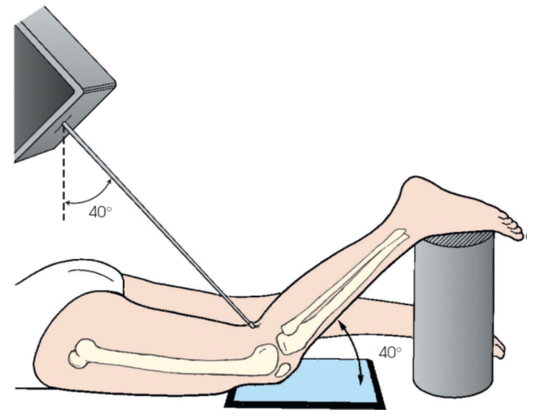
camp-coventry method
camp-coventry method
requires the patient to lie prone with the femur in the same plane as the IR
the knee is flexed so that the lower leg forms approximately a 40 degree angle with the surface of the IR
CR will require a caudad angulation until it is directed perpendicular to the shaft of the lower leg entering at the knee joint (popliteal depression)
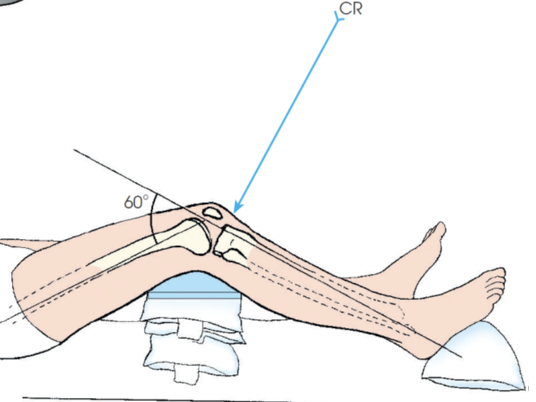
what view is this?
AP axial (beclere method)
AP axial (beclere method)
one knee flexed approximately 30 degrees and the CR directed perpendicular to the shaft of the lower leg
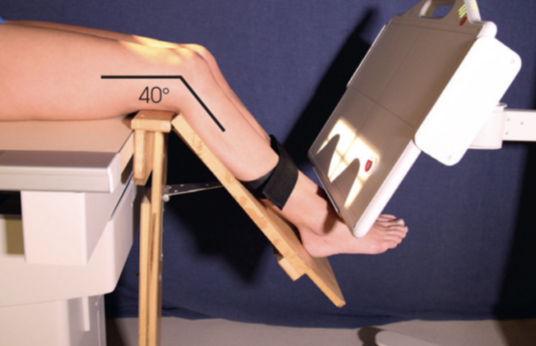
what view is this?
tangential (merchant)
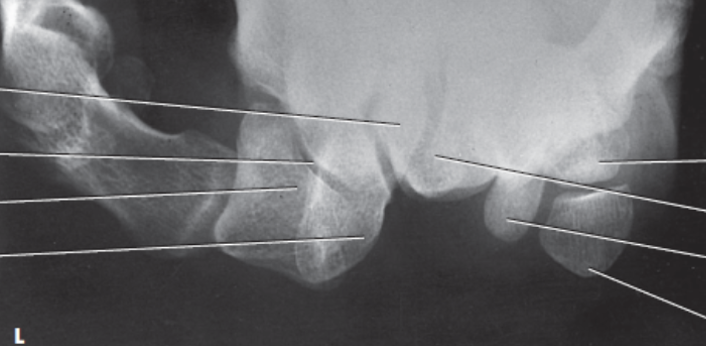
what view is this?
carpal canal (tunnel) (gaynor-hart)
carpal canal (tunnel) (gaynor-hart)
hand and wrist are hyperextended
CR is directed to the palm of the hand approximately 1 inch distal to the base of the 3rd metacarpal at an angle of 25 to 30 degree to the long axis of the hand
demonstrates the carpal bones of the inferior aspect of the wrist

what view is this?
tangential (settegast)
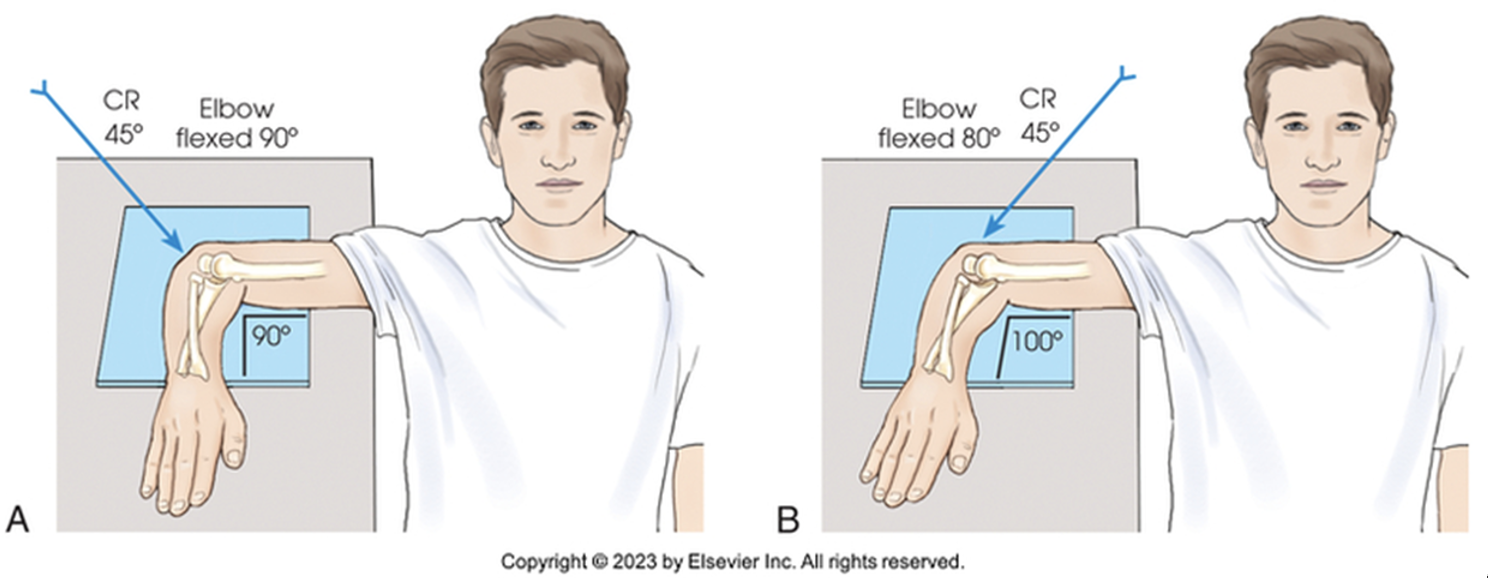
what view is this?
coyle axial lateral
coyle axial lateral
with the elbow flexed to form approximately a 75 degree angle, the forearm is placed parallel to the IR
hand is supinated to prevent rotation of the radius and ulna
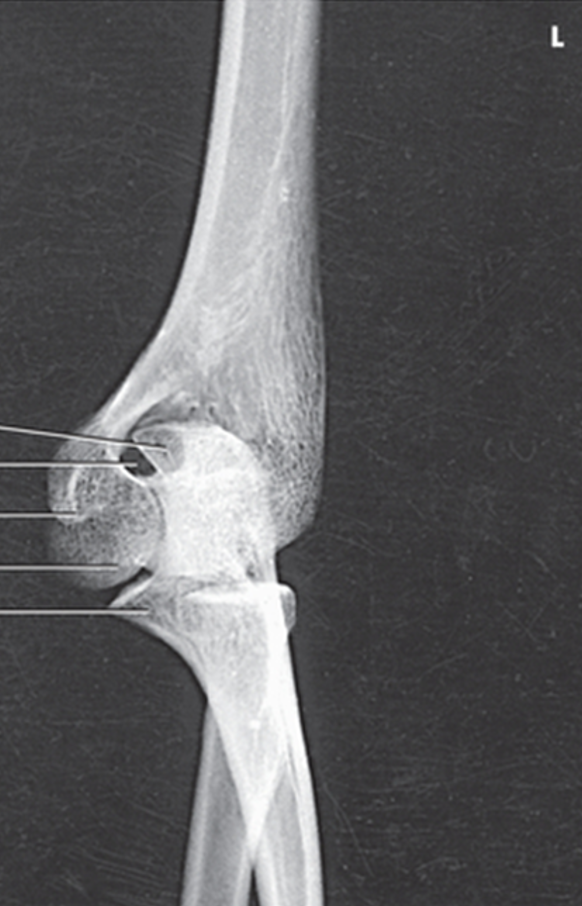
what view is this?
AP internal oblique elbow
AP internal oblique elbow
demonstrates the olecranon and coronoid processes of the proximal ulna
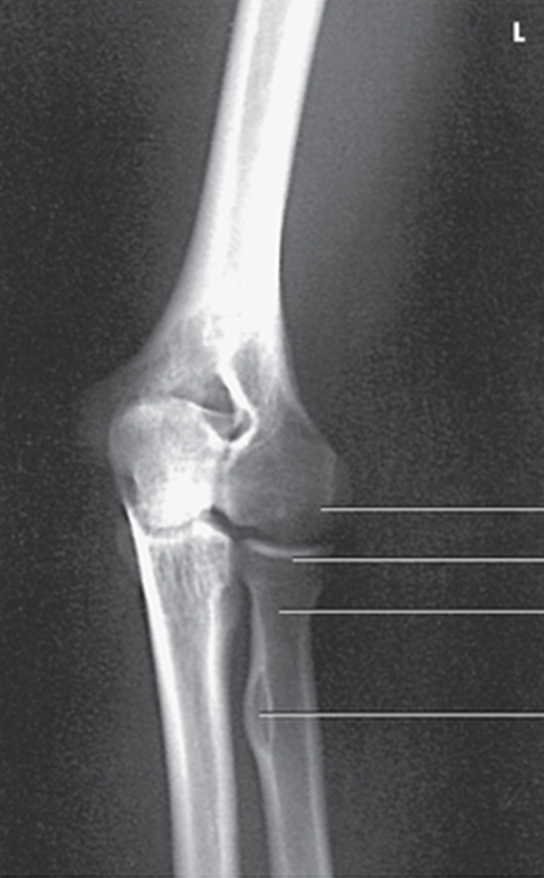
what view is this?
AP external oblique elbow
AP external oblique elbow
demonstrates the radial head with no superimposition over the ulna and capitulum