Paper 3 Notes
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
If a question asks to calculate mean and is worth 2 marks, what should you check for?
Check for anomalies. If there are any, remove them and don’t include them.
What is the difference between accurate and precise?
Accurate is how close the measurement results are to the true value.
Precision is how close repeated measurements are to each other.


Try name 4
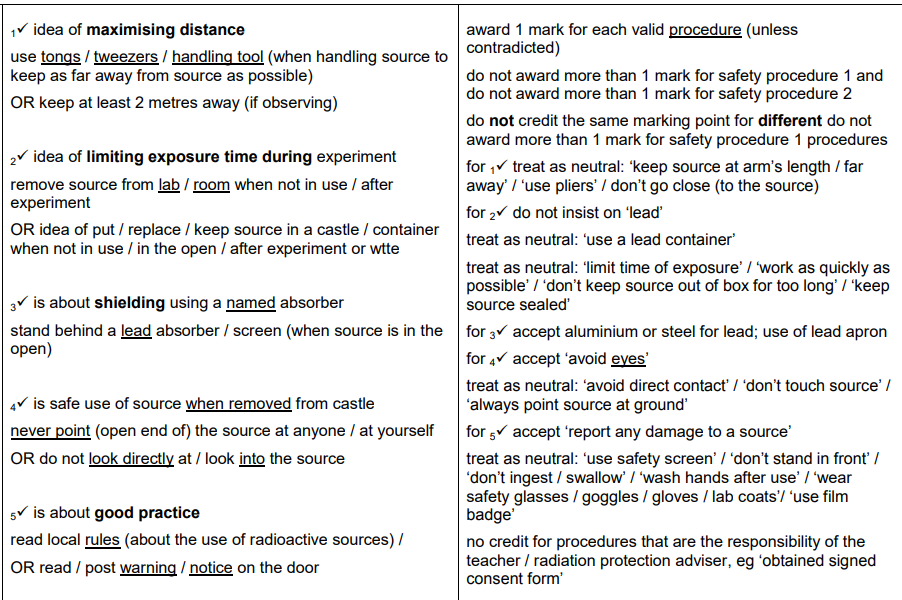

In 01.4 we expected students to know that the background count rate should be measured, with the source effectively removed to eliminate the key source of systematic error. We also hoped that they know enough about the random nature of background radiation to appreciate that a long integration time can reduce percentage uncertainty. These provided the main thrust in many of the arguments put forward, but sometimes examiners found that the expression of these ideas was too vague. We wanted students to return the source to its castle or to remove it entirely from the laboratory; comments such as ‘put the source far away’ were not acceptable. Less popular, but viable, suggestions were to carry out the measurement in the same place (or on the same day) as that of the main experiment. Some students suggested that anomalies should be rejected when determining background count rate. These students need to re-examine their understanding of the nature of radioactive decay. Comments such as ‘check the tube is zeroed’ and ‘use a counter with greater resolution’ gained no credit. A number of students erroneously assumed that Ab was the rate during the test of the inverse-square law. The majority scored no more than 1/3 and only very few scored 3/3.
How can precision be improved?
Carrying out more measurements and removing anomalous results from the dataset
How can BOTH accuracy and precision be improved?
Carry out “bigger” measurements
Difference between repeatable and reproducible?
Repeatable is where YOU can get the same results are repeating an experiment multiple times
Reproducible is where another team can recreate your experiment using different equipment or methods and get the same results.
How can you ensure an object is vertical (e.g a ruler)
Use a set square perpendicular to object and bench
When designing an experiment, what 2 things must the gradient be?
Straight
Go through origin
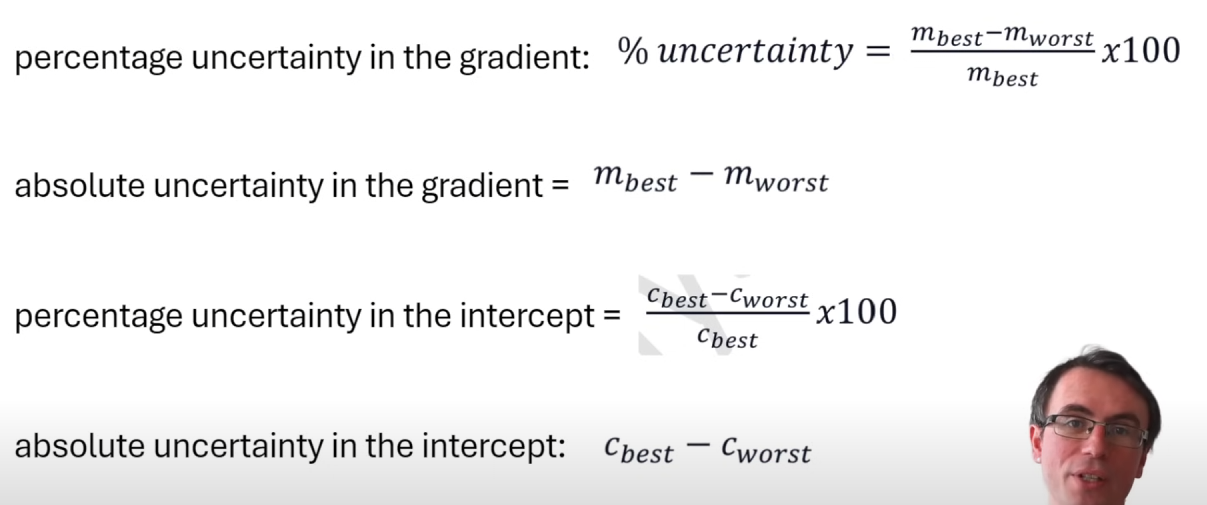
What are equations to work out percentage AND absolute uncertainty in gradient?
What could cause a line of best fit to not go through origin?
If there is a systematic error in the measurements.
3 reasons why you want to measure diameter with a micrometre at different areas on a wire?
Reduce the effect of random errors
Identify anomalous results to reject these
Confirm the uniformity of the wire
If the absolute uncertainty in a diameter stays the same, but the size of diameter is doubled, but what factor does the percentage uncertainty decrease in the area of a wire?
Just using d = 1, area (taking out pi) would be ¼
when d = 2, area = 1 so the PERCENTAGE UNCERTAINTY, given the absolute uncertainty is constant in both, means that when doubled, it is ¼ original percentage uncertainty.
How could a systematic error form when using a ruler to measure?
Zero mark not positioned correctly.
What effect would a systematic error have on a gradient of a graph?
Why may an analogue ammeter rather than a digital ammeter when taking readings?
Easier to read quicker
What is “full scale deflection” on an analogue ammeter and how would you calculate it?
The maximum current that the meter can measure before the needle reaches the end of the scale.
Calculate the minimum current in the circuit and then depends on the context of the question (e.g how much higher the current will get)
Discuss why may a meter be unsuitable for an experiment?
idea that resolution of the meter is not satisfactory
Only small percentage of the meter range may be used in getting values.
Then must show calculation: e.g: (full scale deflection / divisions on meter) to show what each division reads.
If calculating an acceleration, why can’t you use v = u +at , where v = d/t
Since v=d/t is used when v is constant, meaning that acceleration is 0.
What are independent and dependent variables?
Independent = Variable that is changed
Dependent = Variable that is measured
"The dependent depends on the independent."
What are the 3 steps in answering an experimental method to derive a particular value?
1) List independent and dependant variables
2) Experimental technique
3)Graph

What is a measurement error?
The difference between a measured value and the true value
What are 2 ways to reduce percentage uncertainty?
Use larger values for experimental results (e.g instead of measuring 10 oscillations or 10 cm, do 100!) This reduces the percentage uncertainty, since it is defined as % = Absolute/Original x 100 so if the original is larger (keeping the absolute constant), the fraction will be smaller and so the percentage uncertainty will be smaller.
Use a measuring device with a greater resolution. This will reduce the absolute uncertainty, and then again makes that fraction smaller.
What is 1 type of systematic and random error?
Systematic: Zero error
Random: Parallax error
What are the effects of data when plotted on a graph for systematic and random errors respectively?
Systematic will change the intercepts of the graph (NOT the gradient since the error is constant)
Random changes the intercepts AND gradients of the graph, making line of best fit difficult to plot.
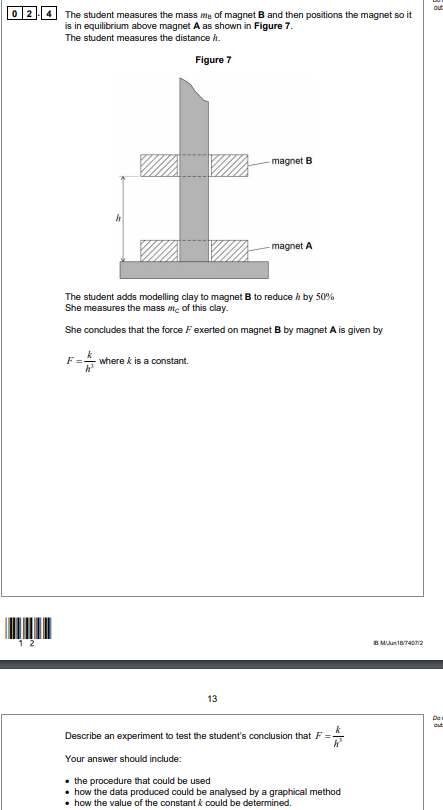

State precautions the student should take to reduce the effect of systematic and random errors when making this measurement.
Systematic: take [zero] the callipers before use. (zero error)
Random (MUST USE FULL WORDING AND NOT JUST REPEAT AND CALCULATE MEAN):
Take measurement several times for different diameters/directions and calculate mean (have to mention what you are measuring!)
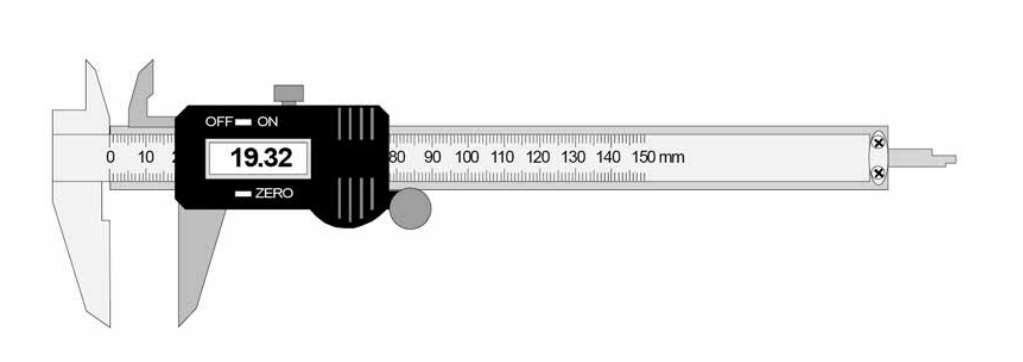
What is the use of the top jaws?
To measure the inside of e.g a cylinder!
How to answer a “show that” question:
any equations used should be written with subjects seen at each stage of the calculation;
• mid-calculation rounding should be avoided;
• the answer should be quoted to more significant figures than the value they have been asked to find.

The at least 6 measurements comes up often, so do 10!
Don’t forget to include how to measure EVERYTHING (e.g thermometer…)

What does the mark scheme say about drawing line of best fits?
Line should pass through all error bars
Even scatter of points on either side of LOBF
Multiple, thick or unruled lines NOT ALLOWED