Microbio bacteria
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lab
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
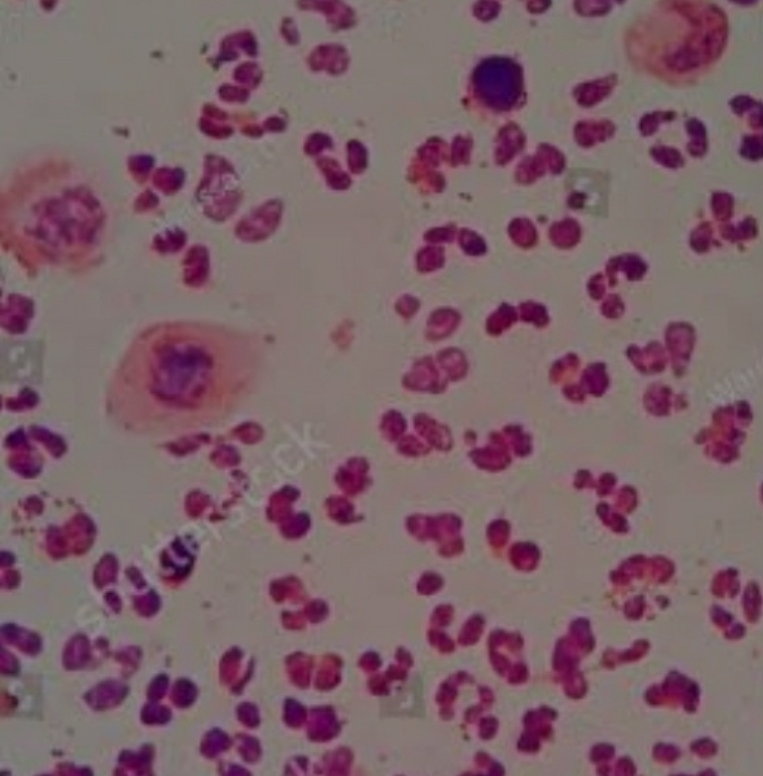
monococcus
is a single, round or spherical bacterial cell
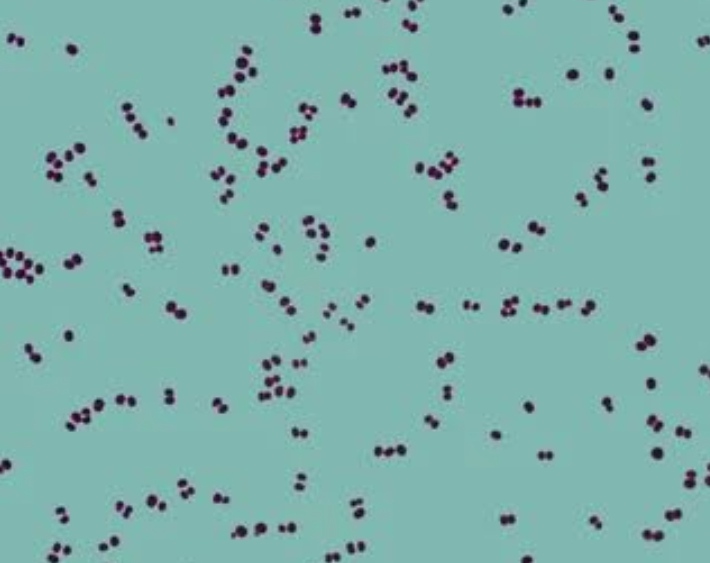

diplococcus
a pair of spherical bacterial cells that are connected together, commonly associated with certain infections.
tetracoccus
a cluster of four spherical bacterial cells that are arranged together.
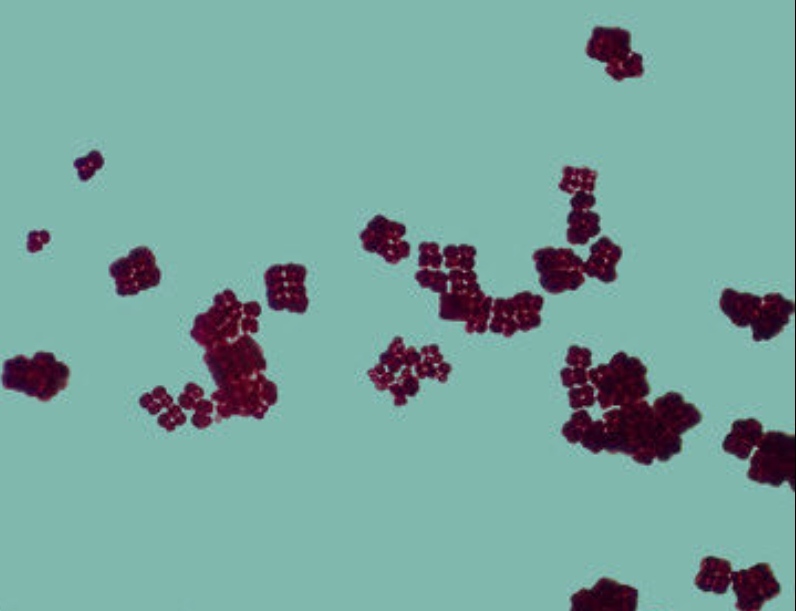
Sarcina
a spherical bacterial cell that forms cube-like arrangements consisting of eight or more cells.
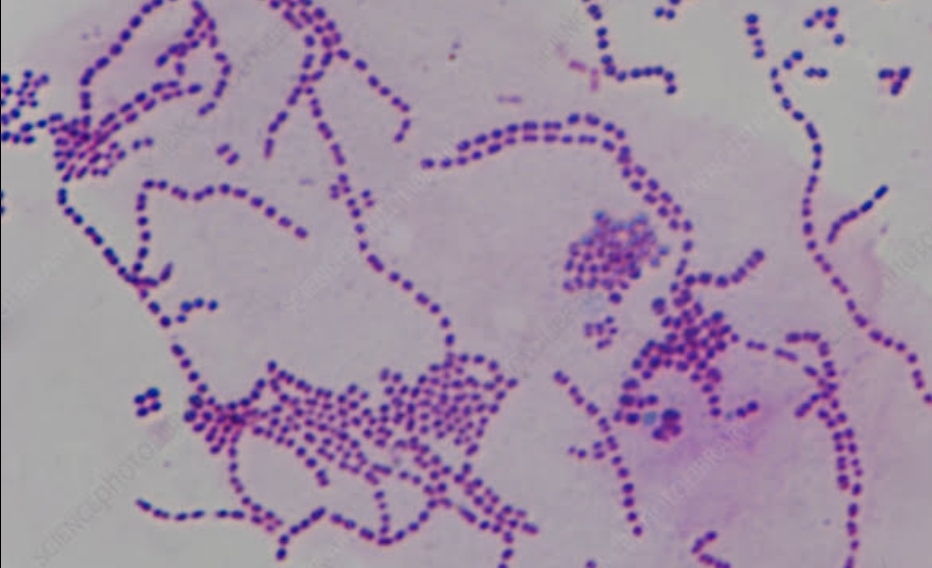
streptococcus
a type of bacteria that forms chains of spherical cells, often associated with various infectious diseases.
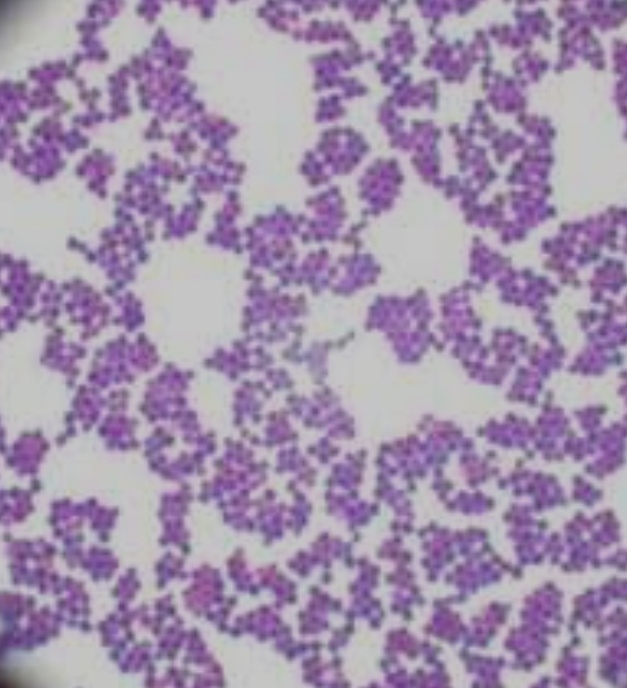
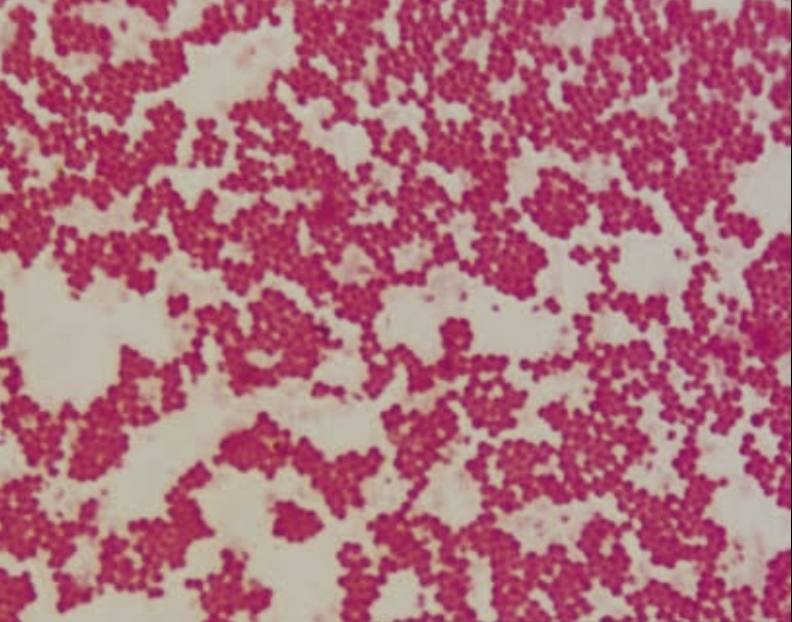
staphylococcus
bacteria that forms irregular clusters of spherical cells, commonly found on the skin and in the respiratory tract.
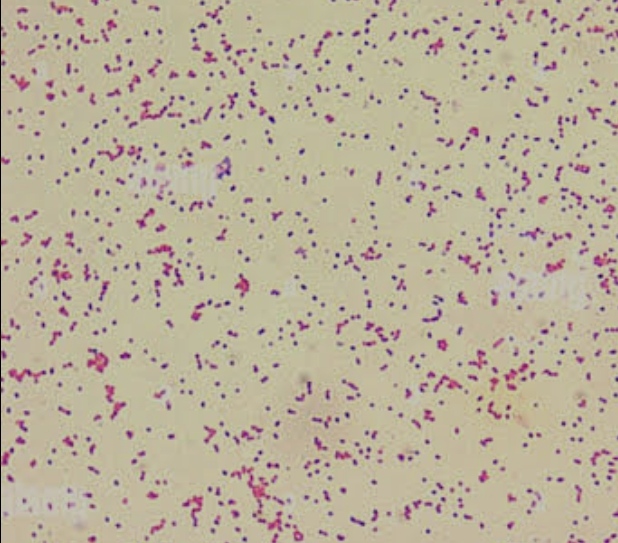
coccibacillus
bacteria with a shapes somewhere between spherical and rod-like, typically involved in respiratory infections.
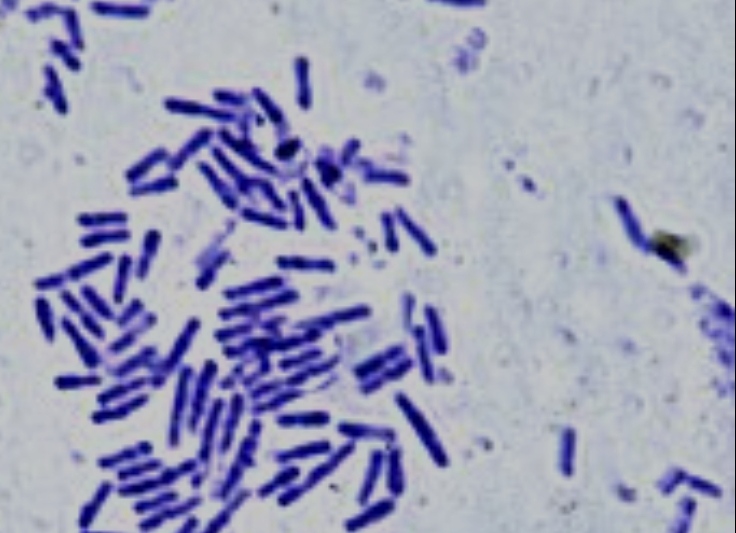
bacilli
a group of bacteria characterized by their rod shape, often associated with various infections.
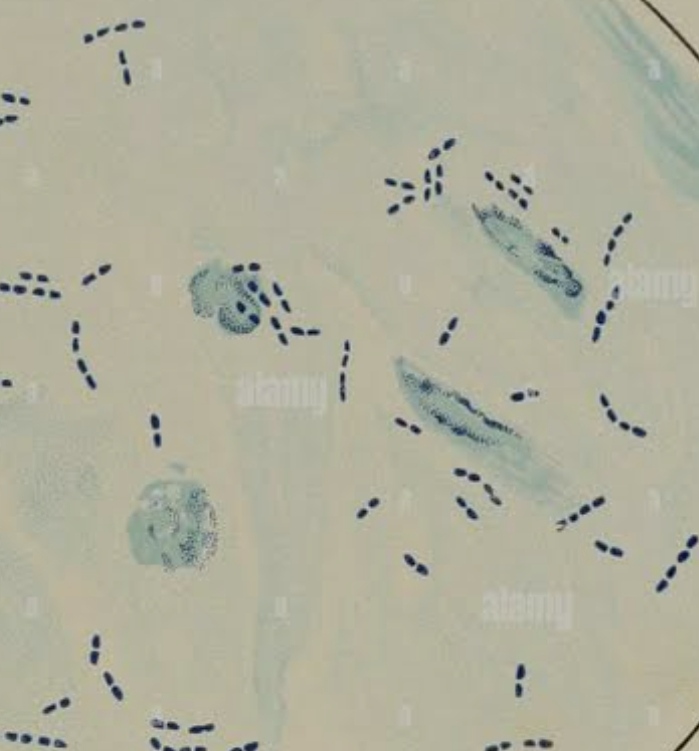
diplobacilli
bacteria that occur in pairs and have a rod-like shape, commonly found in various environments and can be pathogenic.
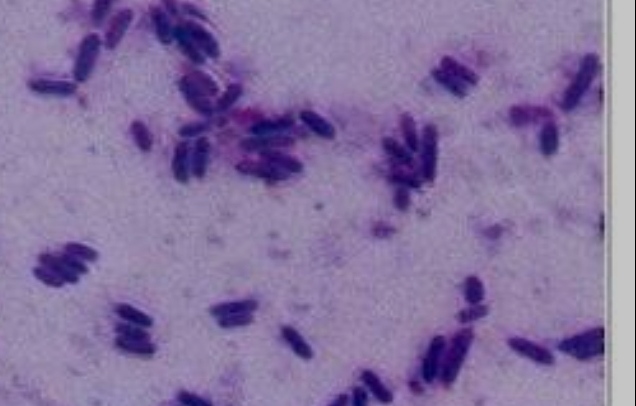
palisades
a arrangement of bacilli that resemble picket fences, often indicating specific bacterial types or characteristics.
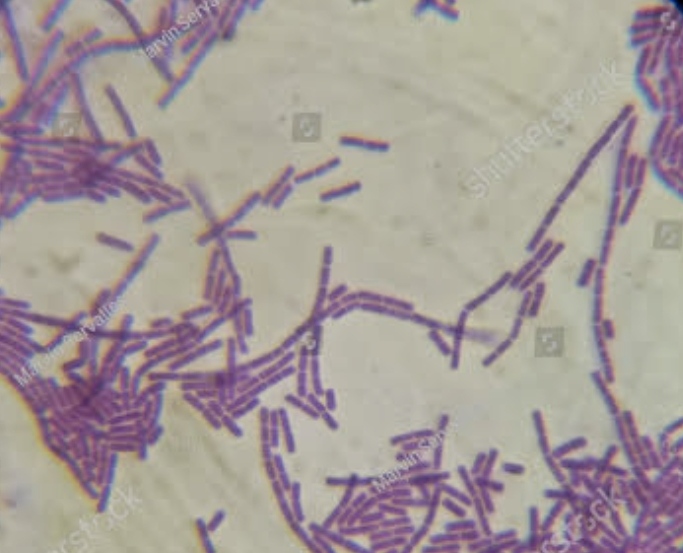
streptobacilli
bacteria that occur in chains and exhibit a rod-like shape, often associated with certain diseases.
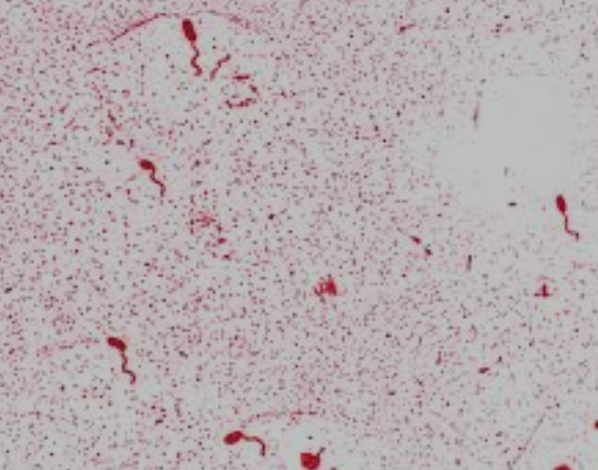
vibrio
a genus of bacteria that are curved or comma-shaped, often found in aquatic environments and can cause gastrointestinal infections.
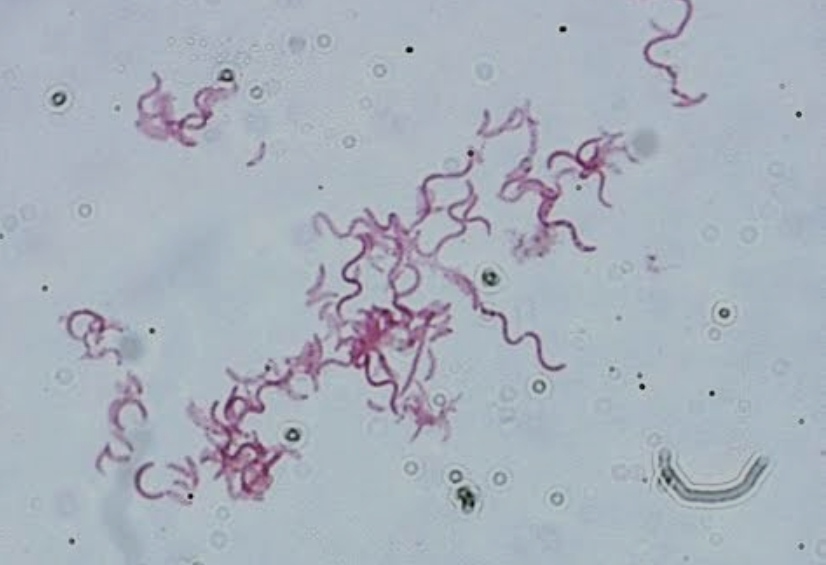
sprillump
a type of bacteria that are spiral-shaped and motile, often seen in aquatic habitats.
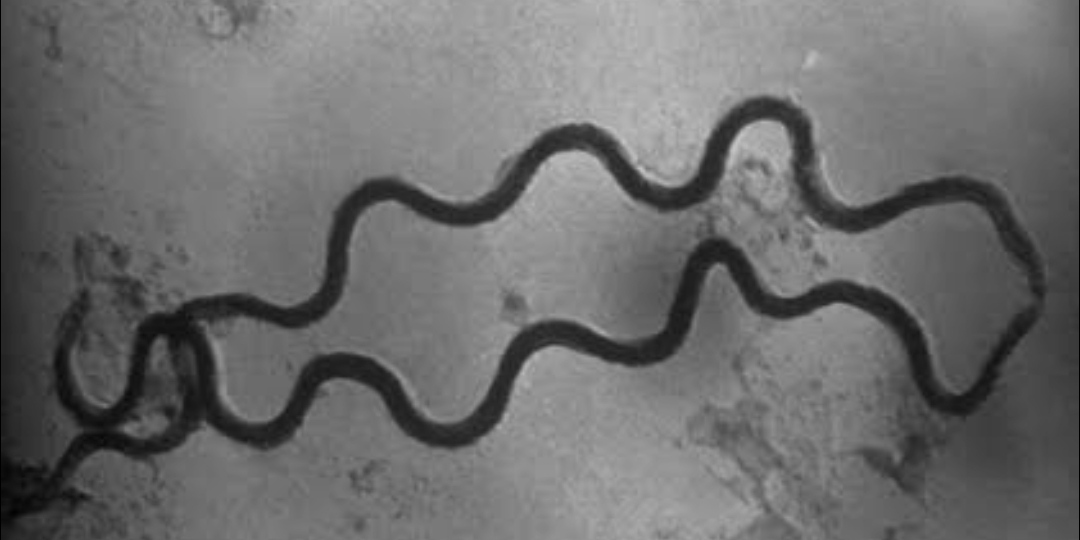
spirochetes
a group of flexible, spiral-shaped bacteria that are known for their unique movement and include pathogens such as those causing Lyme disease and syphilis.
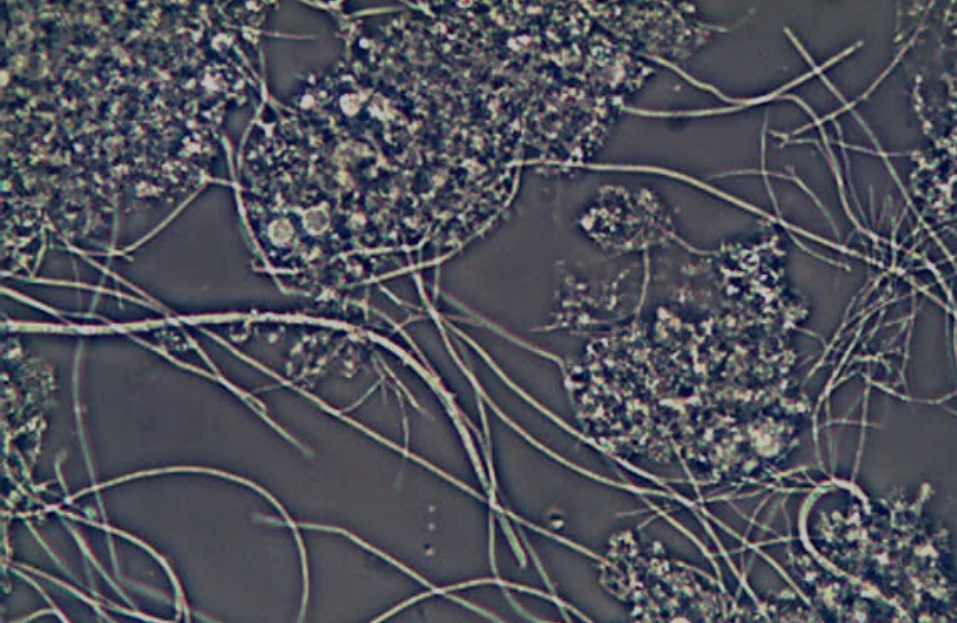
filamentous
bacteria that are thread-like in structure and often found in soil or aquatic environments, contributing to decomposition and nutrient cycling.
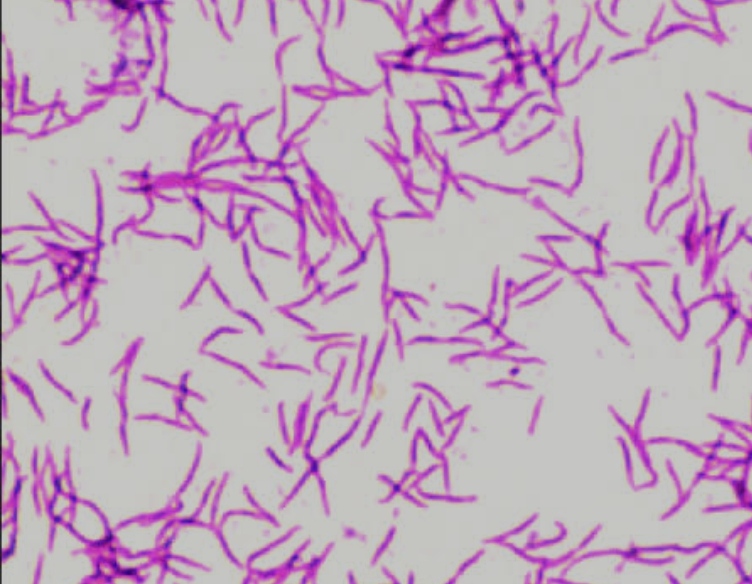
Fusiform
a type of bacteria that are spindle-shaped and often found in human pathogens.