Radio Waves (Week 10)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
1
New cards
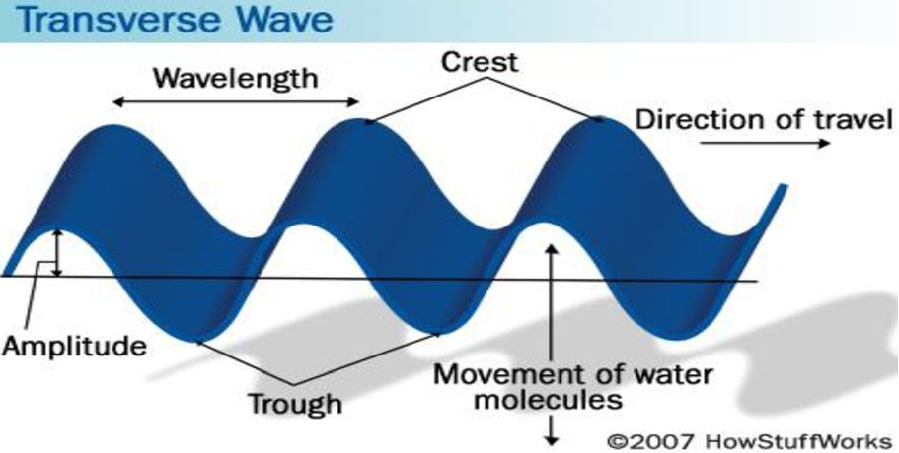
**Electromagnetic Waves**
They travel as vibrations in electrical and magnetic fields.
*(they are separated into two axis, Y-Axis is the Electric Field, X-Axis is the Magnetic Field.)*
*(they are separated into two axis, Y-Axis is the Electric Field, X-Axis is the Magnetic Field.)*
2
New cards
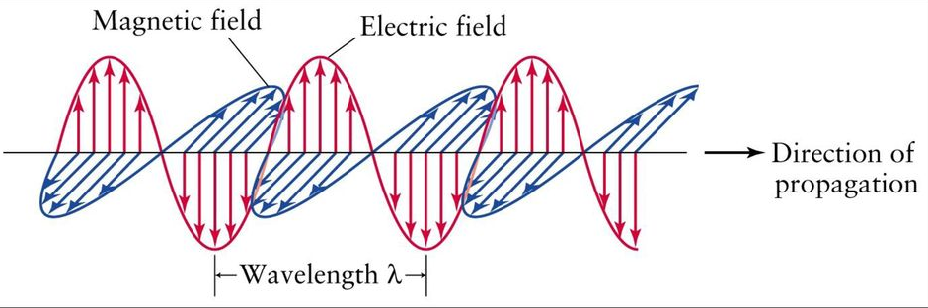
**Changing Magnetic Field**
When an electric field ____________, so does the magnetic field.
The _________________________ causes the electric field to change. When one field vibrates – so does the other.
The _________________________ causes the electric field to change. When one field vibrates – so does the other.
3
New cards
**300,000 km/s**
Electromagnetic Waves travel very fast - comparable to the **speed of light**.
\
How far is the distance traveled by EM waves?
\
How far is the distance traveled by EM waves?

4
New cards
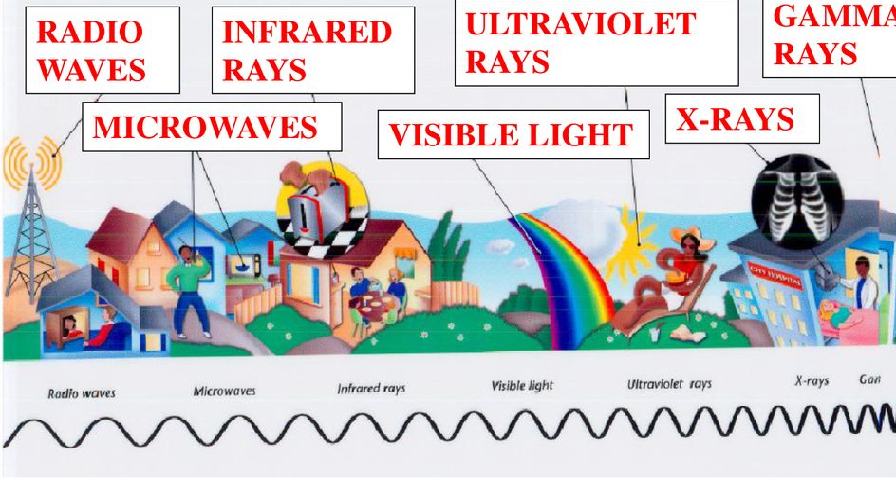
**Radio Waves**
The wavelength is long, low frequency, less energy and gets shorter.
5
New cards
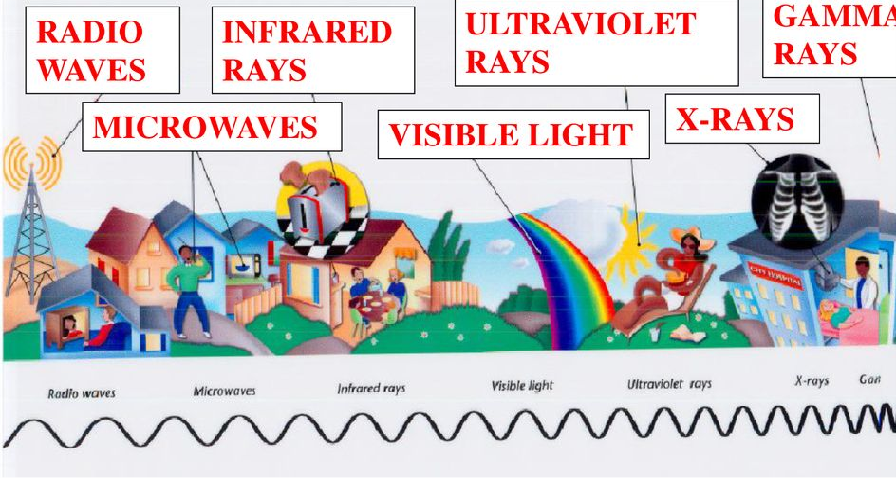
**Gamma Rays**
The wavelength gets shorter, higher frequency, and greater energy.
6
New cards
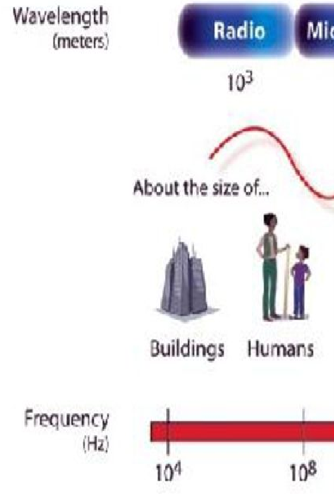
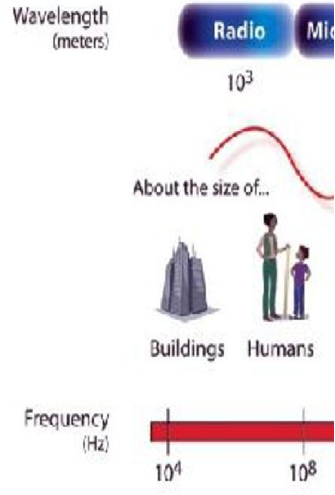
**Radio Waves**
_______________ have the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. They range from the length of a football to larger than our planet.
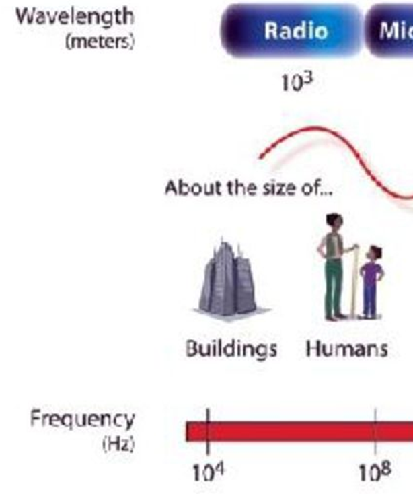
7
New cards
**Heinrich Hertz**
**Who discovered the existence of radio waves?**
\
_____________ proved the existence of radio waves in the late **1880s**. He used a spark gap attached to an induction coil and a separate spark gap on a receiving antenna.
\
_____________ proved the existence of radio waves in the late **1880s**. He used a spark gap attached to an induction coil and a separate spark gap on a receiving antenna.
8
New cards
**Sparks**
When waves created by the sparks of the coil transmitter were **picked up by the receiving antenna**, ___________ would jump its gap as well.
\
Hertz showed in his experiments that **these signals possessed** all the **properties of electromagnetic waves**.
\
Hertz showed in his experiments that **these signals possessed** all the **properties of electromagnetic waves**.
9
New cards
**Radio Transmission**
Radio stations change sound to EM waves & then your radio receiver changes the EM waves back to sound waves again. This process is called a ____________________.
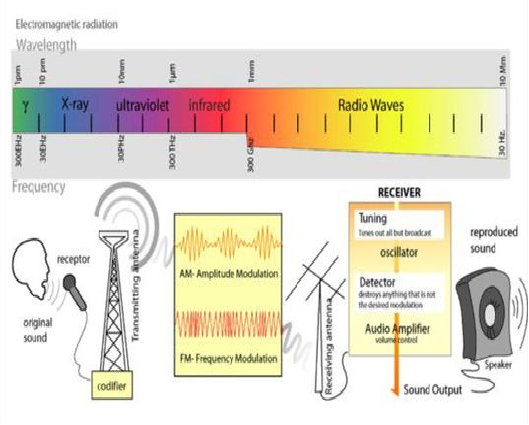
10
New cards
**Frequency**
**How do you tune in to your favorite station?**
\
You can tune a radio to a specific wavelength - or **______________ -** and listen to your favorite music.
\
You can tune a radio to a specific wavelength - or **______________ -** and listen to your favorite music.
11
New cards
**Mechanical Vibrations**
**How do you tune in to your favorite station?**
The radio "**receives**" these electromagnetic radio waves and converts them to ***______________________*** in the speaker to create the sound waves you can hear.
The radio "**receives**" these electromagnetic radio waves and converts them to ***______________________*** in the speaker to create the sound waves you can hear.
12
New cards
**No. (#) on Radio Dial**
Each radio station in an area broadcasts at a ***different frequency***.
**________________** tells frequency.
**________________** tells frequency.
13
New cards
**Global Positioning Systems (GPS)**
They measure the time it takes a **radio waves to travel** from several satellites to the receiver, **determining the distance** to each satellite.

14
New cards
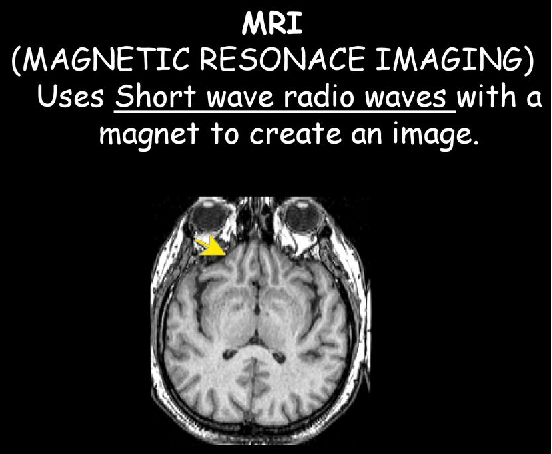
**Magnetic Resonance Imaging** **(MRI)**
It uses *short wave radio waves* with a magnet to create an image.
15
New cards
**Astronomical Objects**
**RADIO EMISSIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM**
\
____________________________ that have a changing magnetic field can produce radio waves.
\
____________________________ that have a changing magnetic field can produce radio waves.
16
New cards
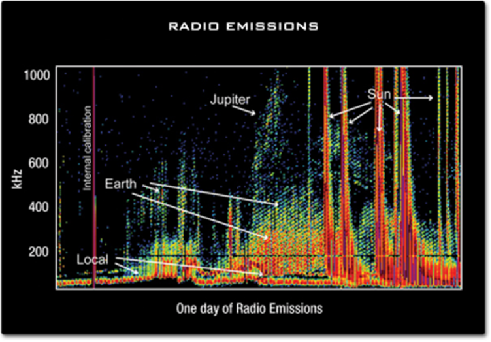
**Radio Emissions in the Solar System**
The radio astronomy instrument called **WAVES** on the **WIND** spacecraft recorded a day of bursts of radio waves from the Sun's corona and planets in our solar system.
17
New cards
**Radio Telescopes**
__________________ look toward the heavens to view planets, comets, giant clouds of gas and dust, stars, and galaxies.
By studying the radio waves originating from these sources, astronomers can learn about their composition, structure, and motion.
**Radio astronomy** has the advantage that sunlight, clouds, and rain do not affect observations.
By studying the radio waves originating from these sources, astronomers can learn about their composition, structure, and motion.
**Radio astronomy** has the advantage that sunlight, clouds, and rain do not affect observations.
