Lab 6 - Green Algae and Seedless Plants
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards focus on key concepts related to green algae and seedless plants, specifically highlighting definitions, reproductive structures, life cycles, and classification within the plant kingdom.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
The two evolutionary lineages of green algae are ___and___ .
Chlorophytes and Charophytes
Green algae and land plants are____ eukaryotes.
Photosynthetic
Land plants are characterized by having a multicellular___ part of life cycle and a multicellular___ part of life cycle.
Diploid; haploid
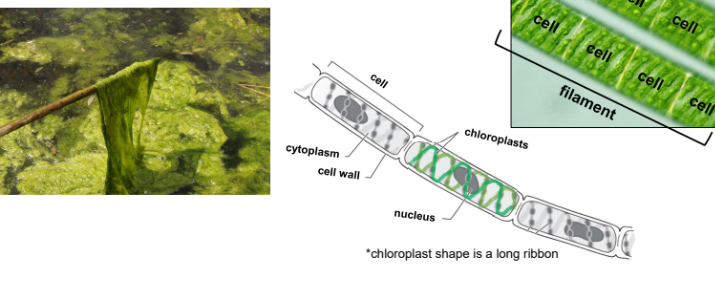
In Charophytes, zygospores are formed during___ reproduction.
Sexual
The protective structures that produce gametes in Charophytes are called___ .
Gametangia
Mosses do___ have seeds.
Not
Ferns are vascular/non vascular plants.
Vascular
The dominant stage in vascular plants is the ____stage.
Sporophyte
In the life cycle of mosses, the____ is always present.
Gametophyte
Fertilization in mosses involves sperm swimming ____through to fertilize eggs.
Water
Angiosperms produce____ as their reproductive structures.
Flowers
Sporophyte generation is more/less dominant than gametophyte generation in vascular plants.
more
The pigment responsible for capturing light energy in both green algae and land plants is _____.
Chlorophyll a and b
The mature gametophyte of ferns produces ___and ___for reproduction.
Eggs; sperm
In nonvascular plants, sperm have ____ and swim through water to fertilize eggs.
Flagella
Mosses belong to the group of plants.
Nonvascular
In Charophytes, during sexual reproduction, _____ forms between filaments.
Conjugation tube
Land plants have well-developed ______ for specialized functions.
Tissues
The life cycle of mosses involves _____ and_____ between generations.
Meiosis; fertilization
The_______ generation of plants develops from the zygote after fertilization.
Sporophyte
The haploid stage of plant life cycles includes structures that produce____ and_____ .
Sperm; eggs
Charophytes and land plants form_____ in protective structures.
Gametes
The life cycle of land plants exhibits _____ of generations.
Alternation
In ferns, the gametophyte is tiny and dies after______ is formed.
Sporophyte
The capsule in mosses produces_____ .
Spores
The sporophyte generation is diploid (2n)/haploid(n) and produces spores by_____ .
Diploid (2n); meiosis
The gametophyte generation is diploid (2n)/haploid(n) and produces gametes by _____.
Haploid (n); mitosis
In alternation of generations, the fusion of two gametes (sperm and egg) forms a ____.
Diploid zygote
The _____ develops into the sporophyte generation through mitotic divisions.
Zygote
______ are single-celled reproductive structures that develop into the gametophyte generation.
Haploid spores
____ is a type of green alga closely related to land plants and has complex reproductive structures called gametangia.
Chara
_____ is a filamentous green alga that reproduces sexually through conjugation, without specialized gametangia.
Spirogyra
Vascular plants possess specialized tissues for water and nutrient transport, namely ___ and ____.
Xylem; phloem
Non-vascular plants (like mosses) typically absorb water and nutrients directly from their surroundings through____ and _____.
Diffusion; osmosis
Vascular plants are characterized by having true ___,____ , and___ .
Roots; stems; leaves
In non-vascular plants, the_____ is the dominant and most conspicuous stage of the life cycle.
Gametophyte
What is the primary function of xylem?
To transport water and dissolved minerals from the roots upwards to all other parts of the plant.
What is the primary function of phloem?
To transport sugars (produced during photosynthesis) from the leaves to other parts of the plant where they are needed for growth or storage.