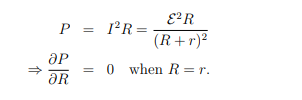10- Electric currents: the electromotive force
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What does Coulomb’s Law describe, and for what type of charges is it applicable?
Coulomb’s Law describes the force between two stationary charges
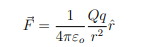
Which of the two laws derived from Coulomb’s Law remains valid for moving charges?
Gauss's Law remains valid even for moving charges
This law is independent of the distribution of the charge Q enclosed by the Gaussian surface.
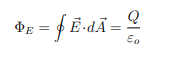
Which law derived from Coulomb’s Law needs amending when dealing with moving charges?
The Circuital Law for the Electric Field needs amending when dealing with moving charges.
The original form is no longer valid and requires modification in the context of moving charges.

What is electric current and how is it defined?
It is the flow of electric charge, and it is defined as the charge flow per unit time
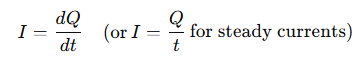
What is required for the flow of electric charge to occur between two points?
There must be an electric field E generating a finite potential difference (p.d.) V between the points.
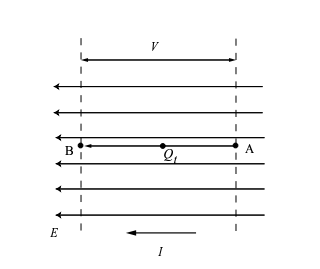
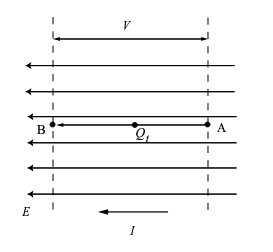
What is the work done by the electric field when charge Q flows between two points A and B?
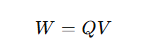
How is power dissipation related to the flow of electric charge?
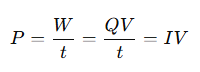
What happens to the charges moving in a metal wire when driven by a constant electric field?
In a metal wire, the charges do not accelerate continuously
They drift at a constant average velocity v
This is due to electric resistance, caused by collisions between moving charges and imperfections in the metal’s crystalline lattice.
What is the effect of resistance in a conductor?
In the presence of resistance, the kinetic energy gained by moving charges is continuously transferred to the metal atoms
This causes the metal’s temperature to rise.
This process results in power dissipation.
What is the formula for electric resistance?
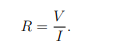
How can power dissipation in a resistive material be expressed?
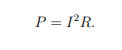
What is the formula for the resistance of a wire?
ρ is the resistivity
l is the length of the wire
A is the cross-sectional area of the wire.
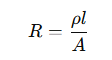
What is conductivity and how is it related to resistivity?
Conductivity (σ) is the reciprocal of resistivity

What is the formula that relates current density, J, and electric field in a conductor?
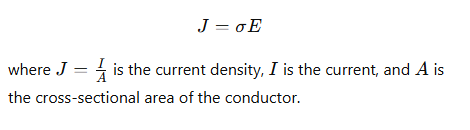
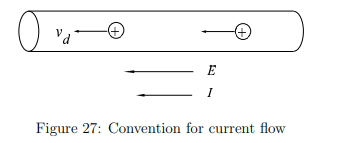
In which direction is electric current defined to flow, even if the actual charge carriers are different?
It flows in the direction that positive charge carriers would move.
This convention holds even if the actual charge carriers are negative (e.g., electrons), which move in the opposite direction.
What is the electromotive force (emf), and what does it represent?
Its the amount of energy gained per unit charge that passes through a device
It is not a force but rather a measure of energy conversion into electric energy.
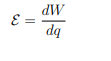
What is the equation for the rate of energy conversion in an energy conversion device?
P is the power
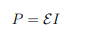
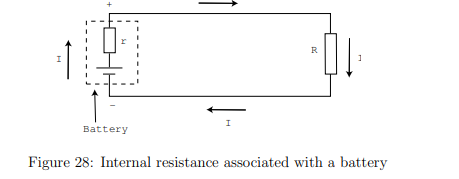
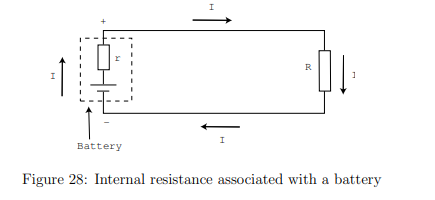
How does internal resistance affect the energy conversion process in a device?
Internal resistance (r) reduces the available voltage for external use.
The energy conversion device’s total resistance is the sum of the internal resistance (r) and the external resistance (R),
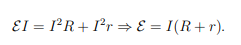
What is the voltage across the terminals of the energy-conversion device considering internal resistance?
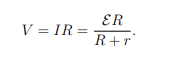
When does maximum power get delivered to the external circuitry in an energy conversion device?
Maximum power is delivered when the external resistance R equals the internal resistance r