2.3: Flows of Energy and Matter
1/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
significant ideas
1) the interactions of species with their environment result in energy and nutrient flows
2) photosynthesis and respiration play a significant role in the flow of energy in communities
3) the feeding relationships of species in a system can be modeled using food chains, food webs and ecological pyramids
fate of solar radiation
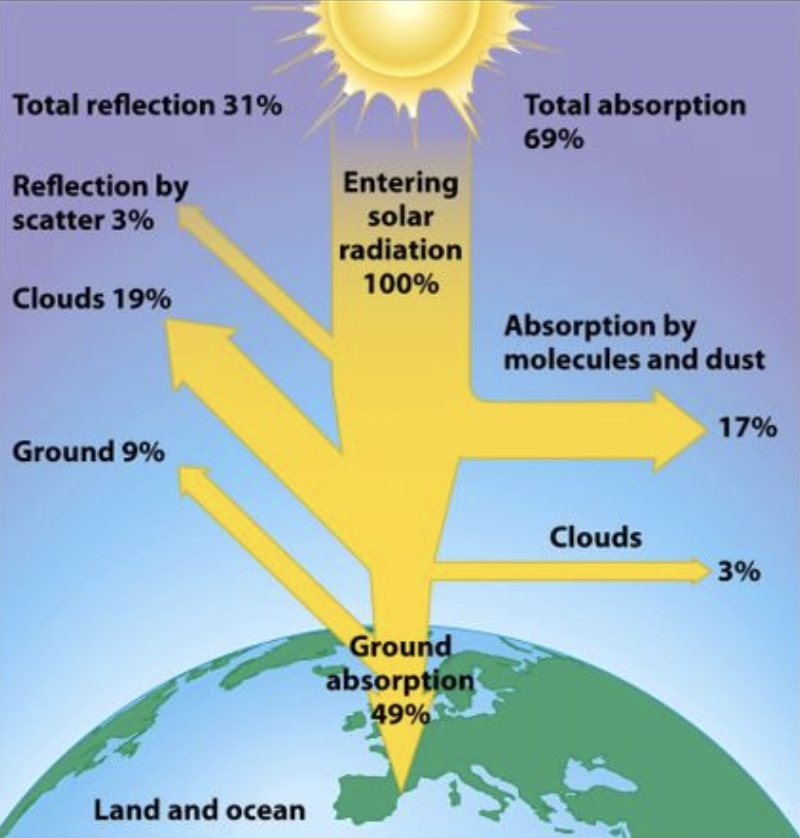
percentage of sun’s radiation available for plants during photosynthesis
1%
albedo
reflectivity of a surface (dark colors = low, light colors = high)
productivity
conversion of energy into biomass over a given period of time (rate of growth or biomass increase in plants and animals)
measured by: UNIT J/m^-2 YR^-1 or G m ^-2 YR^-1
types of productivity
primary: productivity of autotrophs
secondary: productivity of heterotrophs
gross primary productivity (GPP)
total gain in energy or biomass per unit area per time by green plants (biomass that could be gained before deductions)
net primary productivity (NPP)
gain in energy or biomass (per unit area per time) that remains after deduction due to respiration → what is available for consumers to eat
NPP = GPP - R
J/m^-2/yr
respiration
amount of biomass consumed during cellular respiration to keep the producer alive → lost and is not passed to next trophic level
how does biomass vary
spatially (latitude) - near equator more consistent biomass
temporally (seasons) - further from equator, season influences increase and decrease in biomass
gross secondary productivity (GSP)
total energy/biomass assimilated by consumers
GSP = food eaten - fecal loss
J
net secondary productivity (NSP)
total gain in energy/biomass per unit are per unit time by consumers after allowing for losses to respiration
NSP = GSP - R
* growth because it is what is left after other life processes have taken place
J/m^-2/yr^-1
primary vs secondary productivity
plants vs consumers
diff equations
primary productivity accounts for respiration, secondary for fecal loss in gross productivity and respiration for net productivity
methods for measuring primary productivity
harvest method - measures biomass and expresses biomass per unit area per unit time
CO2 assimilation - measures CO2 uptake in photosynthesis and released by respiration
O2 production - measure O2 production and consumption
radioisotope method - use C14 tracer in photosynthesis
chlorophyll measurement - assumes a correlation between the amount of chlorophyll and the rate of photosynthesis
energy flow through ecosystems
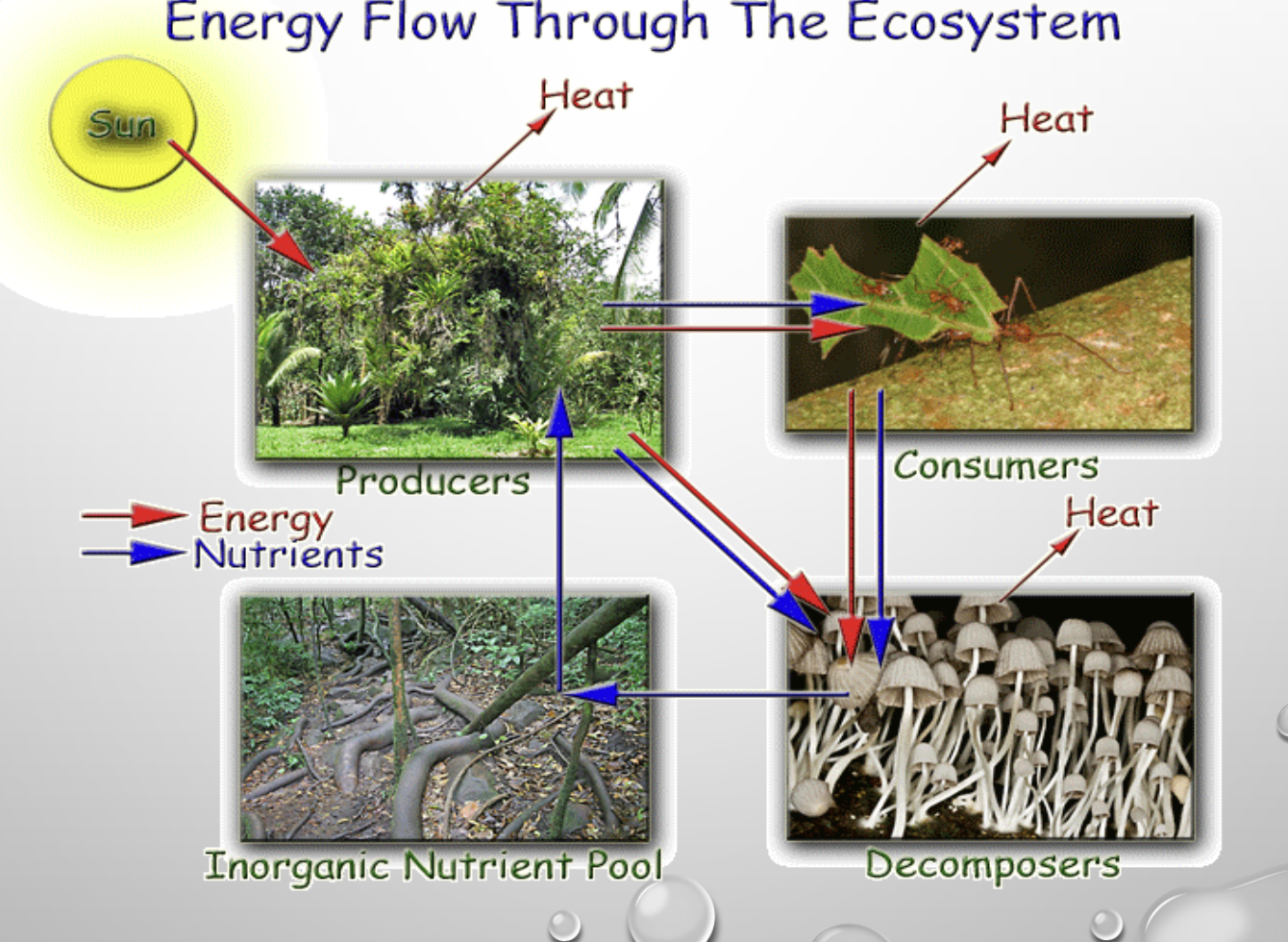
2 ways ecological efficiency can be calculated
* efficiency of transfer from trophic level to the next is 10%
efficiency of assimilation = (gross productivity/food eaten) x 100
efficiency of biomass = (net productivity/gross productivity) x 100
sustainable yield
amount of biomass that can be extracted without reducing natural capital (stock of renewable and non-renewable resources that combine to yield a flow of benefits to people) of the system
maximum sustainable yield
amount of biomass which may be removed from an ecosystem without diminishing the natural income produced by that system each year
transfer b/c matter moves from place to place
must not exceed the income so that capital remains same
eg: cutting trees, hunting, fishing, etc
study 12 on 2.3 notes
energy
flows directly through earth’s ecosystems (mostly as sunlight, exits as heat)
travels through food chains and lost as heat
matter
gets recycled through biogeochemical cyces
moves between stores (sinks)
* nutrients and matter are finite
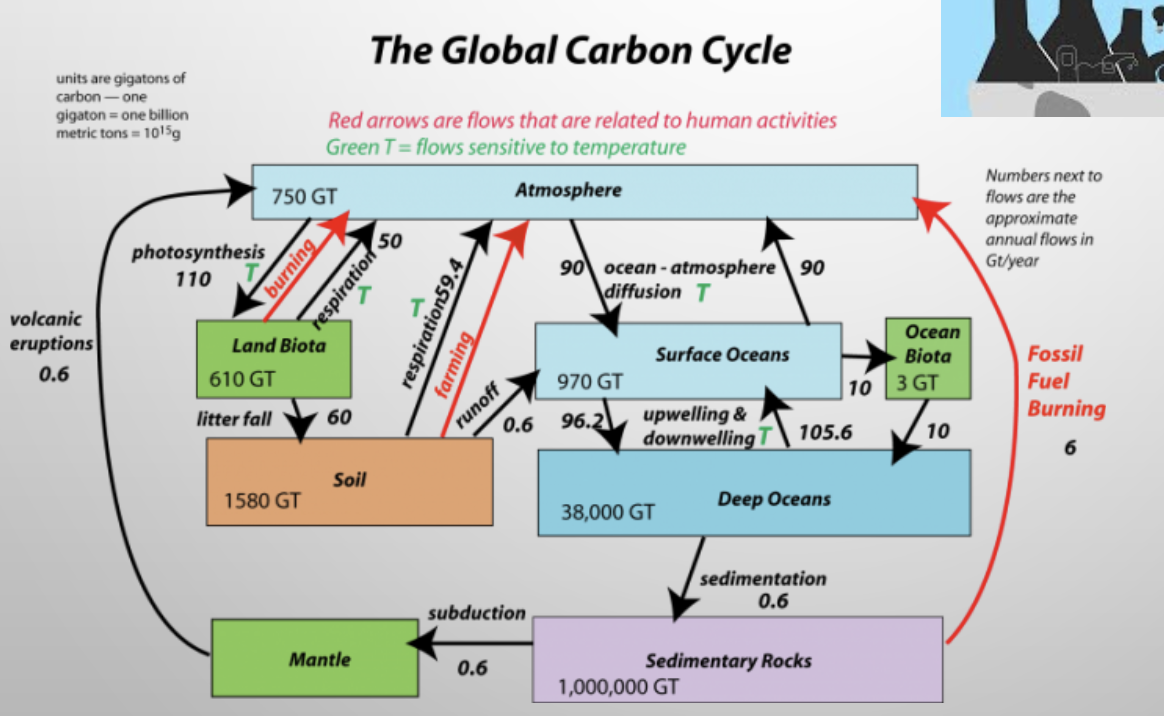
carbon cycle
regulates climate through amount of carbon in atmosphere
when fossil fuels are burned carbon is transferred out of stores and into the atmosphere → affects climate
fires and other disasters that occur from deforestation and climate change add CO2 to atmosphere (but also lets some environments recover)
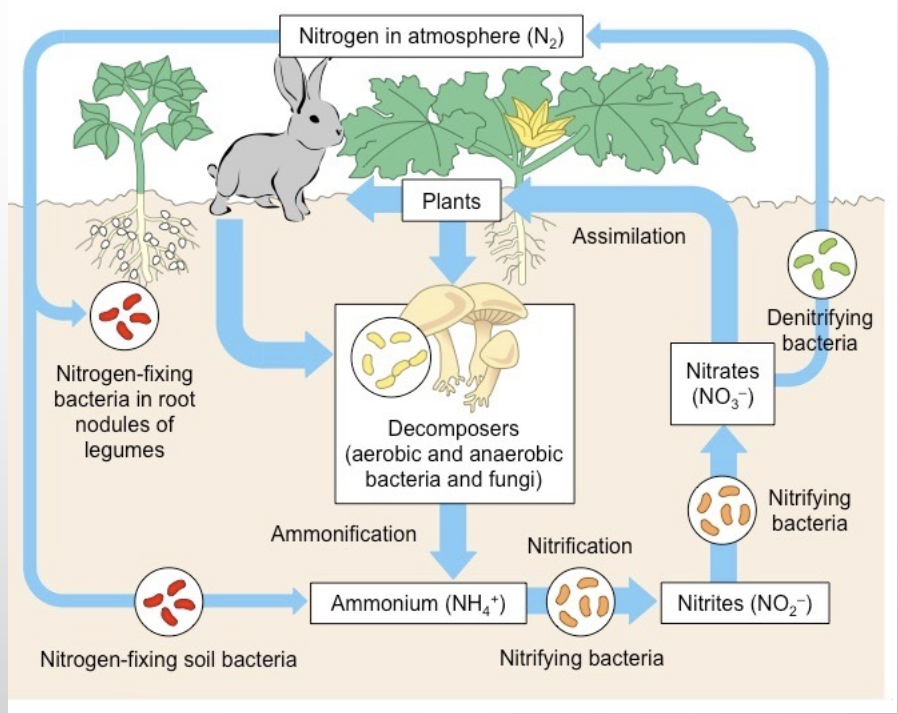
nitrogen cycle
most abundant gas in the atmosphere (but in an unavailable form)
nitrogen fixation
nitrification
denitrification
effects of commercial agriculture: increases air pollution and acid rain, uses inorganic fertilizers, livestock release ammonia, wetland denitrification is reduced so less nitrogen enters atmosphere → fosters environment for weeds, eutrification, altered food web, etc
how does removing biomass relate to growing crops, raising livestock, and harvesting wild animals
this removes food or habitat for native species present, affecting those at top of food chain who have a harder time making up the energy deficit