Staining Technique Micro Lab Final
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
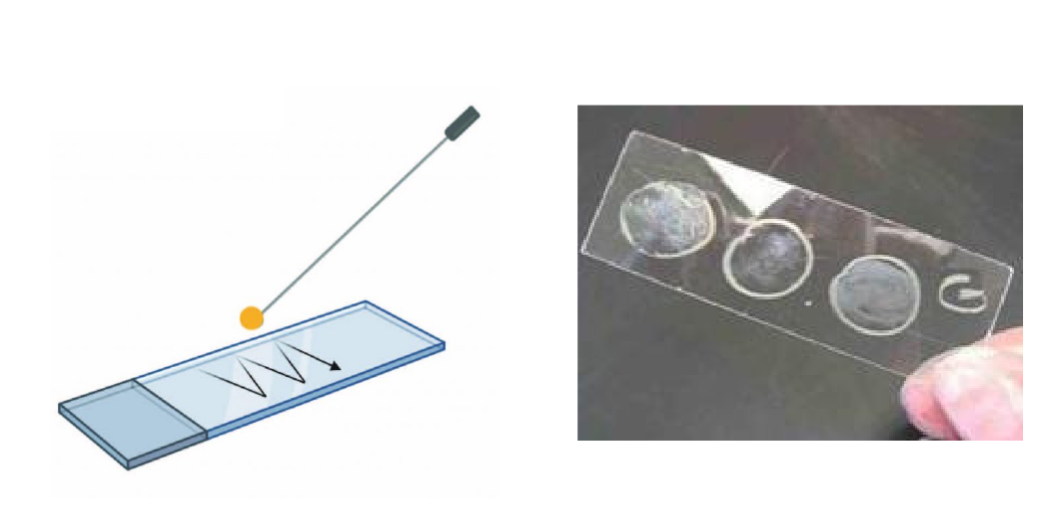
Slide Smear
Explain Slide Smear Technique
Slide smear technique is spreading a sample thinly on a slide for microscope viewing.
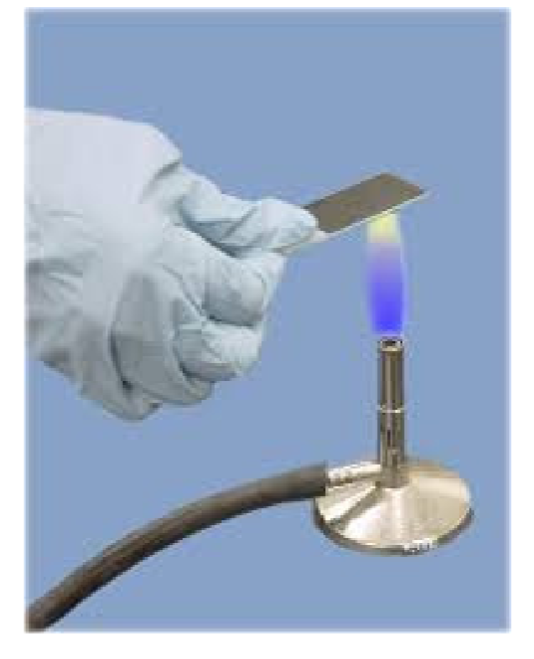

Heat fixing
Explain Heat Fixing Technique
Heat fixing is using heat to stick cells to a slide and preserve the structure while preventing contamination
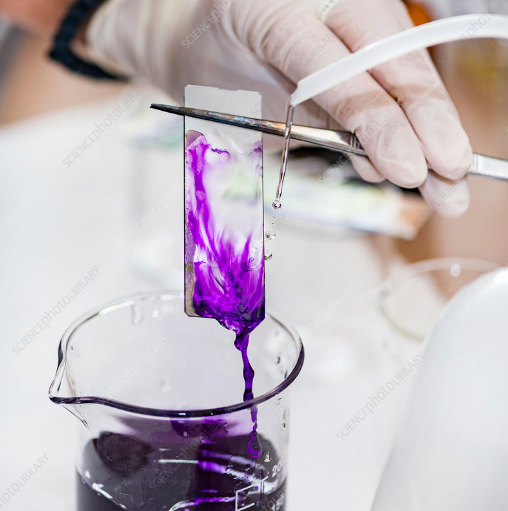

Staining Method
Explain Staining Method Technique
Staining method is adding dye to a sample to color and highlight its parts for easier viewing under a microscope
Simple stain
Explain Simple Stain Technique
Simple stain is using one dye to color cells so their shape and arrangement are easier to see under a microscope (Colors cells or the background)
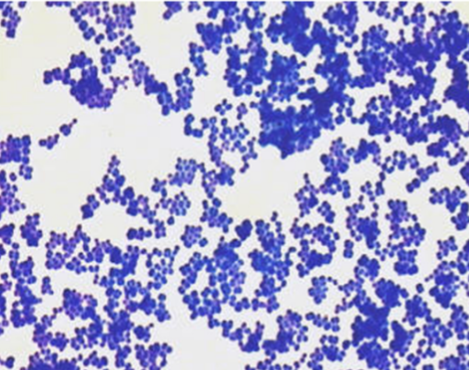
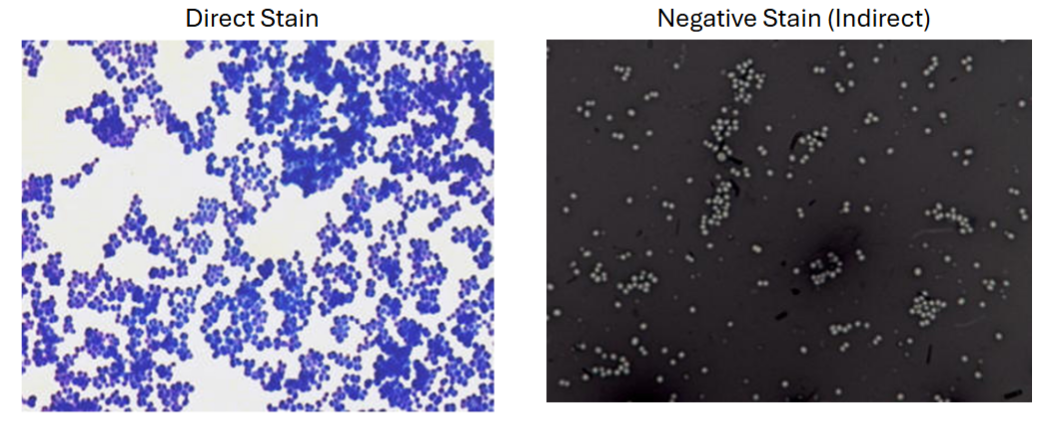
Direct Stain
Explain Direct Staining
Direct stain is a simple stain method that colors the cells or tissues themselves, leaving the background unstained or colorless
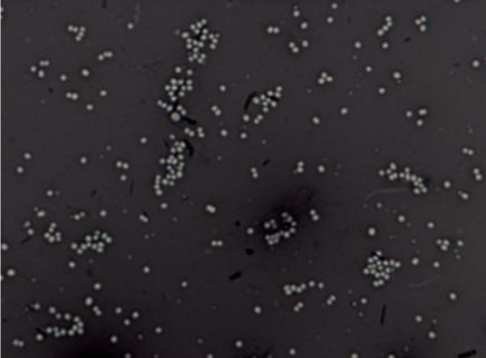
Negative Stain (Indirect)
Explain Negative Stain (Indirect)
Negative Stain is a simple stain method a method of preparing samples for electron microscopy where the background is stained, making the sample appear lighter in contrast
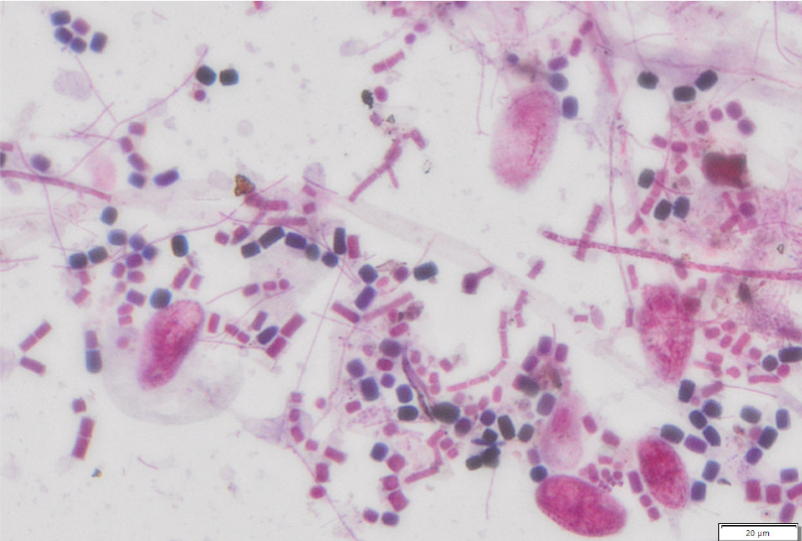
Differential Stain
Explain Differential Stain Technique
A process that uses multiple stains to distinguish between different types of microorganisms or structures/cellular components
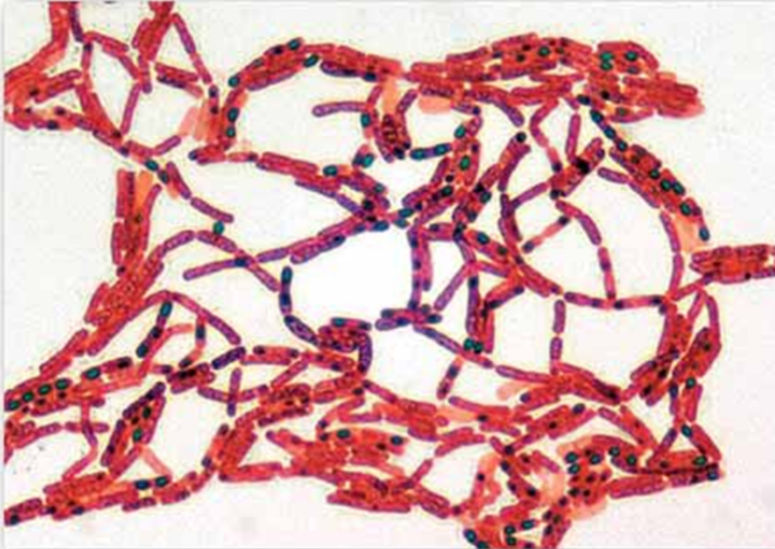
Structural Stain
Explain Structural Stain Technique
helps in the visualization of a bacterial structure
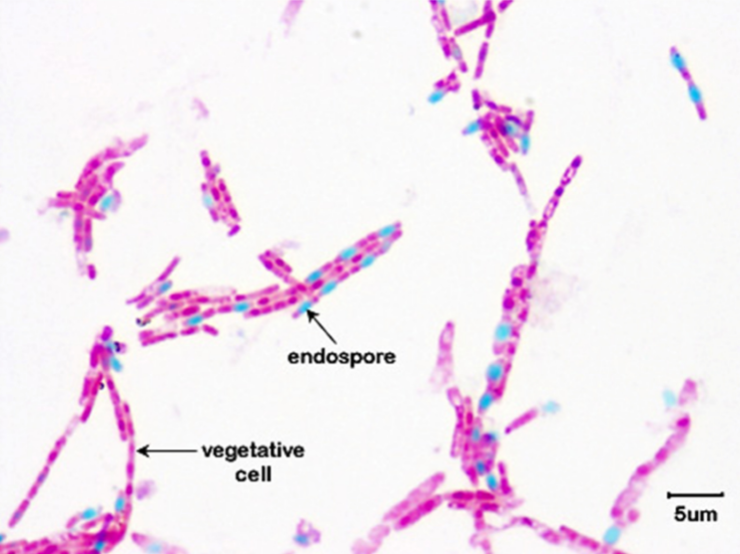
Spore Stain
Explain Spore Stain Technique
A type of microbial staining technique used to identify and visualize bacterial endospores
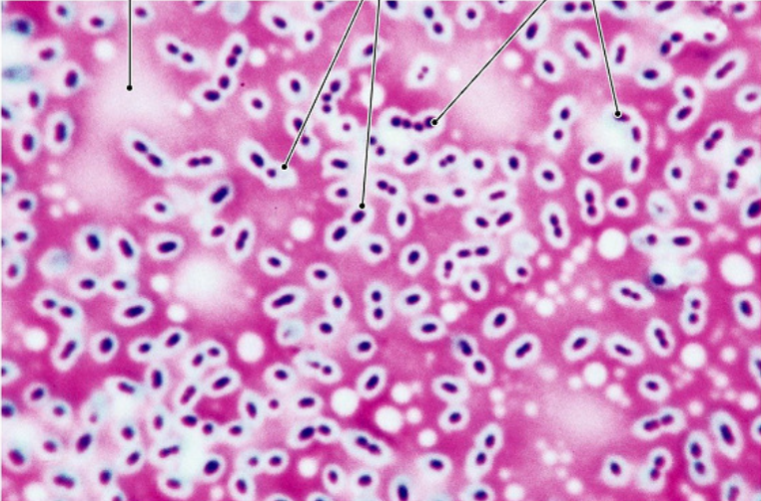
Capsule Stain
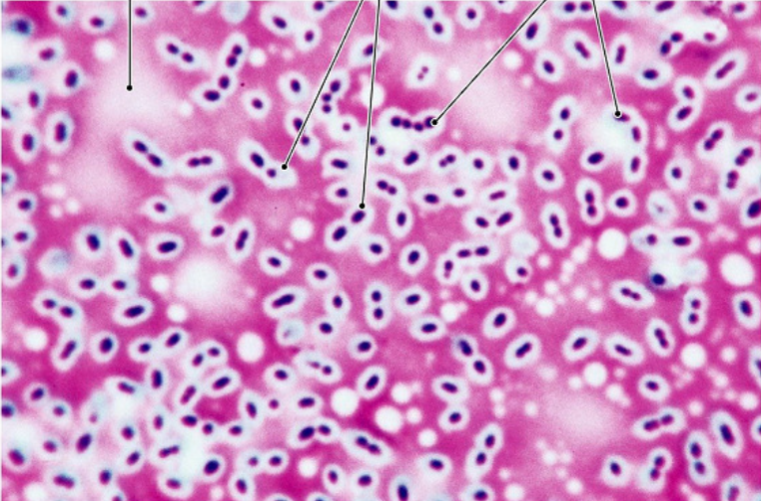
Explain Capsule Stain Technique
A microscopic technique used to visualize bacterial capsules, which are protective, sticky, and often polysaccharide-rich layers surrounding some bacterial cells.
.
Gram- Stain
Explain Gram Stain Technique
A staining technique for the preliminary identification of bacteria, in which a violet dye is applied, followed by a decolorizing agent and then a red dye. The cell walls of certain bacteria (denoted Gram-positive ) retain the first dye and appear violet, while those that lose it (denoted Gram-negative ) appear red. Also called Gram's method.
What color would be a gram positive?
Purple/Violet
What color would be a gram negative?
Red/Pink
What are the steps to Gram Stain Technique?
The steps include applying crystal violet stain, followed by iodine treatment, decolorization with alcohol or acetone, and finally counterstaining with safranin.

What kind of stain is Gram Stain?
Differential
What kind of stain is Acid-Fast Stain?
Differential
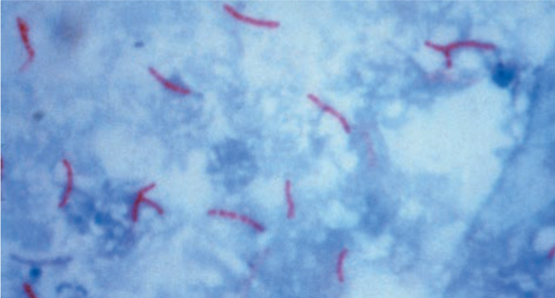
Acid-Fast Stain
Which stain is better to use Basic or acidic stain?
Basic stain because generally all the cell have a negative charge on the outside of their cell wall and basic stain work with the negative stain and allow the cell to stick and colorize JUST the cell. (the acidic stain makes the cell clear)
Difference between Direct and Negative (indirect) stain?
Direct uses heat fixing and Negative stain does not use heat fixing
Fixation
staining method that keeps bacteria preserved on the slide and kills bacteria
chemical fixing
uses chemicals to preserve the structure of the sample
Also:
-stops cell degradation
- denatures proteins and stops enzymatic activity within specimen
chromophore stands for..
Chromo: color
Phore: bearing
basic stain
direct stain/positively charged chromophore (color bearing)
acidic stain
indirect stain/negatively charge chromophore