Chapter 10 Corporate Governance
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Principal-Agent Problem
A conflict of interest between a company's management and the company's stockholders.
Corporate Governance
The system of rules, practices, and processes by which a company is directed and controlled, ensuring its operations are ethical, transparent, and in the best interests of its stakeholders.
Board of Directors (BOD)
Is composed of inside and outside directors, who are elected by the shareholders to represent their interests.
Functions of the Board of Directors
1. Control function: Selecting, evaluating, and compensating the top executives; A compensation committee within the board; CEO succession plan; Ensuring the firm's compliance with laws; An Audit Committee within the board.
Service function of BOD
General strategic oversight and guidance.
Resource acquisition function of BOD
Function related to acquiring necessary resources for the company.
Inside directors
Part of the company's senior management team.
Outside/Independent directors
Are not employees of the firm and are more likely to watch out for the interests of shareholders.
Interlocking directorate
The same person serves on the boards of two or more companies.
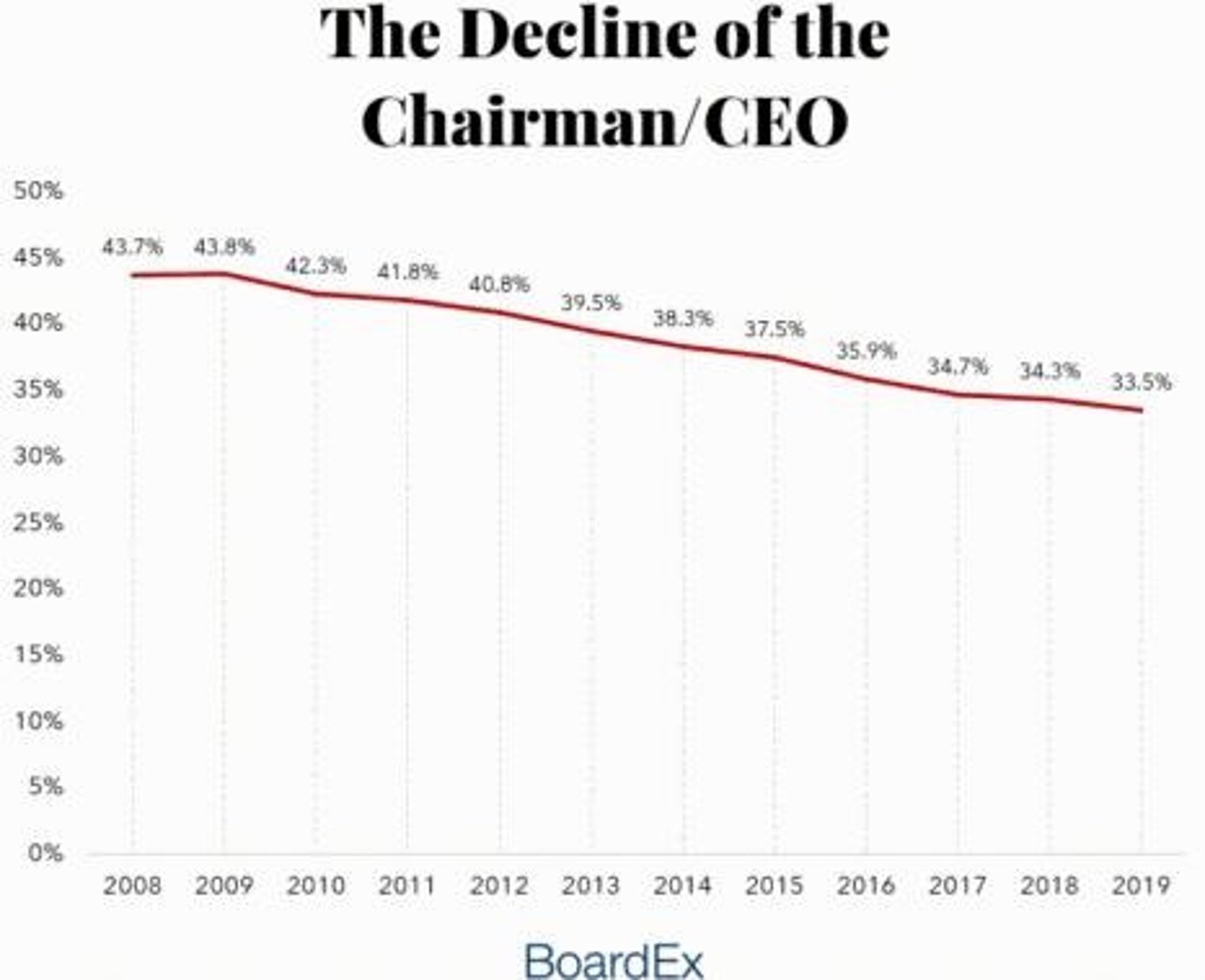
CEO duality
The CEO doubles as the chairperson, common in the US.
Outgoing CEO on the board
Pros: Can lend stability to the transition process; Cons: Can undermine the credibility and leadership of the incoming CEO.
Audit Committee
A committee within the board that ensures compliance with laws.
Compensation committee
A committee within the board responsible for evaluating and compensating top executives.
CEO succession plan
A plan ensuring a smooth transition when a new CEO is appointed.
Research on CEO duality
Research is inconclusive on whether CEO duality (or non-duality) is more effective.