LOM CH. 16 SKIN
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
integumentary system
the skin and its accessory structures such as hair, glands and nails
sebaceous glands
oil glands in the skin, they secrete sebum(oily secretion), located in the dermis
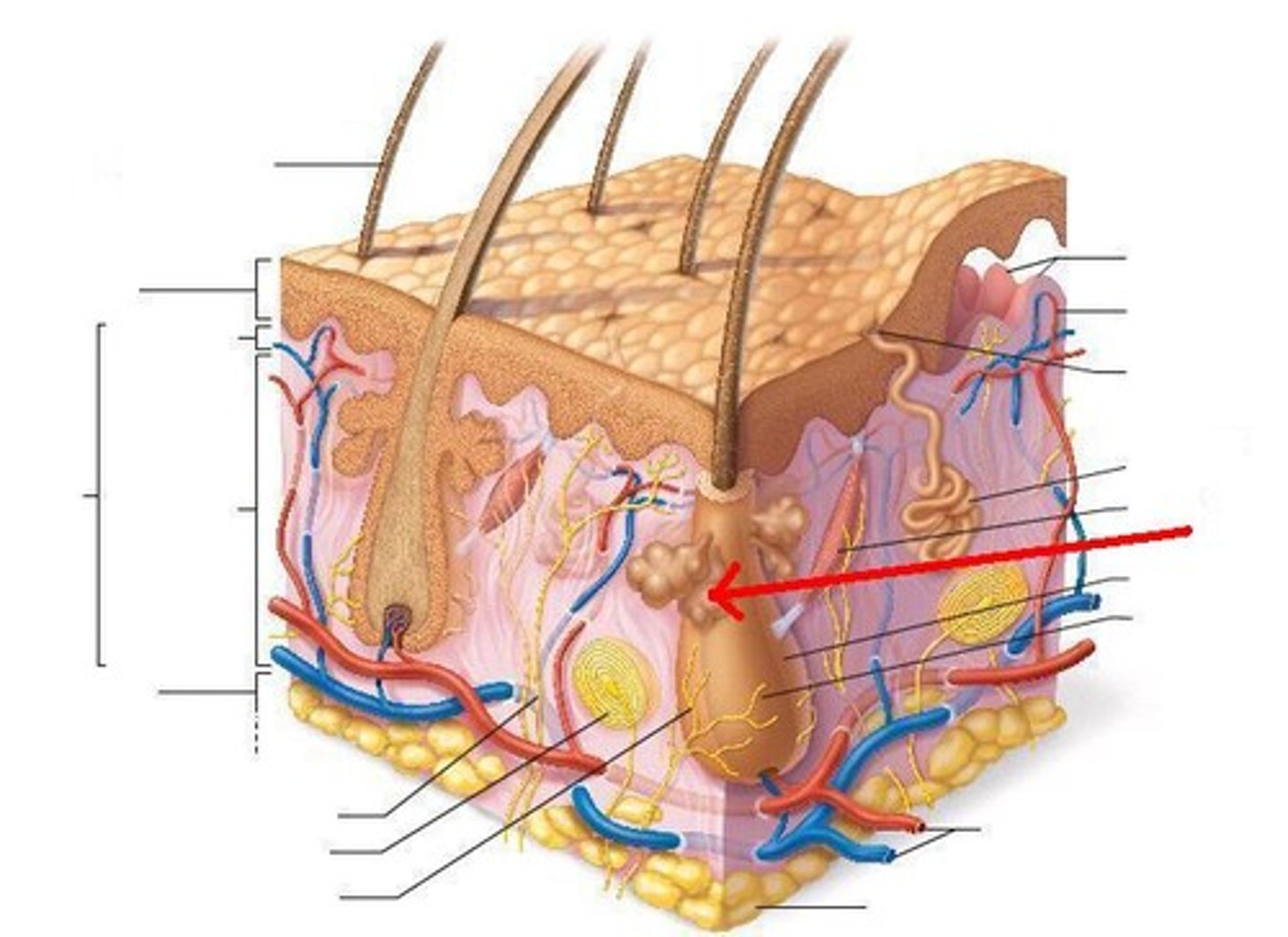
sweat glands
The glands that secrete sweat, located in the dermal layer of the skin.
Epidermis
outermost layer of skin, contains keratin
the cells here are squamous cells arranged in layers(strata) to form Stratified squamous epithelium
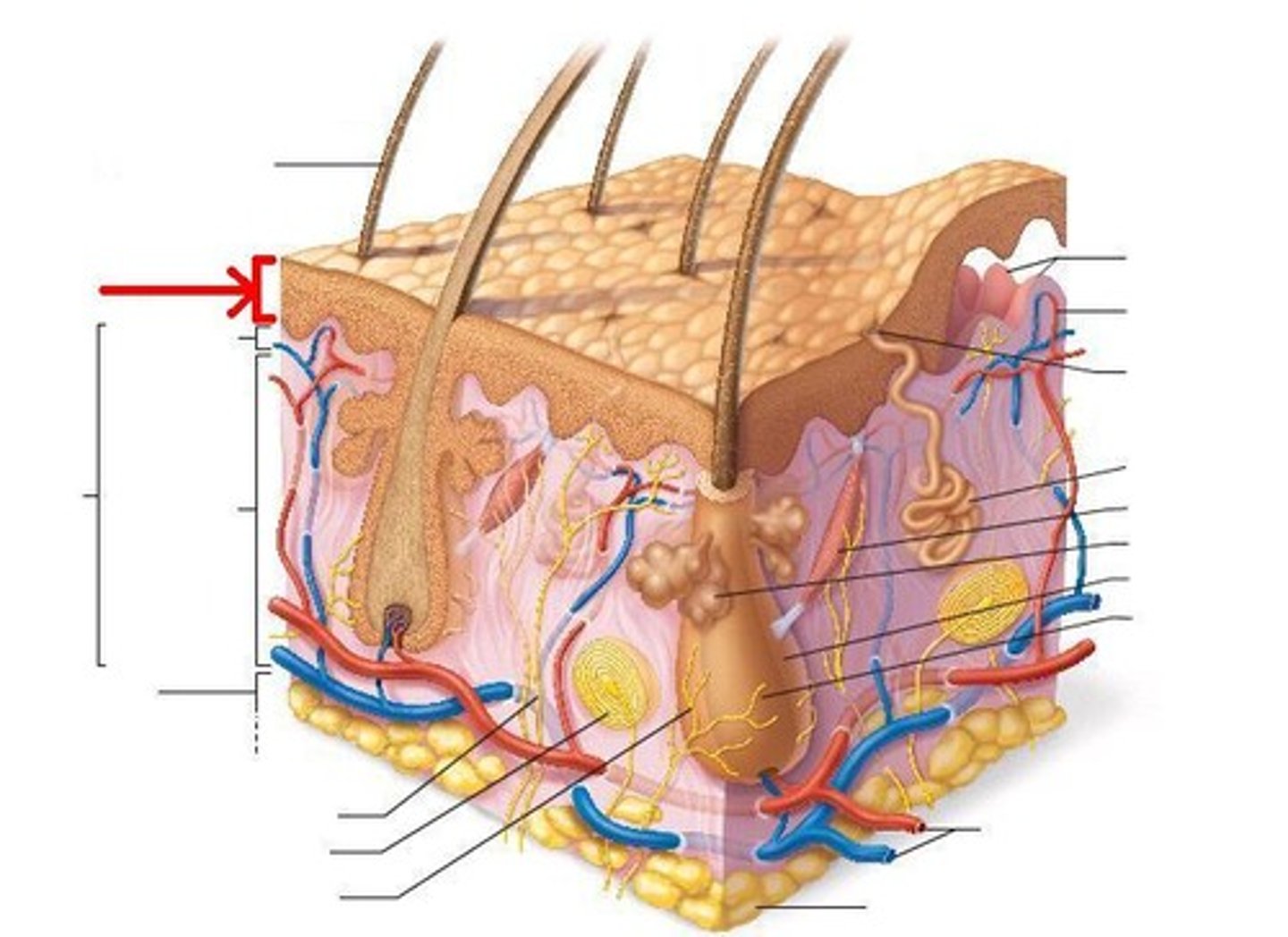
dermis
located just below the epidermis is a dense fibrous layer of connective tissue, it contains collagen
-it is composed of elastin and collagen
Elastin
Protein fiber found in the dermis; gives skin its elasticity and firmness.
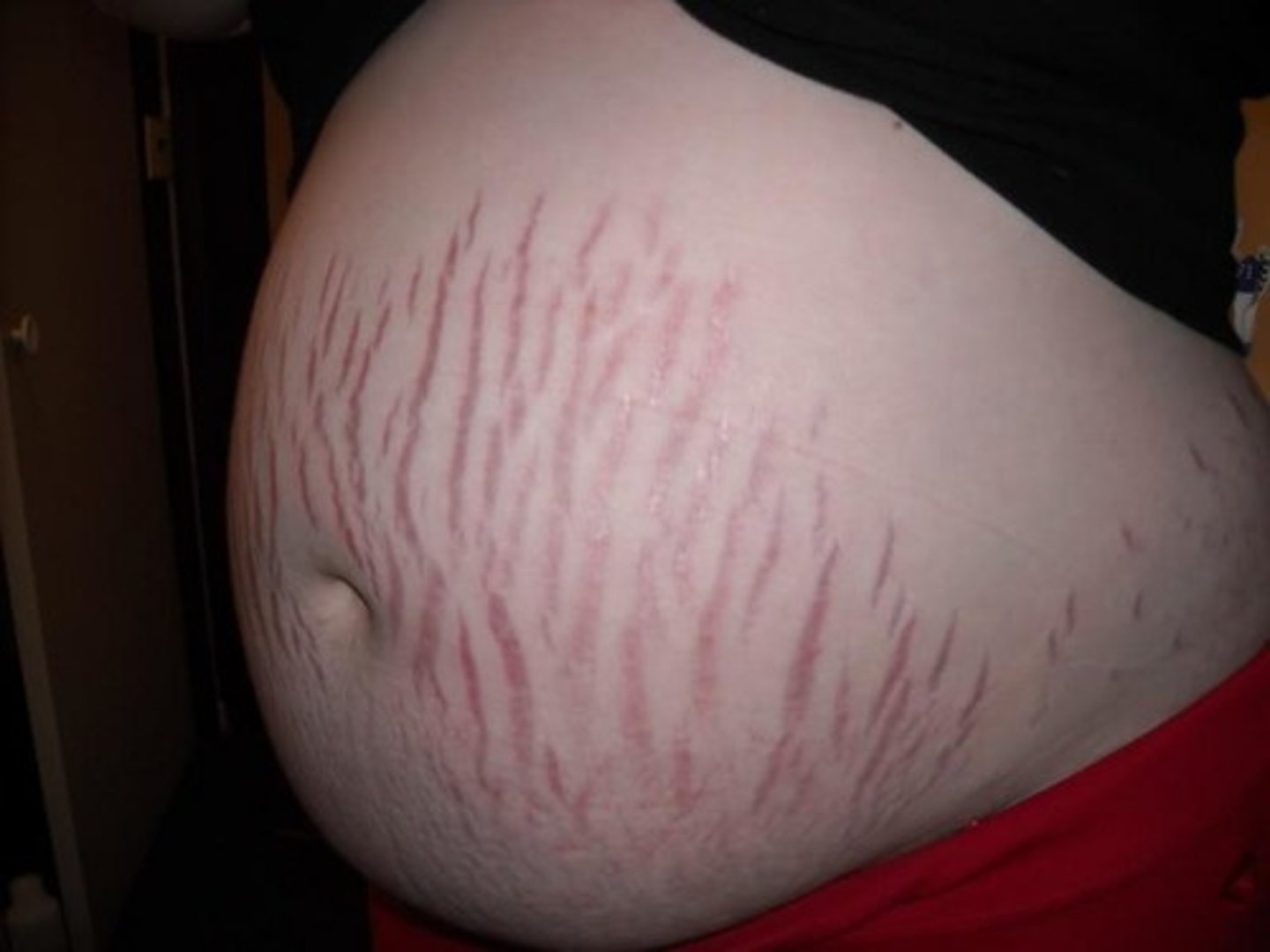
Striae
atrophic pink, purple, or white linear streaks on the breasts, associated with pregnancy, excessive weight gain, or rapid growth during adolescence
aka stretch marks
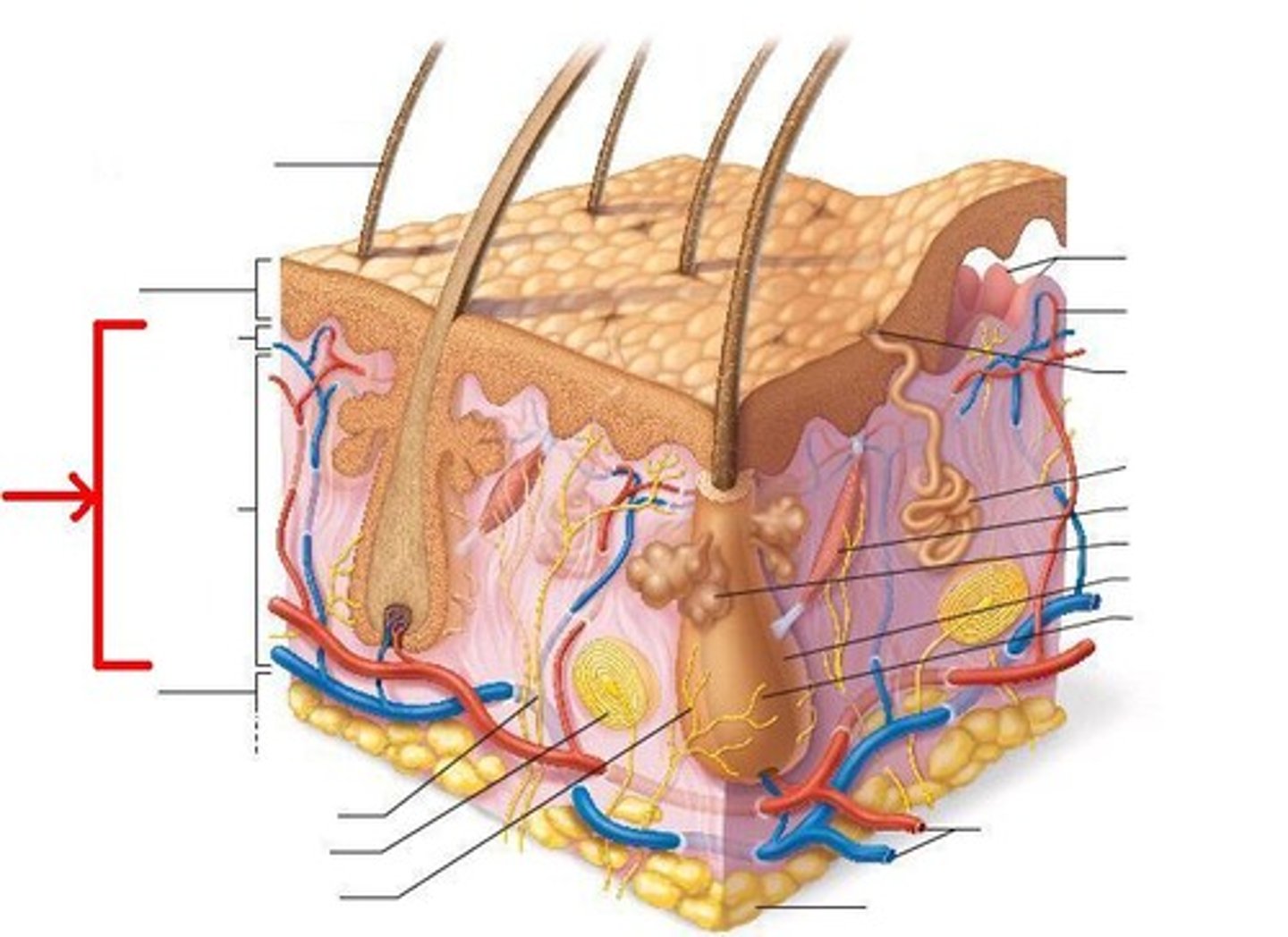
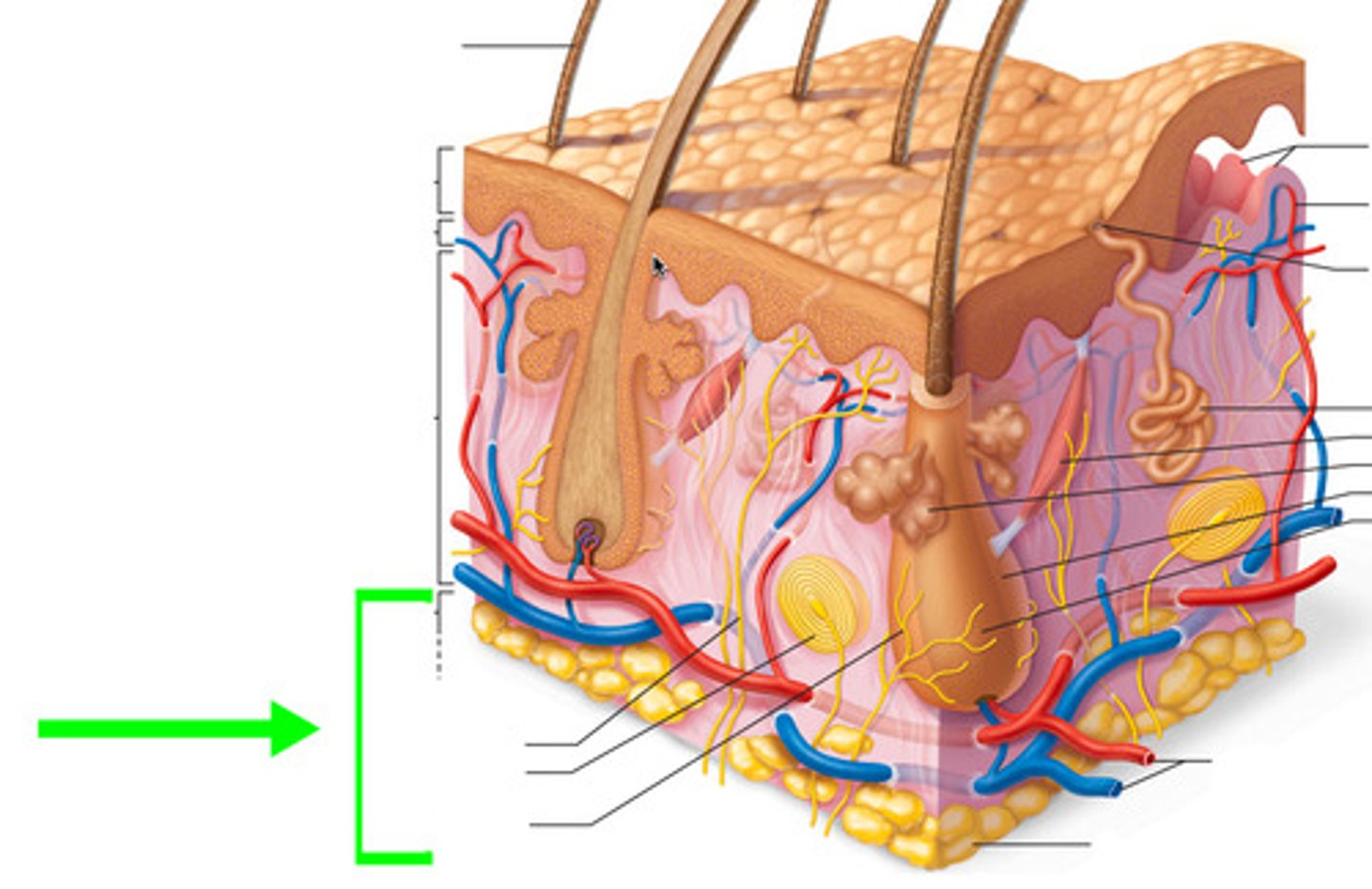
subcutaneous layer
innermost layer of the skin, it specializes in the formation of fat
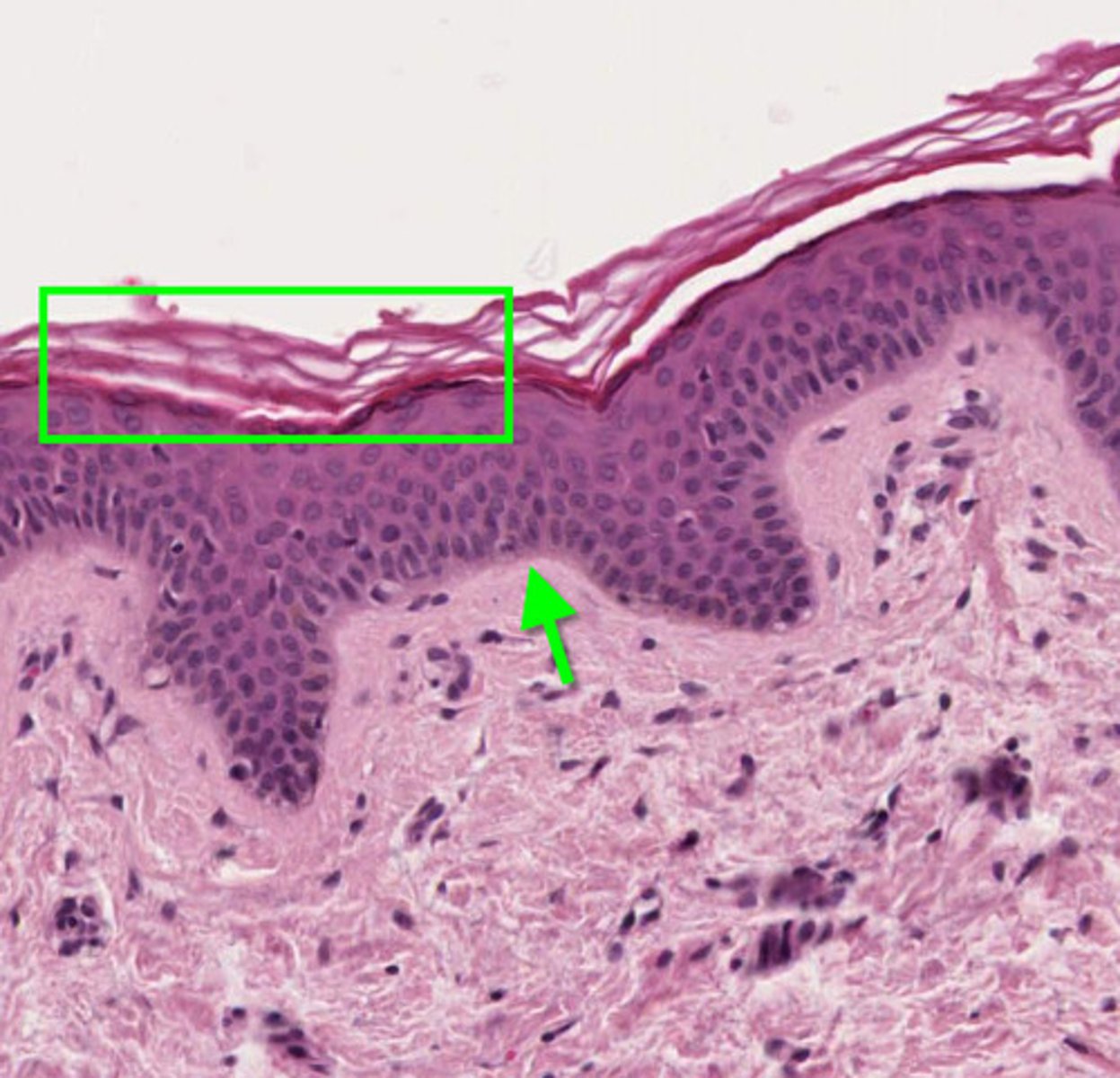
basal layer
deepest region of the epidermis; it gives rise to all the epidermal cells
stratum corneum
outermost layer of the epidermis, which consists of flattened, keratinized cells
Keratin
hard protein material found in the epidermis, hair, and nails
Melanocytes
cells that produce melanin
they give color to the skin the more melanin within each cell accounts for different skin colors
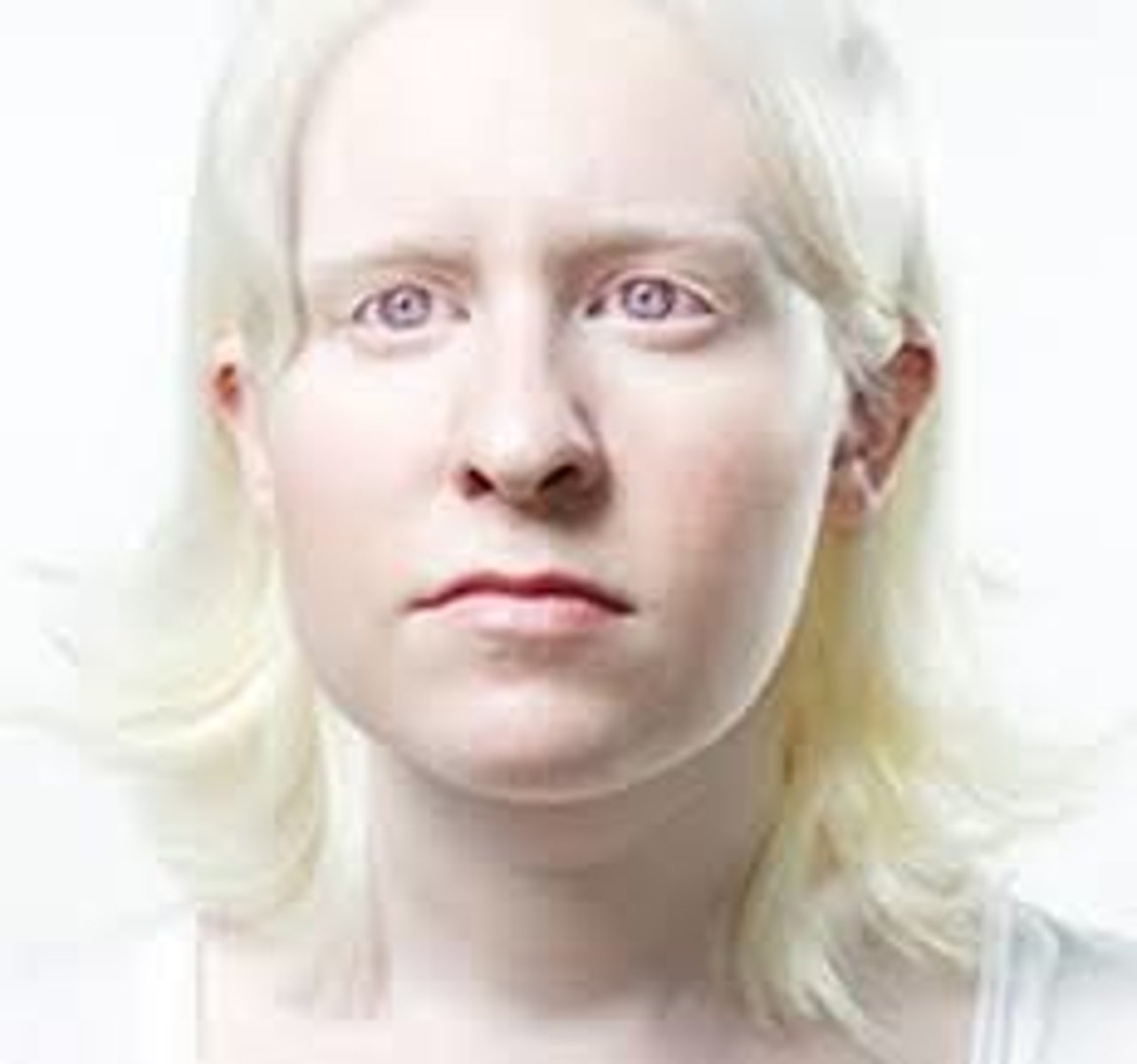
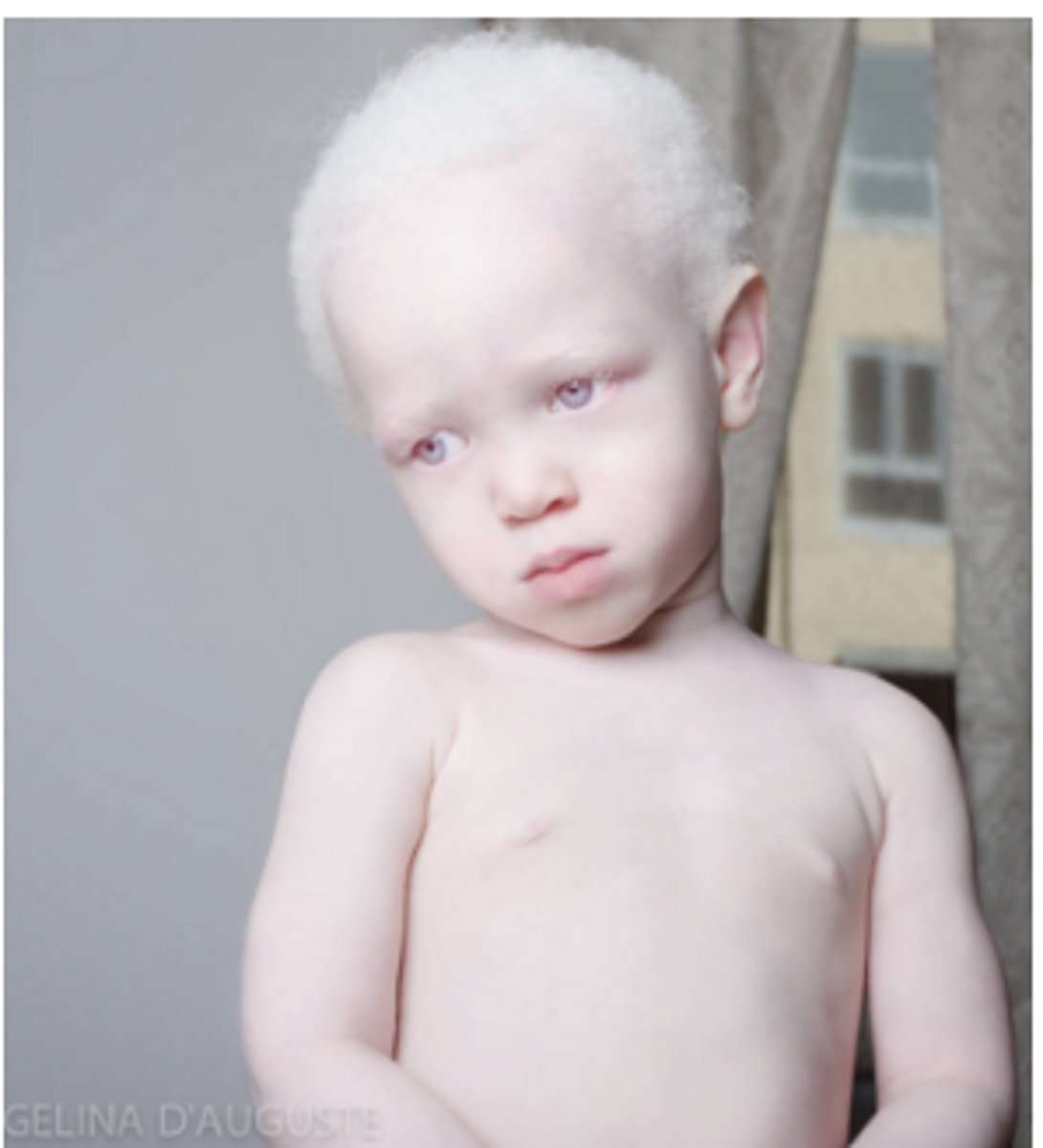
albinos
individuals who are incapable of forming melanin

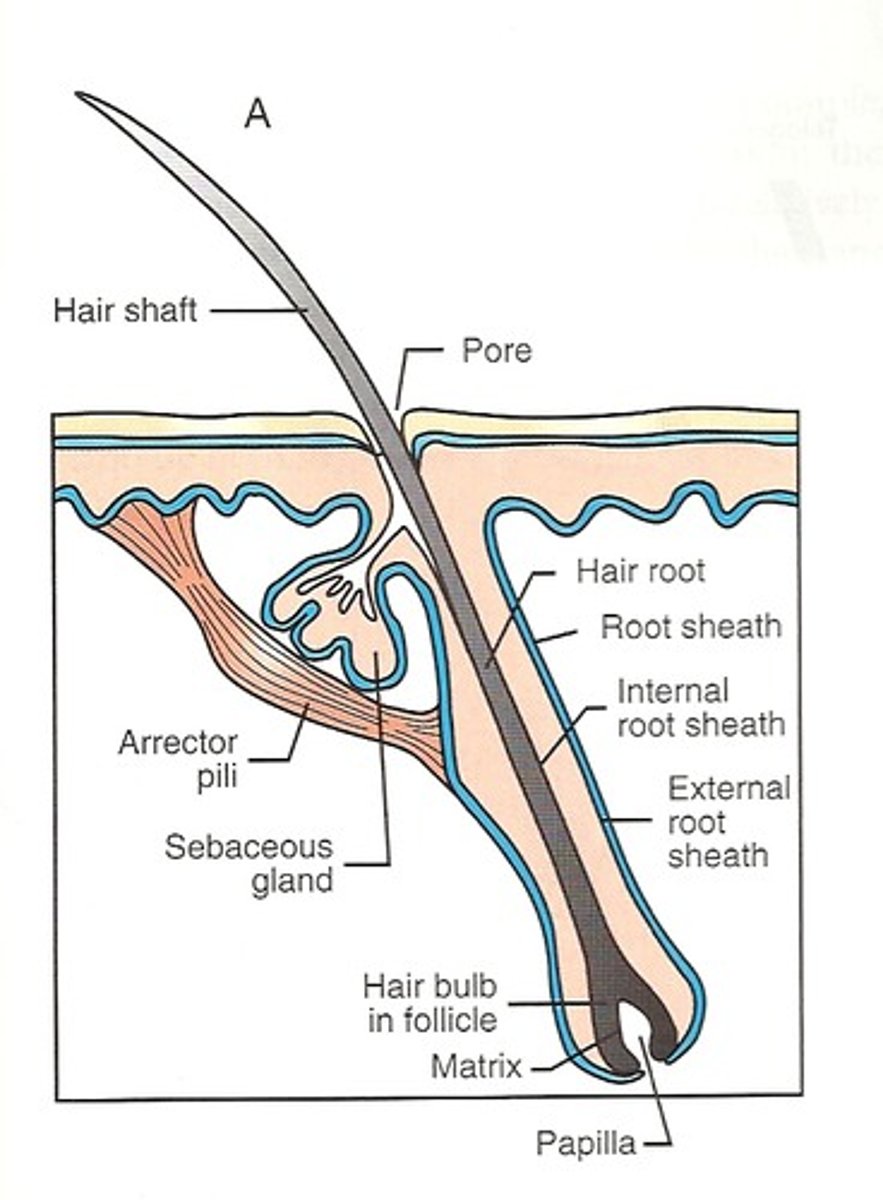
hair follicle
sac within which each hair grows
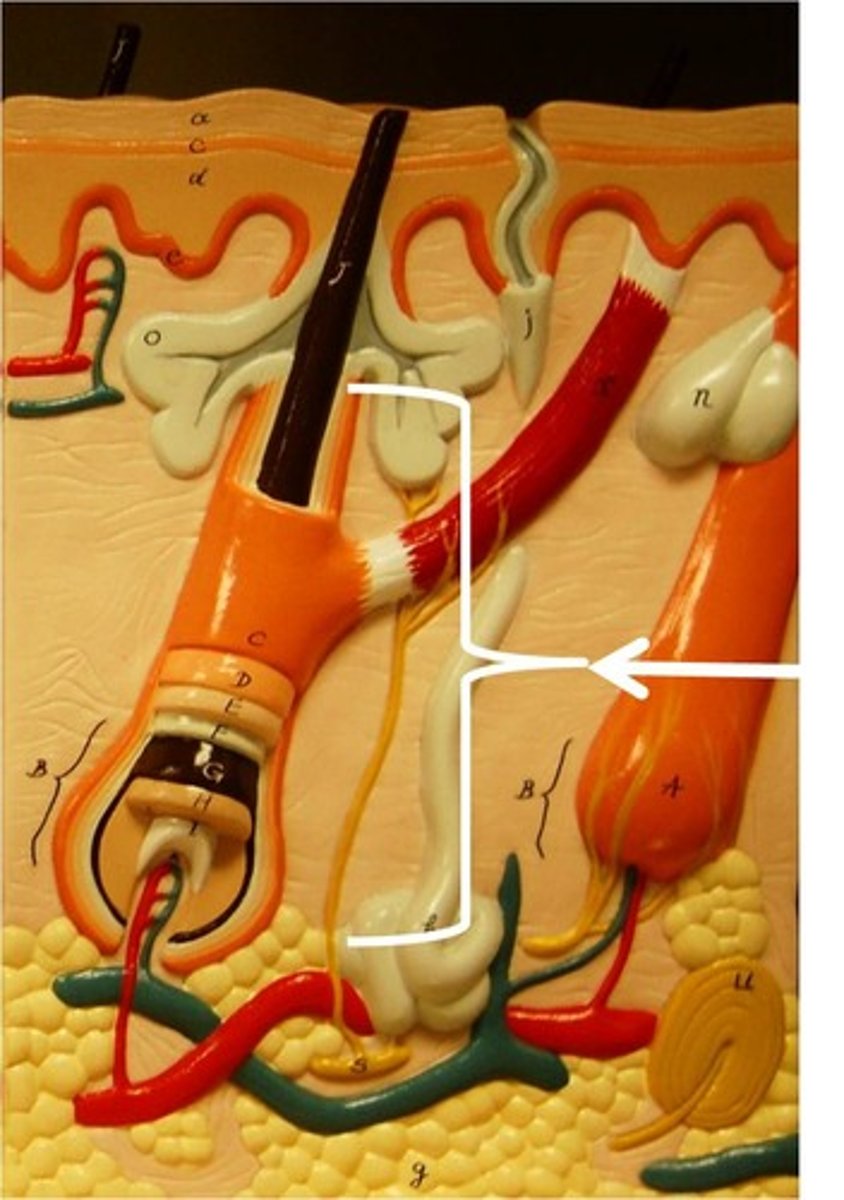
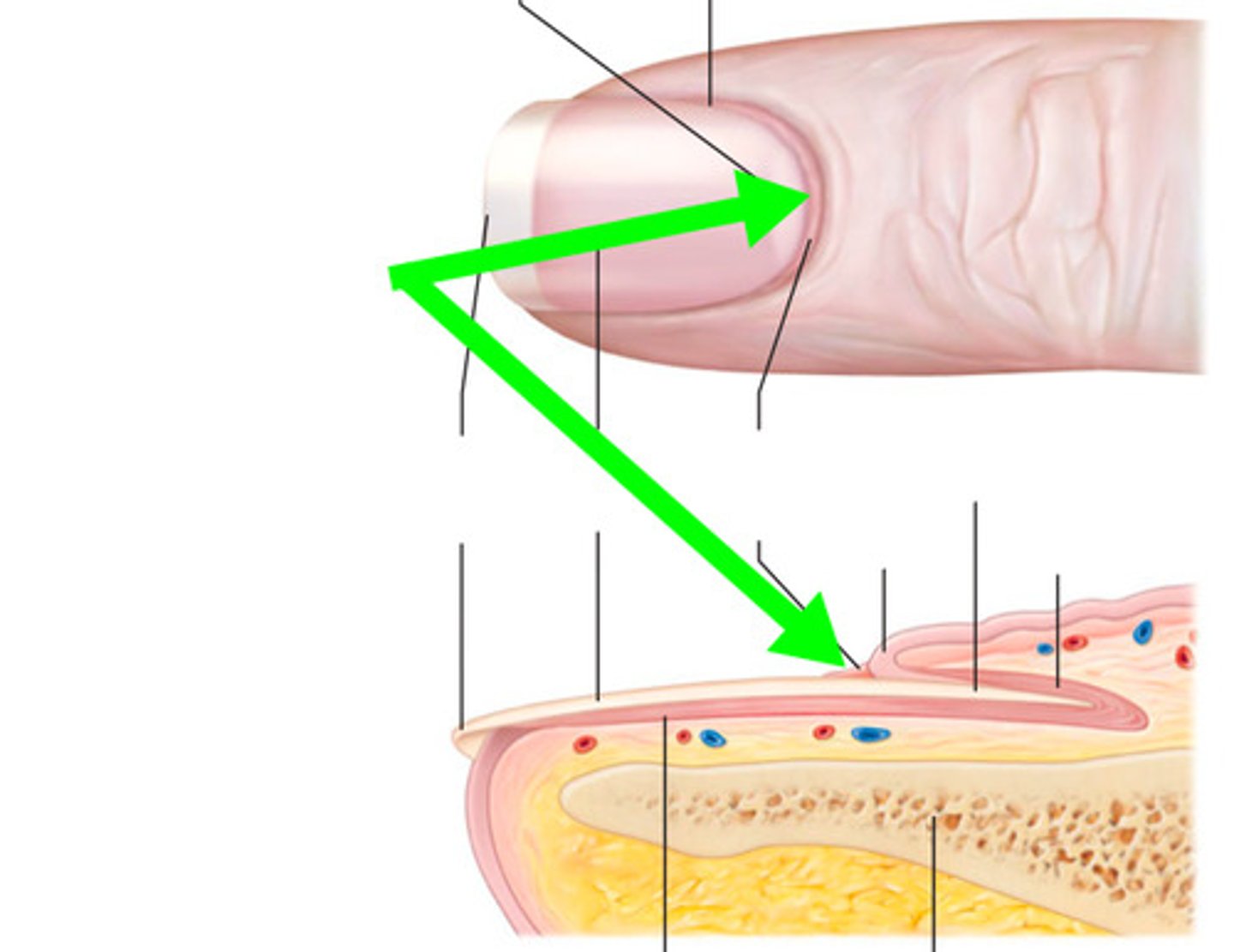
Nails function
Protect and support tips of fingers and toes
they are composed of hard keratin plates
fingernails grow about 1 mm a month, they can completely regrow in about 3 to 5 months
toenails grow slower and it usually takes a year to completely regrow a toenail
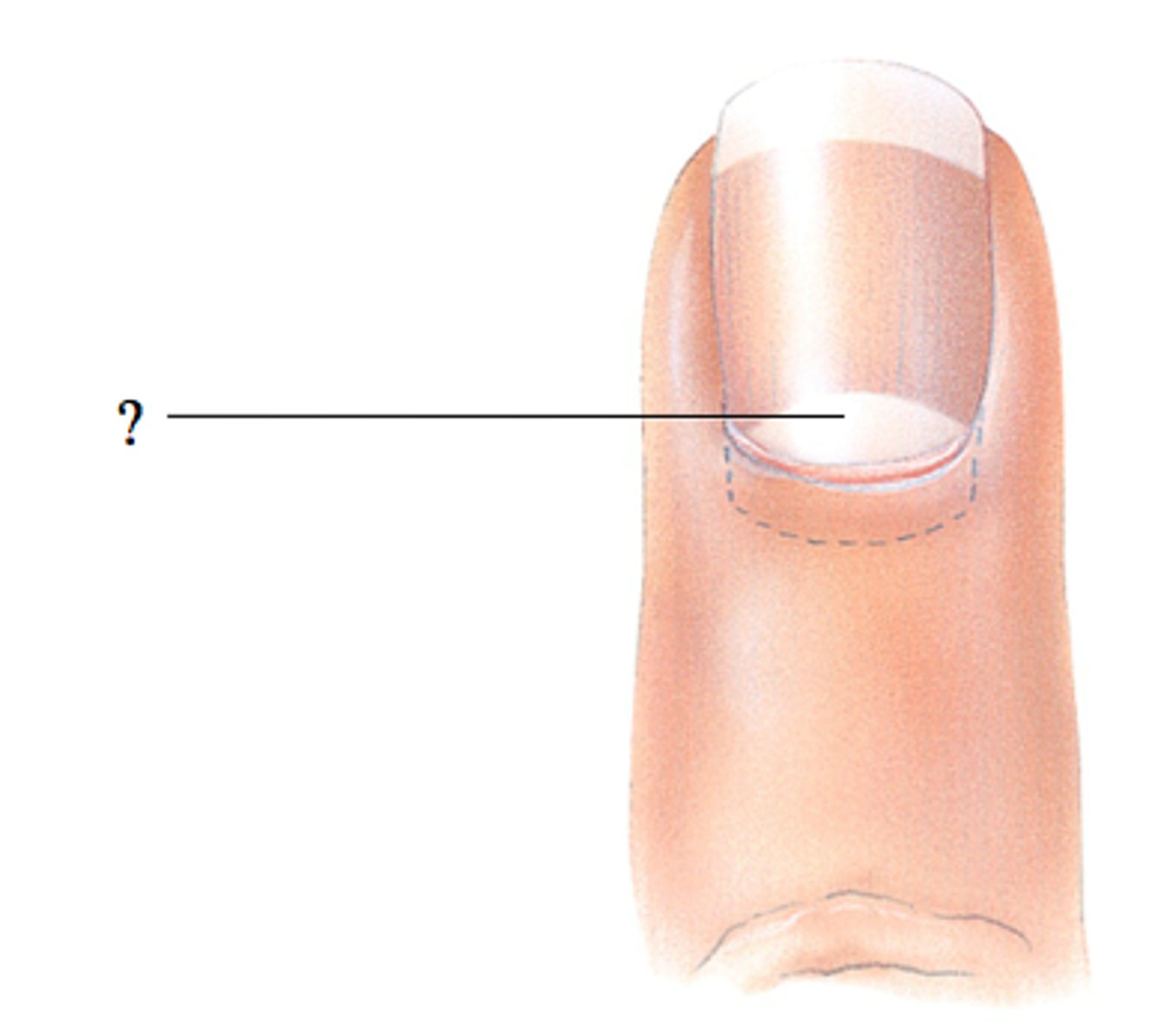
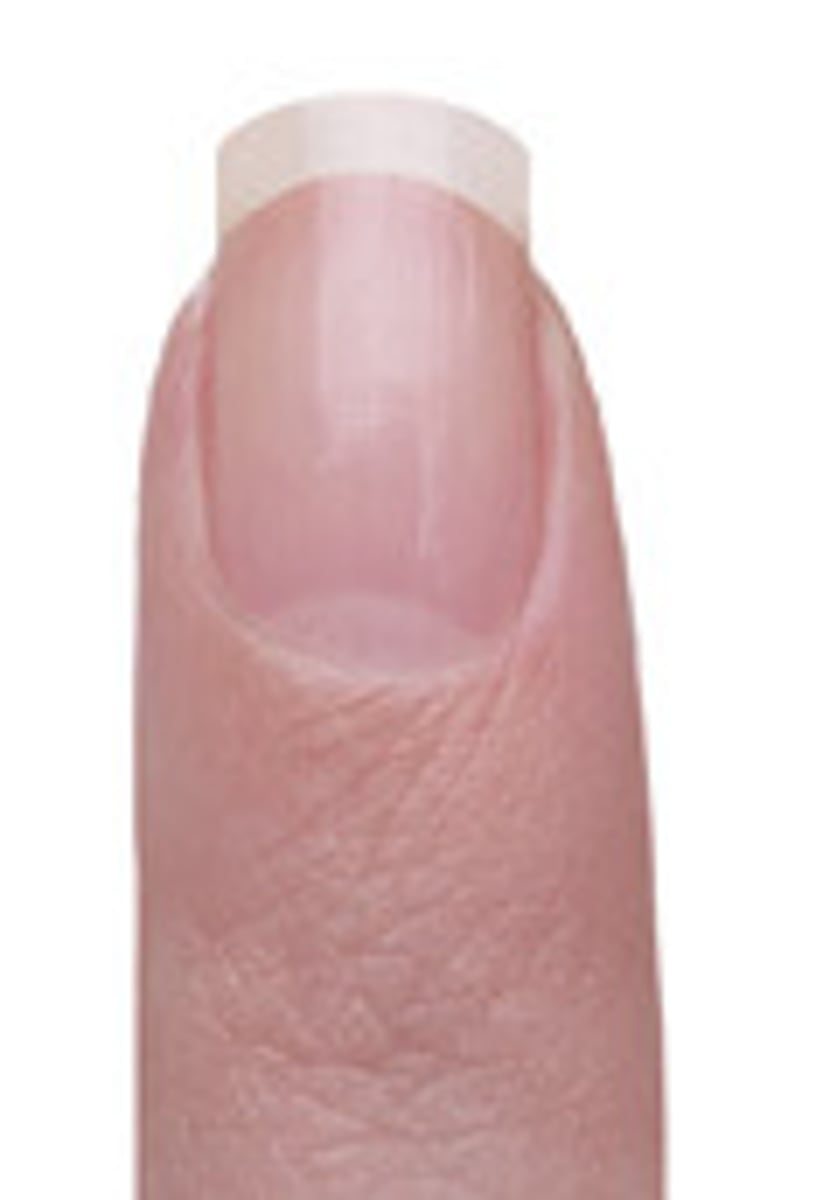
Lunula of nail
the half moon shaped, white area at the base of the nail
Cuticle
Band of epidermis at the base and sides of the nail plate
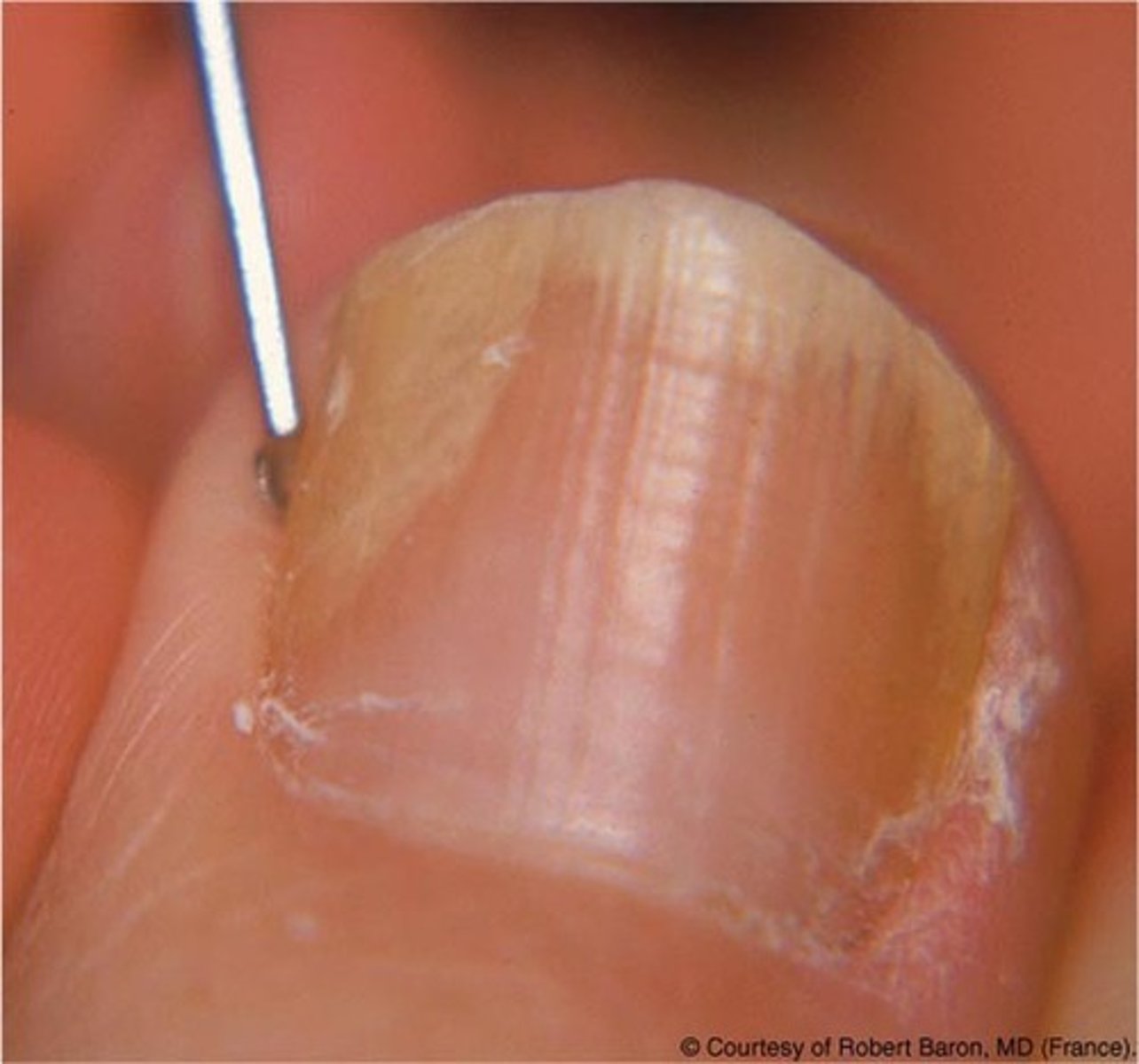
Onycholysis
separation of the nail plate from the nail bed
it may occur with infection of the nail and is often seen in people who suffer from psoriasis
eccrine sweat glands
most numerous sweat-producing exocrine gland in the skin
pore
tiny opening on the surface of the skin
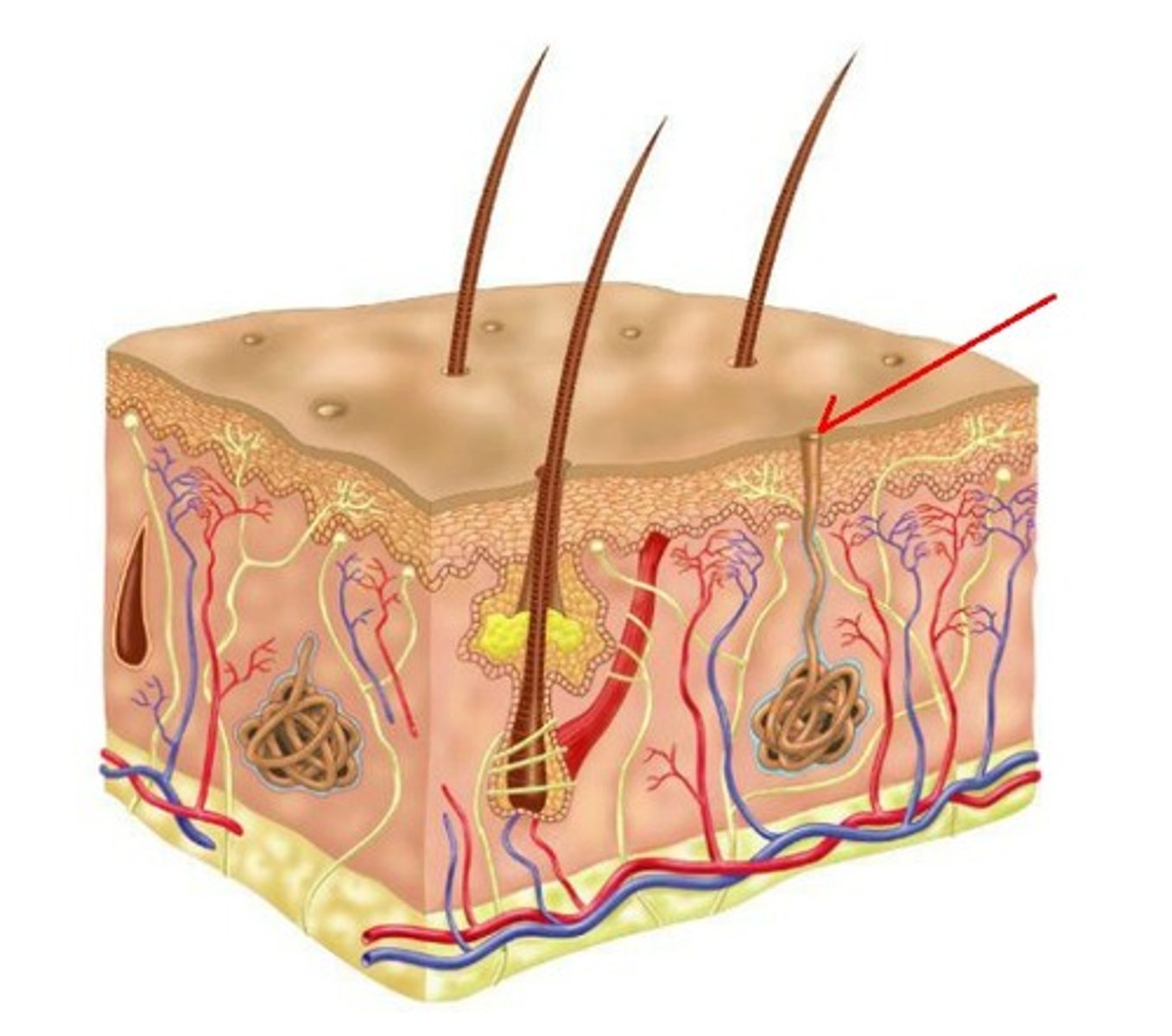
apocrine sweat glands
active from puberty on, concentrated near reproductive organs and armpits
they secrete an odorless sweat but the sweat is easily broken down my bacteria on the skin when this happens then an odor is produced
(the mammary apocrine gland produces milk after childbirth)
adip/o
fat
albin/o
white
caus/o
burn, burning

cauter/o
heat, burn
cutane/o
skin
derm/o, dermat/o
skin

diaphor/o
profuse sweating

erythem/o, erythemat/o
redness
hidr/o
sweat
ichthy/o
dry, scaly
kerat/o
hard
leuk/o
white
lip/o
fat

melan/o
black
myc/o
fungus
onych/o
nail

phyt/o
plant

pil/o
hair, hair follicle
py/o
pus
rhytid/o
wrinkle

seb/o
sebum
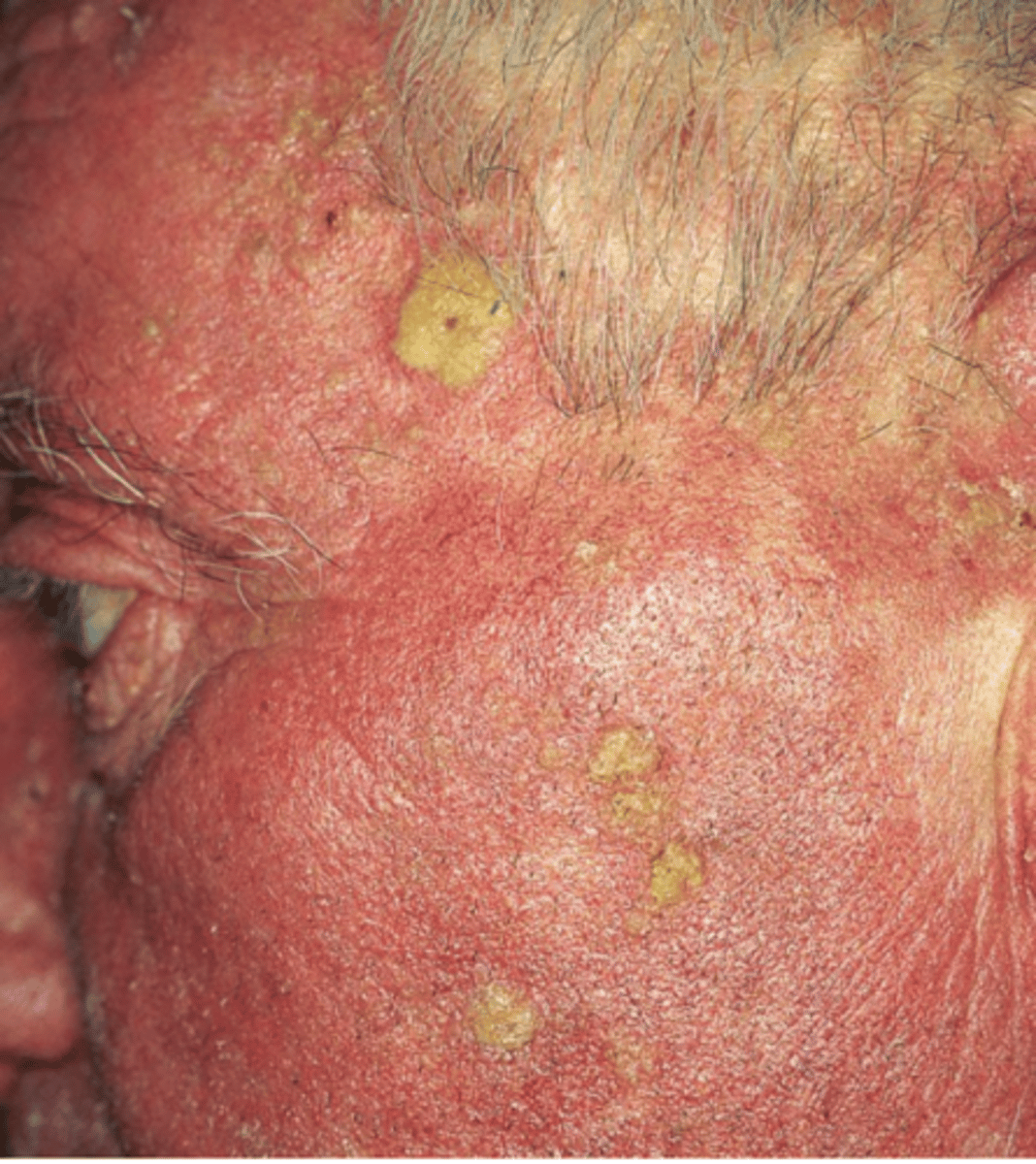
squam/o
scale-like

steat/o
fat

trich/o
hair

ungu/o
nail

xanth/o
yellow

xer/o
dry
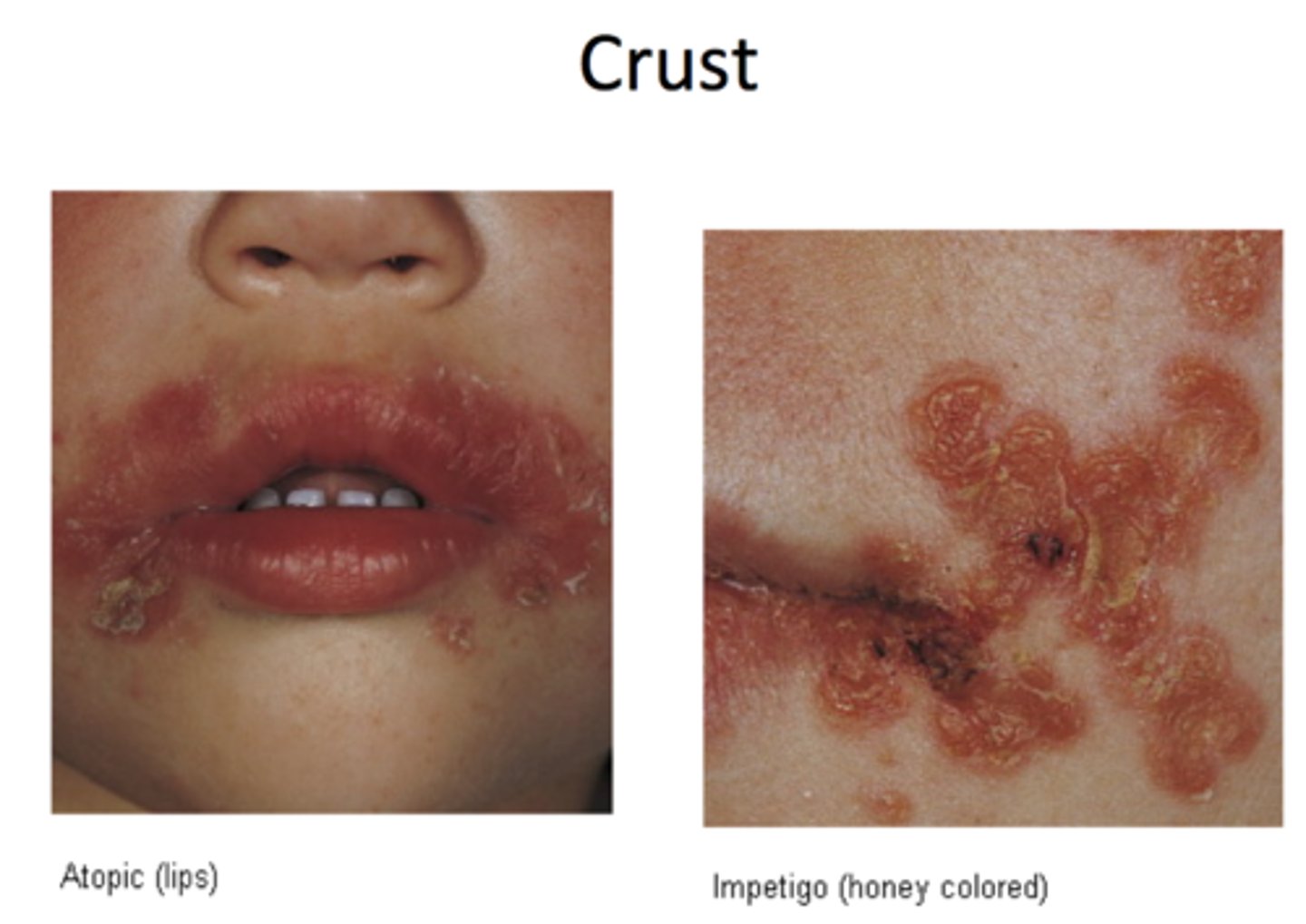
Crust
collection of dried serum and cellular debris
cyst
sac containing fluid
Erosion
wearing away or loss of epidermis
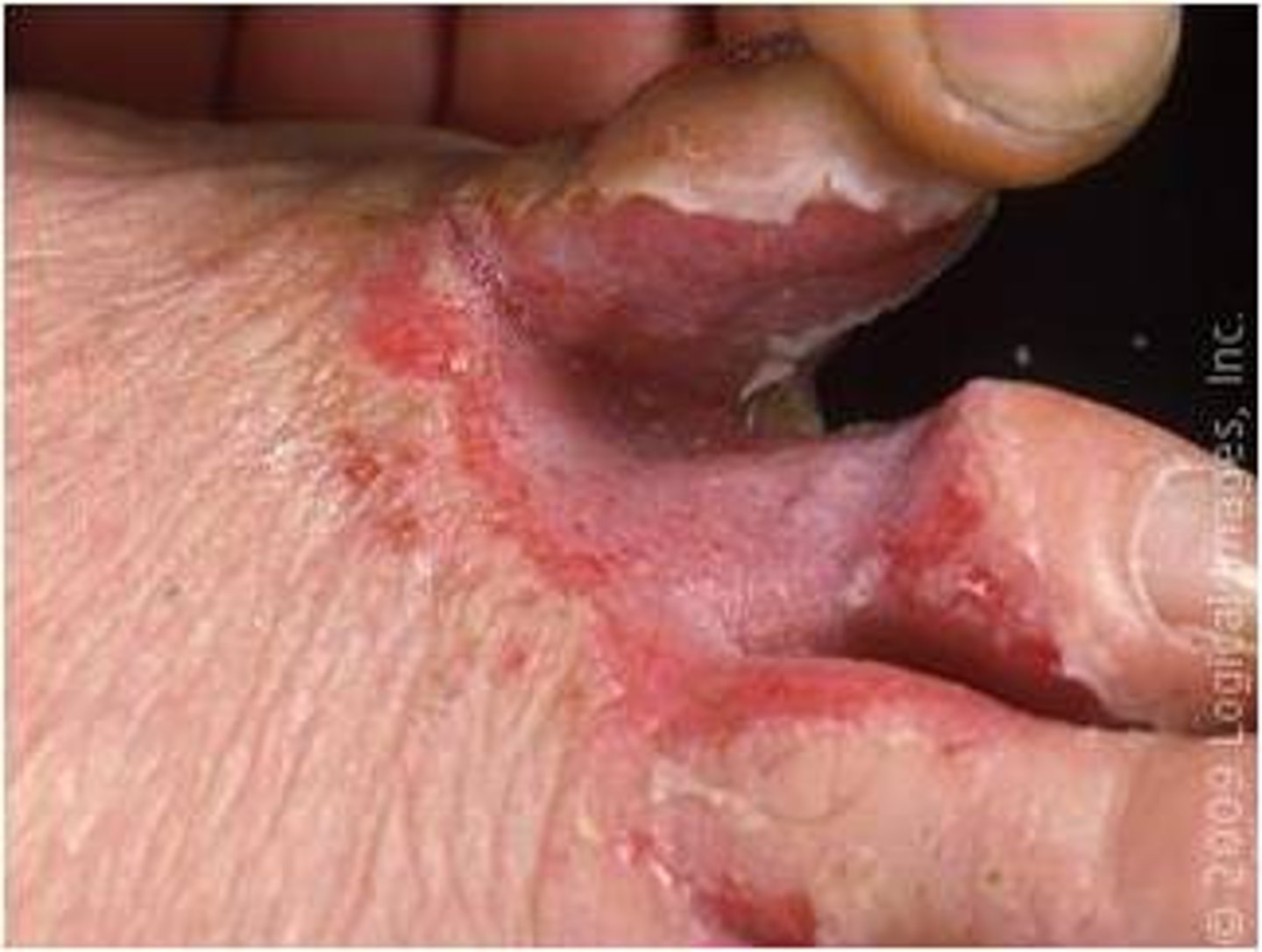
fissure
groove or crack-like sore
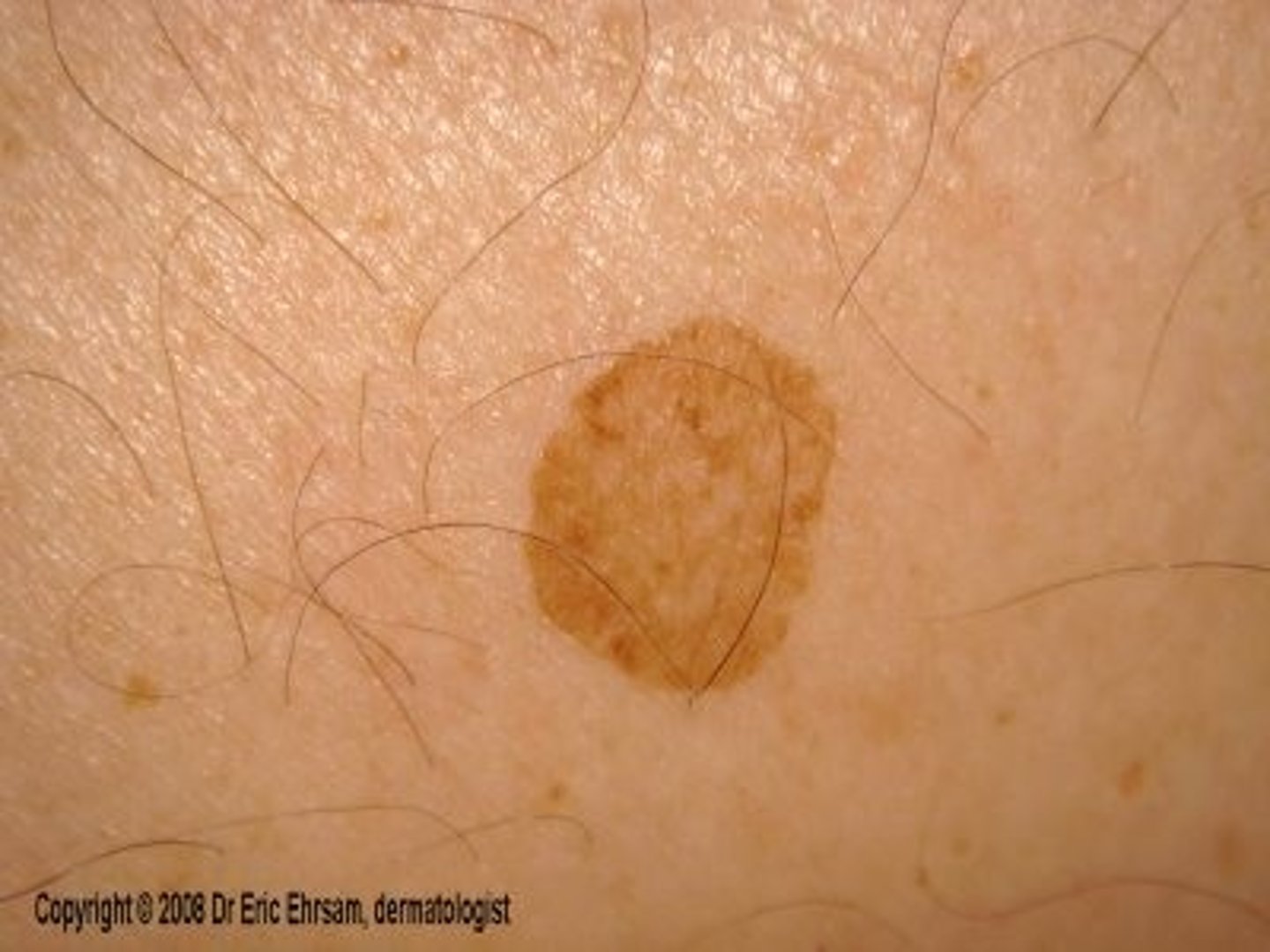
macule
flat, pigmented lesion measuring less than 1 cm in diameter
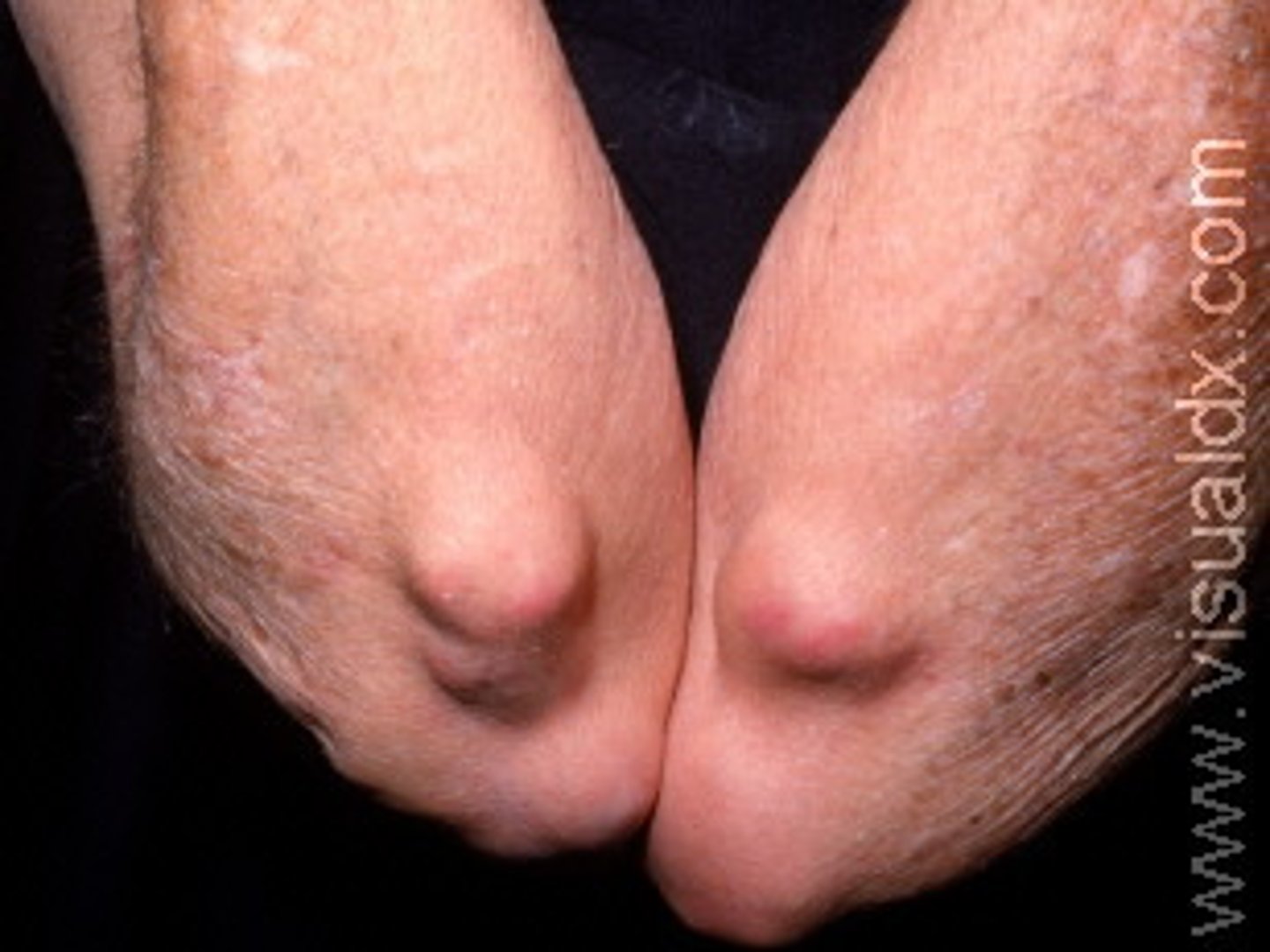
nodule
solid, round or oval elevated lesion 1 cm or more in diameter
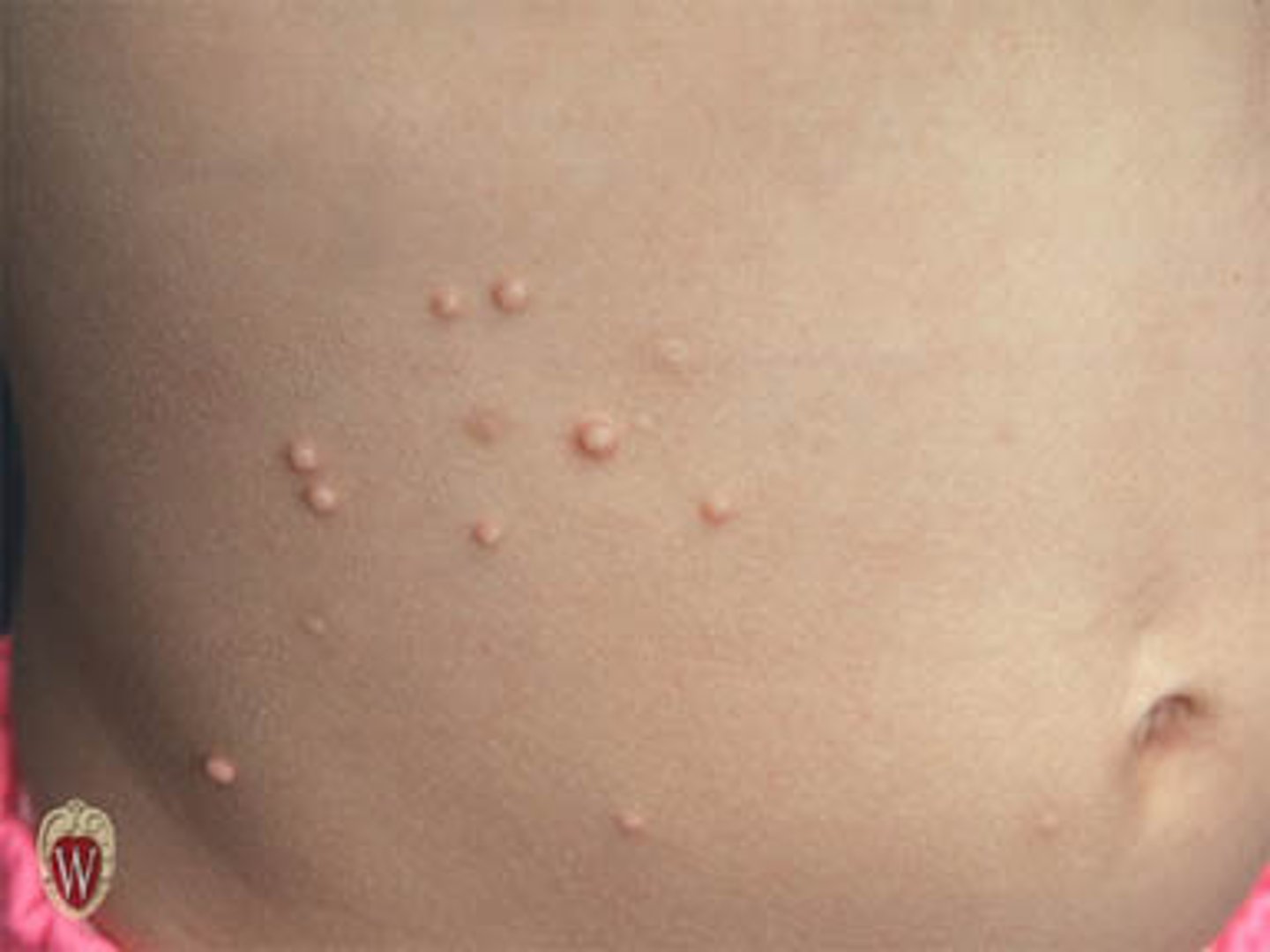
papule
small, solid elevation of the skin (less than 1 cm in diameter)
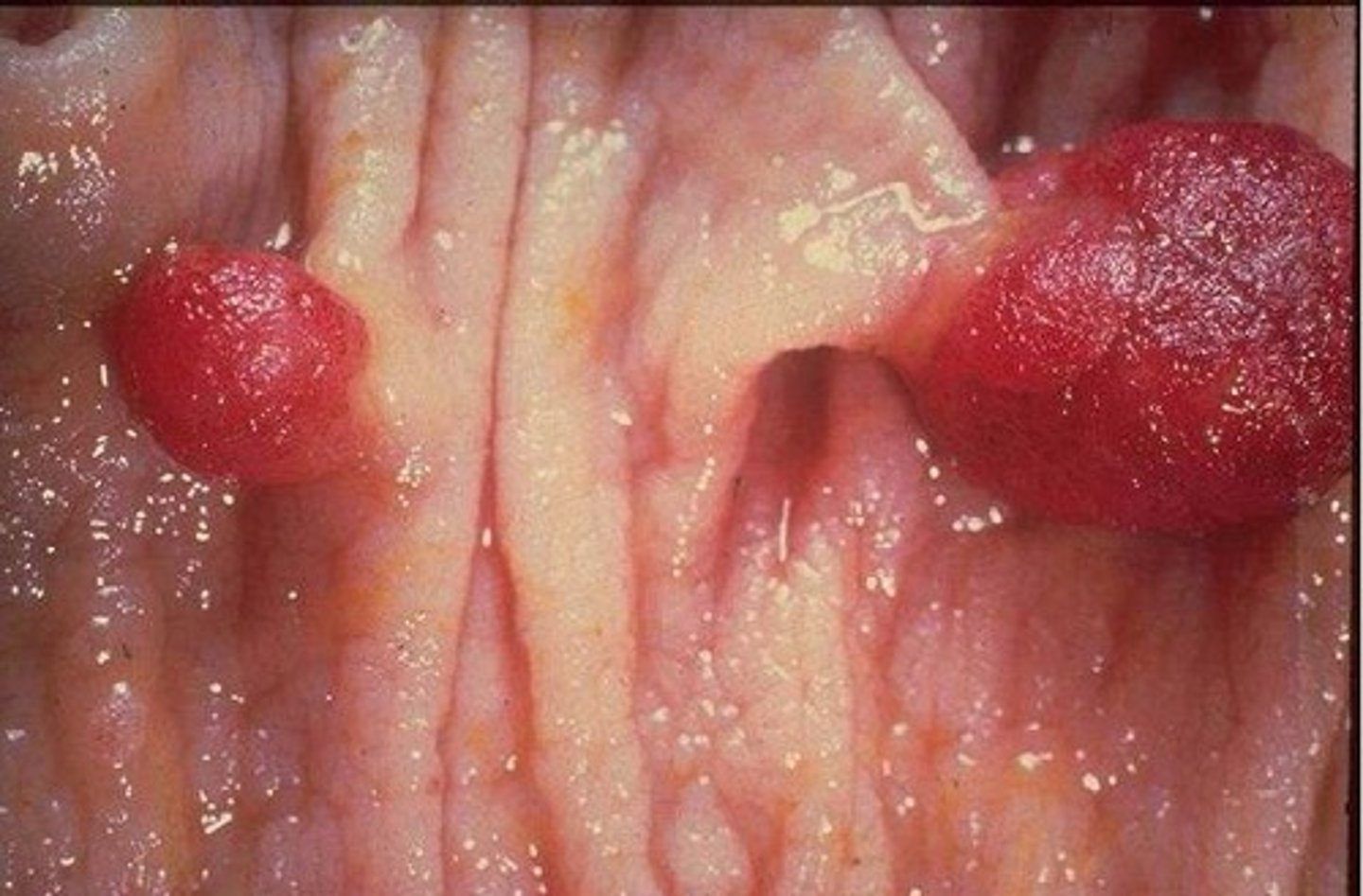
polyp
growth extending from the surface of mucous membrane
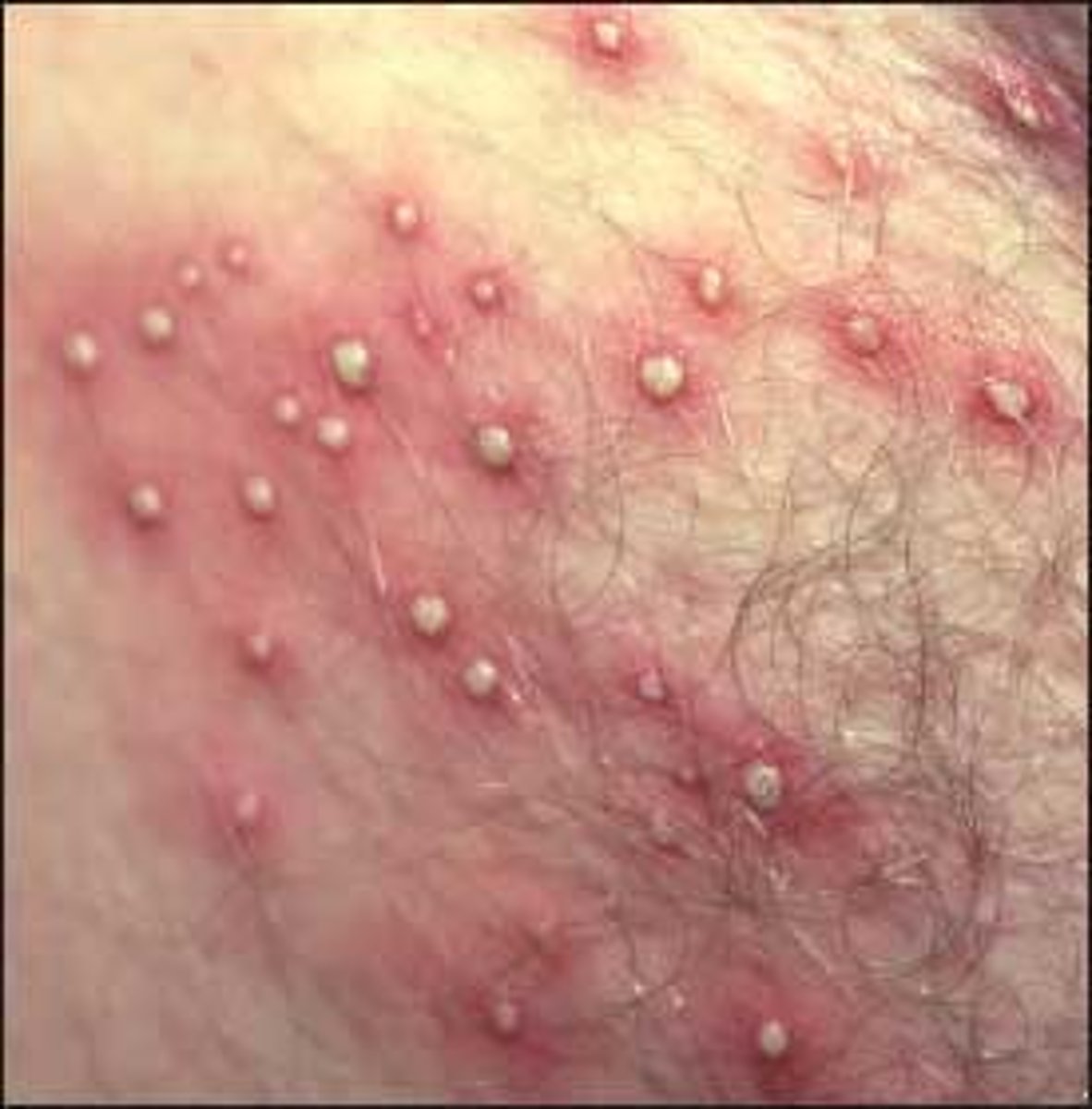
pustule
papule containing pus
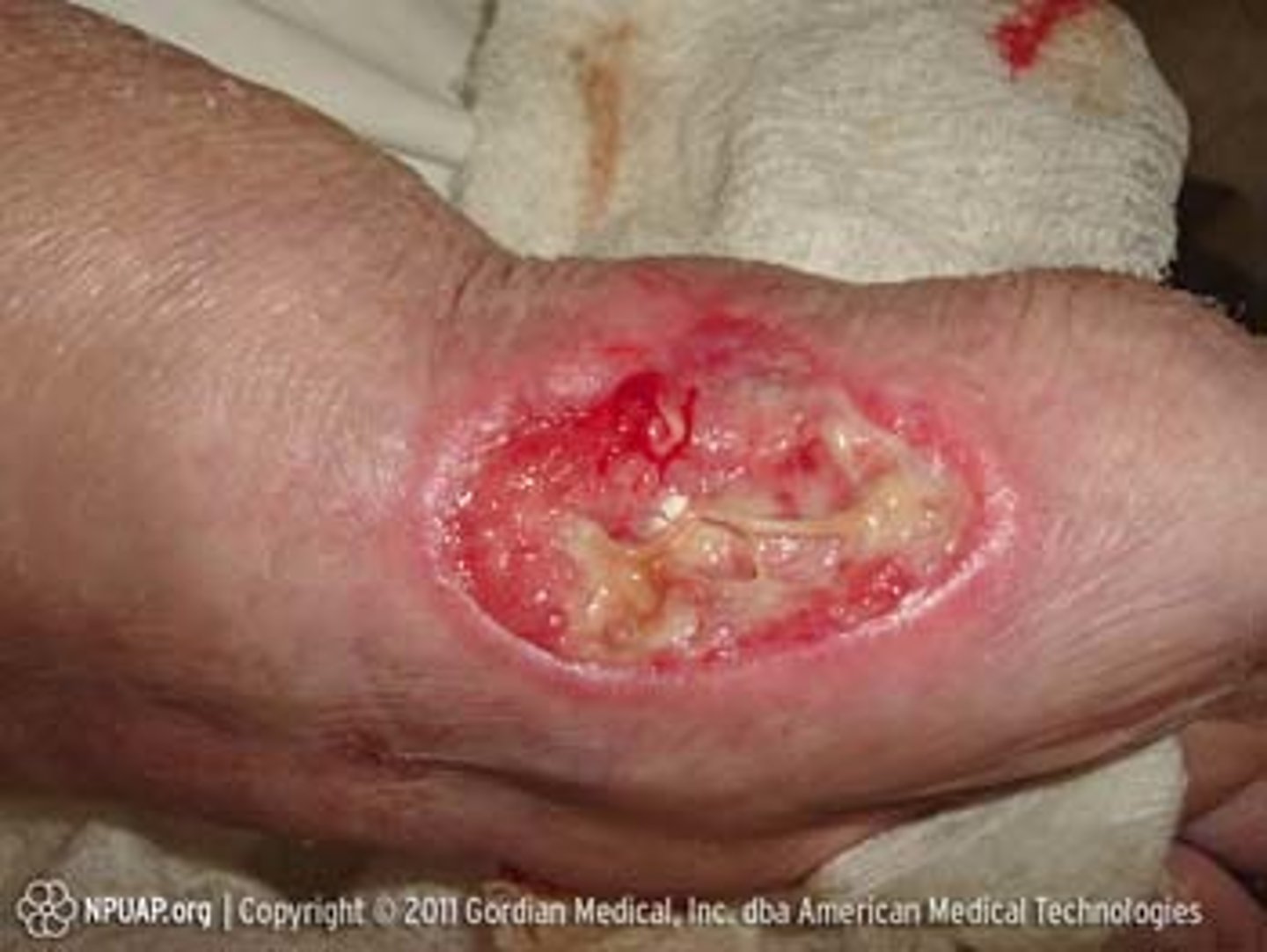
ulcer
open sore or lesion in the skin or mucous membrane (deeper than erosion)
Vesicle
small collection of clear fluid; blister
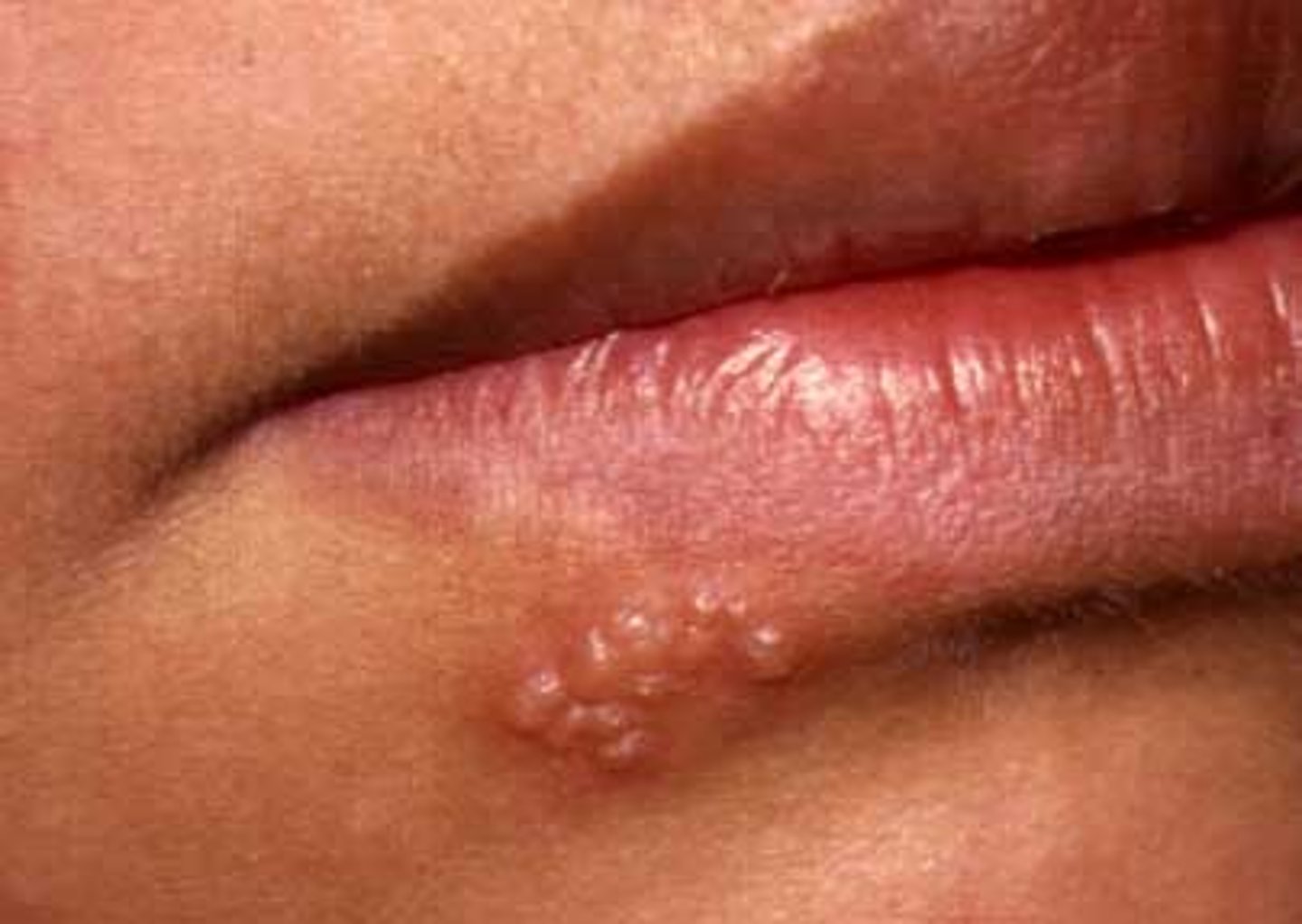
wheal
smooth, edematous (swollen) papule or plaque that is redder or paler than the surrounding skin
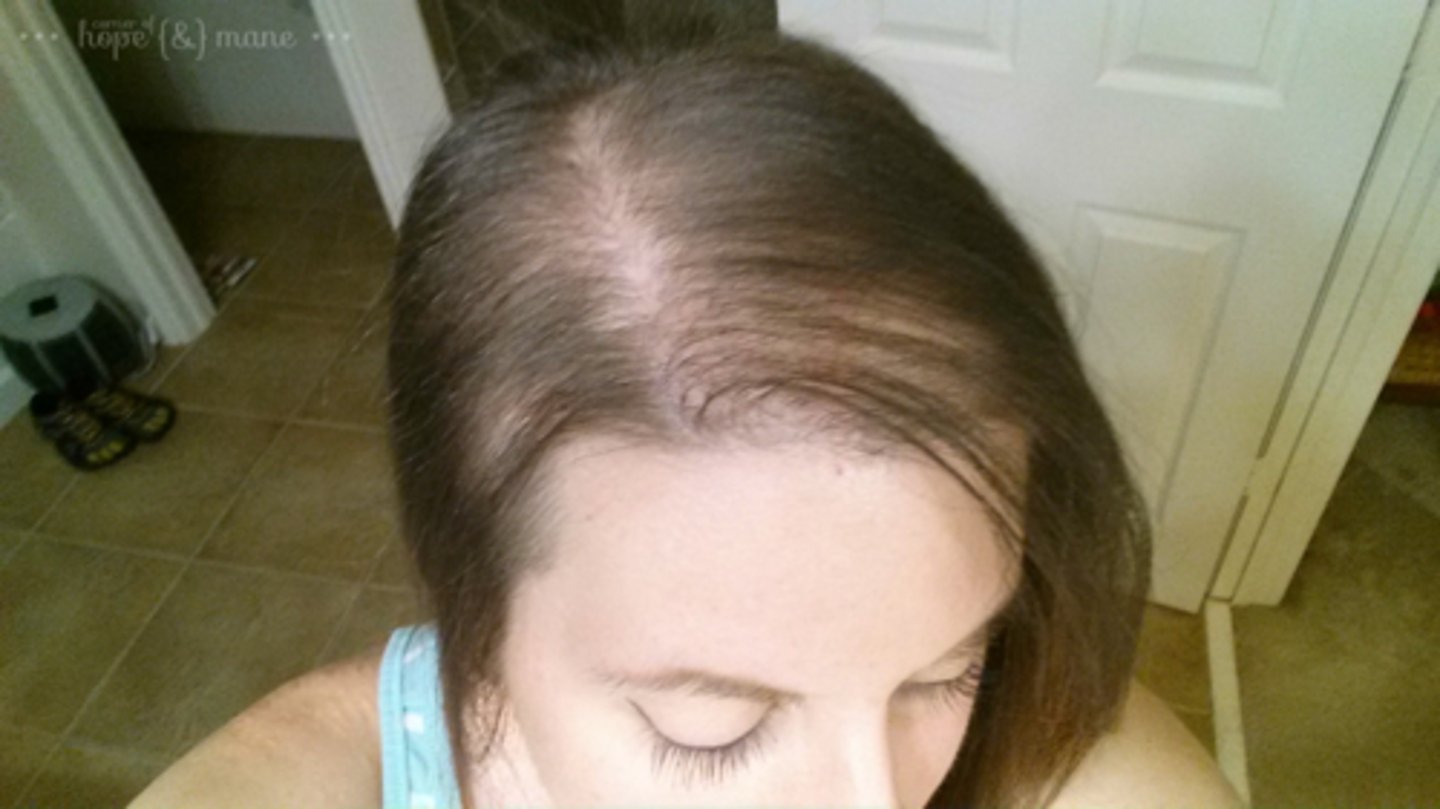
alopecia
absence of hair from areas where it normally grows

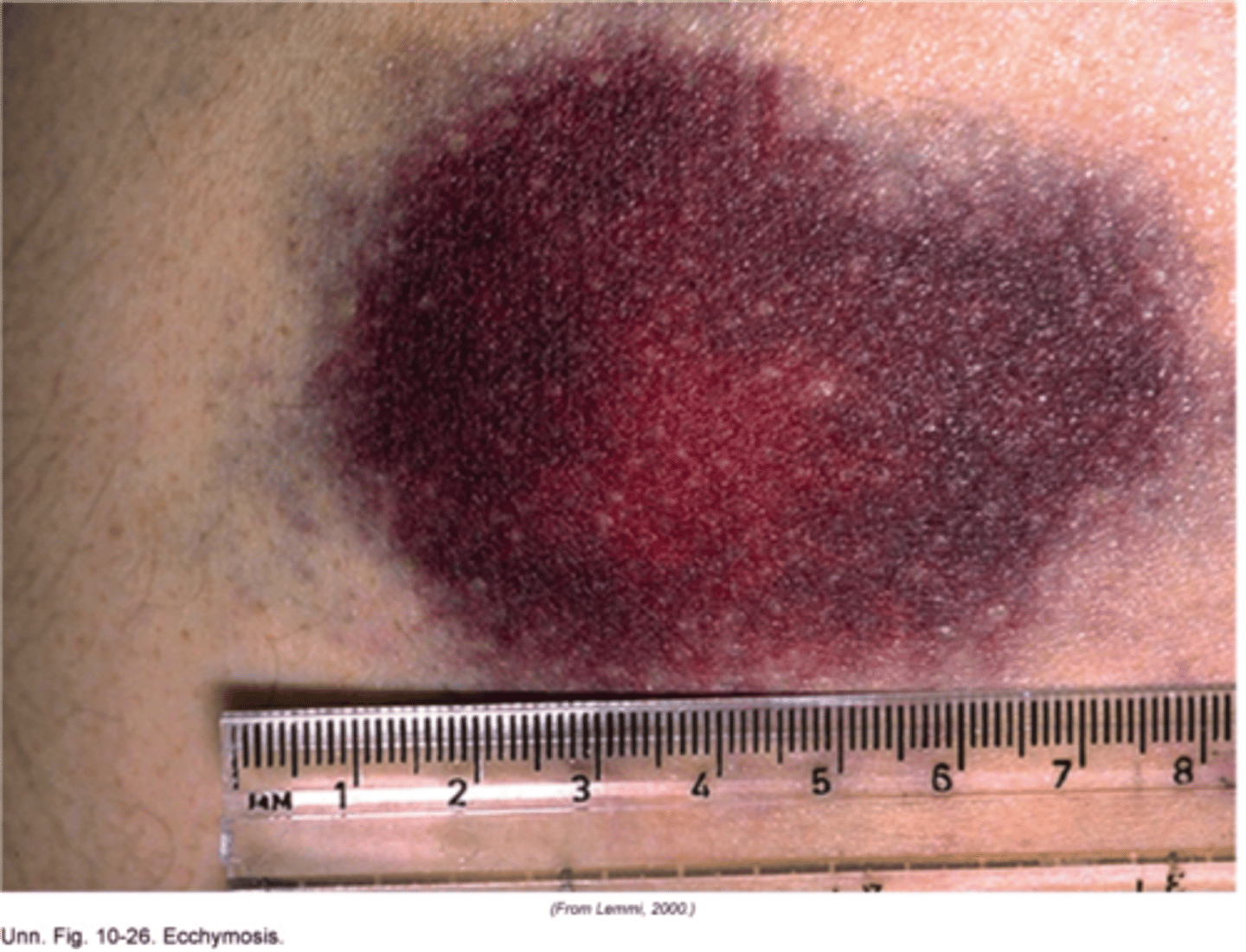
Ecchymosis
bluish-purplish mark (bruise) on the skin
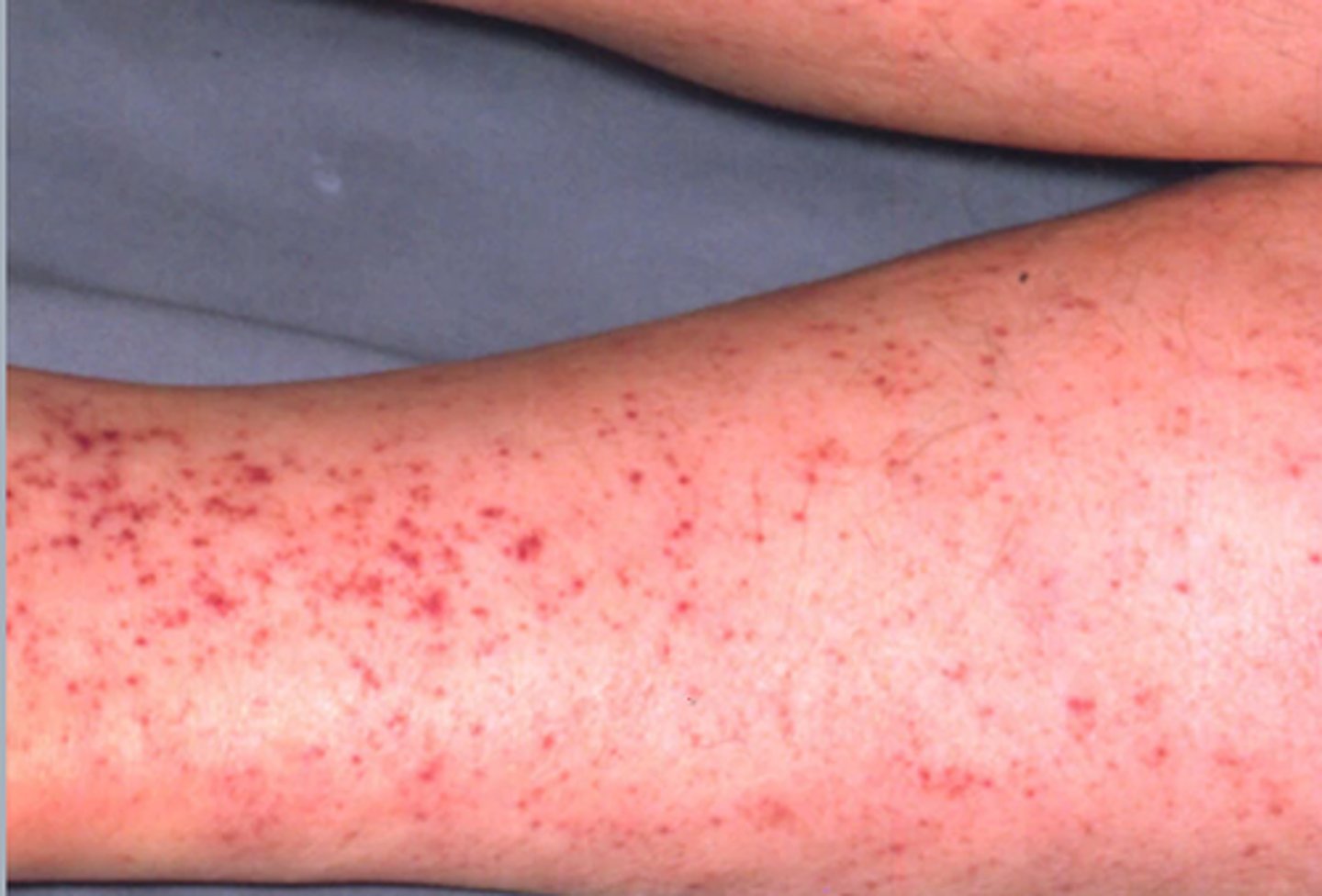
petechia
small, pinpoint hemorrhage
pruritus
itching associated with dermatitis

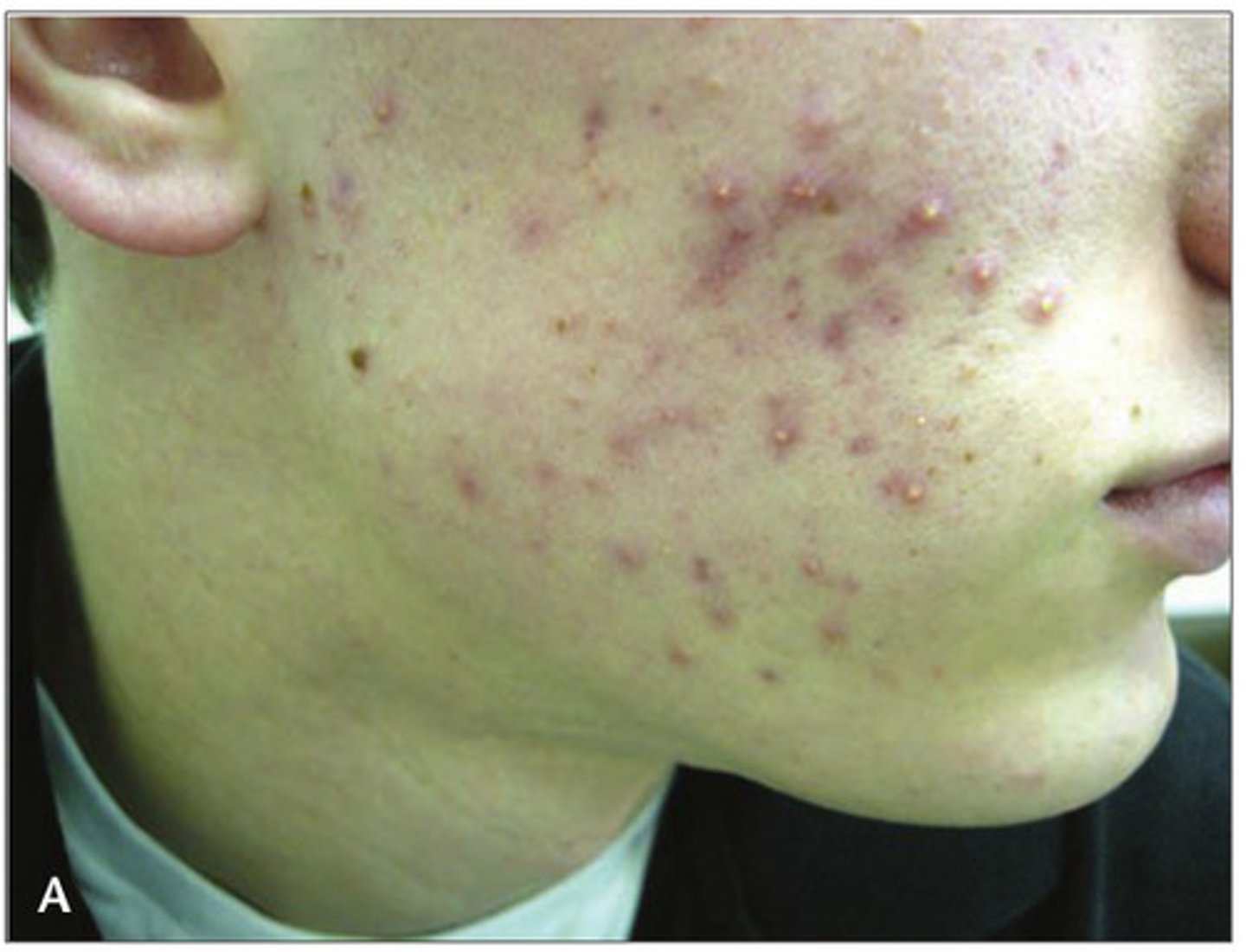
acne
chronic papular and pustular eruption of the skin with increased production of sebum
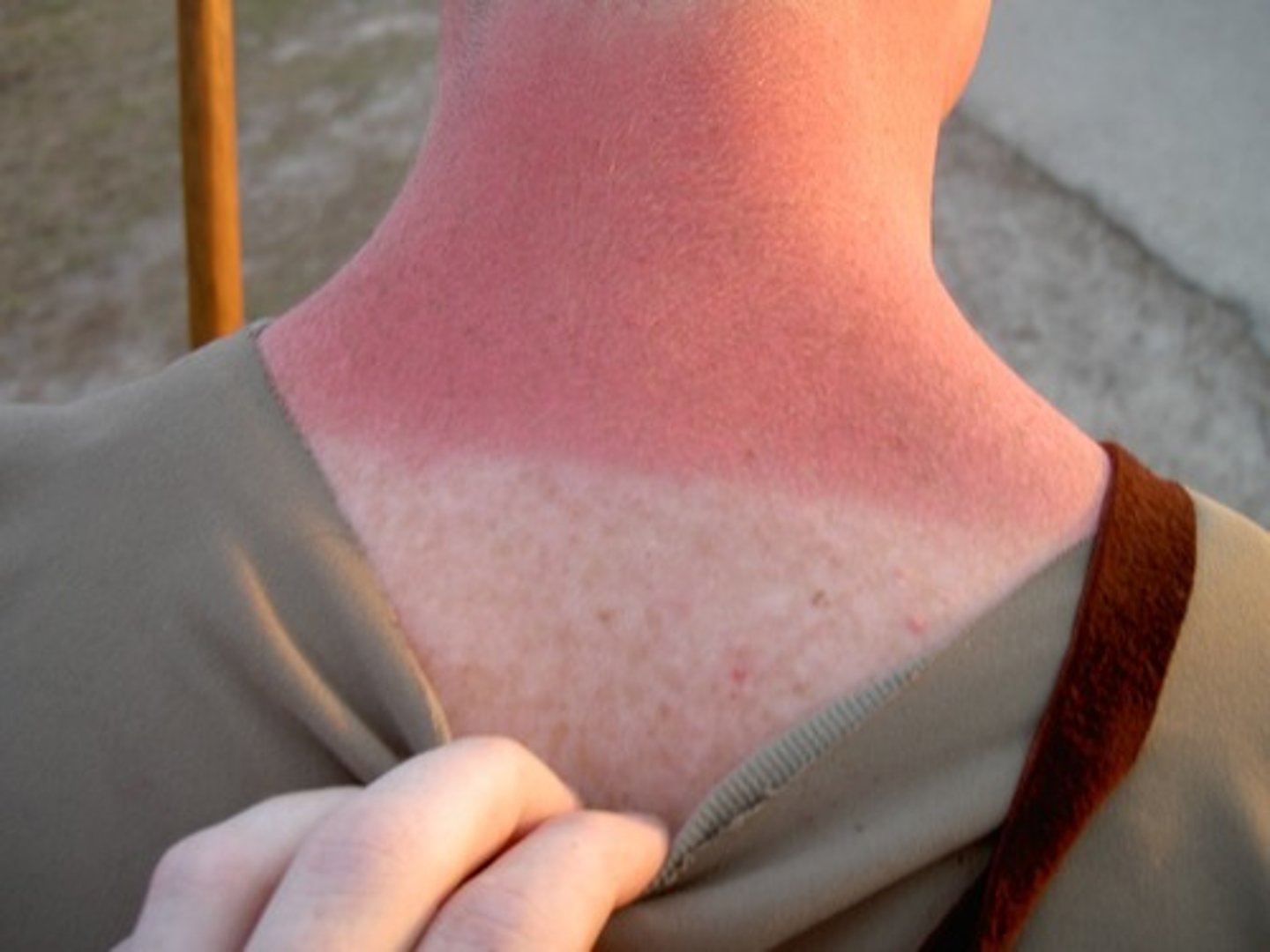
first degree burn
Superficial burns through only the epidermis.
no blisters
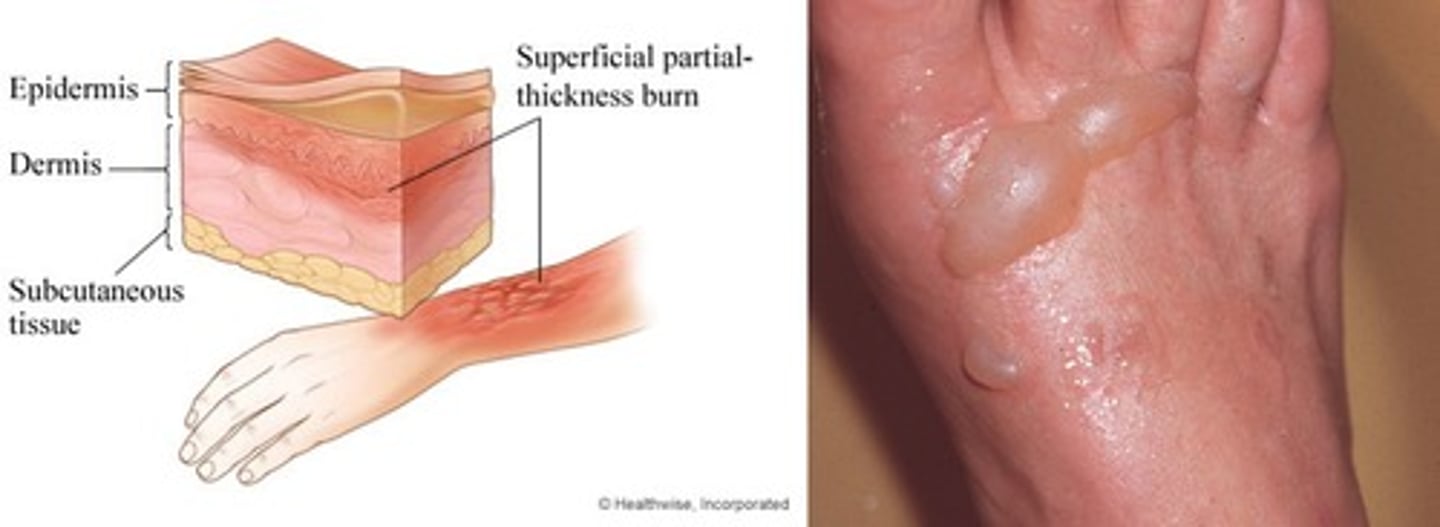
second degree burn
a burn involving the epidermis and the dermis; characterized by erythema, hyperesthesia, and vesications (blisters)
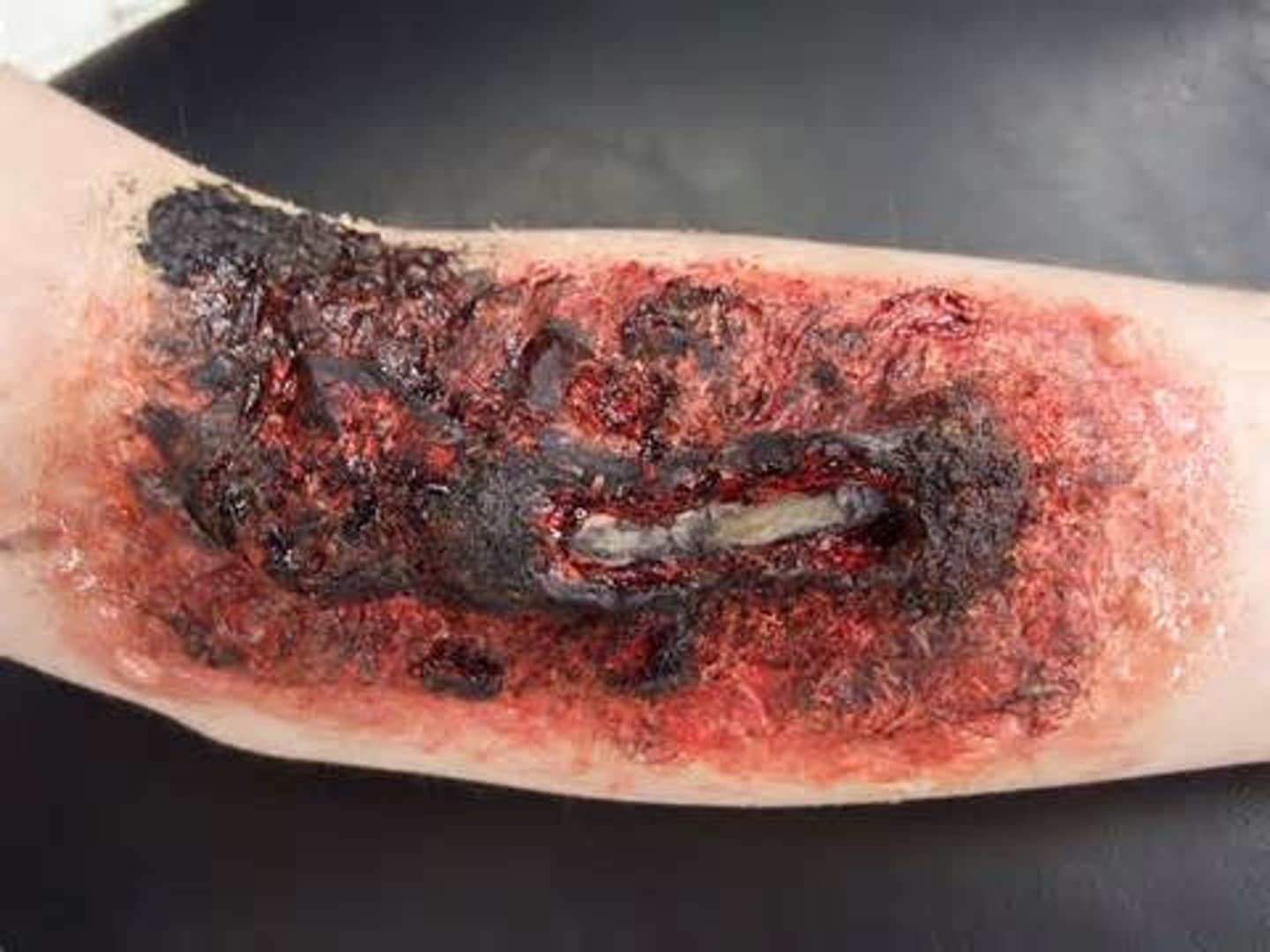
third degree burn
A full-thickness burns that involve the epidermis, dermis, and varying levels of the subcutaneous and underlying structures.
leaves charred white tissue
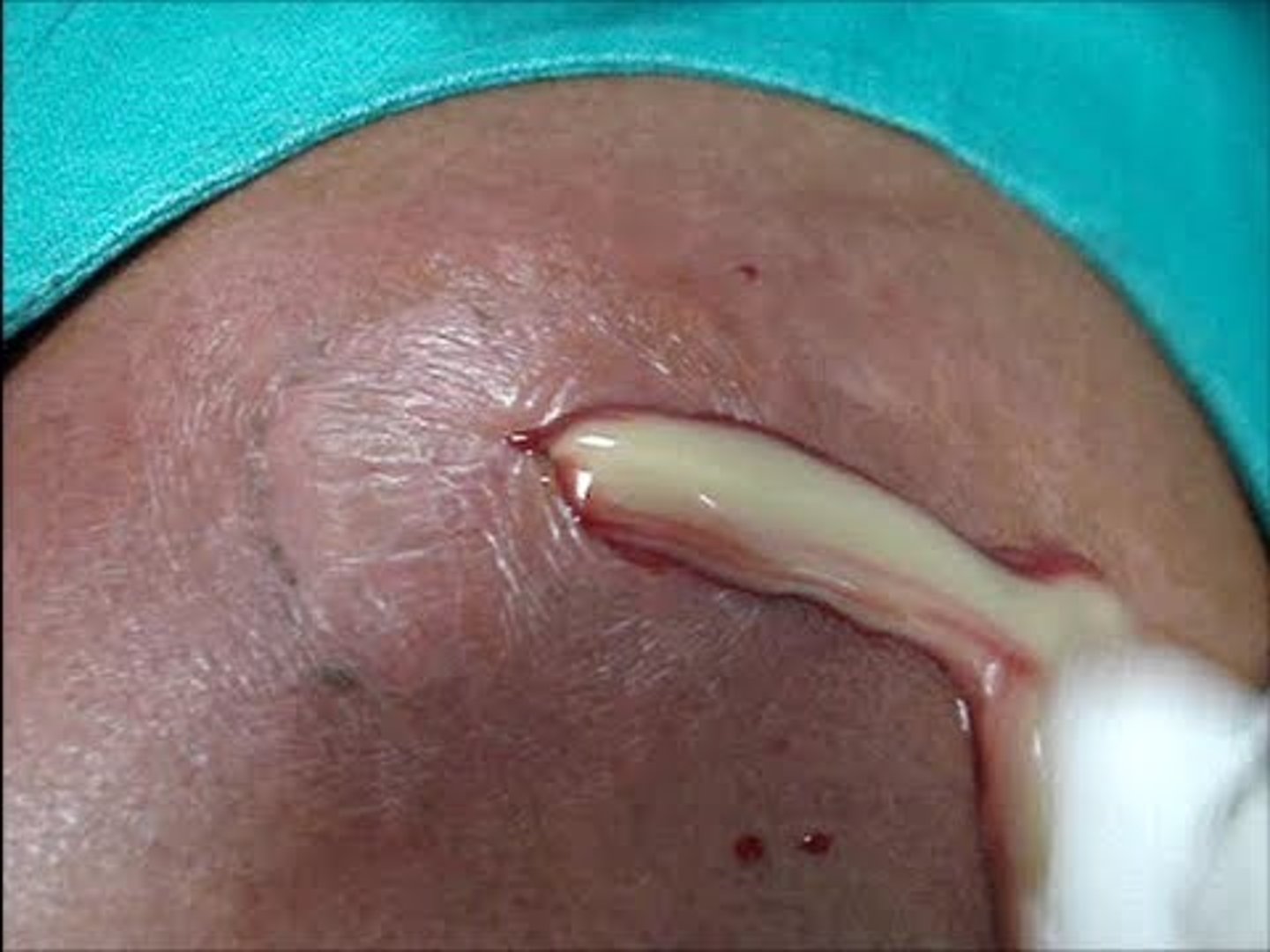
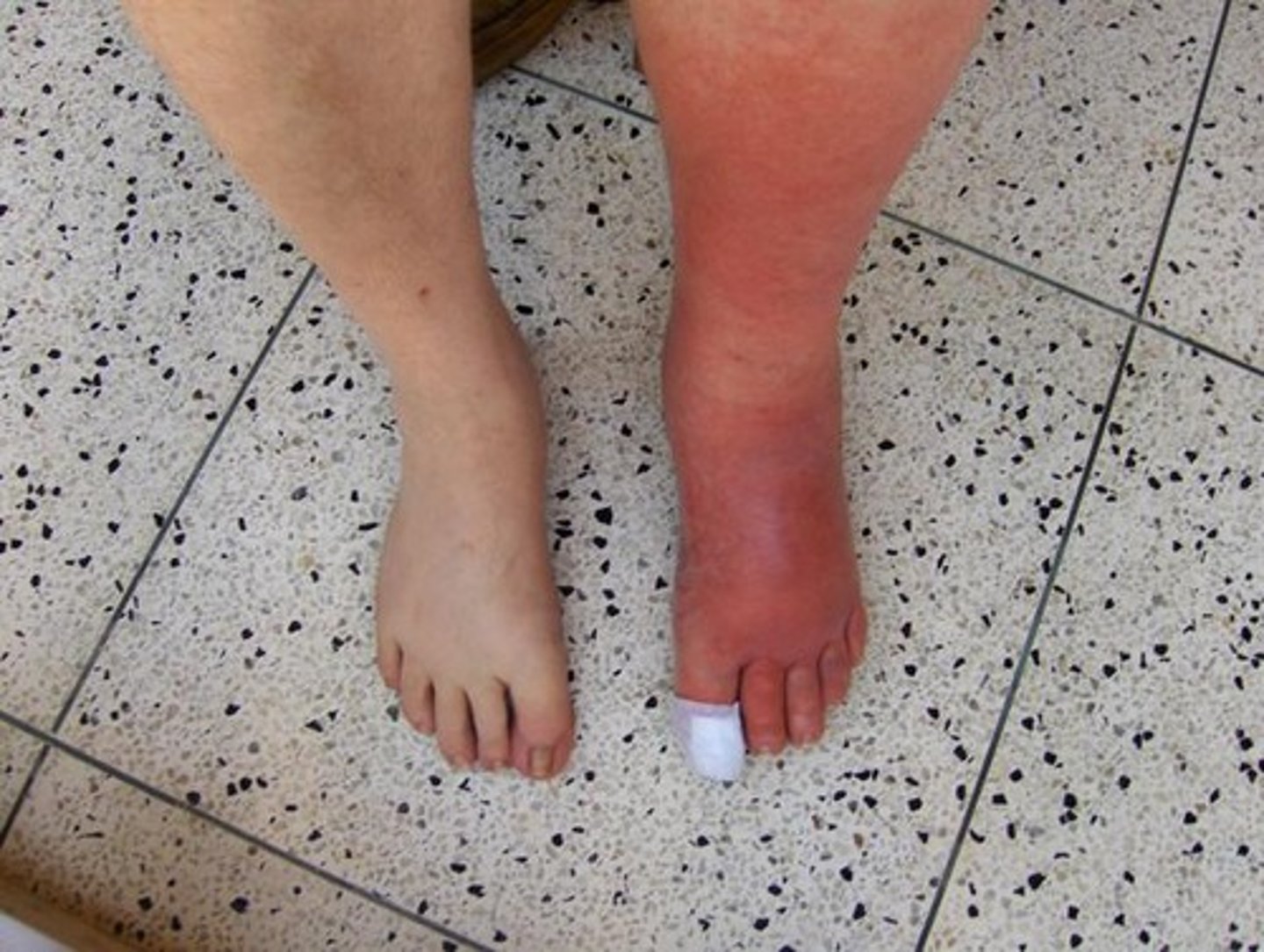
Cellulitis
diffuse, acute infection of the skin marked by local heat, redness, pain, and swelling
seen many times with chemotherapy as a result of damage to the lymph system
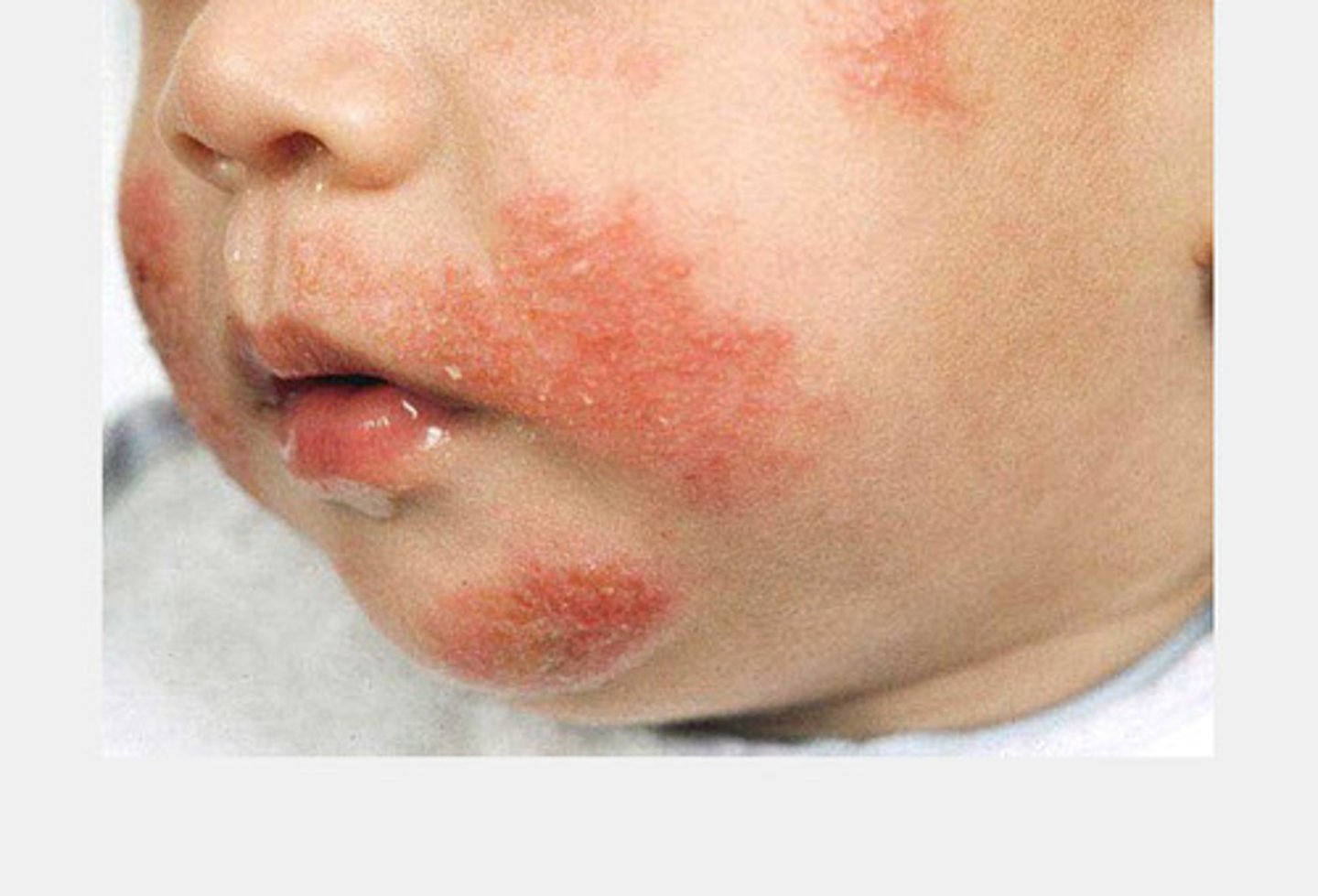
eczema (atopic dermatitis)
inflammatory skin disease with erythematous, papulovesicular, or papalosquamous lesions
usually accompanied with pruritus(itching)
exanthematous viral disease
rash (exanthem) of the skin due to a viral infection
some examples are rubella(german measles), rubeola(measles), and varicella(chicken pox), and hand-foot-mouth disease
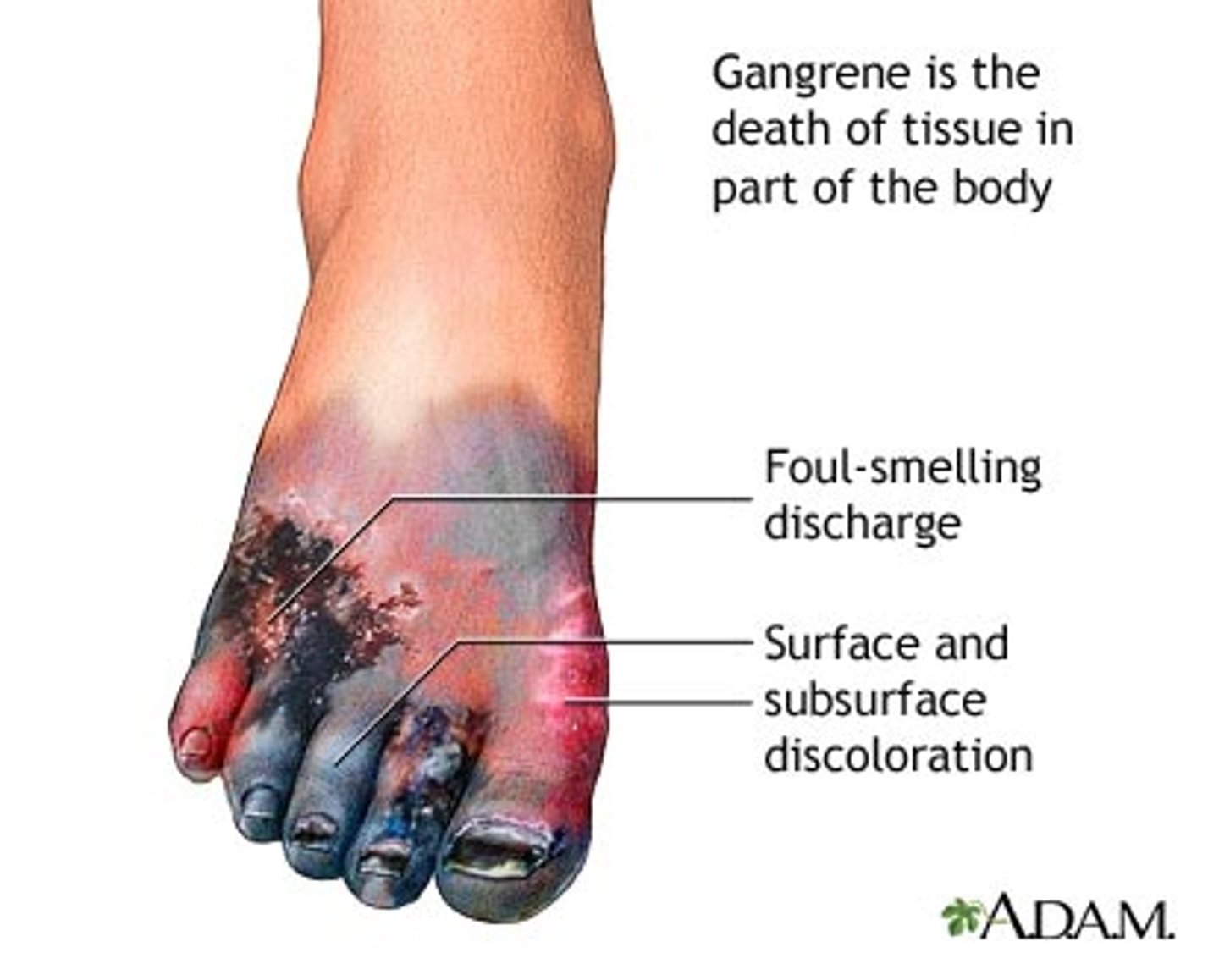
gangrene
death of tissue associated with loss of blood supply
common with frostbite and diabetes
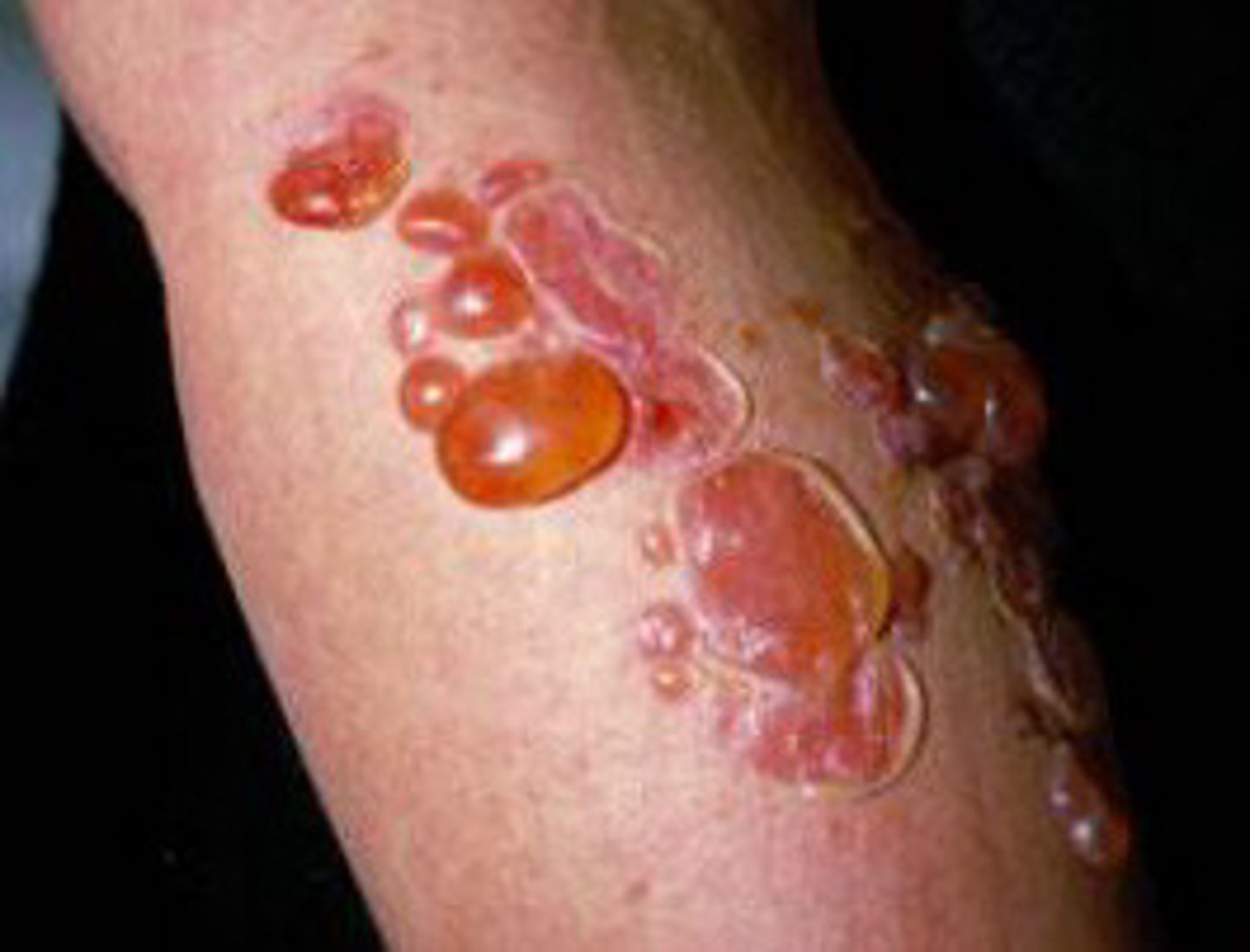
Impetigo
bacterial inflammatory skin disease characterized by vesicles, pustules, and crusted-over lesions
caused by staph or strep bacterial strains
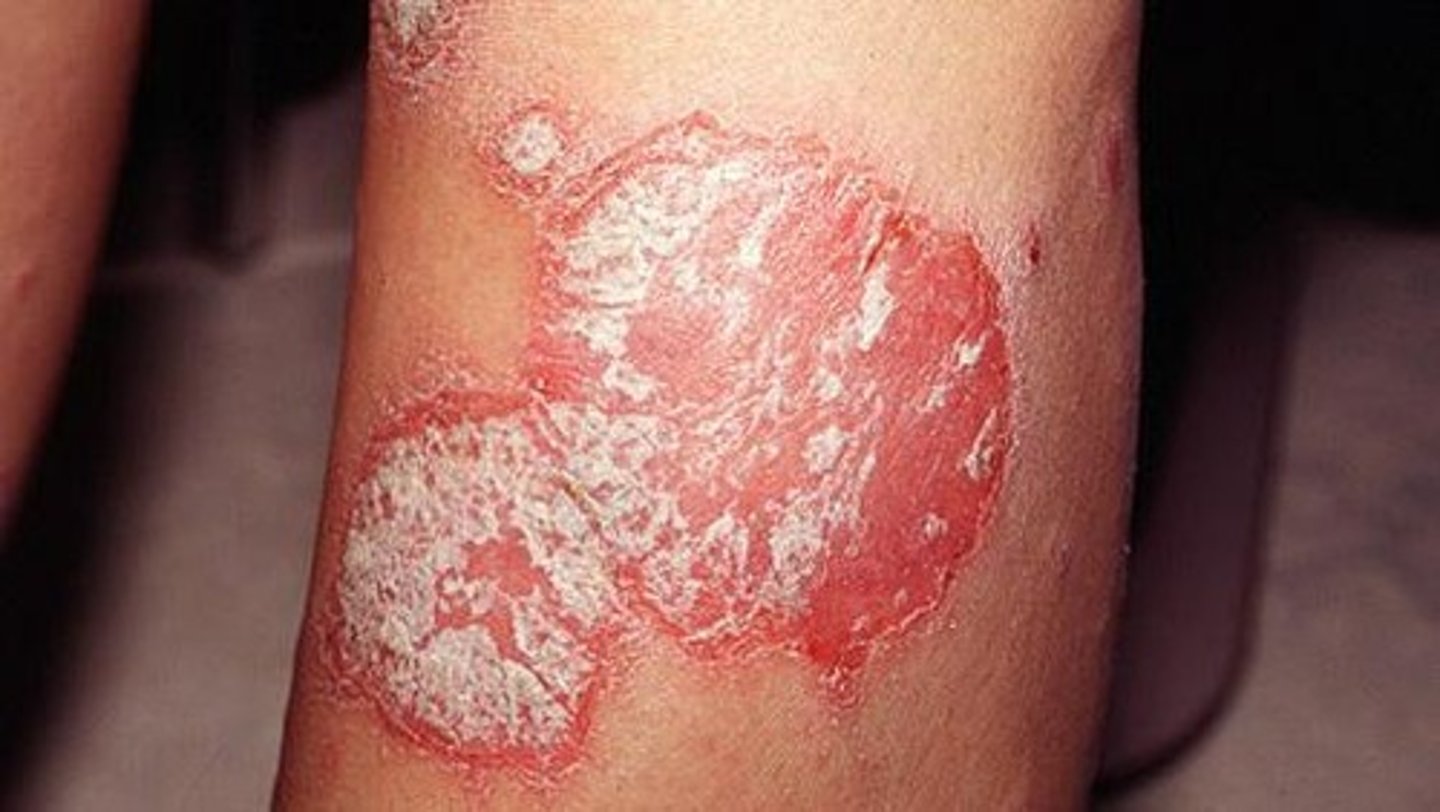
Psoriasis
chronic skin condition producing red lesions covered with silvery scales
it is not infectious or contagious
it is autoinflammatory that can run in families
treatment is only palliative(relieving but no cure)
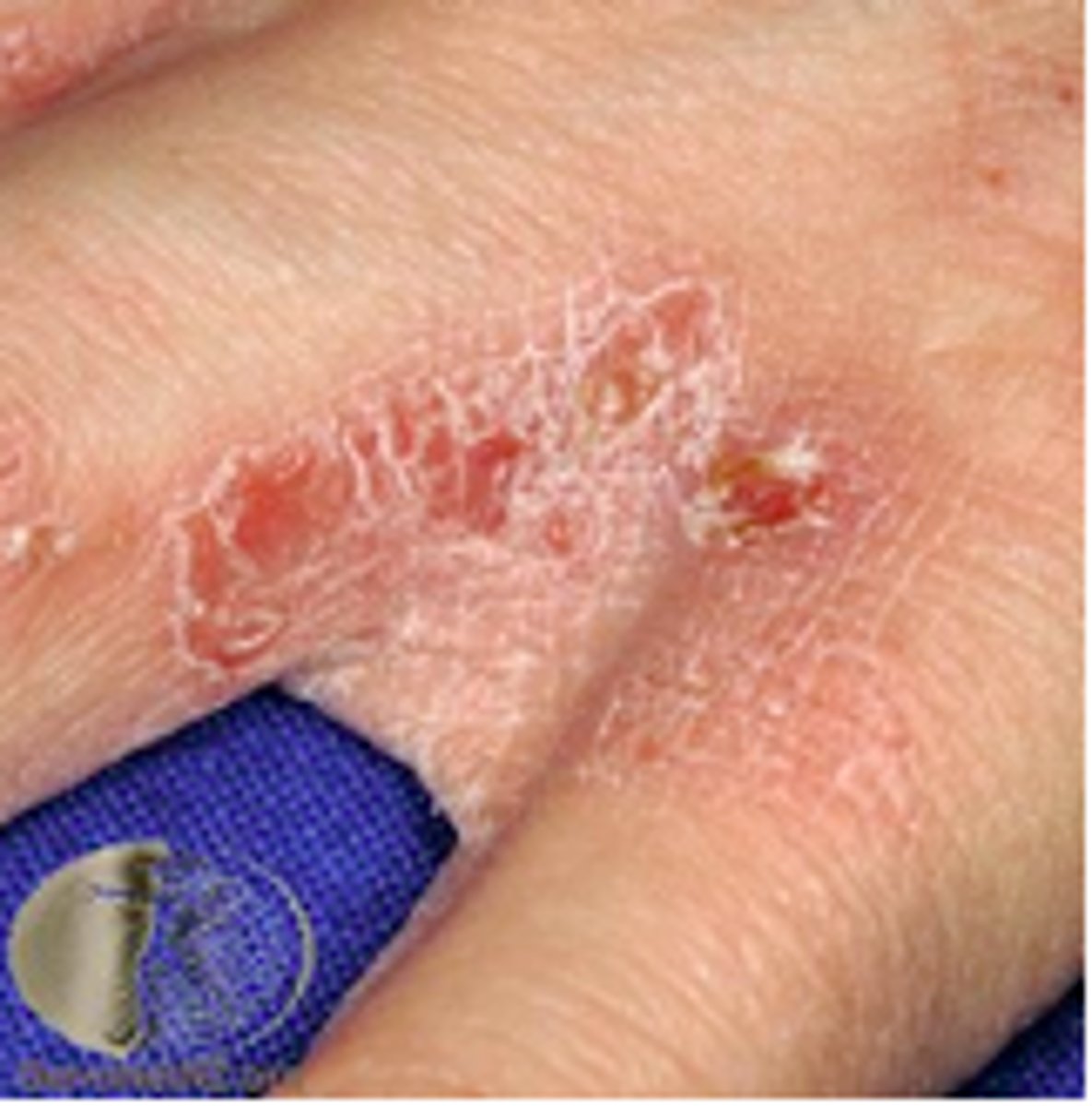
Scabies
contagious, parasitic infection of the skin with intense pruritus
often seen in the groin, nipples and skin between the fingers
treatment is topical cream to destroy scabies mites
scleroderma
is an autoimmune disease where fibrous scar like tissue forms in the skin, heart, lungs, kidney and esophagus some changes of pigmentation may be seen
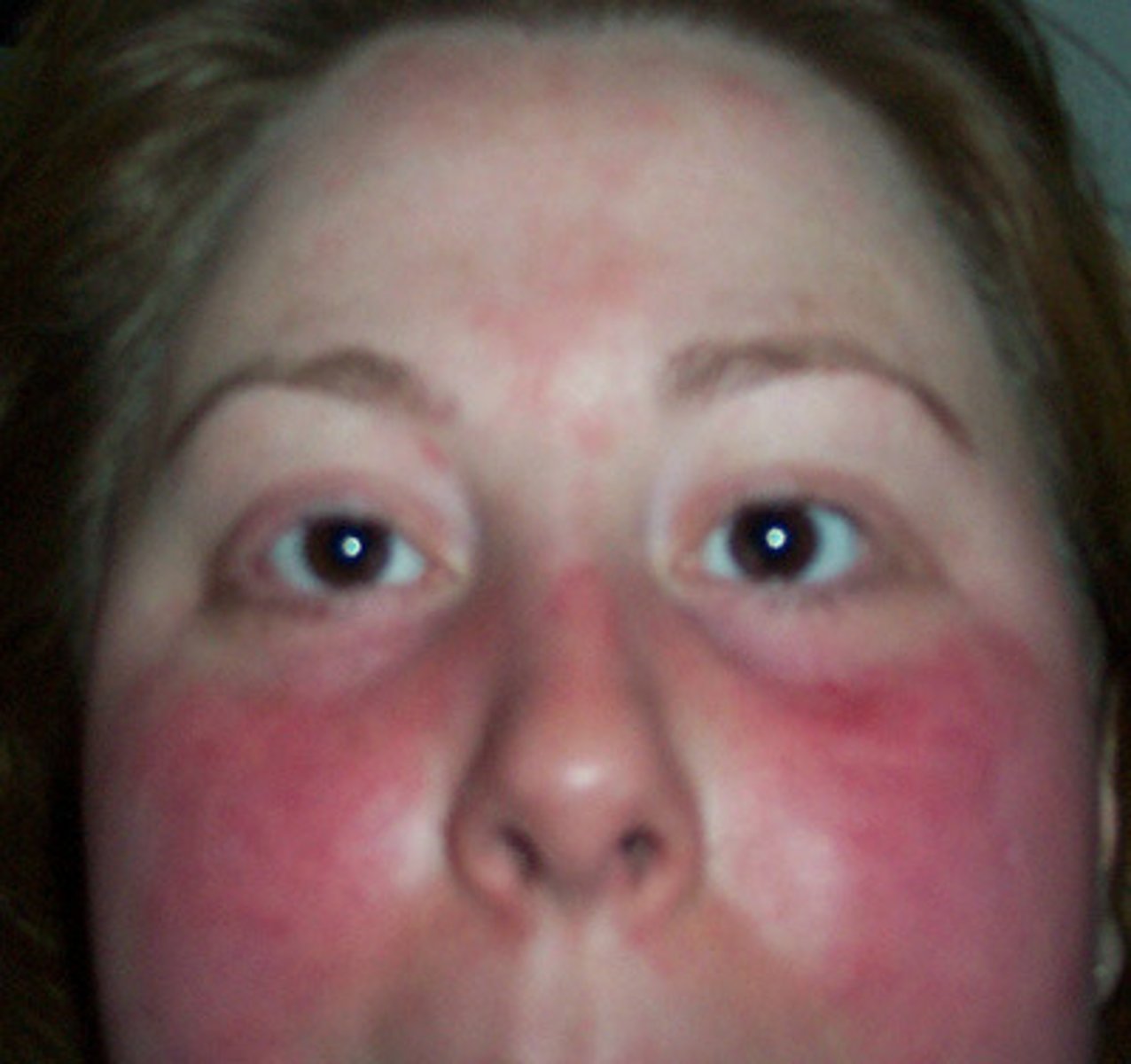
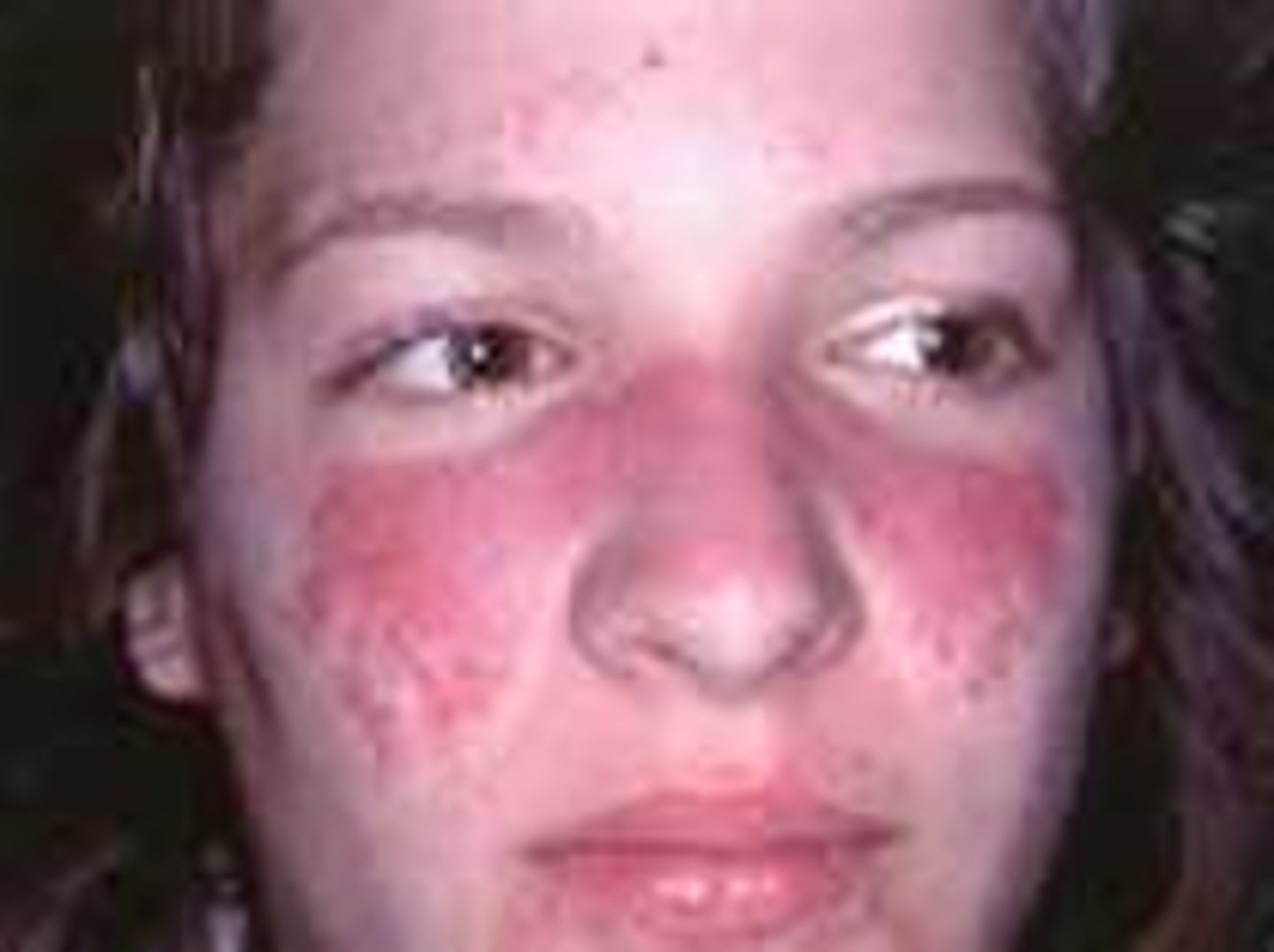
systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
chronic autoimmune inflammatory disease of collagen in skin, joints, and internal organs
seen with a butterfly red rash over the cheeks and nose
primarily seen in females
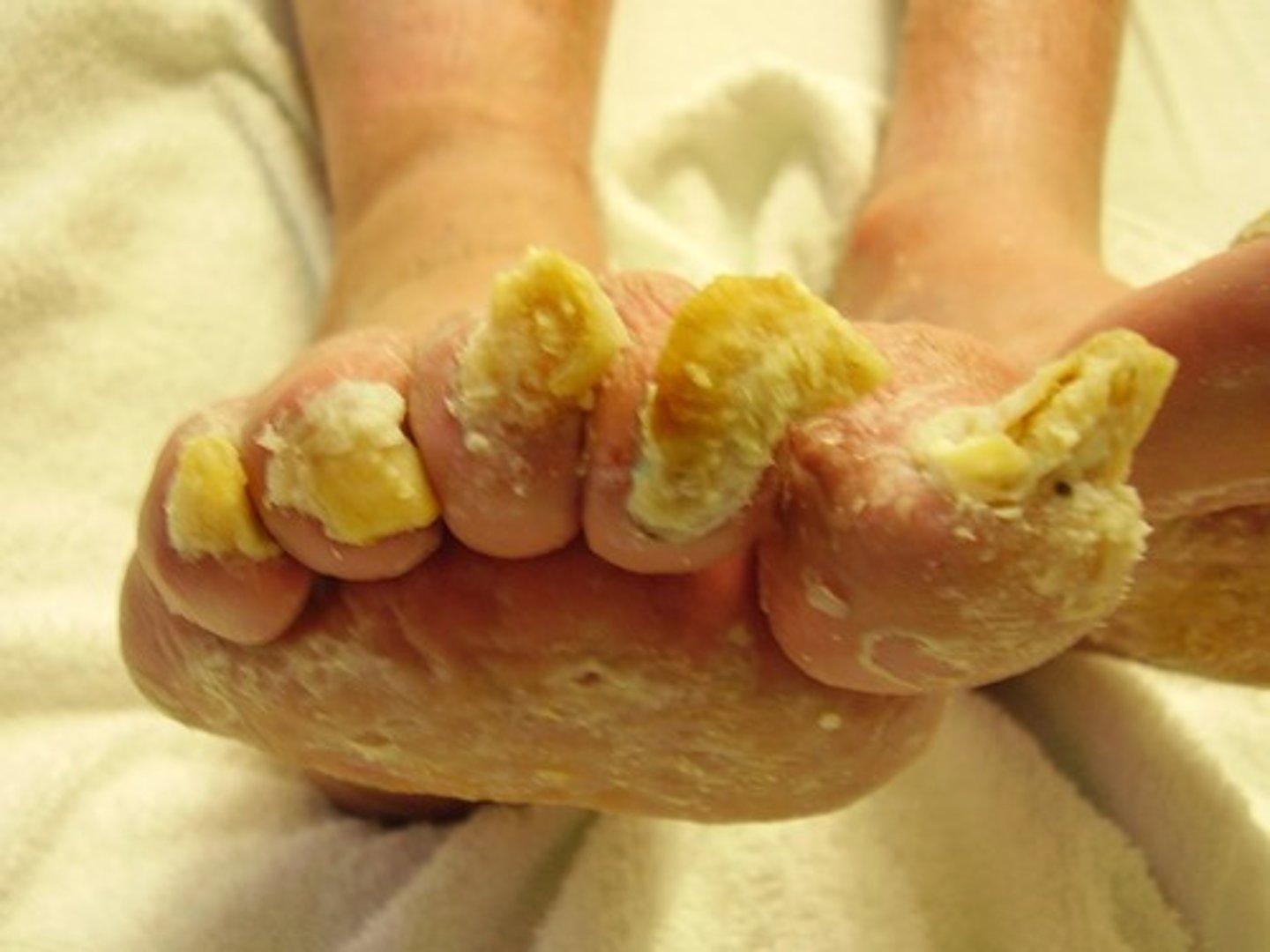
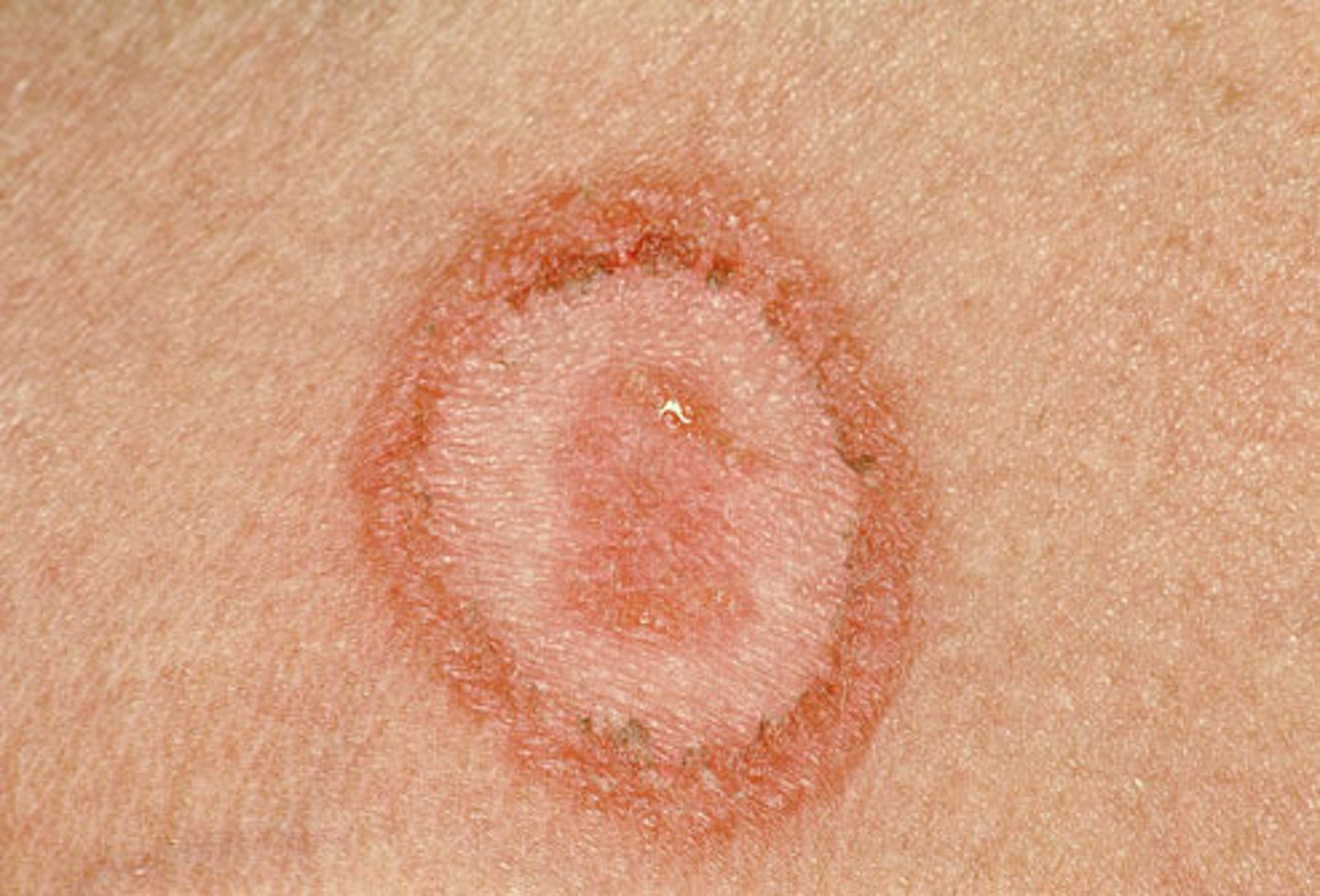
tinea
infection of the skin caused by a fungus
many types, tinea corporis or ringworm, tinea pedis or athlete's foot treated with antifungal
they are highly contagious and cause severe pruritus(itching)
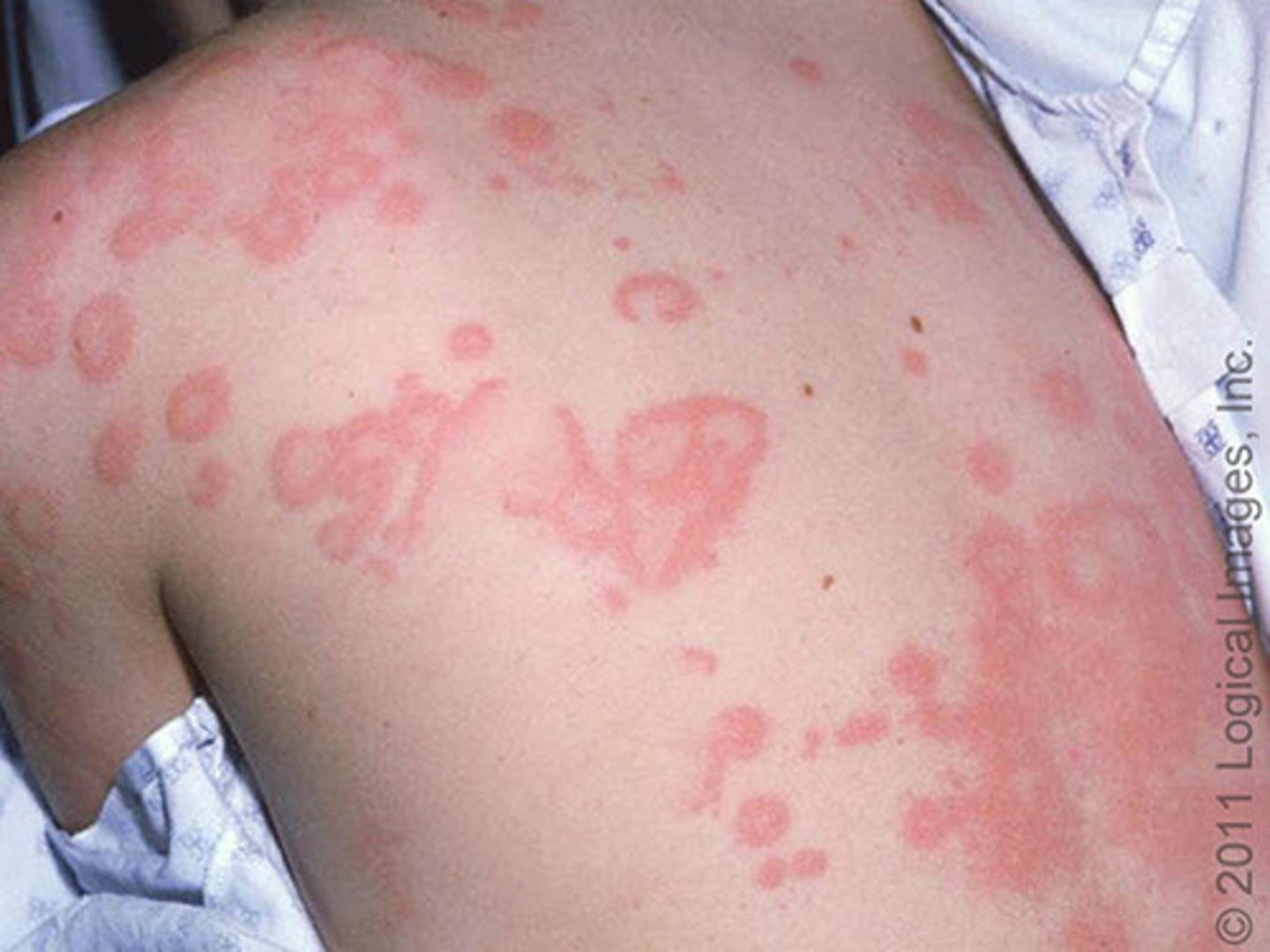
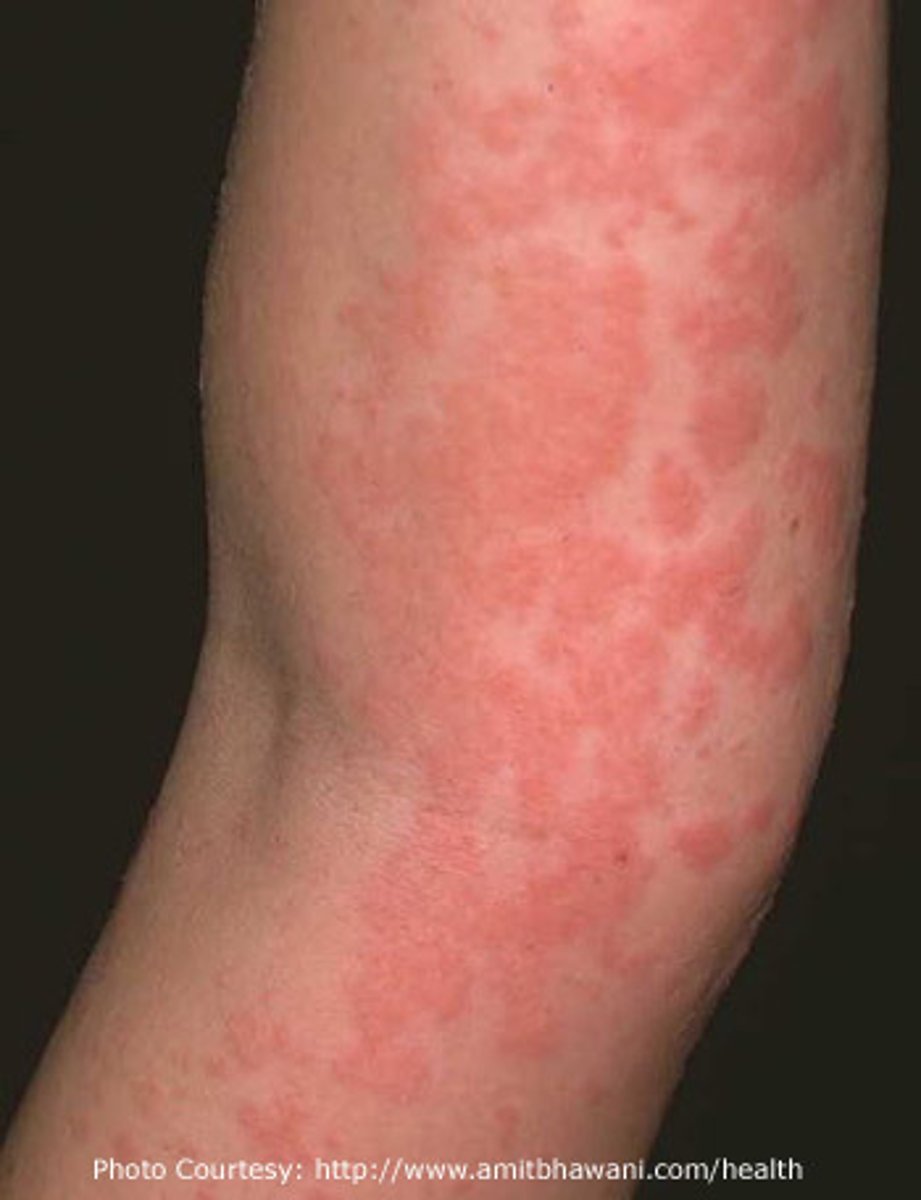
Uticaria(hives)
acute allergic reaction in which red, round wheals develop on the skin
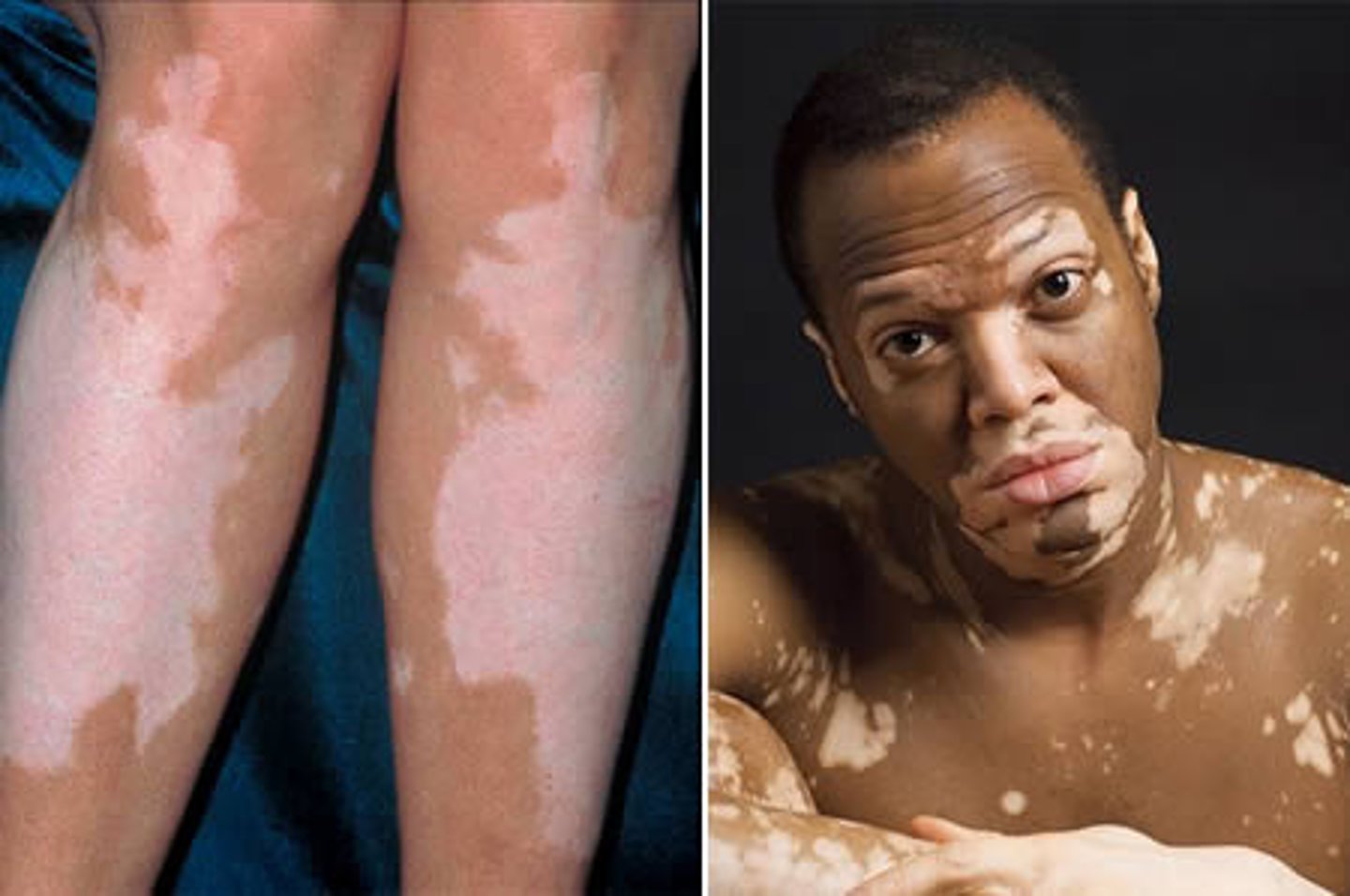
vitiligo
localized loss of skin pigmentation characterized by milk-white patches
it is a form of leukoderma
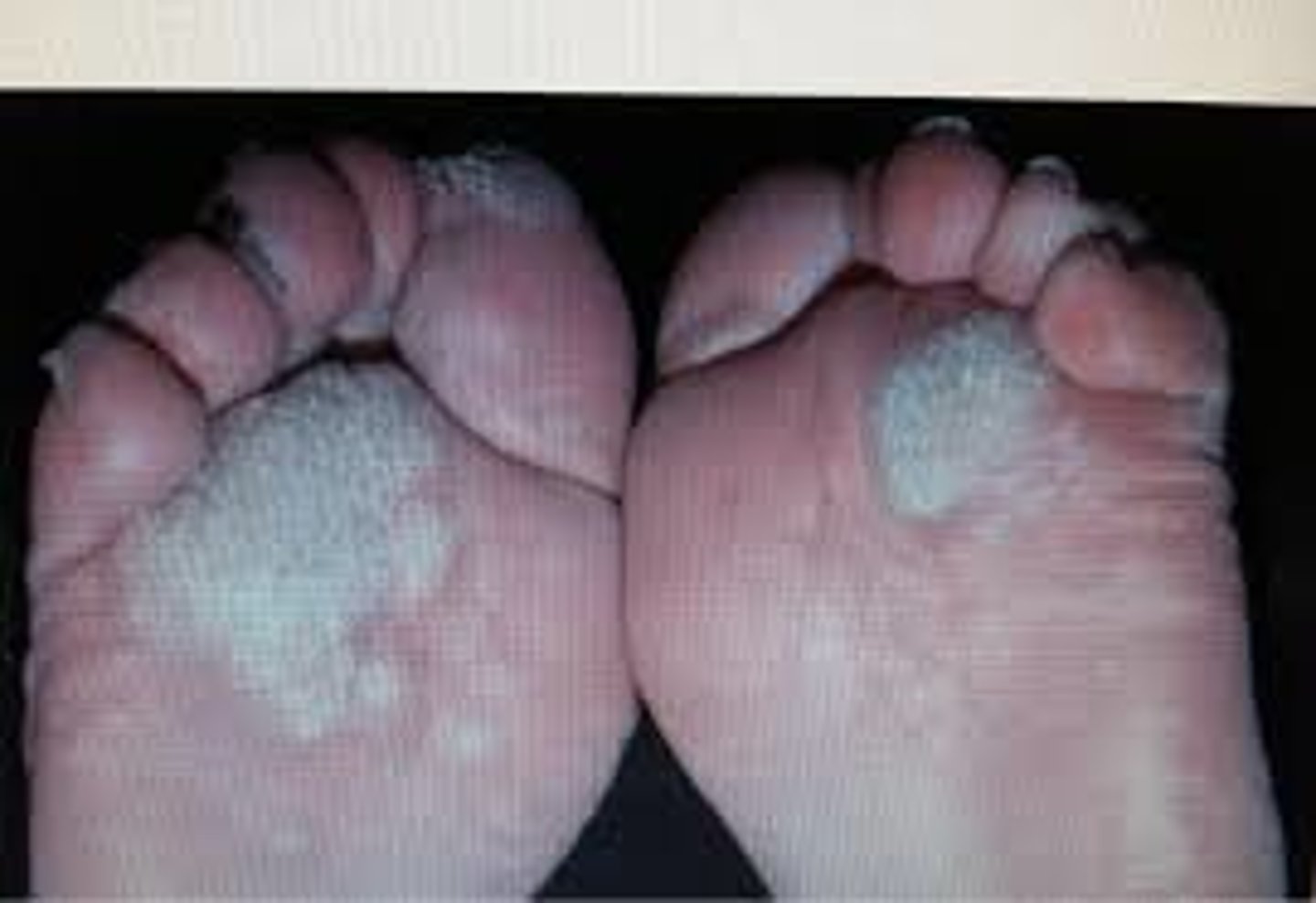
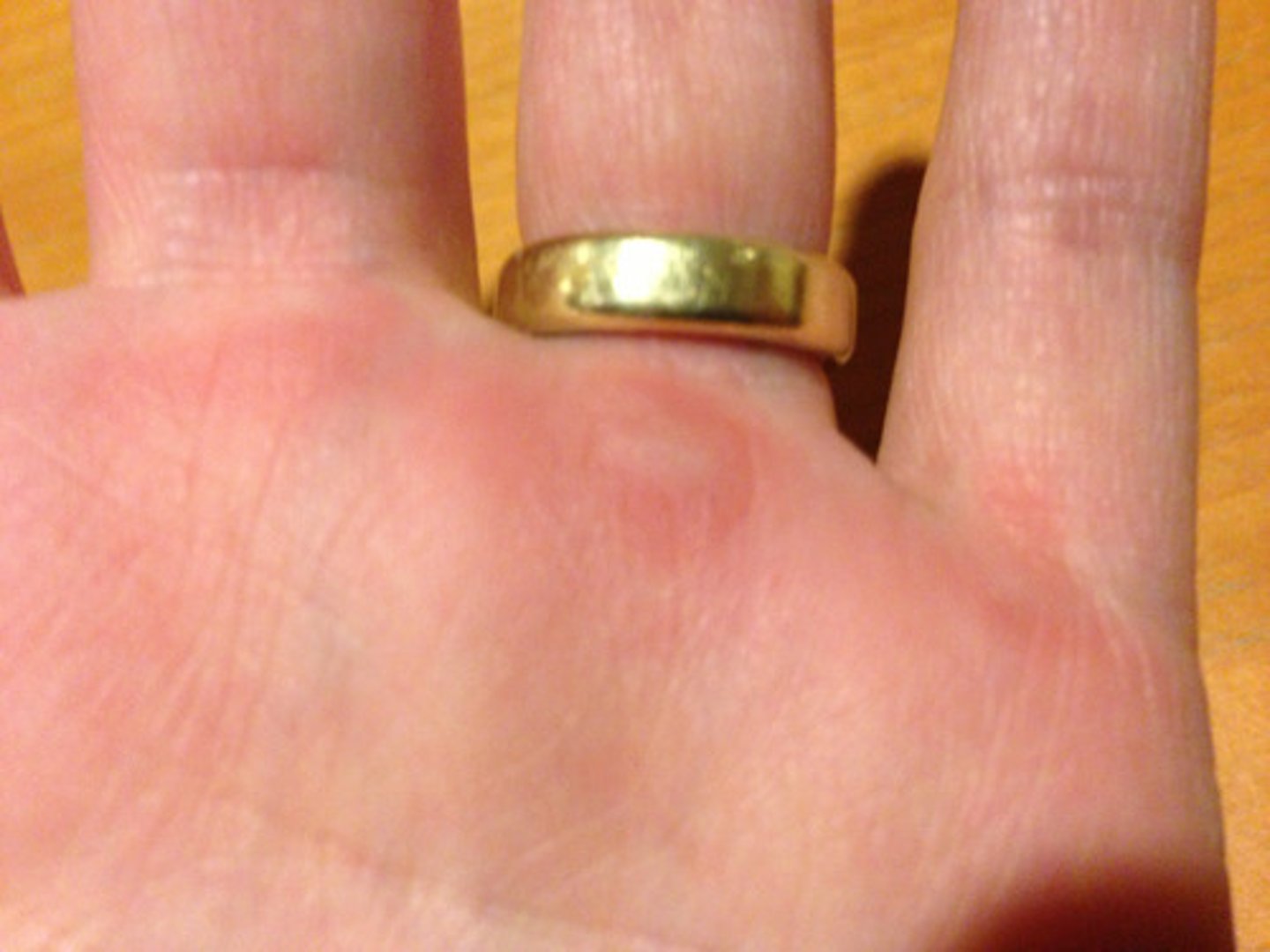
callus
increased growth of cells in the keratin layer of the epidermis caused by pressure or friction
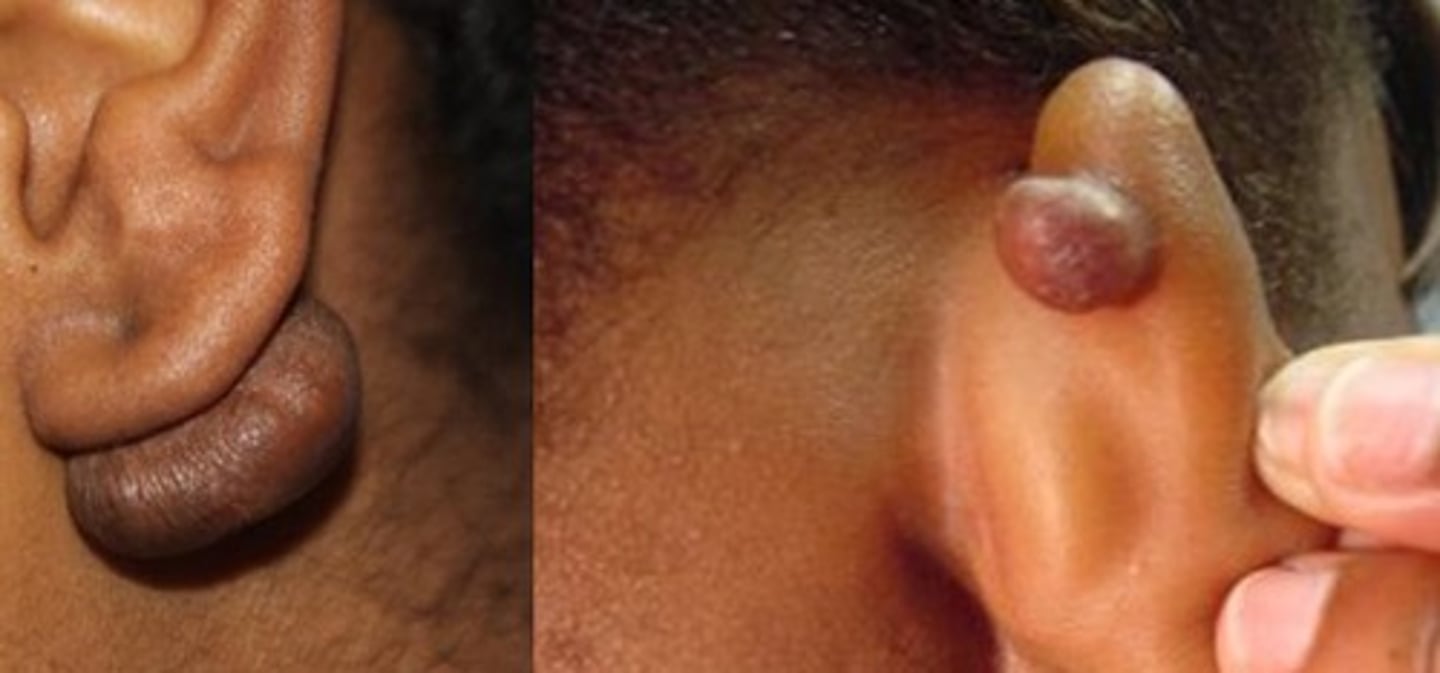
keloid
excess hypertrophied, thickened scar developing after trauma or surgical incision
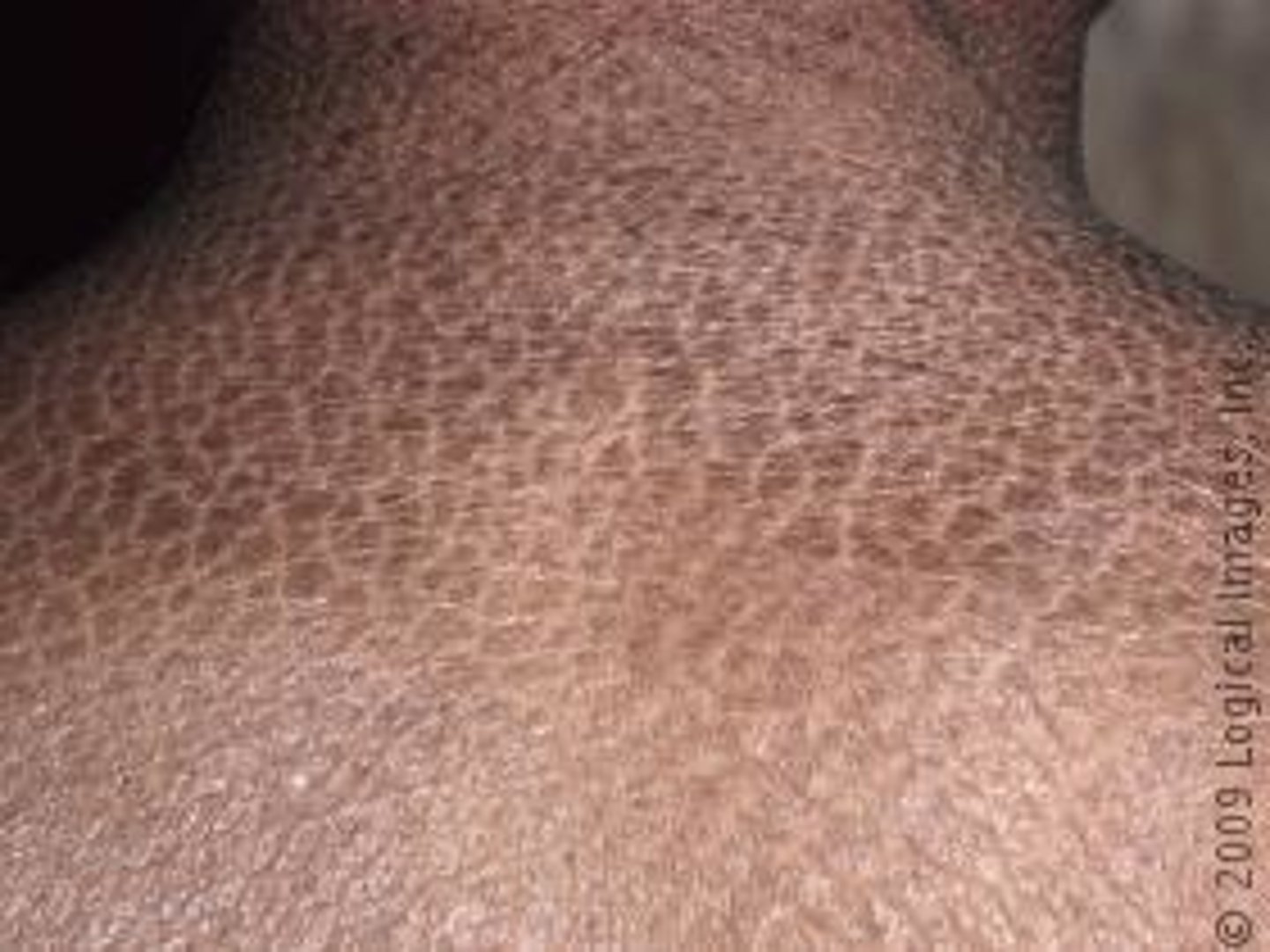
keratosis
thickened and rough lesion of the epidermis; associated with aging or skin damage
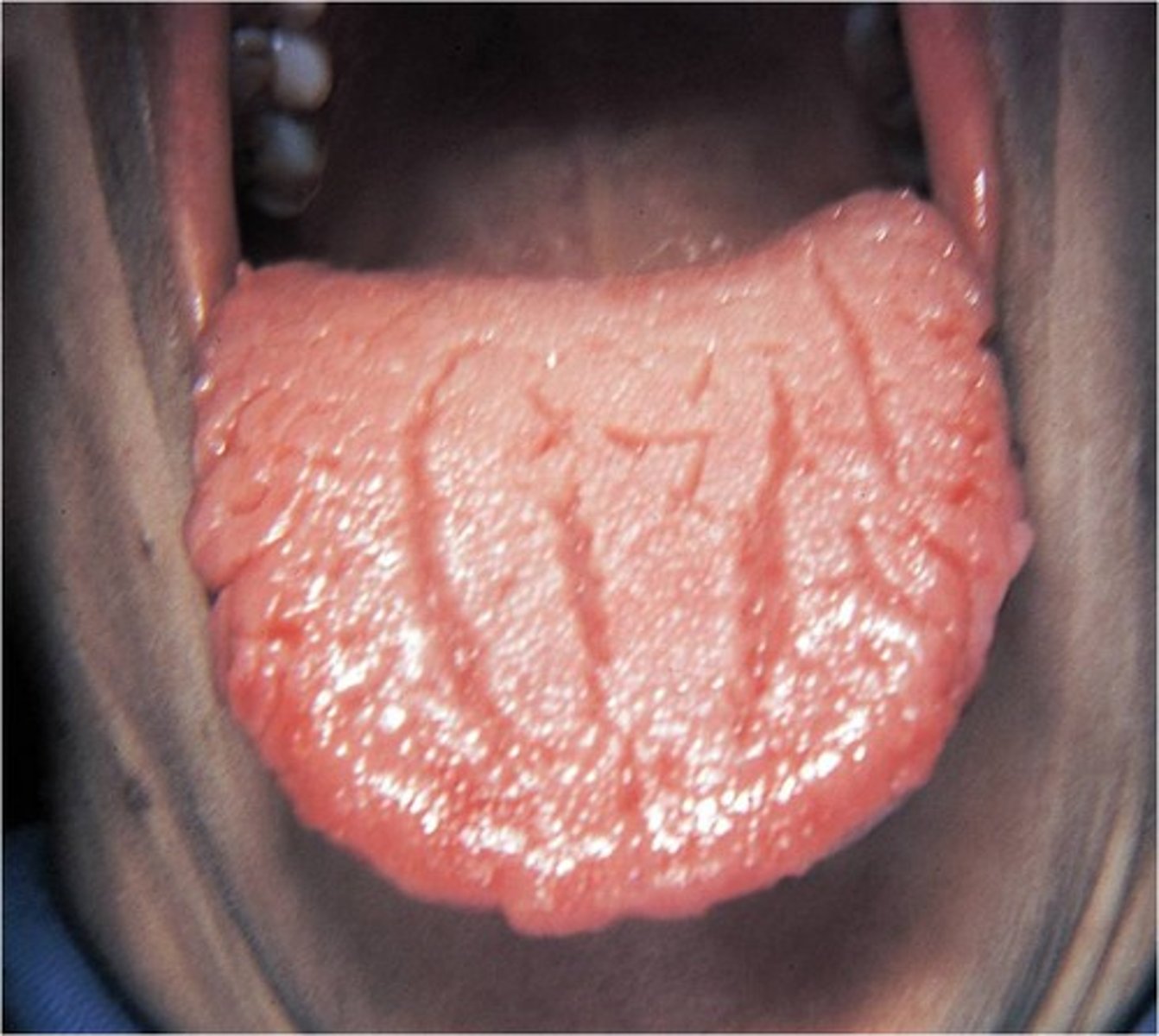
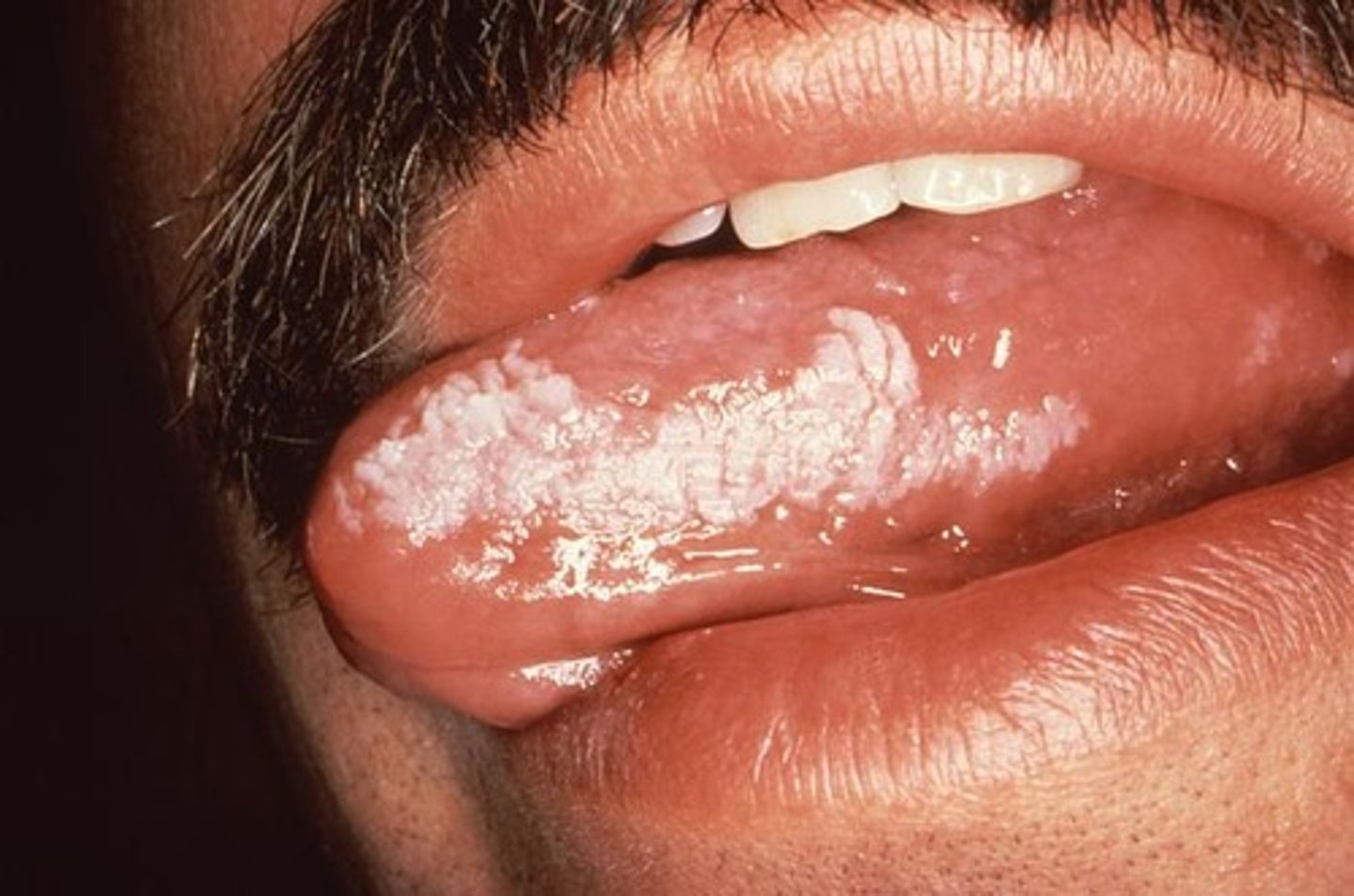
Leukoplakia
white, thickened patches on mucous membrane tissue of the tongue or cheek (evolves to squamous cell carcinoma)
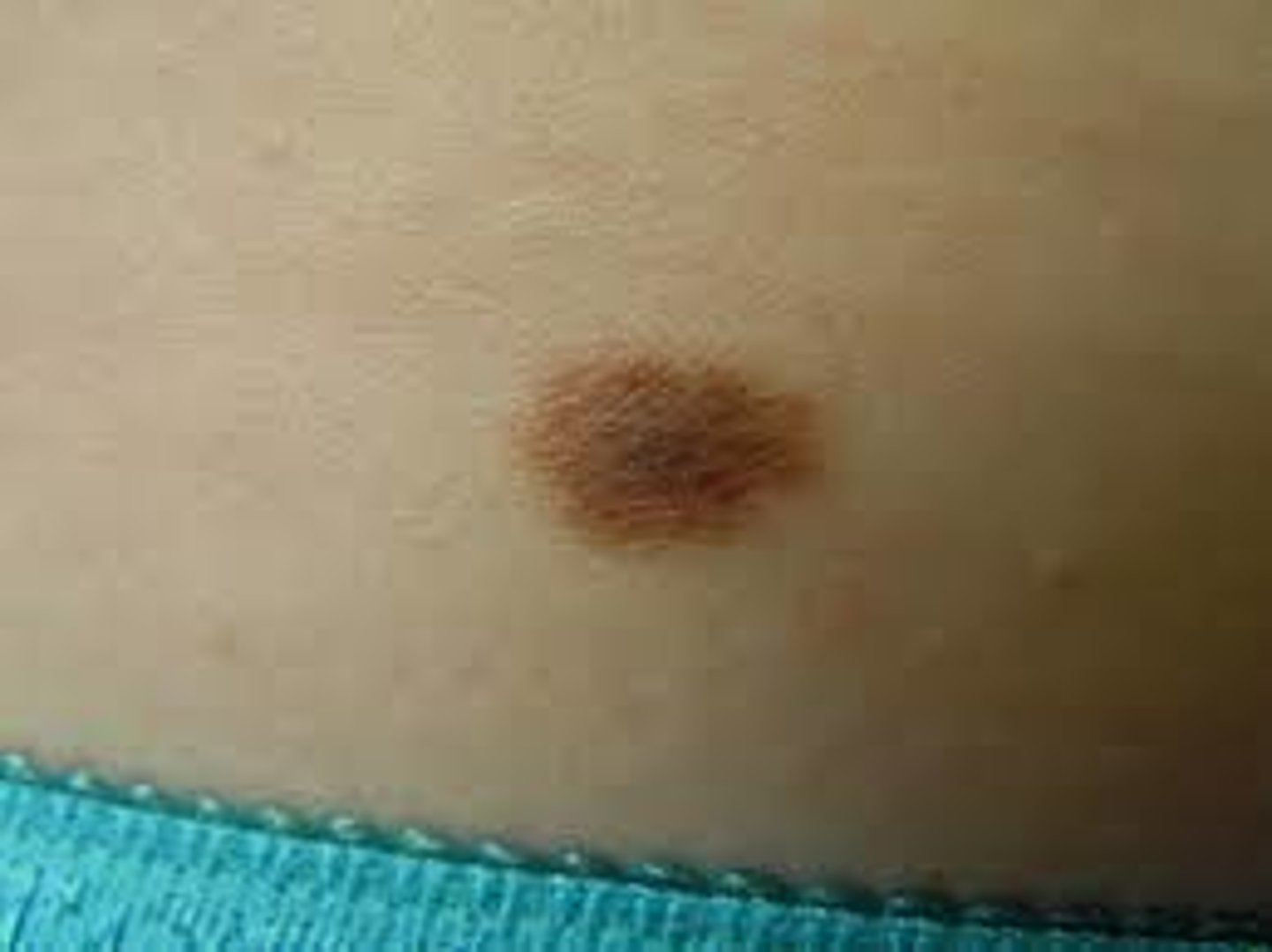
nevus, nevi
pigmented lesion of the skin, benign
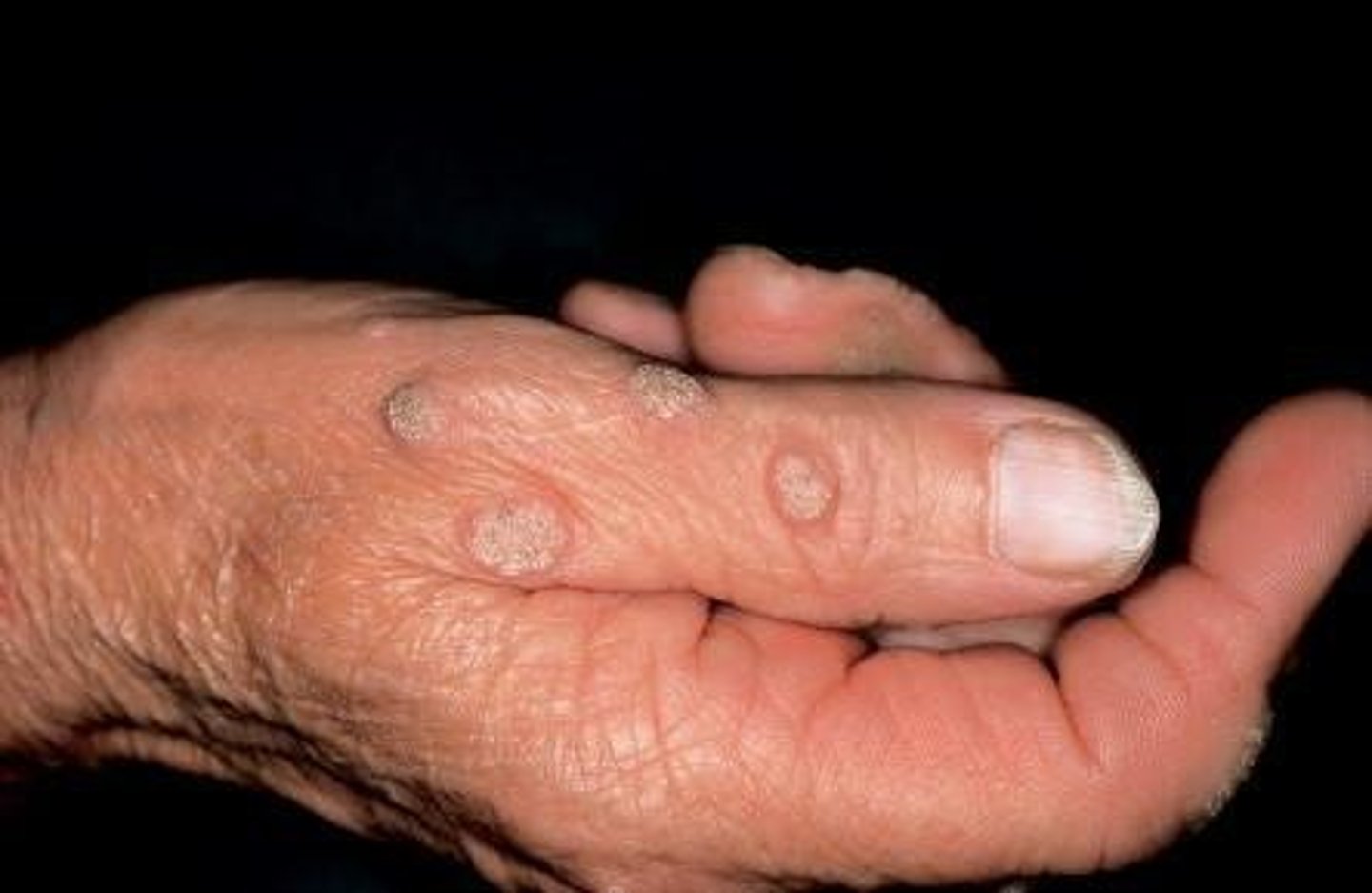
verruca
epidermal growth (wart) caused by a virus
____ vulagaris(common wart)
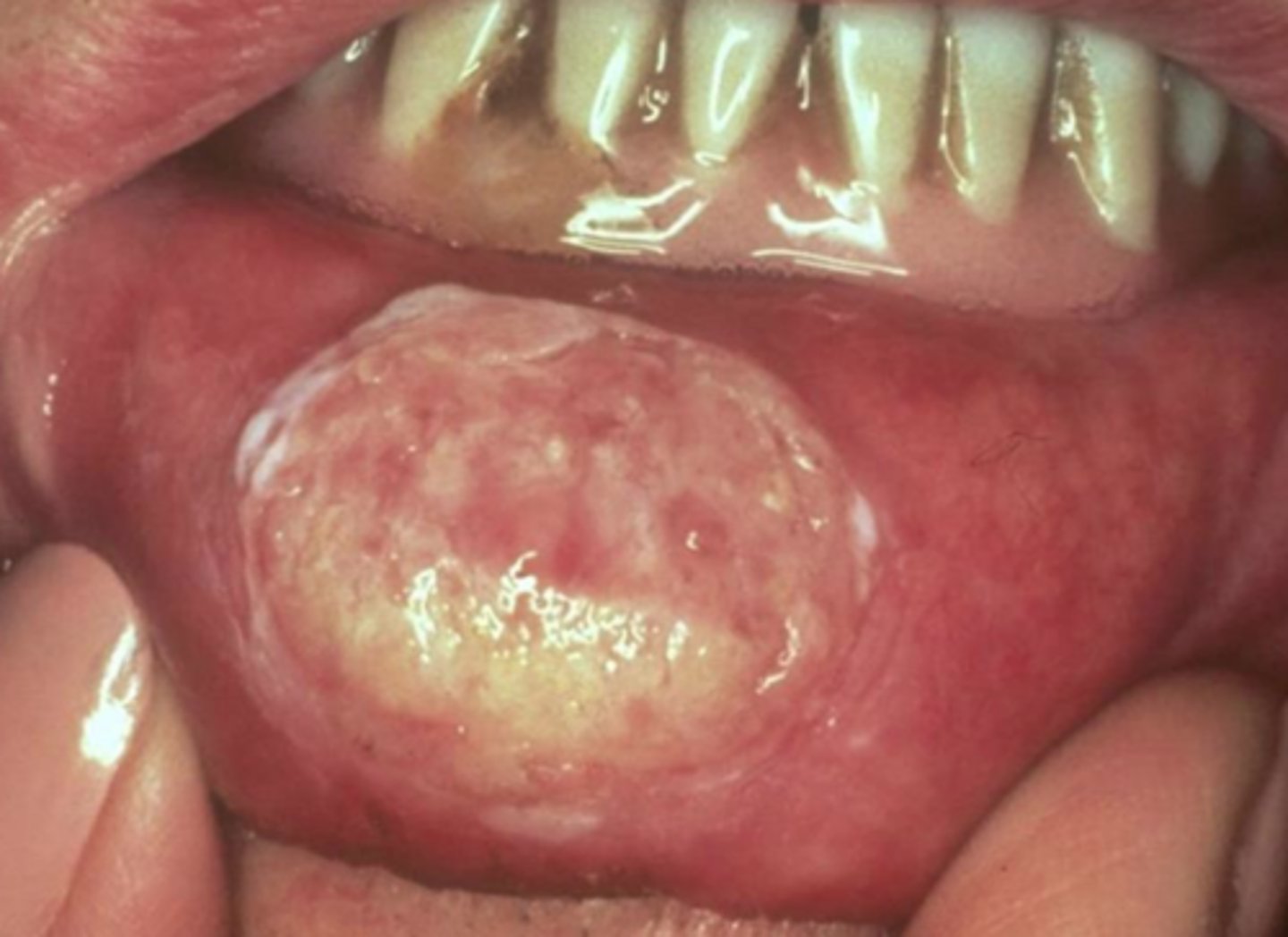
basal cell carcinoma
malignant tumor of the basal cell layer of the epidermis
it is the most common skin cancer
squamous cell carcinoma
malignant tumor of the squamous epithelial cells in the epidermis
it can grow other places than the skin, wherever squamous epithelium is found(mouth, larynx, bladder, esophagus, lungs)
sun damage can be a precursor
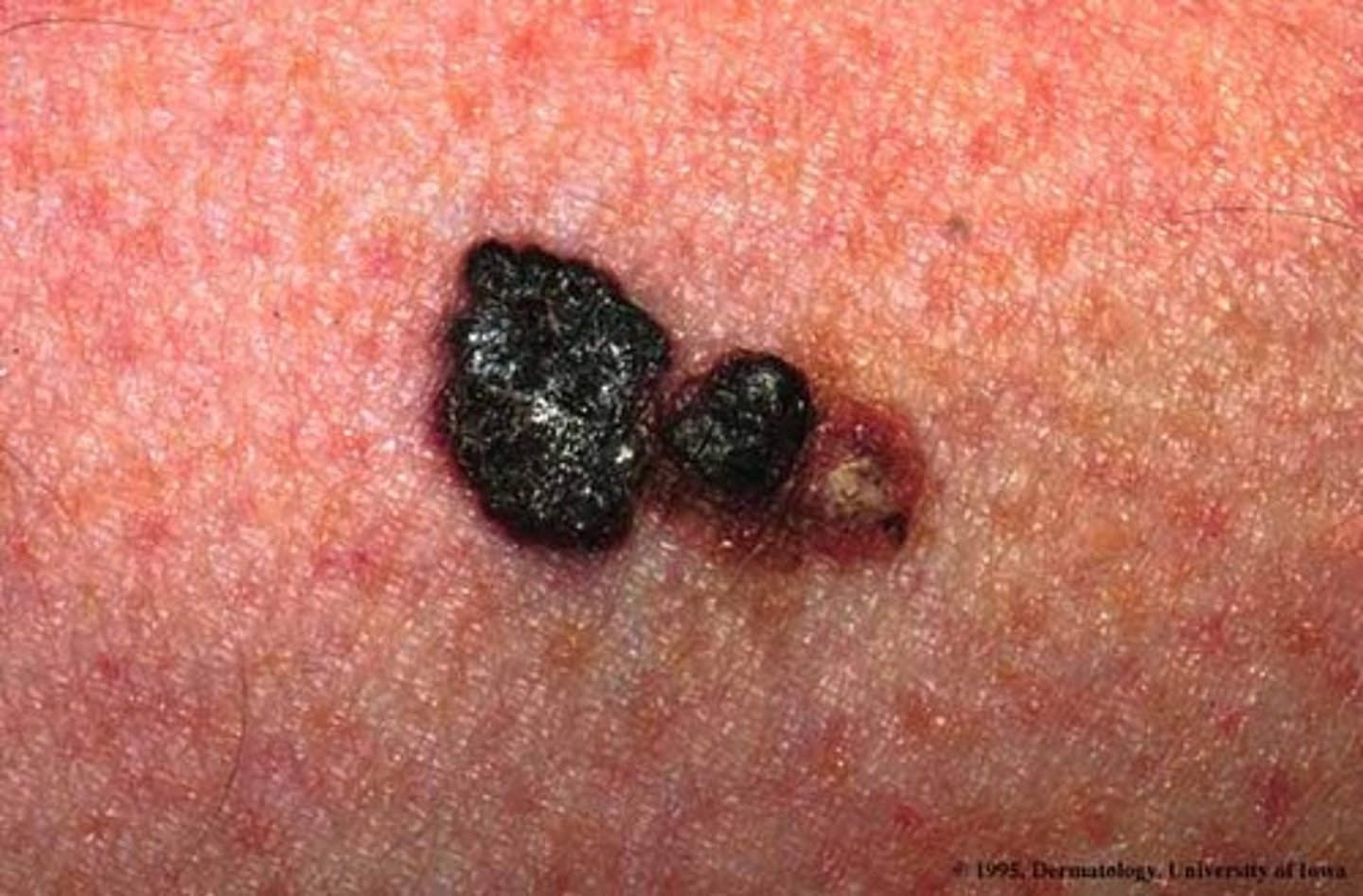
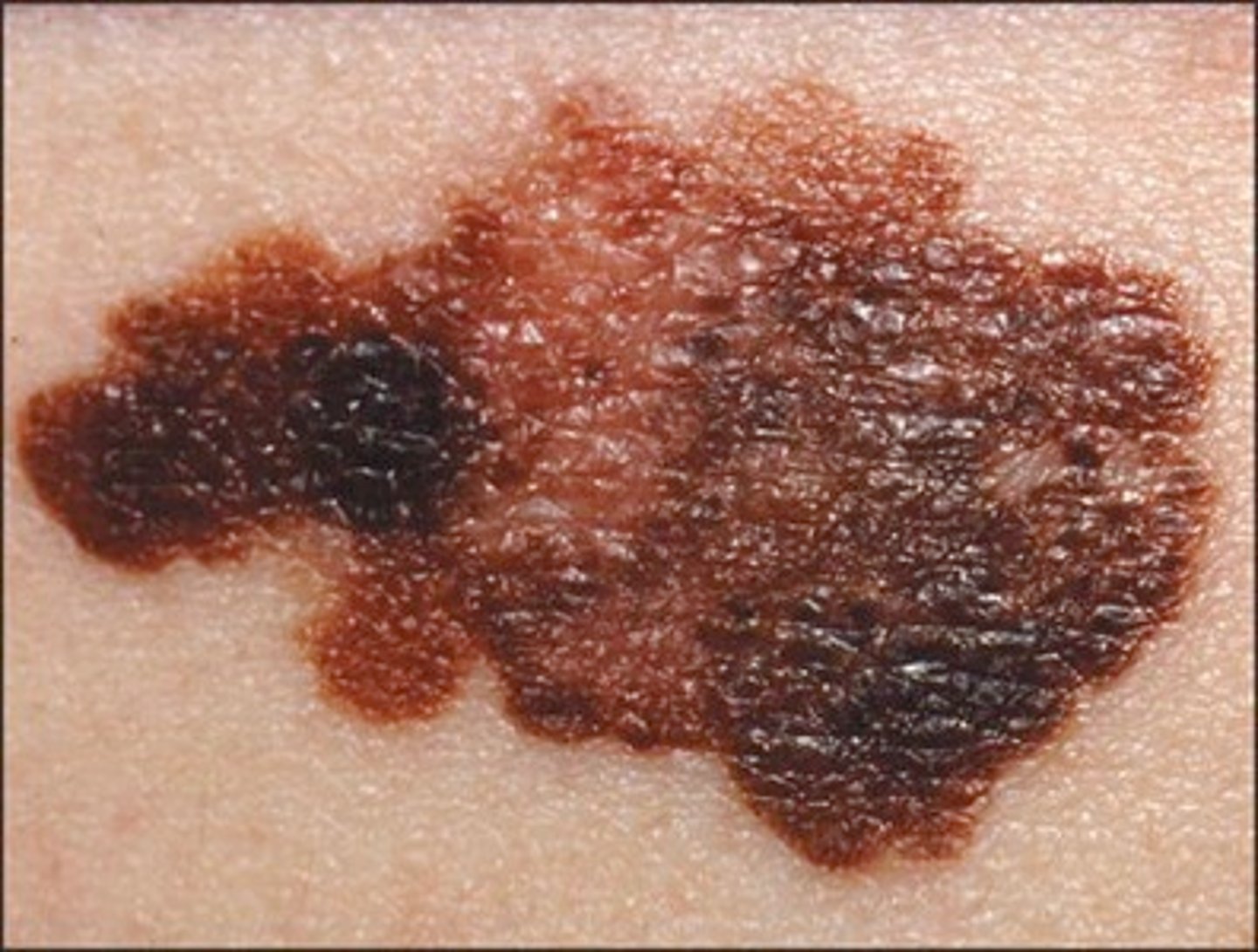
malignant melanoma
cancerous growth composed of melanocytes
they often metastasize to the lung, liver, bone, and brain
often related to exposure to ultraviolet light
there may be a genetic predisposition
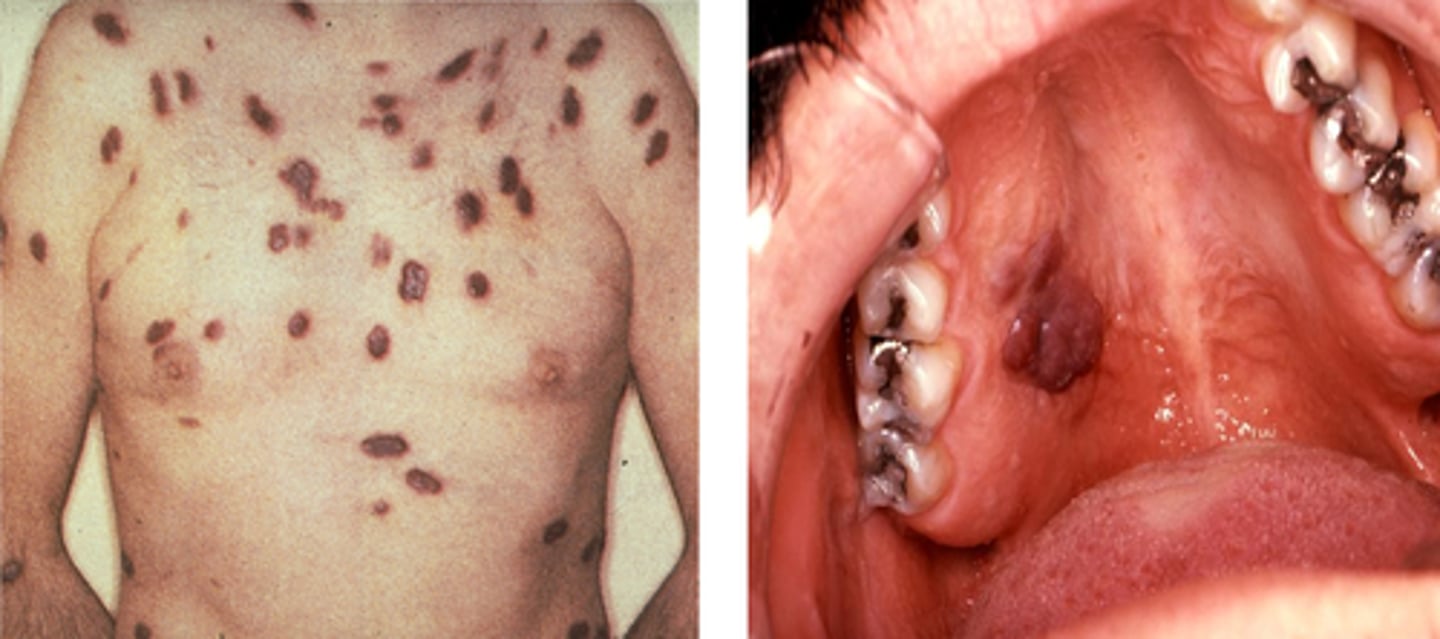
Kaposi's sarcoma
malignant, vascular, neoplastic growth characterized by cutaneous nodules
often seen in the lower extremities
one form is associated with AIDS
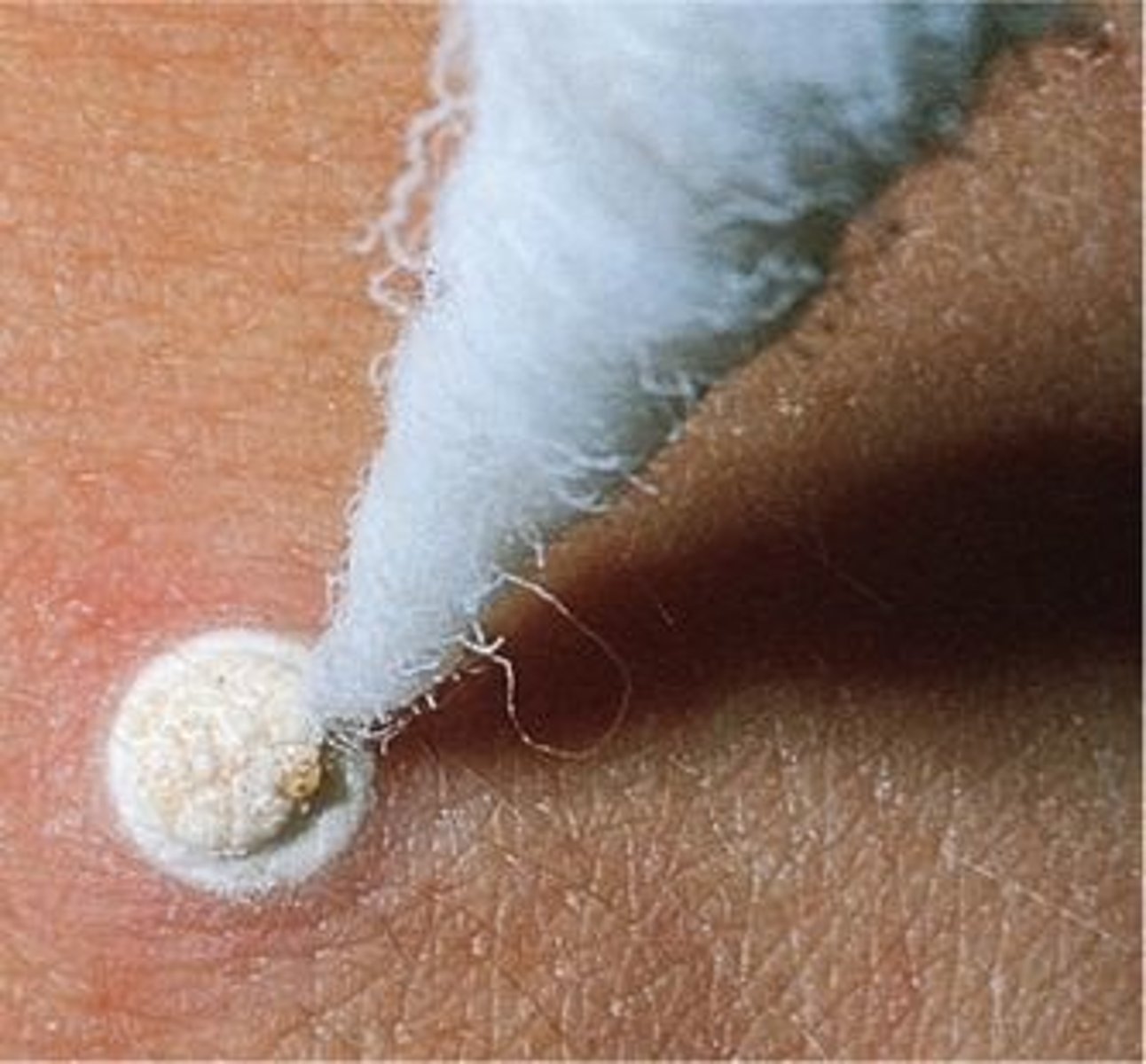
cryosurgery
use of subfreezing temperature to destroy tissue
achieved with liquid nitrogen
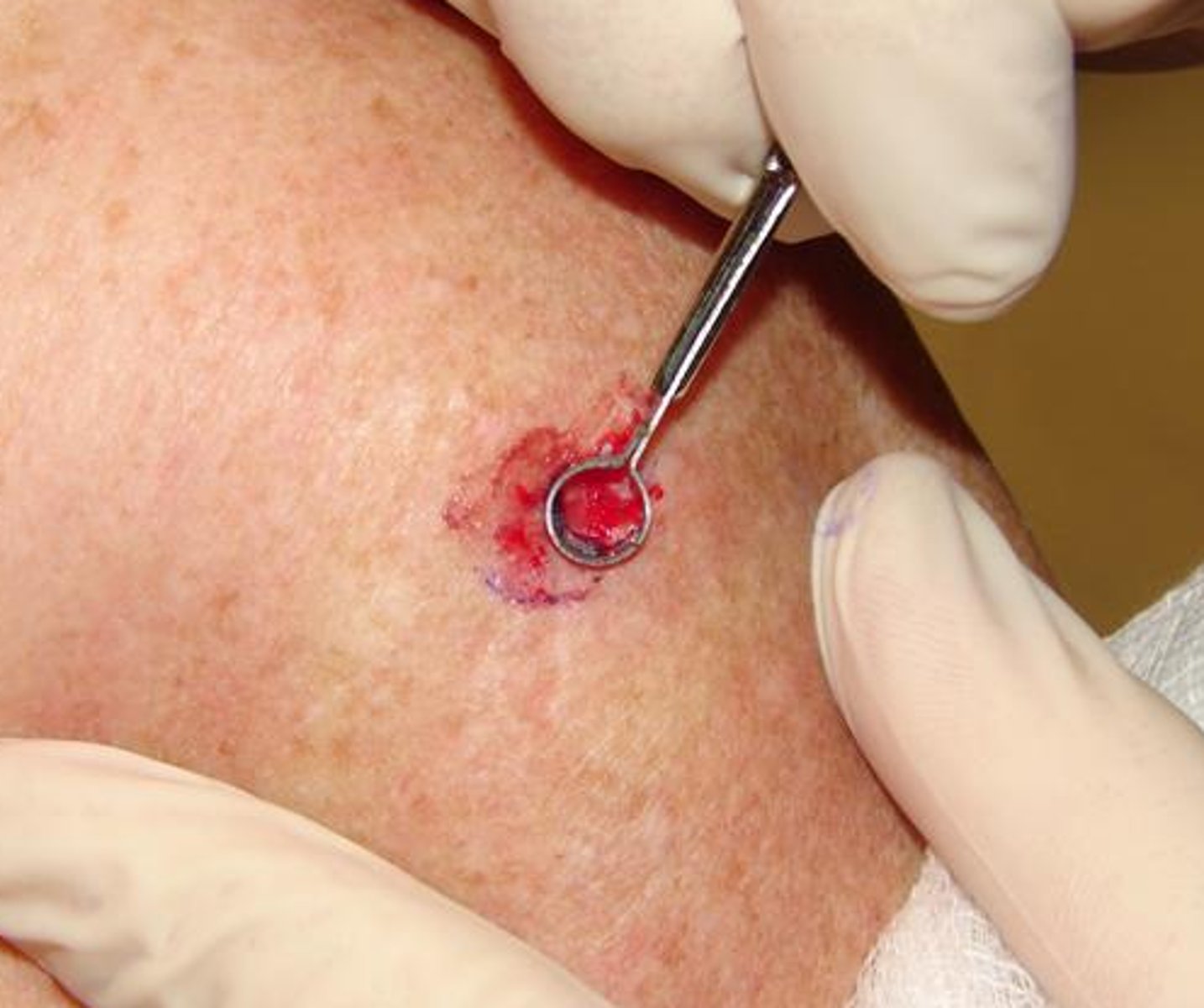
curettage
use of a sharp dermal curette to scrape away a skin lesion
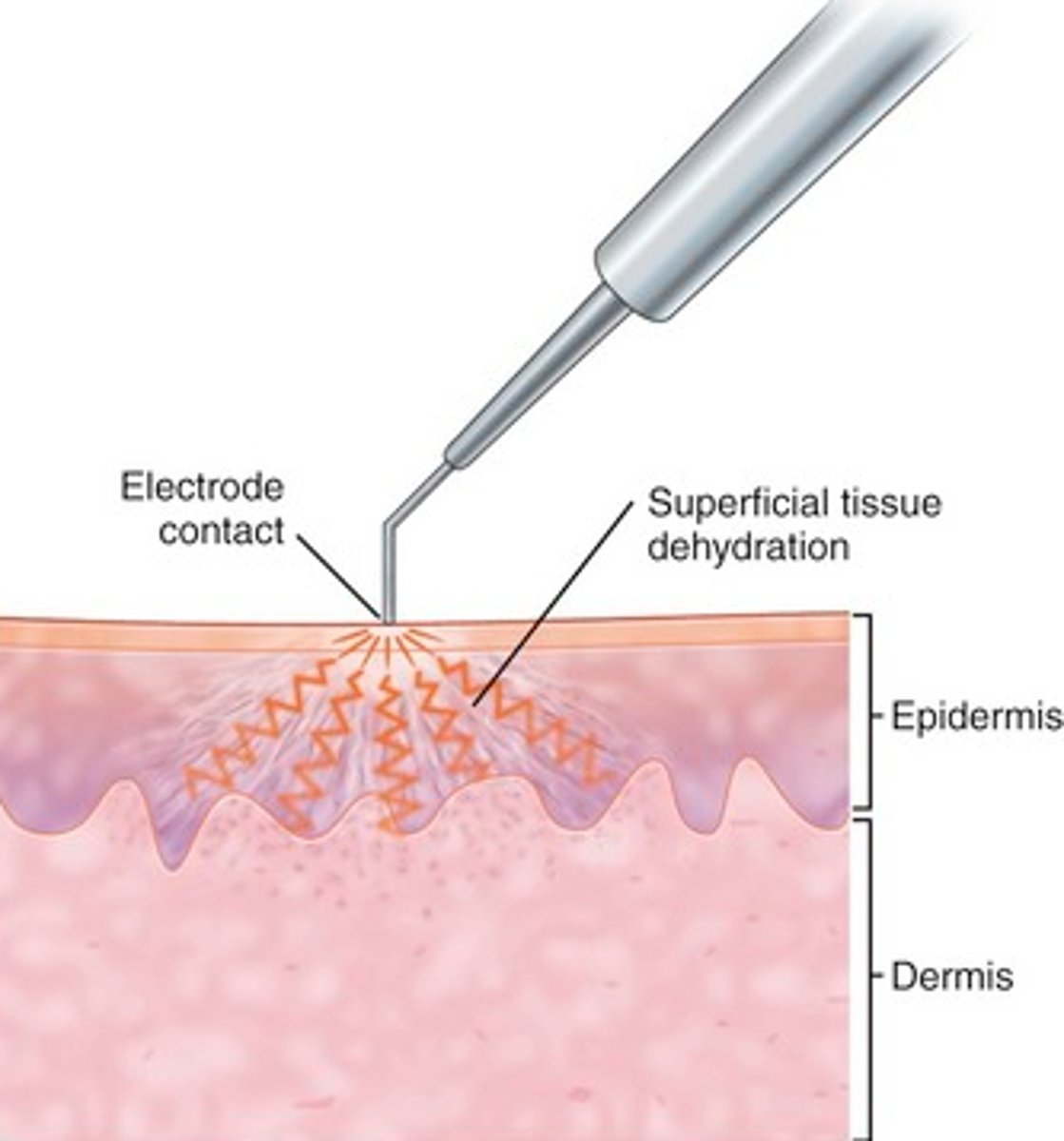
electrodesiccation
tissue is destroyed by burning with an electric spark
can be used with curettage to destroy small cancerous lesions that have well defined borders
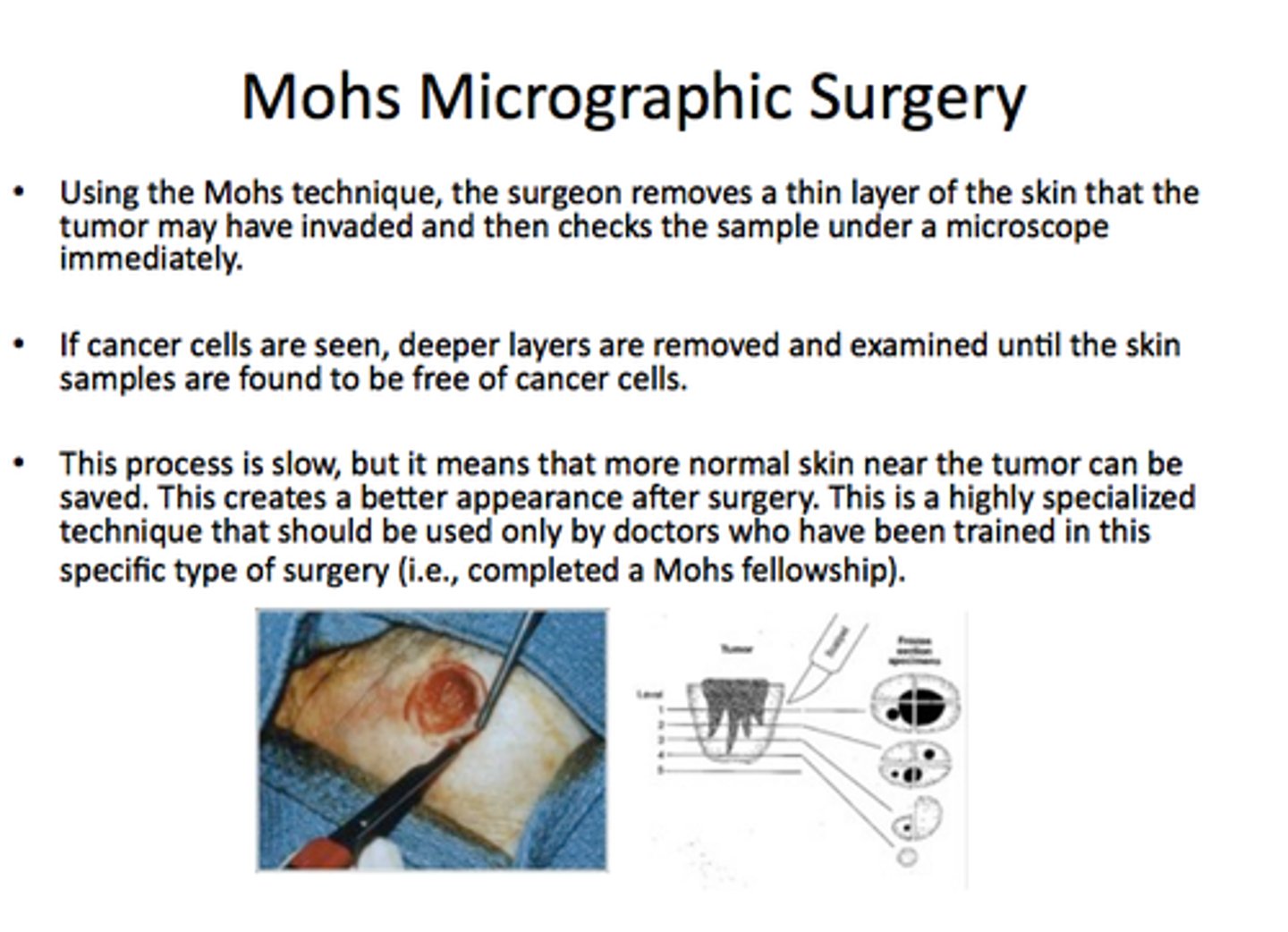
Mohs surgery
thin layers of malignant tissue are removed, and each slice is examined under a microscope to check for adequate extent of the resection
used mainly with basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinomas, and other tumors
skin biopsy
suspicious skin lesions are removed or sampled and examined microscopically by a pathologist
skin test
substances are injected intradermally or applied to the skin, and results are observed