Exam 3 patho: RBC Disorders
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Components of blood (4)
Leukocytes (WBCs)
Thrombocytes (platelets)
Erythrocytes (RBCs)
Plasma (carries waste that is excreted into the kidneys)
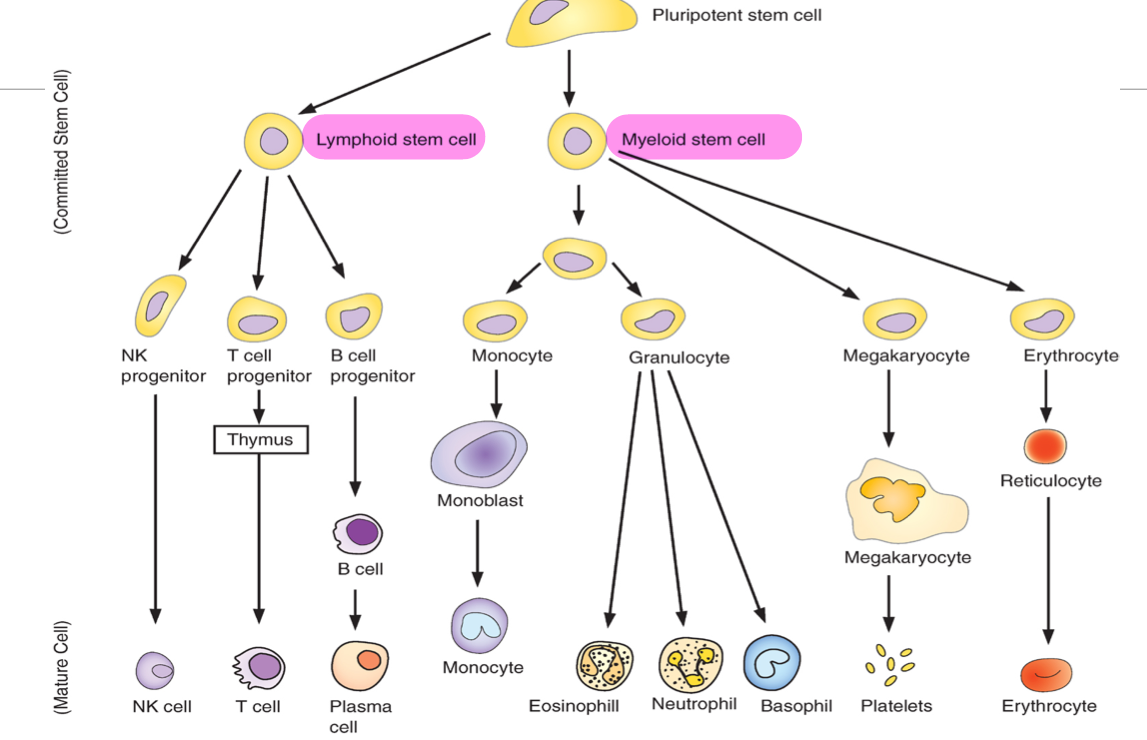
Hematopoietic system
Formation from pluripotent stem cells in BM
Function of hematopoetic system
Transport CO2, O2, and waste
Defense against microorganisms
Perverse integrity of vascular system
All cells of the blood are derived from…
pluripotent stem cells of bone marrow
Progenitor cells and function
Stem cells of BM differentiate into progenitor cells, either lymphoid stem cells or myeloid stem cells
They are mother cells responsible for the lineage of a particular cell line
Differentiation of blood cells from BM stem cells
Erythrocytes
mature RBCs
Shape of RBC
Biconcave
How many O2 can be carried by hemoglobin?
4
What does O2 bind to on a hemoglobin?
Iron center
Why do people with anemia have pale RBCs?
Bc they have low iron
Folate function in blood
Folate is needed for DNA synthesis and aids in RBC formation
Vitamin B12 function
DNA synthesis
Nuclear maturation
Normal cell division
Prevents myelin breakdown
Which of the following is responsible for RBC production?
A. Vitamin B12
B. Thrombopoietin
C. EPO
D. Intrinsic factor
C. EPO
Proerythroblasts
Immature precursor cells in the bone marrow that develop into RBCs
Reticulocyte
immature RBC that has just been released from the bone marrow into the bloodstream
What steps occur after the kidneys sense low O2 in the blood stream?
Release EPO
Tells BM to produce more RBCs
Reticulocyte is formed
Matures into RBC after 24-48 hours
What does measuring Reticulocyte levels tell you?
The index rate of RBC production
Purpose of iron and vit-B
EPO function
Signals for the BM to produce more RBCs
Where is EPO released from?
Kidneys
Hemoglobin
Oxygen carrying capacity
Hematocrit
% of RBCs in the blood
MCV (Mean Corpuscular Volume)
tells us the size of the cells
Microcytic
Macrocytic
MCH (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin)
measures the average amount of hemoglobin per RBC
MCHC (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration)
Measures the concentration of hemoglobin in the RBCs
Helps assess the color of the RBCs
Hypochromic or normochromic
Common symptoms of anemia
**Tissue hypoxia
Weakness + fatigue bc of decrease O2 delivery to tissues
Pallor
Look at tongue to determine (bc it will look different on everyone)
Central NS symptoms
Dizziness/fainting
Acute Blood Loss Anemia
Loss of blood due to sudden bleeding bc of trauma
What % of volume loss will cause symptoms?
10-20%
Blood volume loss causes a decrease in _____ _____
Venous return
Steps that occur after BV loss, result in decrease in venous return
Loss of blood due to trauma
BP decreases, CO decreases, and central pressure decreases
Kidney senses decreased BP
RAAS system activated — conserves salt and H2O
SNS nerve activation
BVs constrict
To compensate for blood loss from ABLA
SNS activation
Megaloblastic Anemia
large RBCs due to excess cytoplasmic growth, which affects the membranes of the RBCs
floppy membranes
2 types of megaloblastic anemia
Pernicious anemia
Folic acid anemia
Pernicious anemia
Anemia due to vitamin B-12 deficiency
What causes the B12 deficiency in pernicious anemia?
Decreased intrinsic factor
Causes of pernicious anemia
Gastric/stomach disorders
Terminal ileum disorder
Strict vegan diet
Why do gastric/stomach disorders result in pernicious anemia?
Bc parietal cells can’t produce intrinsic factor, therefore it cannot act on B12
Symptoms of terminal ileum disorder
Chronic inflammation of the bowels
Ex: Crohn’s
Why can terminal ileum disorders result in pernicious anemia?
Inflammation of the bowel makes it difficult to absorb B12
Why can a strict vegan diet result in pernicious anemia?
Avoiding all diary, fish, and meat —
they are major sources of B12
super concerned about this
Symptoms of pernicious anemia
Changes on mucosal cells
e.g. could cause diarrhea
Neurological deficits
Issues with vibration sensation
Parathesia (numbness in fingers + toes)
Due to demyelinisation
Why does parenthesia occur in relation to pernicious anemia?
Because B12 makes up the myelin on neurons, so the lack of myelination will affect the fingers and toes first because they are the farthest from spinal cord (require more neural transmission to get info)
Folic acid anemia
Deficiency in FA, which is required to synthesize hemoglobin
we keep trying to synthesize RBCs, but they won’t be fully matured
Causes of folic acid anemia
Dietary deficiency
Malabsorption (alcohol prevents absorption)
Drug interactions
Pregnancy (unable to absorb FA)
FA deficiency can result in spinabifida
Symptoms of Folic Acid Anemia
Usual anemia symptoms
Mostly the symptoms as B12 deficiency
No neurological deficits
Iron deficiency anemia
Low Fe levels caused by:
decreased iron intake
higher demands of Fe
bleeding
Is Iron deficiency anemia is microcytic or macrocytic and normochromic or hypochromic?
Microcytic-hypochromic anemia
Symotoms of iron deficiency anemia
tongue becomes really smooth
Bc of epithelial atrophy on the tongue
“Spoon shaped” and brittle nails
What will labs show in Iron Deficiency Anemia (for iron, ferritin, HGB, HCT, MCV, and MCHC)?
Iron: low
Ferritin: low
Hemoglobin: low
Low bc iron is part of hgb synthesis
Hematocrit: low
MCV: low
MCHC: low
Anemia of Chronic Disease
Due to decreased RBC lifespan and decreased EPO
Chronic disease may increase inflammation and can decrease EPO production
What can cause the decreased RBC lifespan?
T-cell activation and production of cytokines
Altered iron metabolism
Renal failure patients
Cancer
Is Anemia of Chronic Disease normochromic or hypochromic, and microcytic or macrocytic?
Normochromic and is a normal size
Reticulocyte count for Anemia of Chronic Disease
Low Reticulocyte count bc EPO isn’t being produced
Aplastic Anemia
Suppressed BM leads to pancytopenia, and affects the whole body (pluripotent)
Pancytopenia
decreased RBC, WBC, and platelets due to:
Radiation
Chemo
infection
Causes of Aplastic Anemia
High doses of radiation therapy (XRT)
Hematopoiesis suppressed by chemicals and toxins
Infections
2/3 of cases are idiopathic — we don’t know why it’s happening
Symptoms of Aplastic Anemia
Treatments for Aplastic Anemia
Initially require blood transfusions
BM or stem cell therapy
Immunosuppressive therapy
Hemolytic anemia
Premature destruction of RBCs
Hemo- = blood
-lytic = lysis
Causes of hemolytic anemia
Hereditary
Acquired
Mechanical trauma (metal replacement valves)
Transfusion rxn (mismatch blood)
Infections
Symptoms of HA
Easily fatigued
Dyspnea
Increased rate and depth of respiration
Jaundice
Sickle cell anemia
Inherited disorder of an abnormal hemoglobin
Sickle cell is an inherited _____ trait
Recessive trait
Sickle cell anemia point mutation
Glutamic acid is replaced with valine
What happens when the cells sickle?
Instead of biconcave shape, cells sickle → stick to wall → hemolysis → occlude vessels
Reversible sickle cells
Oxygenated RBCs are normal shaped, but when they are deoxygenated they become sickled. They can return to normal once oxygenated again
RBCs can become irreversibly sickled
Complications of sickle cell anemia
vaso-occlusion (wherever there is an occlusion, there will be pain)
acute chest syndrome
infections
Triggers for vaso-occlusive pain
Cold weather
Stress
Physical exertion
Acute chest syndrome and triggers
Blocked (occluded) vessels in the lungs due to sickled RBCs, causing vaso-occlusive pain
Why are people with sickle cell anemia prone to infections?
The spleen helps the body fight off certain bacteria
Spleen damage reduces the body's ability to fight off certain bacteria
Polycythemia Vera
Rare blood cancer which BM overproduces RBC, WBC, and platelets
Opposite of Aplastic Anemia
Complications of Polycythemia Vera
Splenomegaly (Enlargement of spleen)
Hypertension (dizziness + headache)
Viscosity increases — results in venous stasis
Age related issues regarding RBCs
Anemia common in elderly
Increases morbidity & mortality if untreated
Usually asymptomatic in iron deficiency & chronic disease
Stress bleeding
RBCs not replaced as quickly
# progenitor cells decrease with age
Decrease in growth factors stimulating new cells
Erythropoietin issues (not as much is released/receptors may not work as well)
___% of people over 80 have anemia, and ___% if you have a chronic illness
25% of people >80
50% of people >80 and have a chronic illness