Neuro 31 pagine 1. Which of the following statements on the inner ear is false? a. The saccule macula is on the vertical plane b. The endolymphatic sac is underneath the mater layering the petrous part of the temporal bone c. The utricle macula is tilted of 30° on the horizontal plane d. Otoliths are composed of calcium phosphate e. Type I hair cells are goblet cells
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
1. Which of the following statements on the inner ear is false?
a. The saccule macula is on the vertical plane
b. The endolymphatic sac is underneath the mater layering the petrous part of the temporal bone
c. The utricle macula is tilted of 30° on the horizontal plane
d. Otoliths are composed of calcium phosphate
e. Type I hair cells are goblet cells
d. Otoliths are composed of calcium phosphate
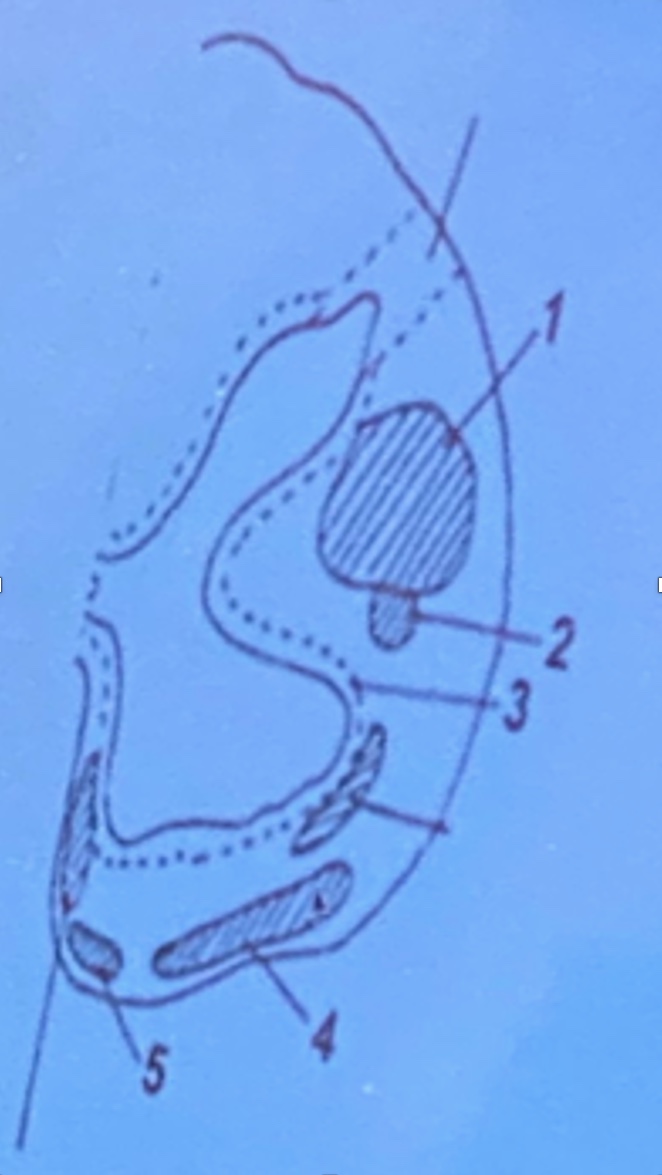
Rubrospinal tract
Fasciculus proprius
Corticospinal tract
Inferior cerebellar peduncle
5
2
1
4
1. The labyrinthine vein drains into the:
a. Inferior sagittal sinus
b. Rectus sinus
c. Sigmoid sinus
d. Superior petrosal sinus
e. Inferior petrosal sinus
Inferior petrosal sinus
1. The trapezoid body:
a. Contains commissural trigeminothalamic fibers
b. Contains transverse pontocerebellar fibers
c. Is a bundle of fibers, derived from spinal lemniscus, which crosses the midline in the pons
d. Consists of acoustic fibers that originate in the cochlear nuclei and cross the midline in the pons
e. Is a grey matter nucleus containing the cell bodies of reticulospinal neurons
d. Consists of acoustic fibers that originate in the cochlear nuclei and cross the midline in the pons
1. A professional musician visits his physician after a morning concert. He complains of painless swelling in his right cheek when he plays his tuba. Physical examination of the patient reveals slight facial asymmetry due to minor swelling on the right side of the face. The skin over the swelling is smooth without any secondary changes. Palpation reveals a soft and non-tender swelling. The oral opening is normal without any trismus. Further examination reveals swelling of the left buccal mucosa extending from the first to the third molar. Bedside ultrasound shows small areas of high echogenicity consistent with pneumoparotid. Which nerve is associated with motor function to prevent air from entering affected duct in this patient?
a. Infraorbital nerve
b. Buccal nerve
c. Zygomatic nerve
d. Maxillary nerve
e. Mandibular nerve
b. Buccal nerve
1. Which of the following statement is false?
a. Gamma motor neuron activation lowers the threshold and increases the sensitivity of tendon reflexes
b. Just like with alpha motor neurons, gamma motor neuron activity is modulated by descending pathways
c. In Parkinson’s disease there is hypertonia of muscles throughout passive movements (rigidity) while tendon reflexes are unaffected
d. When a cortical motor neuron is damaged, as in case of a stroke, this cause hyperactivity of gamma motor neurons that innervate nuclear bags
e. As a consequence of a stroke, tendon reflexes are reduced (hyporeflexia) and muscle tone decreased (flaccidity)
e. As a consequence of a stroke, tendon reflexes are reduced (hyporeflexia) and muscle tone decreased (flaccidity)
1. In the somatosensory cortex, the contralateral part of the body is represented in such a way that:
a. The contralateral half of the face is represented on the medial side of the cortex, facing the midline
b. The side of each cortical representation varies with the size of the corresponding peripheral territory
c. The ipsilateral leg and foot are represented on the lateral side of the cortex
d. The ipsilateral leg and foot are represented on the medial side of the cortex, facing the midline
e. The size of each cortical representation varies with the innervation of the corresponding peripheral territory
e. The size of each cortical representation varies with the innervation of the corresponding peripheral territory
1. Microfilaments:
a. Radiate from the smooth endoplasmic reticulum
b. Permit first intracellular transport of vesicles attached to dynein and kinesins
c. Are the thinnest cytoskeletal components of the cell, with a diameter of about 7 nm
d. Are connected to centrioles in the centrosome
e. Include neurofilaments in neurons and GFAP astrocytes
c. Are the thinnest cytoskeletal components of the cell, with a diameter of about 7 nm
1. The serotonergic fiber descending from the brainstem contributes to the control of pain. This fiber:
a. Facilitates the release of substance P from the incoming Aô and C sensory fibers
b. None of the other options is correct
c. Exacerbates a painful sensation
d. Activates the lamina 2 enkephalinergic neuron and is in turn stimulated by the habenula through the retroflexed fascicle
e. Descends from the median raphe nucleus, which in turn receives an input from the periaqueductal gray
e. Descends from the median raphe nucleus, which in turn receives an input from the periaqueductal gray
1. At its rostral extremity, the head of the caudate nucleus is continuous with the putamen. The nucleus located at the anterior ventral pole of the caudate nucleus is called:
a. Clastrum
b. Insular
c. Amygdala
d. Pulvinar
e. Nucleus accumbens
e. Nucleus accumbens
1. In regard to the substantia nigra:
a. All answers are correct
b. The pars compacta contains dopaminergic neurons
c. Pars compacta neurons project their axons to the striatum
d. Pars reticulata neurons receive axons from the internal segment of the globus pallidus nucleus
e. It consists of two parts: pars compacta and pars reticularis
a. All answers are correct
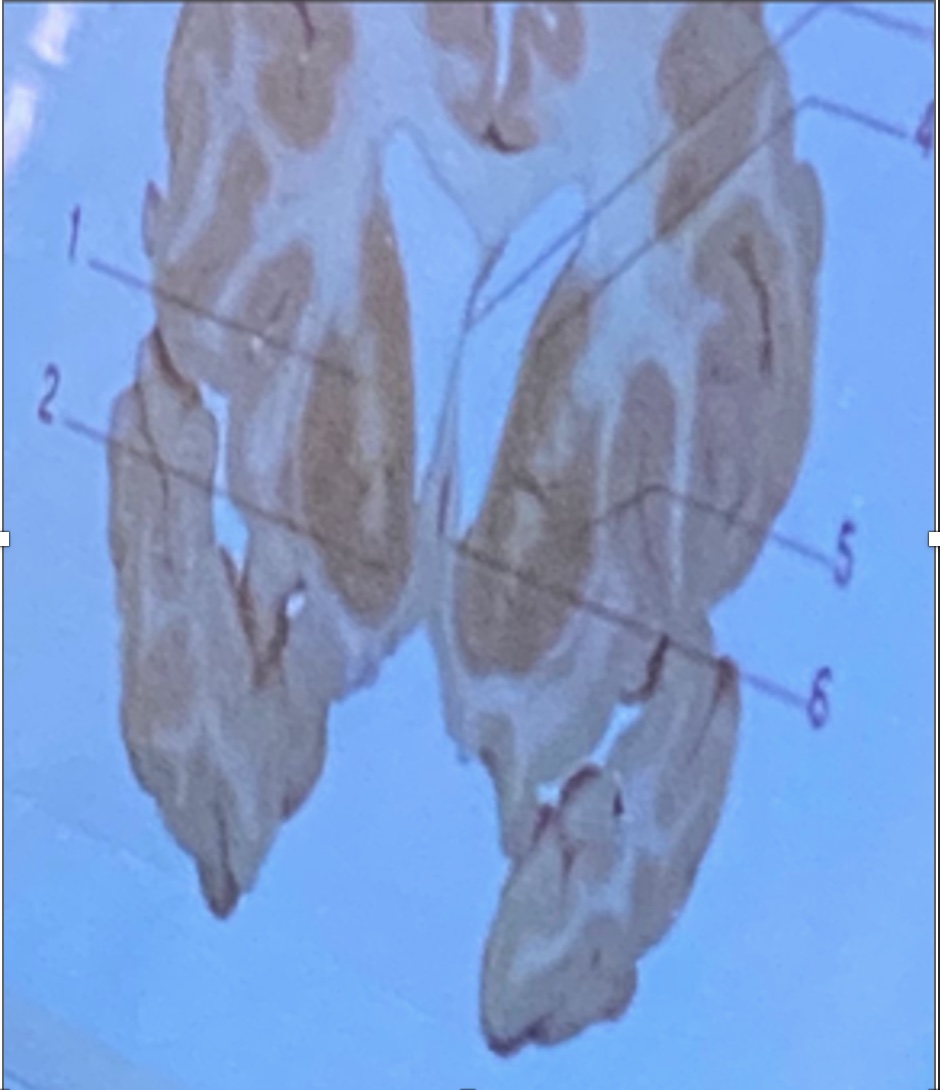
Septum pellucidum
Putamen
Internal capsule
Nucleus accumbent
Caudate nucleus
3
5
1
2
4
1. Which is the dioptric/optical power of the cornea?
a. 50D
b. 60D
c. 42D
d. 48D
e. 18D
c. 42D
1. Purkinje neurons are…
a. Glutamatergic local circuit neurons (=interneurons)
b. Glutamatergic projection neurons
c. GABAergic local circuit neurons (=interneurons)
d. All the other answers are wrong
e. GABAergic projection neurons
e. GABAergic projection neurons
1. The fourth lumbrical m. is innervated by:
a. None of the other options is correct
b. Ulnar
c. Median
d. Radial
e. Musculocutaneous
b. Ulnar
1. In the lateral ventricles, the lateral wall of the anterior horn is provided by:
a. The amygdala
b. The putamen
c. The pallidum (=globus pallidus)
d. The caudate nucleus
e. The subthalamus
d. The caudate nucleus
1. Cerebellar granules…
a. Receive mossy fibers and project to the cerebellar nuclei
b. Receive climbing fibers and project collaterals to the cerebellar nuclei
c. Receive afferent various sources and project to the pontine nuclei
d. Receive mossy fibers from various sources and project axons that bifurcate in the molecular layer, giving raise to parallel fibers
e. Receive climbing fibers and each granule projects its axon to a single Purkinje cell
d. Receive mossy fibers from various sources and project axons that bifurcate in the molecular layer, giving raise to parallel fibers
1. Which of the following muscle is not innervated by spinal segment C1?
a. Sternohyoid
b. Sternothyroid
c. Thyrohyoid
d. Longus colli
e. Geniohyoid
d. Longus colli
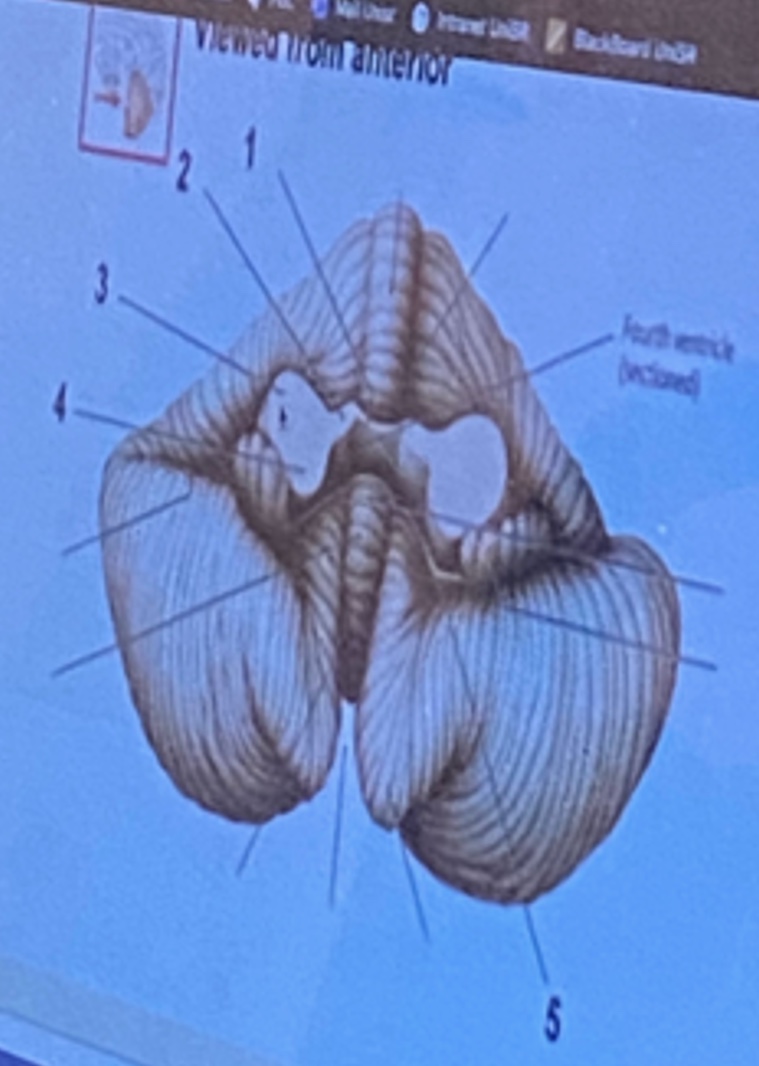
Superior cerebellar peduncle
Middle cerebellar peduncle
2
3
1. Rapidly adapting peripheral receptor, anchored to the epidermis through fibrous tethers. It conducts fine touch stimuli. Its name is:
a. Krause’s corpuscle
b. Merkel’s corpuscle
c. Pacini’s corpuscle
d. Ruffini’s corpuscle
e. Meissner’s corpuscle
e. Meissner’s corpuscle
1. Which of the following statements on the stria vascularis of the inner ear is false?
a. Type 2 fibrocytes are proximal to the Claudius cells
b. It contains capillaries
c. It actively secretes K+ in the scala vestibuli
d. Its marginal cells are connected by tight junctions
e. Its intermediate, basal and type 1 fibrocytes are interconnected by gap junctions
c. It actively secretes K+ in the scala vestibuli
1. The cell bodies of second order neurons that give rise to the spinothalamic tract are located mostly in:
a. Lamina 6
b. Lamina 9
c. Lamina 3/4
d. Lamina 7
e. Lamina 1
c. Lamina 3/4
1. Which of the following nerves collect sensory information from the nasal septum?
a. Infraorbital n.
b. Frontal n.
c. Zygomatic n.
d. Non the nerves listed
e. Anterior ethmoidal n.
e. Anterior ethmoidal n.
1. The interventricular foramen of Monro connects:
a. The lateral ventricles to the third ventricle
b. The fourth ventricle to the cisterna magna
c. The third ventricle to the cerebral (Sylvian) aqueduct
d. To the fourth ventricle to the ependymal (central) canal of the spinal cord
e. The cerebral aqueduct to the fourth ventricle
a. The lateral ventricles to the third ventricle
1. The inferior olivary nucleus:
a. Sends climbing fibers to the CONTROLATERAL cerebellar cortex through the INFERIOR cerebellar peduncle
b. Sends climbing fibers to the IPSILATERAL cerebellar cortex through the MIDDLE cerebellar peduncle
c. Sends climbing fibers to the IPSILATERAL cerebellar cortex through the SUPERIOR cerebellar peduncle
d. Sends climbing fibers to the CONTROLATERAL cerebellar cortex through the MIDDLE cerebellar peduncle
e. Sends climbing fibers to the CONTROLATERAL cerebellar cortex through the SUPERIOR cerebellar peduncle
a. Sends climbing fibers to the CONTROLATERAL cerebellar cortex through the INFERIOR cerebellar peduncle
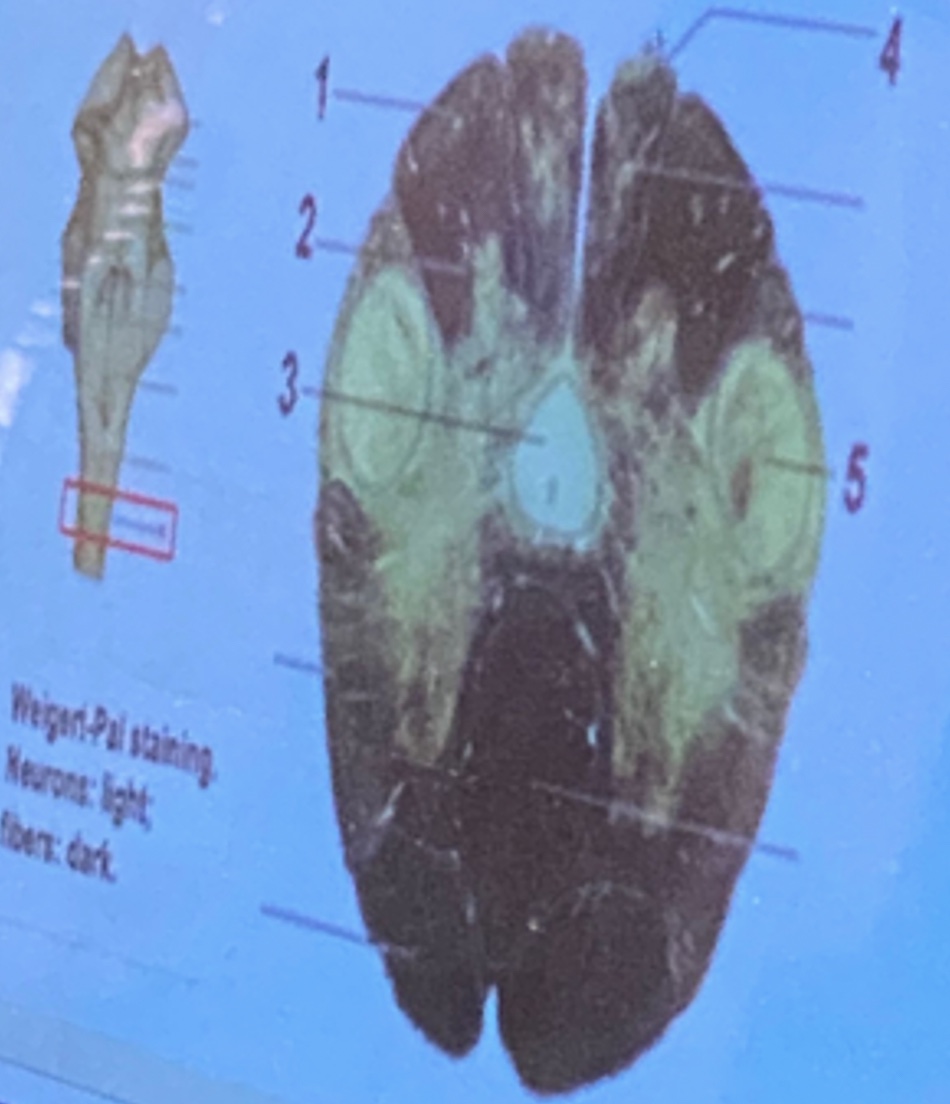
1. Gracile fascicle
Nucleus of trigeminal spinal tract
Cuneate fascicle
4
5
1
1. Which of the following combinations of synapses is NOT correct?
a. CN X - pterygopalatine ganglion
b. Splanchnic nerves - terminal ganglia of the hindgut and pelvic area
c. CN IX – otic ganglion
d. CN III – ciliary ganglion
e. CN VII – submandibular ganglion
a. CN X - pterygopalatine ganglion
1. Herb, a 62-year-old man who has smoked two packs of cigarettes per day for 35 years was suffering from a chronic cough that was attributed to the smoking habit by his physician. One day, Herb noticed that his right eyelid drooped slightly and that his right pupil was smaller than the left. He also noticed that the inner side of his right hand was numb and that he had begun to drop things from his right hand. He had no other symptoms. Herb consulted his physician who directed him to a neurologist. The neurologist noted than although the right pupil was smaller than the left, it was still reactive to light. Although Herb’s right eyelid drooped slightly, he could close his eyes tightly when asked to do so. The neurologist noted that Herb did not sweat on the right side of his face. He was unable to feel pinprick on the inner surface of his right hand, and his right triceps and hand muscles were weak.
Where in the nervous system has damage occurred?
a. Left oculomotor nerve
b. Parasympathetic fibers coursing from the Edinger-Westphal nucleus
c. Right oculomotor nerve
d. Sympathetic fibers coursing from the hypothalamus to the intermediolateral celi column
e. Edinger-Westphal nucleus
d. Sympathetic fibers coursing from the hypothalamus to the intermediolateral celi column
1. Which of the following statements about CN IX is false?
a. Collects sensory info from the choanae
b. Collects sensory info from carotid chemoreceptors and baroreceptors
c. Innervates the stylopharingeus
d. Collects sensory info from the palatine tonsils
e. Collects somatic and special sensory info from the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
a. Collects sensory info from the choanae
1. A 50 year old man presents to his primary care provider complaining of double vision and trouble seeing out of his right eye. His vision started worsening about 2 months ago and has slowly gotten worse. It is now severely affecting his quality of life. His past medical history is significant for poorly controlled hypertension and hyperlipidemia. He takes amlodipine, atorvastam, and a baby aspirin every day. He smokes 2-3 cigarettes a day and drinks a glass of wine with every dinner. Today his blood pressure is 145/85 mmHg, the heart rate is 90/min, the respiratory rate is 14/min… Examination of the eyes revealed a dilated left pupil that is positioned inferolateral, with ptosis. An angiogram of the head is performed and he is referred to a neurologist. The angiogram reveals a 1-cm berry aneurysm at the junction of the posterior communicating artery and the posterior cerebral artery that is imprinting on and compressing the ocular nerve.
Which of the following statements best describes the mechanism behind the oculomotor findings seen in this patient?
a. The unopposed medial rectus muscle rotates the eye in the lateral direction
b. Sympathetic nerve fibers of this patient’s eye are inhibited
c. The parasympathetic nerve gibers of this patient are activated
d. The unopposed superior oblique muscle rotates the eye downward
e. The unopposed inferior oblique muscle rotates the eye downward
d. The unopposed superior oblique muscle rotates the eye downward
1. Gamma motor neurons:
a. Represent about 90% of the nerve fibers directed to the muscle
b. Are important in that they maintain muscle spindles taut, enhancing their responsiveness to muscle stretching
c. Have their cell body in lamina VI of the spinal cord
d. Directly regulate the contraction of muscles
e. Project a myelinated axon that is thicker than the one that ensheathes alpha motor neurons
b. Are important in that they maintain muscle spindles taut, enhancing their responsiveness to muscle stretching
1. Which of the following statements about the Tenons’s capsule is false?
a. It thickens to form the check ligaments
b. It extends from the limbus to the optic nerve
c. It forms the suspensory ligament of the eyeball by means of the lockwood’s ligament, upon which the globe rests
d. It is composed of loose connective tissue
e. It is continuous with the EOM’s epimysium
d. It is composed of loose connective tissue
1. Climbing fibers:
a. Originate from the contralateral red nucleus and innervate the cell body of Purkinje cells
b. Originate from the ipsilateral inferior olive and innervate Purkinje cell dendrites
c. Originate from the contralateral pontine nucleus and innervate Purkinje cell dendrites
d. Originate from the ipsilateral pontine nuclei and innervate Purkinje cell dendrites
e. Originate from the inferior olive and innervate Purkinje cells in the contralateral cerebellum
e. Originate from the inferior olive and innervate Purkinje cells in the contralateral cerebellum
1. What is the diameter of collagen fibers in the Bowman’s membrane/layer of the eye?
a. 32nm
b. 52nm
c. 12nm
d. 42nm
e. 22nm
e. 22nm
1. Which of the following statements is inaccurate?
a. The activation of the flexor reflex in one lower limb causes the simultaneous activation of postural muscles in the contralateral limb. This is called the “extensor reflex”
b. Golgi tendons are innervated by 1B afferent axons that reach the gray matter of the spinal cord
c. A painful lstimulation of the sole of the foot causes a flexor reflex
d. Through an interneuron afferent fiber originating in tendon organs excite alpha motor neurons, causing the contraction of the innervated muscle
d. Through an interneuron afferent fiber originating in tendon organs excite alpha motor neurons, causing the contraction of the innervated muscle
1. Motor and sensory cortices for the lower limb are supplied by:
a. Anterior cerebral artery
b. Middle cerebral artery
c. Heubner artery
d. Choroidal artery
e. Posterior cerebral artery
a. Anterior cerebral artery
1. The opponens digiti minimi is innervated by:
a. Median
b. Lower subscapular
c. Ulnar
d. Radial
e. Musculocutaneus
c. Ulnar
1. Fibers directed to the cerebellus arise from all the structures listed below, except:
a. The ipsilateral side of the lumbar spinal cord, through the ventral spinocerebellar tract
b. The ipsilateral side of the thoracic spinal cord, through the dorsal spinocerebellar tract and the inferior peduncle
c. The ipsilateral side of the cervical spinal cord, through the cuneocerebellar tract
d. The contralateral inferior olivary nucleus, through the inferior cerebellar peduncle
e. The ipsilateral pontine nuclei, through the middle cerebellar peduncle
e. The ipsilateral pontine nuclei, through the middle cerebellar peduncle
1. Betz giant cells of the motor cortex are mainly contained in which layer:
a. Layer I
b. Layer II
c. Layer V
d. Layer III
e. Layer IV
c. Layer V
1. .In regard to cortical association fibers, which of the following statements is wrong?
a. The inferior longitudinal fasciculus connects the frontal and occipital lobe
b. U fibers are short and connect adjacent areas of the cortex
c. The superior longitudinal fasciculus connects the frontal and occipital lobe
d. The arcuate fasciculus connects gyri localized in the temporal and frontal lobes that are important for language production and understanding
e. The uncinated fasciculus connects parts of the temporal lobe such as the hippocampus and amygdala in the temporal lobe to areas of the frontal lobe such as orbitofrontal cortex
a. The inferior longitudinal fasciculus connects the frontal and occipital lobe
1. In regard to the pretectal nucleus:
a. It projects axons to the Edinger-wetphal nucleus, which controls the smooth muscle of the eye
b. It is connected to the contralateral counterpart through the posterior commissure
c. All the answers are correct
d. It is part of the circuitry that mediated the pupillary light reflex
e. It receives a small number of fibers that course in the optic tract
c. All the answers are correct
1. Which of the following structures can be seen in a midline sagittal image?
a. Gyrus rectus
b. Internal carotid artery
c. Quadrigeminal plate
d. Pineal gland
e. Red nucleus
d. Pineal gland
1. Axons originating from the ventral tegmental area of the midbrain innervate:
a. The prefrontal cortex
b. The septum
c. All the answers are correct
d. The amygdala
e. The nucleus accumbens
c. All the answers are correct
1. Which of the following statements is true in regard to the cervical spinal cord?
a. Spinal nerve C1 emerges above the body of vertebra C1
b. Spinal nerve C8 does not exist
c. Spinal nerve C8 emerges below vertebra C8
d. Spinal nerve C7 emerges under vertebra T1
e. Spinal nerve C1 only has a dorsal (sensory) root
a. Spinal nerve C1 emerges above the body of vertebra C1
1. The lateral fissure of the brain cortex…
a. separates the occipital lobe posteriorly from the temporal lobe anteriorly
b. separates the premotor cortex from the precentral gyrus
c. separates the superior frontal gyrus from the middle frontal gyrus
d. Gives access to the entorhinal cortex
e. Gives access to the insular cortex
e. Gives access to the insular cortex
1. From which of the following nerves does the inferior hypogastric plexus receive fibers?
a. Pudendal and obturator nerves
b. Pelvic splanchnic and hypogastric nerves
c. Inferior gluteal and lumbosacral nerves
d. Sciatic and superior gluteal nerves
e. Sacral sympathetic and obturator nerves
b. Pelvic splanchnic and hypogastric nerves
1. The receptor called nuclear bag:
a. Is a skin mechanoreceptor
b. Is a slowly adapting receptor that signals muscle fiber stretch throughout its duration
c. Is a sensor of joint twisting
d. Is a rapidly adapting receptor that signals the speed of muscle stretching
e. Is a sensor of tendon stretch
d. Is a rapidly adapting receptor that signals the speed of muscle stretching
1. Which of the following is muscles is NOT innervated by CN VII
a. Levator labii superioris alique nasi
b. Orbicularis oculi
c. Orbicularis oris
d. Masseter
e. Depressor anguli oris
d. Masseter
1. Which of the following statements about the parasympathetic division of the ANS is TRUE?
a. Ganglia are situated close to the spinal cord
b. Each preganglionic neuron gives rise to many postganglionic neurons
c. Cell bodies of preganglionic neurons reside in the brain stem and the sacrum
d. Preganglionic fibers are short, and postganglionic fibers are long
e. It has a stimulatory effect on most of the organ systems
c. Cell bodies of preganglionic neurons reside in the brain stem and the sacrum
1. What is a dermatome?
a. Any skin area densely innervated by C-fibers
b. The area of the skin innervated by a dorsal root ganglion
c. A surgical instrument used to section bodies
d. The area of the skin supplied by axons from a single vertebral horn
e. A region the sensory motor cortex associated with one area of the skin
d. The area of the skin supplied by axons from a single vertebral horn
1. A 35. Year old woman had a partial thyroidectomy for the treatment of thyrotoxicosis. During the operation a ligature slipped off the right superior thyroid artery. To stop the hemorrhage, the surgeon blindly grabbed for the artery with artery forceps.
The following statements would explain the husky voice, except which?
a. The vocal cord is tensed by contraction of the cricothyroid muscle
b. The cricothyroid muscle is innervated by the recurrent laryngeal nerve
c. The superior thyroid artery is closely related to the external laryngeal nerve
d. The cricothyroid tilts back the cricoid cartilage and pulls forward the thyroid cartilage
e. Laryngoscopic examination of revealed that the right vocal cord was slack, causing the huskiness of the voice
b. The cricothyroid muscle is innervated by the recurrent laryngeal nerve
1. Which of the following statements on radicular arteries is correct?
a. Divide into superior and inferior branches
b. Supply the spinal cord at cervical level only
c. Doesn’t supply the spinal cord
d. Pass through intervertebral foramina
e. Originate directly from the aorta
d. Pass through intervertebral foramina
1. Which of the following statements on the inner hair cells is true?
a. Are supported by the Claudius cells
b. Have long stereocilia
c. Make synapse with Deiters cells
d. Are covered by the tectorial membrane containing otoliths
e. Have no kinocilium
e. Have no kinocilium
1. By which of the following nerves is the pronator teres innervated?
a. Thoracodorsal
b. Radial
c. Ulnar
d. Median
e. Musculocutaneus
d. Median
1. All the following symptoms are associated with CN VII palsy, except which?
a. Loss of facial expression
b. Decreased lacrimation
c. Loss of taste on anterior 2/3 of tongue
d. Rhinorrhea
e. Hyperacusis
d. Rhinorrhea
1. Which of the following statements on the lachrymal system is false?
a. The fundic part of the lacrimal sac is extending vertically for about half a cm
b. The lacrimal gland is connected to the superior inferior orbital fornixes by up to a dozen on excretory lachrymal ducts
c. The lacrimal gland is separated in two portions by the orbital septum
d. The interosseous part of the nasolacrimal duct has a vertical length of about a cm
e. The meatal part of the nasolacrimal duct has a vertical extension of about half a cm
. The lacrimal gland is separated in two portions by the orbital septum
1. Which of the following statements on the vascular supply of the eye is true?
a. There are two anterior ciliary arteries
b. The episcleral veins are draining the ciliary process
c. The central retinal artery is the first branch of the ophthalmic artery
d. The short posterior ciliary arteries are supplying the choroid
e. There are 7-8 long posterior ciliary arteries
d. The short posterior ciliary arteries are supplying the choroid
1. A 17 y.o. girl was dealing drugs on a street corner when she became involved in a fight. She received a deep knife wound to the front of her right thigh. After a thorough examination in the emergency department of her local hospital, it was determined that the knife point had severed the trunk of the right femoral nerve just below the inguinal ligament. This had the following signs and symptoms except which:
a. Weak extension of the knee was possible when walking because of the use of the adductor muscle
b. Skin sensation was lost over anterior and medial sulcus of the thigh
c. Skin sensation was lost along the medial border of the big toe
d. Skins sensation was lost on the lower part of the leg and the medial border of the foot as far as the half of the big toe
e. The right quadriceps femoris muscle failed to contract when the patient was asked to extend her right knee joint
c. Skin sensation was lost along the medial border of the big toe
1. A 22-year-old medical student fell off her bicycle onto her outstretched hand she thought she had sprained her right wrist joint and treated herself by binding her wrist with an elastic bandage. Three weeks later however, she was still experiencing pain on moving her wrist and so decided to visit the emergency department. On examination of the dorsal surfaces of both hands with the fingers and thumbs fully extended, a localized tenderness could be felt in the anatomic snuffbox of her right hand. A diagnosis of fracture of the right scaphoid bone was made. the following statement concerning this patient are correct except which?
a. A bony fragment deprived of its blood supply may undergo ischemic necrosis
b. The fracture line on the scaphoid bone may deprive the proximal fragment of its arterial supply
c. Because the scaphoid bone articulates with other bones, the fracture line may enter a joint cavity and become bathed in synovial fluid which would inhibit repair.
d. The scaphoid bone is in any easy bone to immobilize because of its small size
e. Fractures of the scaphoid bone have a high incidence of nonunion
d. The scaphoid bone is in any easy bone to immobilize because of its small size
1. The gastrocnemius Medius is innervated by the
a. femoral nerve
b. deep peroneal nerve
c. sural nerve
d. saphenous nerve
e. tibial nerve
e. tibial nerve
1. Which of the following nerve fibers is not contained in the short ciliary nerves?
a. All of the listed fibers are present in the short ciliary nerves
b. Unmyelinated somatic sensory fibers
c. Unmyelinated visceral motor fibers
d. Myelinated visceral motor fibers
e. Myelinated somatic sensory fibers
d. Myelinated visceral motor fibers
1. Which of the following nerve fibers is not contained in the short ciliary nerves?
a. All of the listed fibers are present in the short ciliary nerves
b. Unmyelinated somatic sensory fibers
c. Unmyelinated pain fibers
d. Visceral motor fibers
e. Myelinated somatic sensory fibers
a. All of the listed fibers are present in the short ciliary nerves
1. A 10-year old boy was playing darts with his friends, He bent down to pick up a fallen dart when another dart fell from the dart board and hit him on the side of his face. On examination in the emergency department a small skin wound was found over the right parotid. Then, 6 months later, the boy's mother noticed that before mealtime the boy began to sweat profusely on the facial skin close to the healed dart wound. The following statements can explain the phenomenon except which?
a. The point of the dart had entered the parotid salivary gland and damaged the parasympathetic secretomotor fibers to the gland
b. The skin over the parotid salivary gland is innervated by the great auricular nerve which was also damaged by the dart.
c. The preganglionic parasympathetic fibers for the parotid gland originate in the superior salivatory nucleus of the facial nerve
d. On regeneration of the damaged nerves some of the parasympathetic nerves to the parotid salivary gland had crossed
e. over and joined the sympathetic secretomotor nerves to the sweat gland in the distal end of the greater auricular nerve.
f. The secretomotor fibers to the parotid gland arise in the optic ganglion
c. The preganglionic parasympathetic fibers for the parotid gland originate in the superior salivatory nucleus of the facial nerve
1. Patients suffering lesions of the Wernicke area in the left hemisphere:
a. stutter
b. speak fluently but produce long, meaningless sentences, making up words and failing to correct themselves
c. are totally incapable of articulating speech
d. show a global motor impairment that affects muscles of mastication
e. express themselves eloquently but don't understand what other people are saying
b. speak fluently but produce long, meaningless sentences, making up words and failing to correct themselves
1. The gluteus Medius is innervated by:
a. III sacral nerve
b. L4-S1 lumbar nerve
c. IV lumbar nerve
d. Il sacral nerve
e. I sacral nerve
b. L4-S1 lumbar nerve
1. A 17-year-old boy was seen in the emergency department after receiving a stab wound at the front of his neck the knife entrance wound was located on the left side of the neck just lateral to the tip of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone. During the physical examination the patient was asked to protrude his tongue, which deviated to the left. The following statements would explain the physical signs in this patient except which?
a. The hypoglossal nerve descends in the neck between the internal carotid artery and the internal jugular vein.
b. The genioglossus muscle is supplied by the glossopharyngeal n.
c. Paralysis of the left genioglossus muscle permitted the right genioglossus to pull the tongue forward and turned the tip to the left side.
d. None of the other answers is correct.
e. The point of the knife blade severed the left hypoglossal nerve.
b. The genioglossus muscle is supplied by the glossopharyngeal n.
1. Which of the following statements on the autonomic innervation of the KIDNEY is true?
a. Spinal parasympathetic fibers reach the kidney by means of the ureter
b. The kidney receives parasympathetic innervation by the spinal division, via spinal splanchnic nerves
c. The kidney is innervated by the cranial division of the parasympathetic system, via the side branches of the vagus nerve.
d. Postganglionic sympathetic fibers for the kidney arise from the inferior mesenteric ganglion
e. Preganglionic sympathetic fibers are supplied to the kidney by the lesser splanchnic n. and the least splanchnic n.
e. Preganglionic sympathetic fibers are supplied to the kidney by the lesser splanchnic n. and the least splanchnic n.
1. Which of the following nerves is not contained in the infratemporal fossa?
a. Greater petrosal nerve
b. Lingual nerve
c. Inferior alveolar nerve
d. Auriculotemporal nerve
e. Buccal nerve
a. Greater petrosal nerve
1. The iliohypogastric nerve supplies all the following except:
a. transverse abdominal muscle
b. skin over the lateral gluteal region
c. skin above the pubis
d. internal oblique muscle
e. external oblique muscle
e. external oblique muscle
1. Which of the following statements on the geniculate ganglion is false?
a. It contains somatosensory neurons
b. It collects the taste sensitivity of the anterior 2/3 of the tongue
c. It contains visceral sensory neurons
d. It sends projections to the nucleus of the solitary tract
e. It contains postganglionic parasympathetic neurons
e. It contains postganglionic parasympathetic neurons
1. The red nucleus:
a. projects some of its efferent fibers into the ventral tegmental decussation
b. is an important station along the somatosensory pathway
c. projects motor fiber to the ipsilateral spinal cord
d. Receives axons from contralateral inferior olive
e. receives fibers from the ipsilateral side of the cerebellum.
a. projects some of its efferent fibers into the ventral tegmental decussation
1. Clear synaptic vescicles do not contain:
a. Glutammate
b. Gaba
c. Aspartate
d. noradrenaline
e. Glycine
d. noradrenaline
1. The corona radiata in the brain is formed by:
a. Cerebello-cortical fibers
b. Commissural fibers
c. projection fibers
d. Inhibitory fibers
e. associative fibers
c. projection fibers
1. Intermediate filaments:
a. Are associated to tight junctions
b. can polymerize and depolimerize fast in response to cell signals changing cell shape rapidly
c. Interact with connexins
d. Have a diameter of 25 nm
e. insert into desmosomes at cell-cell junction and help maintain connectivity between neighboring cells and shape of cells.
e. insert into desmosomes at cell-cell junction and help maintain connectivity between neighboring cells and shape of cells.
1. In a form of brown-sequard syndrome due to a hemilesion of the thoracic spinal cord functional defects include one of the following?
a. loss of motor coordination in the upper limbs
b. loss of proprioception and fine touch caudal to the lesion, contralateral to the injured side
c. Increased tendon reflexes in the lower limb on the injured side
d. loss of nociception and thermal sensation, caudal to the lesion ipsilateral to the injured site
e. None of the answers is correct
c. Increased tendon reflexes in the lower limb on the injured side
1. The lenticular fasciculus and ansa lenticularis?
a. converge in a fascicle that reaches the pretectal nucleus
b. converge in a fascicle that reaches the substantia nigra pars reticulata
c. converge in a fascicle that reaches the subthalamus
d. converge in a fascicle that reaches the striatum
e. Converge in a fascicle that reaches the thalamus
e. Converge in a fascicle that reaches the thalamus
Gracilis muscle innervated by?
L2-L3 (anterior division of obturator nerve)
1. A 15-year-old boy is brought in the emergency department after an accident on his father’s farm. The examination reveals weakness of the left lower extremity but no frank paralysis. There is also loss of a pinprick sensation on the right side beginning at the T8 dermatome (about half way between the nipple and the umbilicus), and dorsiflexion of the great toe in response to plantar stimulation. Based on this examination which of the following represents the most likely approximate location of this lesion based on this examination? (COMES FROM HAINES)
a. T6 on the left side
b. T6 on the right side
c. T8 on the left side
d. T8 on the right side
e. T10 on the left side
a. T6 on the left side
1. After a major abdominal operation a patient was given a course of antibiotics by intramuscular injection. The nurse was instructed to give the injections into the right buttock. Later when the patient left the hospital he developed several symptoms and signs that suggested that the injections into the gluteus maximus muscle had been given over the course of the sciatic nerve and had caused a lesion of the common peroneal nerve. The symptoms and signs displayed by this patient include the following except which?
a. He experienced numbness and tingling sensations down the anterior and lateral sides of the right leg and the dorsum of the foot
b. His right foot tended to catch on steps and on the edges of the carpet
c. On testing, he had impaired skin sensation on the lateral side of the right thigh
d. The patient tended to hold the foot plantar flexed and slightly inverted
e. dorsiflexion of the right ankle joint was weaker than the same movement of the left ankle
c. On testing, he had impaired skin sensation on the lateral side of the right thigh
1. Hemiballismus is characterized by
a. Bilateral tremor in the extremities
b. Tremor at rest
c. couldn’t read
d. sharp unilateral involuntary movement
e. Progressive dementia
d. sharp unilateral involuntary movement
1. Parkinson’s disease (?)
a. increase in sub thalamic nucleus activity
b. as increased inhibitory activity by the internal segment of the pallidum that leads to a repression of the thalamus
c. increased release of choleosystokinin in the striatum
d. increased dopamine release in the neostriatum
e. as decreased inhibitory activity by the internal segment of the pallidum that leads to a de-repression of the thalamus
b. as increased inhibitory activity by the internal segment of the pallidum that leads to a repression of the thalamus
1. The crus cerebri:
a. contains trigemin-thalamic fibers
b. contains corticobulbar and corticospinal fibers
c. contains spinothalamic fibers
d. consists of both ascending and descending fibers
e. contains fibers of the medial lemniscus
b. contains corticobulbar and corticospinal fibers
1. Which cranial nerve crosses the midline upon emerging from the brainstem?
a. Abducens (VI)
b. Oculomotor (III)
c. Trochlear (IV)
d. Glossopharyngeal (IX)
e. Facial (VII)
c. Trochlear (IV)
1. The pectineus is innervated by:
a. Accessory obturator
b. Femoral n.
c. Sural n.
d. Sciatic n.
e. Obturator n.
b. Femoral n.
1. The extensor pollicis longus is innervated by the:
a. Ulnar n.
b. Median n.
c. Posterior interosseous n.
d. Axillary n.
c. Posterior interosseous n.
1. The Papez circuit connects all the following structures except one:
a. Cingulate gyrus
b. Anterior nucleus of the thalamus
c. Mamillary bodies
d. Hippocampus
e. Amygdala
e. Amygdala
1. Which of the following statements on the otic ganglion is false?
a. It contains synaptic postganglionic neurons
b. It receives parasympathetic preganglionic fibers from the superior salivatory nucleus
c. It is traversed by somatic motor neurons
d. It sends postganglionic parasympathetic fibers to the submandibular gland
e. It carries sensory fibers coming from the auriculotemporal nerve
d. It sends postganglionic parasympathetic fibers to the submandibular gland
1. Which sensory nerve shows the unique feature of having the cell body of some first -order neurons located within the brainstem?
a. The vestibular nerve
b. Spinal tract of the fifth pair
c. –
d. –
e. The mesencephalic tract of the fifth pair
e. The mesencephalic tract of the fifth pair
1. The ilioinguinal nerve supplies all of the following except:
a. Labium majus
b. Mons pubis
c. Skin covering the femoral triangle
d. Root of penis
e. Scrotum
c. Skin covering the femoral triangle
1. The otic ganglion is annexed to:
a. Maxillary nerve
b. Palatine nerve
c. Mandibular nerve
d. Pterygoid nerve
e. illegible
c. Mandibular nerve
1. Limbic association areas include all of the following except:
a. Orbital gyri
b. Parietal association cortex
c. Cingulate gyrus
d. Temporal pole
e. Parahyppocampal gyrus
b. Parietal association cortex
1. In regard to the subarachnoid spaces, which of the following statements is wrong?
a. The interpeduncular cistern communicates with other subarachnoid spaces
b. The subarachnoid space contains cerebrospinal fluid provided by the choroid plexuses
c. The subarachnoid space contains a trabecular meshwork that connects the arachnoid mater to the pia mater
d. There is no connection between the ventricular system and the subarachnoid space
e. The subarachnoid space is traversed by arteries and veins
d. There is no connection between the ventricular system and the subarachnoid space
1. Which of the following statements is false in regard to the superior cerebellar peduncle?
a. It receives fibers from the ventral spinocerebellar tract
b. It contains fibers directed to the contralateral red nucleus
c. It contains fibers directed to the contralateral thalamus
d. It provides the lateral wall of the fourth ventricle in the pons
e. It contains ascending fibers directed to the ipsilateral ventro-lateral nucleus of the thalamus
e. It contains ascending fibers directed to the ipsilateral ventro-lateral nucleus of the thalamus
1. The pyriformis muscle is innervated by:
a. L2-L3
b. T12-L1
c. L1-L2
d. None of the listed
e. L4-L5
d. None of the listed
1. Hippocampal mossy fibers connect
a. Dentate gyrus with CA3
b. Subiculum with entohinal cortex
c. Dentate gyrus with CA1 neurons
d. Entohinal cortex with the dentate gyrus and CA3
e. CA3 neurons with the contralateral hippocampus through the hippocampal commissure
a. Dentate gyrus with CA3
1. Compared to other nuclei of the third pair cranial nerves, how is the nucleus of Edinger-Westphal positioned?
a. It is between the nucleus for the upper … and the nucleus for the elevator of the superior eyelid
b. It is between the nucleus for the lower oblique and the nucleus for the medial rectus
c. It is between the nucleus for the lower rectus and the core? For the lower oblique muscle
d. It is posterior to all the other nuclei of the oculomotor
e. It is between the nucleus for the medial rectus and the nucleus for the upper rectus
d. It is posterior to all the other nuclei of the oculomotor
1. In regard to cortical association fibers which of the following statement is wrong?
a. Fibers are short and connect adjacent areas of the cortex
b. The arcuate fascicle connects gyri in the temporal and frontal lobe that are important for language
c. The inferior longitudinal fascicle connects the frontal and occipital lobes
d. The superior longitudinal fascicle connects the frontal and occipital lobes
c. The inferior longitudinal fascicle connects the frontal and occipital lobes
1. A 41-year-old woman complains to her family physician about recurring episodes of sharp pain that seem to originate from around her mouth and cheek. The pain is so intense that she is unable to eat, brush her teeth, or apply make-up. Which of the following cranial servers is the most likely source of this pain?
A. Facial nerve
B. Glossopharyngeal
C. Hypoglossal
D. Trigeminal
E. Vagus
D. Trigeminal
2. A 63-year-old man has hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing or buzzing sounds in the ear), vertigo and unsteady gait; all of these have developed over several years. MRI reveals a large tumor (3cm in diameter) at the cerebellopontine angle, most likely a vestibular schwannoma (sometimes called an acoustic neuroma). What additional deficit could this patient also have?
A. Anosmia
B. Hemianopsia
C. Numbness on the face
D. Visual field deficits
E. Weakness of the tongue
C. Numbness on the face