SAS 9: Parenteral Therapy
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Ampul
a single-use container composed entirely of glass.
Cannula
a tube-like needle or catheter used to infuse parenteral fluids and medications into the vascular system or other body spaces.
Electrolyte
dissolved ions that include sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium, phosphate and others
Epidural
the space superior to the dura mater of the brain and spinal cord and inferior to the ligamentum flavum
outside the subarachnoid space where the CSF flows
Extravasation
inadvertent administration of vesicant medication or solution into the tissue
surrounding an artery or vein
Incompatibility
incapable of being mixed or used simultaneously without undergoing chemical or physical changes or producing undesirable effects.
Infiltration
the inadvertent administration of non-vesicant medication or solution into the tissue surrounding an artery or vein. It is an ADE unless it is intended.
Intrathecal
the space within the spinal canal.
Parenteral
intended for injection through one or more layers of skin or other external boundary tissue
Sharps
objects in the health care setting that can be reasonably anticipated to penetrate the skin and to result in an exposure incident
Standard Precautions
guidelines designed to protect workers with occupational exposure to blood borne pathogens
Total Parenteral Nutrition
also known as hyperalimentation
the IV provision of total nutritional needs for a patient who is unable to take appropriate amount of food enterally
carbohydrates
proteins
fats
electrolytes
vitamins
trace elements
Vehicle
water for injection (USP) is the liquid in which active ingredients are dissolved, suspended, or emulsified for most parenterals
Vial
a plastic or glass container with a rubber closure secured to its top by a metal ring.
Isotonic
concentrations of solute = blood plasma
Hypotonic
concentration of solutes < blood plasma
Hypertonic
concentration of solutes > blood plasma
Isotonic IV Fluids
most IV fluids are isotonic
expand both the intracellular and extracellular fluid spaces
do not alter the osmolality of the vascular component
total electrolyte content is approximately 310 mEq/L
total osmolality is close to that of the ECF
do not cause red blood cells to shrink or swell
Isotonic IV Fluids
0.9% NaCl (Normal Saline Solution, NSS)
Dextrose 5% in Water (D5W)
Lactated Ringer’s 5% Dextrose in Water (D5LRS)
Ringer’s Solution
0.9% NaCl (Normal Saline Solution)
crystalloid ; contains water, sodium (154 mEq/L), and chloride (154 mEq/L)
osmolality = 308 mOsm/L
no calories
the % of NaCl dissolved in the solution is similar to the usual concentration of Na and Cl in the intravascular space
the isotonic solution of choice for expanding the ECF because it does not enter the ICF
administered to correct ECF volume deficit
0.9% NaCl (Normal Saline Solution)
IV fluid used alongside the administration of blood products
replace large sodium losses such as in burn injuries and trauma
should not be used for heart failure, pulmonary edema, and renal impairment, or conditions that cause sodium retention
Dextrose 5% in Water (D5W)
provides free water when dextrose is metabolized (making it a hypotonic solution), expanding the ECF and ICF
supply water and correct an increase in serum osmolality
should not be used for fluid resuscitation (can cause hyperglycemia)
should be avoided in clients at risk for increased intracranial pressure (can cause cerebral edema)
Lactated Ringer’s 5% Dextrose in Water (D5LRS)
also known as Ringer’s Lactate or Hartmann solution
near-physiological solution of balanced electrolytes
contains bicarbonate precursors to prevent acidosis
does not provide calories or magnesium
has limited potassium replacement
the most physiologically adaptable fluid
its electrolyte content is most closely related to the composition of the body’s blood serum and plasma
Hartmann Solution
correct dehydration, sodium depletion, and replace GI tract fluid losses
used in fluid losses due to burns, fistula drainage, and trauma
first choice for first-line fluid resuscitation of certain patients
administered to patients with metabolic acidosis
metabolized in the liver; thus, it should not be given to patients who cannot metabolize lactate
used in caution for patients with heart and renal failure
Ringer’s Solution
content is similar to Lactated Ringer’s Solution but does not contain lactate
indications are the same for Hartmann’s solution but without the contraindications related to lactat
Hypotonic IV Fluids
lower osmolality and solutes < plasma
cause fluid shifts from the ECF into the ICF to achieve homeostasis
causes cells to swell (and may even rupture)
total electrolyte content = <250 mEq/L
provide free water for excretion of body wastes, treat cellular dehydration, and replace the cellular fluid
Hypotonic IV Fluids
0.45% NaCl
0.33% NaCl
0.225% NaCl
2.5% Dextrose in Water (D2.5W)
0.45% Sodium Chloride
used for replacing water in patients who have hypovolemia with hypernatremia
excess use may lead to hyponatremia due to the dilution of sodium
0.33% Sodium Chloride
allow kidneys to retain the needed amounts of water
typically administered with dextrose to increase tonicity
used in caution to patients with heart failure and renal insufficiency
0.225% Sodium Chloride
maintenance fluid for pediatric patients
the most hypotonic IV fluid available at 77 mOsm/L
used together with dextrose
2.5% Dextrose in Water
treat dehydration and decrease the levels of sodium and potassium
should not be administered with blood products (can cause hemolysis of RBC)
Hypertonic IV Fluids
concentration of solutes > plasma
cause fluids to move out of the cells and into the ECF
causes cells to shrink
aka volume expanders as they draw water out of the intracellular space, increasing ECF volume
Hypertonic Sodium Chloride IV Fluids
acute treatment of sodium deficiency (severe hyponatremia) and should only be used in critical situations
infused at a very low rate (to avoid the risk of overload and pulmonary edema)
3% NaCl |
|
5% NaCl |
|
Hypertonic Dextrose Solutions
isotonic solutions that contains 5% dextrose
provide kilocalories for the patient in short term
Hypertonic Dextrose Solutions
Dextrose 10% in Water (D10W)
Dextrose 20% in Water (D20W)
Dextrose 50% in Water (D50W)
D10W
hypertonic
treatment of ketosis of starvation and provides calories (380 kcal/L), free water, and no electrolytes
administered using a central line if possible
should not be infused using the same line as blood products
D20W
hypertonic
an osmotic diuretic
causes fluid shifts between various components to promote diuresis
D50W
treat severe hypoglycemia
administered rapidly via IV bolus
Colloids
contain large molecules that do not pass through semipermeable membranes
for expanding the intravascular volume and raising blood pressure
for patients in malnourished states and cannot tolerate large infusions of fluid
Colloids
Human Albumin
Dextrans
Low-molecular-weight
High-molecular-weight
Etherified Starch
Gelatin
Plasma Protein Fraction
Human Albumin
derived from plasma
two strengths: 5% albumin and 25% albumin
increase the circulating volume and restore proteins in conditions such as burns, pancreatitis, and plasma loss through trauma
25% albumin = used together with sodium and water restriction
blood transfusion products
contraindicated in the following:
severe anemia
heart failure
known sensitivity to albumin
ACE inhibitors (must be withheld for at least 24 hrs)
Dextrans
polysaccharides that act as colloids
available in either saline or glucose solutions
interferes with blood cross-matching, so draw the patient’s blood before administering dextran
Low-molecular-weight dextran (LMWD) | High-molecular-weight dextran (HMWD) |
|
|
contraindications:
| contraindication:
|
Etherified Starch
derived from starch
used to increase intravascular fluid but can interfere with normal coagulation
Gelatin
lower MW than dextrans
remain in the circulation for a shorter period of time
Plasma Protein Fraction (PPF)
prepared from plasma and is heated before infusion (like albumin)
infused slowly to increase circulating volume
Syringe
a sterile, single-use device that has a Luer lock or non-Luer lock tip, which influences its name
smaller volumes = SC and IM
larger size = lower pressure flow
10 to 12 mL = central lines, catheters, medical tubing
20 to 70 mL = irrigation
Needles
made of stainless steel, are sterile and disposable, and come in various lengths and sizes
made up of the hub, shaft, and bevel
bevel = tip of the needle that is slanted to create a slit into the skin
hub = fits onto the tip of the syringe
the gauge is the diameter; vary from very small dm (from 25 to 29 gauge) to large dm (18 to 22 gauge)
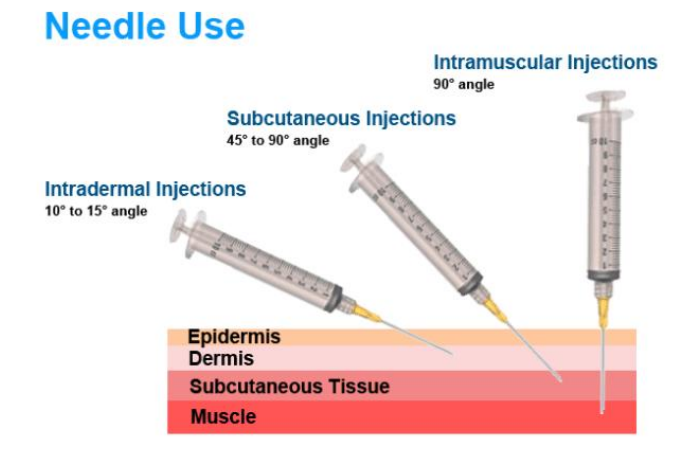
Needle Use
IV Push
aka bolus
rapid injection of medication
syringe is inserted into the catheter to quickly send a one-time dose of drug in the bloodstream
IV Infusion
controlled administration over time
Pump Infusion = attached to the IV line and sends medication and a solution into the catheter in a slow, steady manner (used when medication dosage must be precise and controlled)
Drip infusion = uses gravity to deliver a constant amount of medication over a period of time