2 - Slow response tissue and ECG
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
If you denervate the heart (cut off it’s nerve supply), how can it still contract or beat?
Some parts of the heart exhibit automaticity: Nodal tissue (SA and AV node), Purkinje fibers
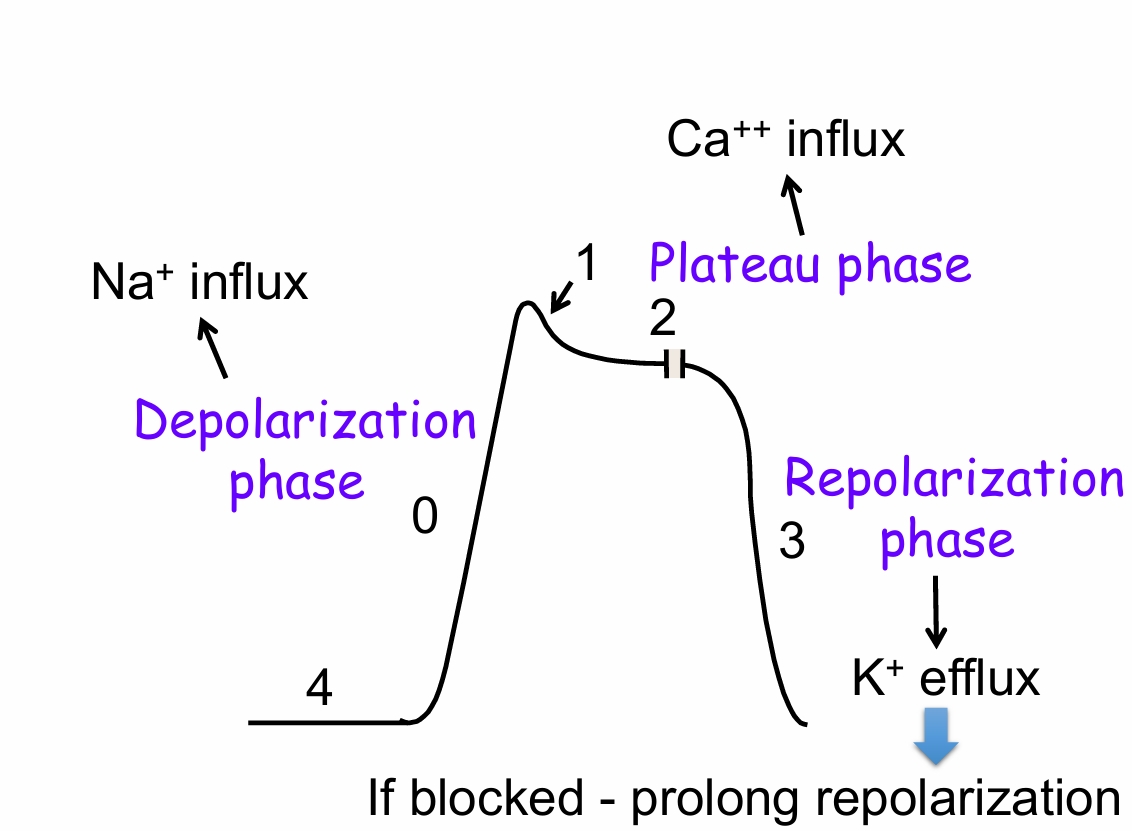
Action potential in nodal tissue (slow response tissue) (3)(2)
4 - Slow depolarization to threshold
0 - Less steep slope
3 - Repolarization phase
No phase 1 or 2 No plateau
No true RMP
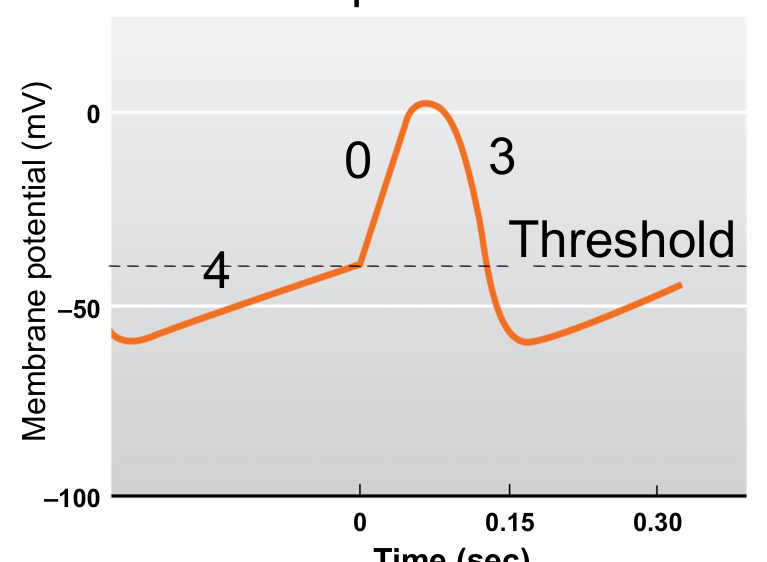
Slow response tissue Depolarization to threshold (3)
4
Pacemaker current gradually brings the membrane potential to threshold (no stimulation needed!)
K+ permeability decreases
Na+ enters (funny current) INa,f
Slow response tissue depolarization phase
0
Slow L-type Ca ++ channel opens, Influx
Slow response tissue repolarization phase (2)
3
Ca++ channels inactivate
K+ channels open, efflux
Cells in the SA node, AV node and Purkinje fibers all have a pacemaker current. So why is it that the SA node normally acts as the pacemaker for the heart? (3)
The inherent rate of the SA node is about 100 depolarizations or beats/min
AV → about 60
Purkinje → about 40
A person develops a problem with their SA node where it doesn’t function any more. Why does their heart not stop beating?
A. The autonomic nervous system takes over and initiates contraction
B. The AV node can take over as the pacemaker
B. The AV node can take over as the pacemaker
Escape rhythm (form of ectopic pacemaker)
The ANS only modulates the activity of the heart
Acetylcholine released from the parasympathetic nervous system will slow conduction velocity in the AV node by most likely affecting: (hint: think of conduction velocity in fast response tissue)
A. Phase 4
B. Phase 0
C. Phase 2
D. Phase 1
E. Phase 3
B. Phase 0
Norepinephrine released from the sympathetic nervous system will increase heart rate by most likely:
A. Increasing Na+ conductance in phase 4 of the SA node
B. Decreasing the slope of phase 4 of the SA node
C. Increasing Ca++ conductance in phase 0 of the AV node
D. Decreasing the slope of phase 0 of the AV node
A. Increasing Na+ conductance in phase 4 of the SA node
To increase heart rate:
SA node → phase 4 → get to threshold faster
To increase conduction from atria to ventricles thru the AV node:
AV node → phase 0 → Make a more steep slope
A 58-year-old male presents to the emergency department with an unusual feeling in his chest. He states that it feels like his heart is beating out of his chest. How can you tell what is going on with this heart?? (2)
Cardiac auscultation (listen with a stethoscope)
Electrocardiogram
What is an electrocardiogram?
Graphical record of the electrical activity of the heart
Cell at rest charges
Negative inside, positive outside
Isoelectric or 0 potential
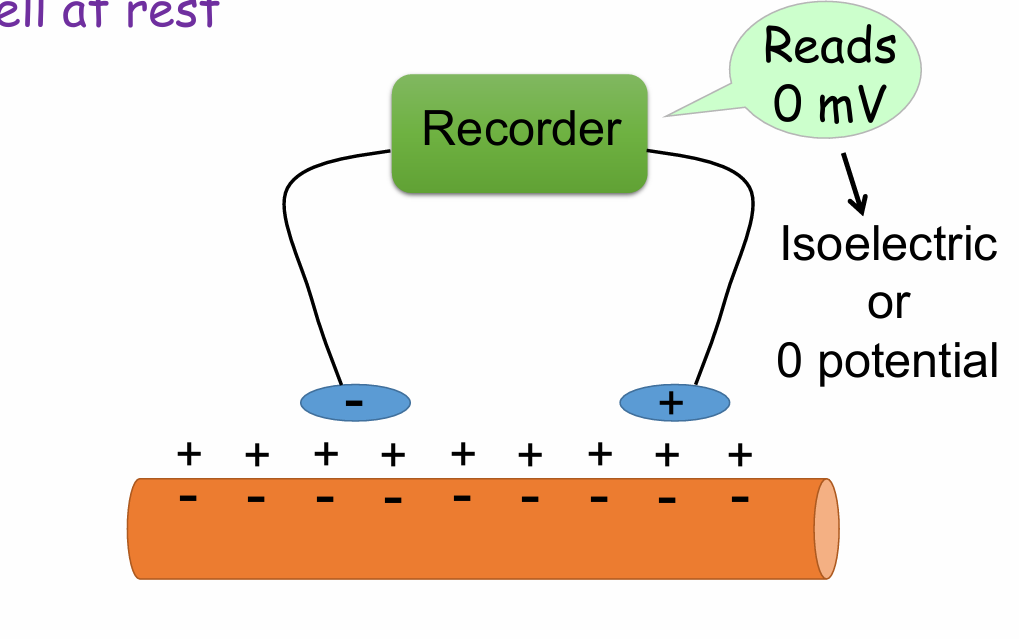
What would you see on the recording when the cell is at rest?
A. Downward deflection
B. Upward deflection
C. Straight, horizontal line
C. Straight, horizontal line
Cell starts to depolarize charges
Inside positive, outside negative
Produces a dipole
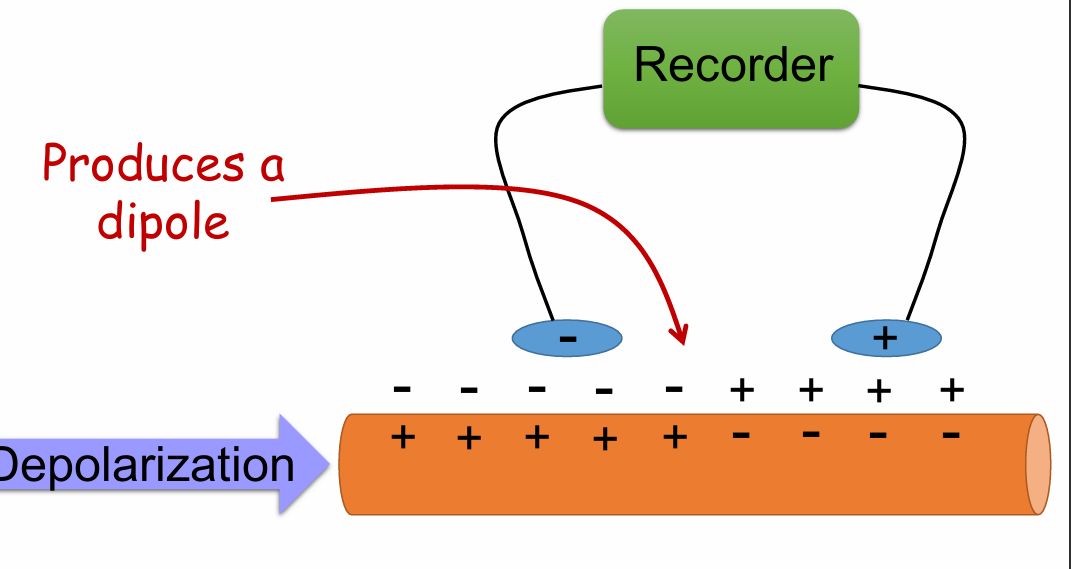
What would you see on the recording when the cell starts to depolarize - as on the previous slide?
A. Downward deflection
B. Upward deflection
C. Straight, horizontal line
B. Upward deflection
What would you see on the recording when the cell finishes depolarizing - as on the previous slide?
A. Further upward deflection
B. Goes back to baseline
B. Goes back to baseline
Cell starts to repolarize charges
Negative inside, positive outside
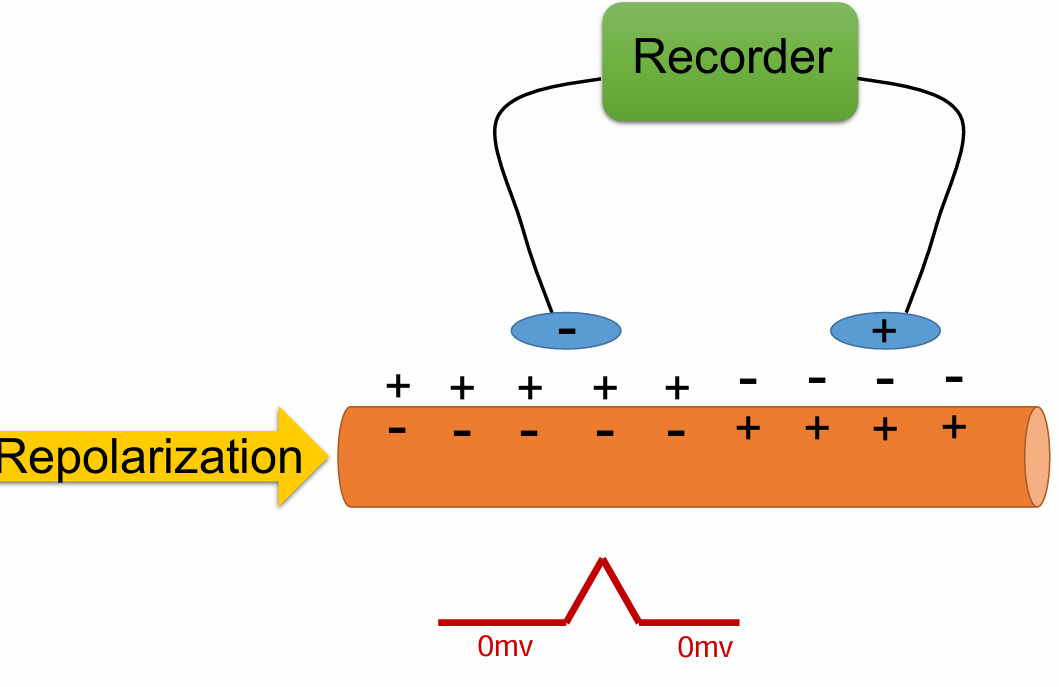
Does an upward deflection on the ECG always represent depolarization?
No
Repolarization in opposite direction can be an upward deflection
Things an ECG can tell you (4)
HR
Heart rhythm
If the left ventricle is enlarged
If the person is either having or had a myocardial infarction (MI, or heart attack) and what part of the heart is affected
Lead II
Electrode on right arm negative
Electrode on left leg positive
P wave
Atrial full depolarization
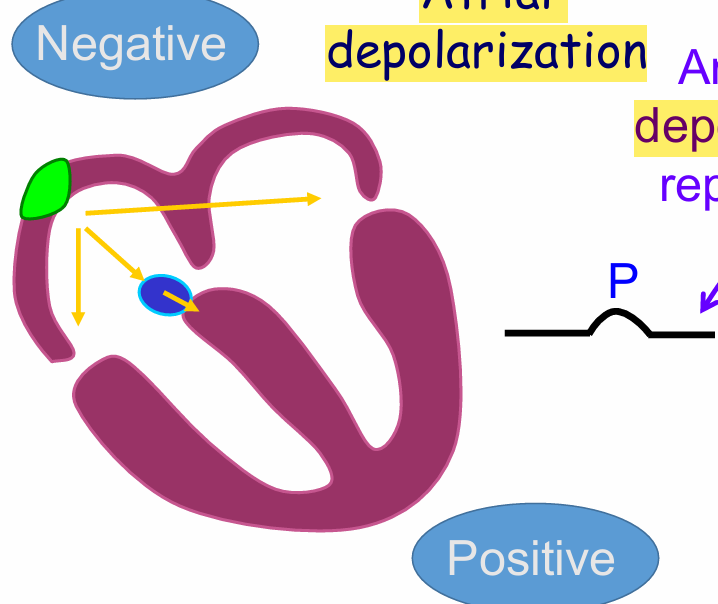
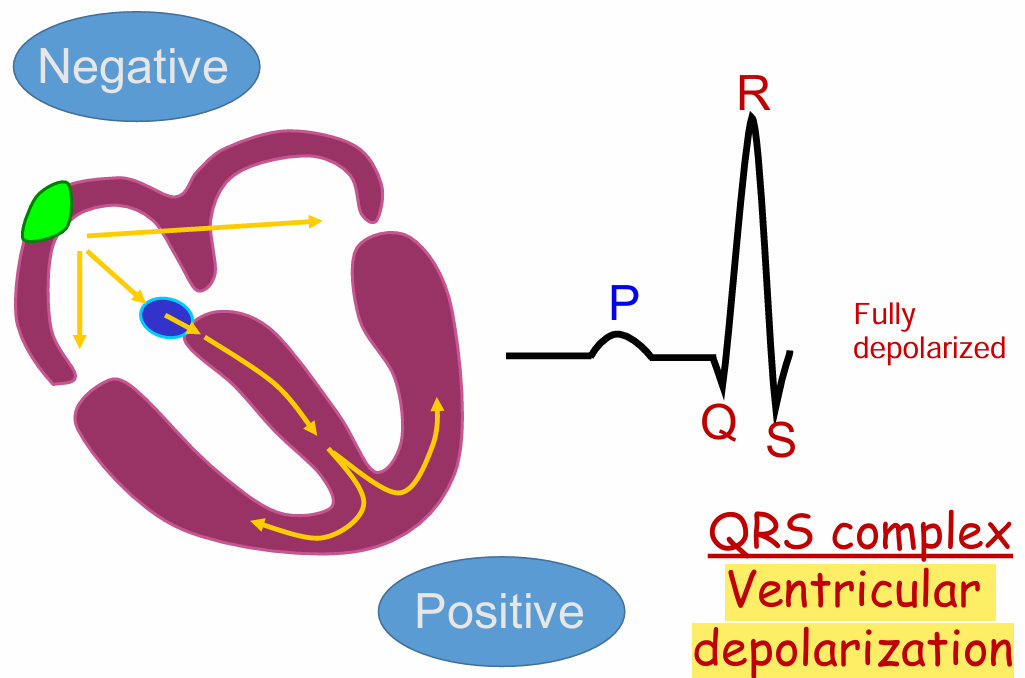
QRS complex
Full ventricular depolarization
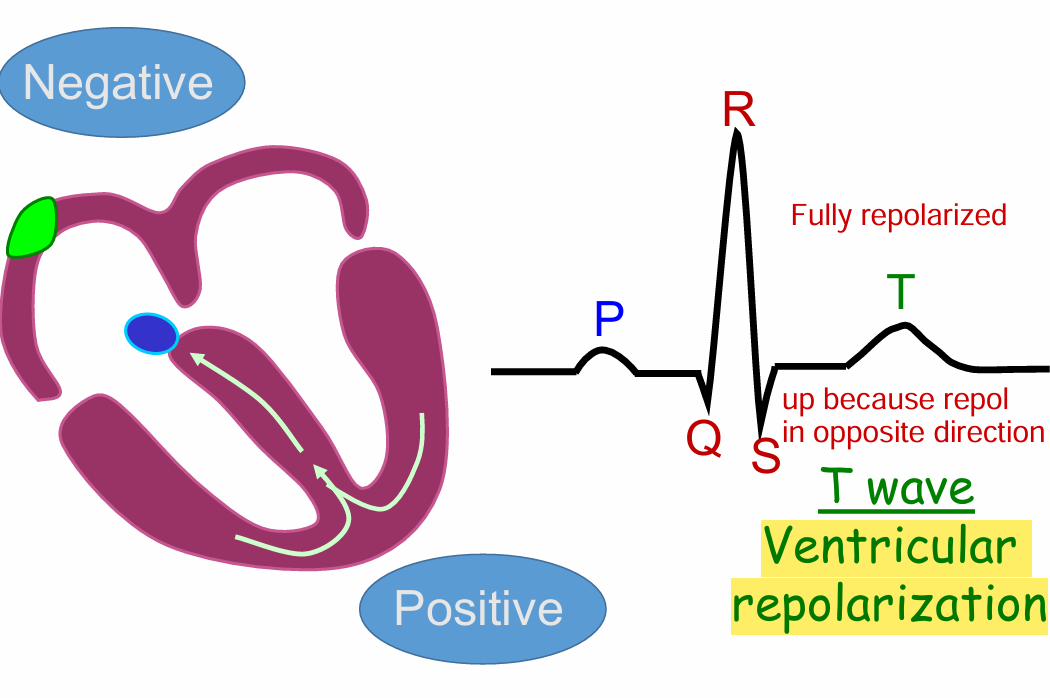
T wave
Full Ventricular repolarization
Upwards because in opposite direction
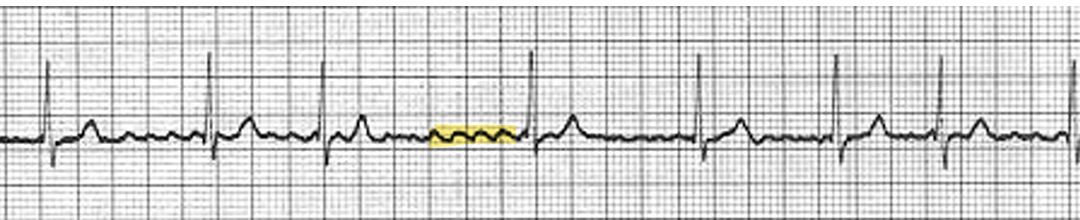
Atrial fibrillation (4)
Trigger site at junction of pulmonary veins
Wavelets of reentry cause chaotic electrical activity
The atria quiver instead of contracting
Because AV node is not in refractory, electrical impulses reach the AV node causing QRS complex
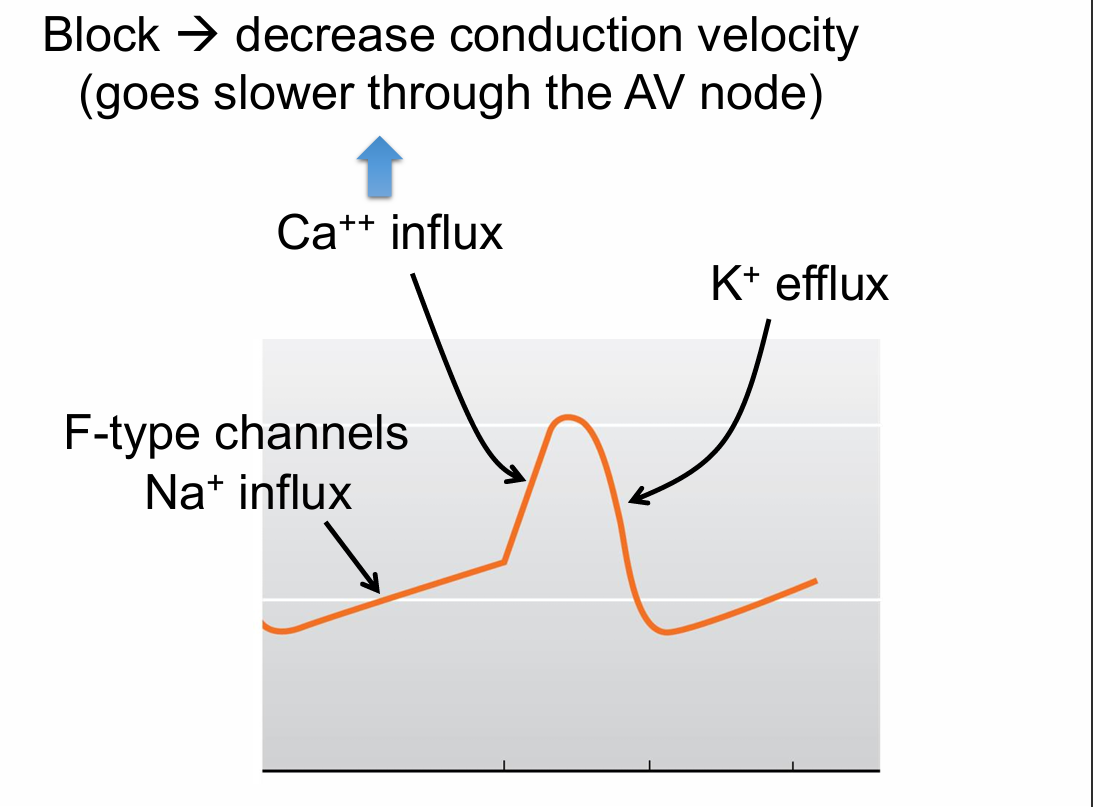
AV block (3)
P wave is further from QRS complex (PR interval)
Conduction through the AV node is too slow when
Blocking L-type Ca++ channels (slower depolarize, slower conduction velocity)
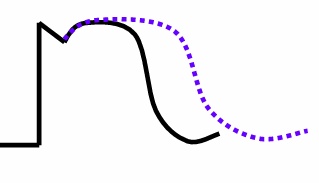
The QT interval
Time of ventricular depolarization and repolarization
What would happen to the QT interval if the plateau was prolonged ?
Longer AP duration
A person has an ECG done. The ECG reveals a prolonged QT interval. The PR interval, QRS interval, P wave, QRS complex are all ‘normal’. They had recently started a new medication. This drug most likely blocked:
A. Cl- channels on ventricular myocytes
B. K+ channels on ventricular myocytes
C. Ca++ channels on the AV node
D. Na+ channels on ventricular myocytes
E. Ca++ channels on ventricular myocytes
B. K+ channels on ventricular myocytes
Ventricular fibrillation
Wavelets of reentry → No coordinated contraction, just quivering of the ventricles