Environmental Science Final
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Water provides the habitat for more than half the species on Earth
True
Biodiversity is declining faster in freshwater systems than in ocean habitats, and this is associated with human activities
True
What is one of the largest threats to freshwater species?
Fishing and Harvesting
Embedded water
Concept that accounts for the water that is used to produce goods that we consume
How much water do we use per day?
80-100 gallons
Water reservoirs
Any part of Earth where water remains for a period of time
What world would we use to describe all of the water reservoirs on the planet?
hydrosphere
What is residence time?
The average time that water spends in a reservoir or part of the hydrological cycle before moving to another reservoir.
How much of Earth’s fresh water is frozen?
70-80%
How much of Earth’s water is not in the ocean?
About 2.5% of Earth's water is fresh water, with the rest being saline water in the oceans.
Earth’s groundwater is stored in subsurface areas of rock or sediment where water can accumulate or pass through, and these area are known as
Aquifers
How does groundwater affect surface water?
Groundwater can contribute to surface water bodies through seepage, impacting their flow and quality. It acts as a natural reservoir, supporting streams and rivers during dry periods.
How do lakes and ponds form?
Lakes and ponds form by glaciers retreat, volcanoes erupt, and rivers change course
What are the two variables that define the zones of lentic ecosystems?
The distance from the shore and the penetration of sunlight
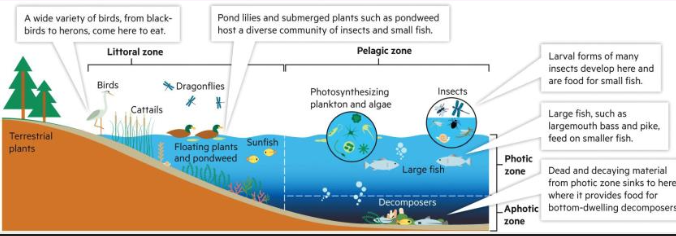
You should definitely know what characterizes in each zone within lentic ecosystems in the figure below
This includes the littoral, and pelagic zones (goes into deeper detail)
Littoral zone
This is closest to the shore, so shallow water. This zone has the biggest biodiversity and supports various aquatic plants and animal species. Plants can root at the bottom.
Pelagic Zone
This is open water away from the shore (opposite of Littoral). It is divided into two different zones, photic and aphotic zones.
Photic Zone
receives enough sunlight for photosynthesis
Aphotic Zone
Area that is deprived of light.
What are the 3 main
Wetlands
area where the ground is seasonally or permanently saturated with water
Swamps
forested wetlands, often dominated by trees and shrubs, characterized by standing water.
Marshes
Wetland areas dominated by grasses and cattails.
bogs or peatlands
when wetlands are fed by groundwater and organic matter accumulates faster than it can be decomposed.
Estuaries
Wetlands where fresh water meets salt water.
salt marshes
estuaries in temperate climate (hot)
mangrove swamps
estuaries in tropical and subtropical climates.
Be able to talk about peat moss: How does it form? What role does it play in the environment? How is harvesting peat moss detrimental for the environment?
it is an absorbent moss that grows in dense masses on boggy ground, where the lower parts decay slowly to form peat deposits. This serves as a habitat for other plants. Also, under natural conditions it stores carbon (when it’s wet)
What are the two main ways in which we impact freshwater systems?
How we withdraw/divert water and how we pollute them.
What is recharge?
process of adding water to groundwater system.
What are fossil water aquifer and why is it not a good idea to withdraw water from them?
fossil water aquifer’s can have a residence time of millions of years. They are considered nonrenewable. Withdrawing water from them is considered water mining.
What is subsidence, what causes it, and how does it affect an aquifer?
Subsidence is when land settles as fromerly water-filled spaces collapse under the weight of overlying rock and soil. Permanently reduces the ability of an aquifer to store water.
Know the difference between the two broad categories of water pollution
Point source and nonpoint source pollution.
Point Source Pollution
A clearly identifiable source of pollution, such as a drainpipe, channel, or ditch (Factory drainpipes or sewer systems)
Nonpoint Sources
A broad diffuse source of pollution such as agricultural or residential runoff (vehicle pollutantswashing out of a parking lot)
Sediment pollution is the most common of all types of pollution (True/False)
True
Which techniques or developments have been made that improve water usage in agriculture?
Several techniques include drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and soil moisture sensors that optimize water use and reduce waste.
Water Recycling
Strategy of taking residential water, treating it, and then using it typically for other agricultural or industrial uses.
Nearly 80% of all energy used to power our modern lifestyle comes from fossil fuels
True
Greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuel production and use are the leading cause of climate change.
True
The original source of all fossil fuels is the Sun.
True
Oil, natural gas, and coal are composed of strands of hydrogen and carbon molecules derived from ancient, solar energy-capturing photosynthesis and therefore can also be called
hydrocarbons
Be able to describe the difference in how oil and natural gas form in comparison to how oil forms
Oil is a liquid fossil fuel that formed from plants and microscopic animals that lived millions of years ago, while natural gas is a gaseous fossil fuel that formed deep beneath Earth’s surface and contains primarily methane. Natural gas forms from higher temperatures and pressures.
We derive the least energy from this fossil fuel in the U.S.
Coal
The transportation sector consumes the most of this fossil fuel in the U.S.
petroleum
Coal is consumed more by this sector of fuel consumption than any other in the U.S.
production of electric power
Which fossil fuel is the most evenly split in terms of its usage across the 4 sectors of fuel consumption in the U.S.
Natural gas
Biofuels
recently living matter or by-products of its decomposition used as an energy sources
This person (____) was responsible for developing a ___ that ultimately made coal more accessible in the 18th century. Describe how the previous sentence relates to the concept of proven reserves.
James Watt; steam engine. The steam engine greatly increased the efficiency of coal use, leading to higher rates of extraction and recognition of proven reserves as it demonstrated the viability of coal as a primary energy source for industrial applications.
You can count on me asking about specific details about each fossil.
.
Coal
This was the first fossil fuel widely used by humans and has the highest reserves of any fossil fuelin the world. It is primarily used for electricity generation and steel production. Coal contributes significantly more CO2 per unit of energy than oil or natural gas.
Oil
When refined, it turns to gasoline (most consumed fuel in the world), the middle east has more than half of the world's oil reserves. It is primarily used for transportation and heating and can also produce various other petrochemicals. It forms in porous rocks and can be extracted by drilling and pumping
Natural gas
First used in China in 500 BCE in bamboo pipes to boil seawater (commercial usage is recent). Over the past 10 years —> it has been the fastest-growing fossil fuel energy source produced and consumed
What are some of the concerns associated with idling your car as opposed to driving it, and what are some of the policies and innovations that have been put into place to mitigate the issues associated with idling?
If you idle your car for more than 10 seconds, it consumes more gas than it would take to restart the engine, efficiency decreases when idling and pollutes more carbon monoxide, particulate matter, and nitrogen oxides than driving.
Atmosphere
A dynamic envelope of gases extending up from earth’s surface that clings to our planet because of gravitational pull.
The atmosphere is primarily composed of which two gases:
Nitrogen and Oxygen
All gases move from areas of (high/low) pressure to areas of (high/low) pressure
high, low
As elevation increases, air density (increases/decreases)
decreases
Know the names of each atmospheric layer as well as the details for each of them. You can guarantee this will be on the exam
The atmospheric layers include the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere, each characterized by decreasing temperature with altitude and varying properties.
Troposphere
Lowest area of earth’s atmosphere where Earth’s weather occurs. The air here is dynamic, it rises, sinks, churns, mixes as it warms and coolsand contains most of the atmosphere's mass. Also most of the water vapor
Stratosphere
The second layer of Earth's atmosphere, located above the troposphere, has very little water vapor, relatively calm. Has 1,000 times more ozone than at ground leveland is where the ozone layer is situated, absorbing and scattering ultraviolet solar radiation.
Mesosphere
Earth’s coldest temperatures found here (-100 degres C). this is above maximum altitude of aircraft and below orbit of satellites. Meteors burn up here as they encounter friction from air molecules.
Thermosphere
Top layer of atmosphere, it is warmer than mesosphere due to solar and cosmic radiation. Air molecules are highly scattered here. 99.9997% of the atmosphere’s mass lies below 100 km away from Earth in the upper Thermosphere. The International Space Station and most satellites orbit here with little air resistance
How do weather and climate differ in terms of how they are defined?
Weather is short-term variations in conditions such as temperature, moisture, and wind in a specific place. Climate is the long-term average of weather conditions for a given region.
Temperature
A measure of how vigorously the atoms in a material are moving and colliding with each other
What are the 3 reasons that we have different temperatures on the planet?
half of the planet faces away from the sun at any given time
Amount of solar radiation as a function of latitude
Heat gain and loss is affected by bodies of water and land features
How can we measure barometric pressure?
How the weight of the air in the atmosphere presses against a confined substance (mercury)
The electrical resistance of atmospheric pressure in your smartphone
Be able to recognize what high- and low-pressure pressure systems are in terms of what characterizes them and how that might be graphically depicted
High-pressure systems is a system of air formed that becomes denser and heavier and then sinks to form an area of high pressure. It is associated with clear and dry conditions. High-pressure systems that don’t move can cause deserts. Low-pressure systems are areas where air is less dense and rises, often leading to cloudy and rainy weather. They are typically associated with stormy conditions and are depicted on weather maps with a "L" symbol.
Why do the interiors of continents typically receive less precipitation than coastal areas?
This is because it is further from the ocean
Be able to explain how air masses interact with mountains in terms of precipitation and how rain shadows are formed
Precipitation occurs when air masses meet mountains and are forced upwards. When air masses cool they produce precipitation on windward side of the mountain. After moisture is lost it is cooler, drier air sinks and heats on the leeward side of the mountain. Arid region on the leeward side is known as a rain shadow.
Carbon monoxide can be produced when organic materials are burned without____
abundant oxygen
Particulate matter (PM)
Tiny particles and droplets less than 10 micrometers in size that are suspended in the air we breathe
Volatile organic compounds are typically found in higher concentations outdoors than indoors (True/False)
False. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are often found in higher concentrations indoors due to sources like paints, cleaners, and furnishings.
Smog
Forms when VOCs and nitrogen oxides (NOx) from the combustion of fossil fuels interact in the presence of sunlight at warm temperatures
Where is the ozone layer located and how does it protect life?
it prevents 99% of UV radiation from reaching earth’s surface. UV radiation damages the surface tissues of all life forms.
Understand what chlorofluorocarbons were used for, the researchers involved in studying their effects and what they found, the steps involved in how chlorine destroys ozone, what stopped the damage, and when we can expect the ozone layer to significantly improve
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) were used as refrigerants, propellants, and solvents, researched by scientists like Mario Molina and F. Sherwood Rowland, who discovered that CFCs deplete the ozone layer by releasing chlorine atoms that catalyze ozone destruction. The 1987 Montreal Protocol implemented regulations to phase out CFCs, and significant improvement in the ozone layer is anticipated by the mid-21st century.
Which two policy strategies did the Clean Air Act of 1970 establish?
Air-quality standards and regulations on the source of pollutants
What is the instrumental period, what is its significance, and when did it begin?
The instrumental period refers to the time when systematic measurements of environmental variables began, significantly contributing to our understanding of climate and weather patterns. It began in the late 19th century.
How do satellites measure temperatures of different atmospheric layers?
They measure infrared radiation from vibrating gas molecules in the air
What do Argo floats and Jason satellites measure?
They measure ocean temperature, salinity, and currents through profiling and altimetry.
Proxies
An observable and measurable phenomenon that serves as an indirect indicator of changes in climate
What needs to occur before proxies can be used to estimate temperatures from pre-instrumental time periods?
Calibration and validation against modern measurements.
Can you explain global temperature based off of the type of oxygen isotopes
found in ice cores; higher ratios of oxygen-18 indicate warmer temperatures, while lower ratios suggest cooler temperatures.
Know the relationship between atmospheric temperatures and carbon dioxide and ocean temperatures and carbon dioxide
Atmospheric temperatures rise with increased carbon dioxide levels, while ocean temperatures also correlate positively with carbon dioxide concentrations, affecting overall climate patterns.
The Greenhouse Effect
Any system where a barrier causes the inflow to outpace the outflow in a way that warms the interior
The more greenhouse gasses there are in the atmosphere, the
less infrared radiation emitted from Earth’s surface is absorbed
by the atmosphere and re-emitted (True/False)
False; the more greenhouse gases, the more infrared radiation is absorbed and re-emitted, enhancing the greenhouse effect.
Life on earth would improve for humans if we could find a way to remove the greenhouse effect entirely (True/False)
False; the greenhouse effect is essential for maintaining temperatures that support life.
Water vapor is the dominant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere (True/False)
that contributes significantly to the greenhouse effect. It traps heat, maintaining Earth’s temperature and supporting life.
Describe the relationship between the albedo value of earth, the amount of snow and ice on earth, the amount of planetary warming that occurs, and the amount of reflected light.
The albedo value represents the reflectivity of Earth's surface; higher albedo values, due to increased snow and ice, lead to more reflected light and less absorption of heat, reducing planetary warming. Conversely, as snow and ice melt, lower albedo contributes to more absorption of solar energy, enhancing warming.
What are surface currents and whar causes surface currents to move?
Surface currents affect the top 100-400 meters of water and start because of air moving above them
Gyres
are the large circular patterns that surface currents move in. These gyres are primarily driven by the Earth's rotation, the wind patterns, and the position of continents, influencing oceanic circulation.
What causes deep currents to form?
Shaped by differences in water density due to temperature and salinity variations, deep currents are influenced by thermohaline circulation.
The density of water increases as its temperature (increases/decreases) and its salinity (increases/decreases)
increases; increases
Most sources of carbon dioxide emissions are normally balanced given these processes: ___ & ___ add carbon dioxide to the atmosphere and ____ removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
plant respiration and decomposition, photosynthesis
Currently, volcanoes release more carbon dioxide each year than humans (via fossil fuel combustion and industrial processes (True/False)
False
80% of human CO2 emissions come from combusting fossil fuels and producing cement
This fact highlights the significant contributions of energy production, transportation, and industrial processes to overall carbon dioxide emissions.
Cement production produces so much pollution because ____ is produced when making clinker, a key ingredient for cement
carbon dioxide
When CO2 that was once locked away in the lithosphere is released (i.e., “new” CO2), ____% is absorbed by the oceans or vegetation and most of the rest of this “new” CO2 is accumulates in the ___
45%, atmosphere
Natural sources of methane may include forest fires, volcanoes,and ____, defined as microorganisms that live in digestive tracts of animals or in wetlands
methanogens
Up to ____% of global methane emissions may be attributed to wetlands
30