Test 1 Human Bio
1/165
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Everything up to Test 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
166 Terms
science of biology
the study of living organisms and the environment they live in
cell
smallest structural and functional unit of an organism
tissue
group of similar cells that perform a particular function
organ
composed of several tissue types
organ system
group of organs that work together to form a common purpose
organism
a collection of organ systems
species
a group of interbreeding organisms
population
the members of one species in a particular area at a particular time
community
interacting populations
ecosystem
community of populations interacting with the physical environment
biosphere
includes all of the places on the earth where living organisms exist
energy
the capacity to do work (food provides nutrients which are used as building blocks for energy)
metabolism
the sum of all the chemical reactions that occur within a cell or organism
what is the ultimate source of energy for life on earth
the sun
photosynthesis
used by plants, algae and some bacteria; harvests energy from the sun and converts it to chemical energy, produces sugars which serve at the basis for the food chain
what are the 2 different types of metabolism and their function
catabolism; breakdowns complex molecules to smaller molecules (cellular respiration)
anabolism: generates complex molecules from simple molecules (photosynthesis)
homeostasis
process of maintaining a relatively stable internal environment despite changes in external surroundings
homeostasis would be impossible to maintain without what?
ability to respond to stimuli (internal and external stimuli)
genes
short segments that specify traits
mutations
variations in genes; can be beneficial and make organisms better suited for its environment
evolution
how a population changes over time
natural selection
the process by which evolution occurs
adaption
over time, a population has more individuals with this advantageous variation
prokaryotes
single celled organism that lack a nucleus, bacteria and archaea contain these
invertebrates
most animals, lack internal skeletal support structure (worms, insects)
vertebrates
have a nerve cord protected by vertebral column (fish, reptiles, birds)
mammals
vertebrates with hair/fur and mammary glands (humans, raccoons, seals)
culture
activities and items passed down from one generation to the next
science
a way of knowing about the natural world
discovery science
collection and analysis of data without a preconceived hypothesis
observation
formal way of watching the natural world
matter
anything that has mass and takes up space
elements
basic building blocks of matter; cannot be broken down by chemical means
90% of the human body is made up up which 4 elements
carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen
atom
smallest unit of an element that retains its physical and chemical properties
molecules
atoms bonded together
subatomic particles (parts of an atom)
neutrons, protons, electrons
isotopes
atoms of the same element but a different number of neutrons
radioisotopes
unstable isotopes, they emit energy called radiation (can damage cells and cause cancer)
compounds
molecules made of different types of atoms
what two types of bonds join atoms
ionic bonds and covalent bonds
ionic bonds
the attraction between a positive or negative ion, atoms donate or take electrons to fill their shell, resulting in formation of ions,
covalent bonds
atoms share electrons to fill their shells, these electrons will spend time in both atom shells
hydrogen bond
attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen to a slightly negative oxygen, nitrogen or fluorine
calorie
amount of heat required to raise one gram of water by one degree celsius
what must break for water to boil
hydrogen bonds
hydrophobic
molecules that do not attract water; are non-polar
hydrophilic
molecules that attract water; polar molecules
cohesion
water molecules cling to each other through hydrogen bonds
adhesion
water molecules cling to surfaces like blood vessels
extraterrestrial hypothesis
meteorites brought organic carbon to earth which includes amino acids and nucleic acid bases
deep sea vent hypothesis
Biologically important molecules may have been formed in the temperature gradient between extremely hot vent water and cold ocean water
what are the organic molecules found in living cells
carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins
dehydration reaction
type of reaction that removes water, linking subunits together into macromolecules (large molecules)
hydrolysis reaction
the addition of water to break macromolecules into their subunits
monosaccharides
simplest sugars (5-6 carbons); pentoses, hexose
polysaccharides
many monosaccharides linked together to form long polymers; starch, cellulose
lipids
40% of organic matter in humans, nonpolar, very insoluble in water; fats, phospholipids, steroids, waxes
phospholipids
building blocks of cellular membrane
membranes
amphipathic phospholipids with saturated or unsaturated tails associate noncovalently to form bilayer membrane structure
amphipathic
having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts
nucleic acids
carry coded information for making proteins at the right time and place; DNA, RNA
how many amino acids do we have
20- 11; can be synthesized, 9; from diet (essential)
carbohydrates
used as an energy source, carbon atoms linked to a hydrogen atom and a hydroxyl group; monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides
simple carbohydrates; monosaccharides
made up of single sugar molecule, has carbon backbone (3-7 carbons); glucose used as an immediate energy source
disaccharides
made of 2 monosaccharides (from dehydration rxn); sucrose table sugar
complex carbohydrates; polysaccharides
long polymers of glucose subunits
what are the different types of polysaccharides you learnt about in class
starch: energy storage in plants
glycogen: energy storage in animals
cellulose: structural in plant cell walls
lipids
do not dissolve in water, lack hydrophilic polar groups; triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids
triglycerides
type of hydrophobic lipid, made up of one glycerol and three fatty acids. Energy storage and insulation; fats, waxes and oils
emulsifiers
molecules that surround triglycerides and disperse or emulsify them.
waxes
one fatty acid attached to an alcohol, many plants and animals will produce waxes that are secreted onto their surface (ear wax)
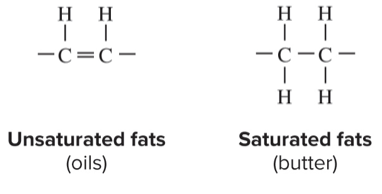
fats vs oils
fats: usually animal origin, solid at room temp, energy storage, structural, insulation
oils: usually plant origin, liquid at room temp
fatty acids
long chains of carbons and hydrogens, end in COOH, 16-18 carbons, saturated or unsaturated
saturated vs unsaturated fatty acids
saturated: no double covalent bonds between carbons, they are saturated with hydrogen
unsaturated: one or more double covalent bond because hydrogens are missing
which type of fat contributes to heart disease the most
trans fats; man-made fats
phospholipids
similar structure to triglyceride but one fatty acid replaced with polar phosphate group. Have polar hydrophilic head and non-polar hydrophobic tails. Primary components of plasma membranes (form a bilayer)
steroids
four rings of carbon atoms, insoluble in water; estrogen, testosterone
nucleic acid structure
polymers of nucleotides: a phosphate, 5 carbon sugar, nitrogenous base
nucleic acid functions
store information, instructions for essential life activity, chemical reactions; DNA, RNA
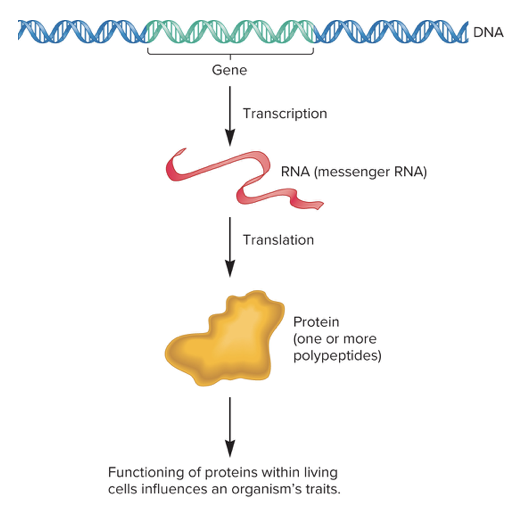
DNA vs RNA function
DNA: stores information on how to copy itself, specifies order of amino acids
RNA: regulate enzyme action, stores energy, many functions, various types
DNA makeup
formed from nucleotides; phosphate group, pentose sugar, nitrogenous base:(A,G,C,T)
RNA makeup
phosphate group, pentose sugar, nitrogenous base; (A,C,G,U)
DNA structure
double stranded, antiparallel and complementary strands. Bases on the inside, stabilized by H-bonding
RNA structure
typically single stranded, nucleotides attached by 5’-3’ phosphodiester bonds between sugars. Base pairing via hydrogen bonds is basis of RNA secondary structure, tertiary structure is result of RNA folding.
ATP
high energy molecule, nucleotide like bases of DNA and RNA but it stores and transports energy within cells.
proteins
organic compounds built with chains of amino acids. Thousands of different types of proteins built by the body
protein functions
support, enzymes, defence, hormones, motion, transport
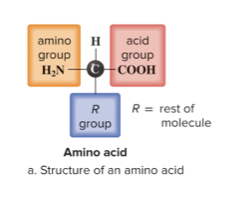
components of amino acids
an amino group, carboxyl group, and an R group. Each amino acid differs in its R group
peptide bond
the polar covalent bond between two amino acids, formed by a dehydration reaction
polypeptide
three or more amino acids linked together
denaturation
the change in shape of a protein caused by extreme heat or pH; disrupts shape and function of protein
cell biology
the study of individual cells and their interactions with each other
cell theory
all living organisms composed of one or more cells
cells are the smallest units of life
new cells come only from pre-existing cells by cell division
what are the two categories of cells
prokaryotic and eukaryotic
prokaryotic cells
lack a nucleus, include two groups of bacteria; eubacteria and archaebacteria
eukaryotic cells
have a nucleus, include animals, plants, fungi, protists
what do both cell types have
a plasma membrane that surrounds the cell made of phospholipid bilayer, a cytoplasm the semifluid substance inside the cell

what were the first cells on earth
prokaryotes, when the atmosphere had no oxygen
what did eukaryotic cells evolve from
from archaea via endosymbiosis; organelles may have developed from eukaryotes engulfing prokaryotic cells