Water and Energy
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
What are the key properties of water?
Density ( Mass/Volume), Transparency to light, High specific heat capacity,High latent heat of vaporization, Solvent
Why is density important?
For most substances, density decreases as temperature increases. This is true for water that is above 4 degrees celsius but if less then density decreases as water gets colder.
This is why oceans expand and sea levels rise as the ocean warms
Why is transparency to light an important property of water?
It allows photosynthesis to occur underwater
Why is water having a HIGH specific heat capacity important?
Warming water absorbs alot of energy and cooling water releases a lot of energy meaning the movements of water move energy around the world.
Why is Northern Europe warmer than the same latitude in North America?
when water sinks it cool and releases a lot of heat in the air
Why does high latent heat of vaporization an important property of water?
Movements of water vapor transport energy around the globe which is released when vapor condenses?
Why is water being a solvent so important?
Since water dissolves and transports nutrients and oxygen, it can healp feed plants and animals as well as dilute pollution
What are the 2 major stocks of freshwater?
Glaciers and icecaps ( Inaccessible) , Ground water ( some is accessible but in other places they are too deep)
Aquifers
An aquifer is an underground layer of porous rock or sediment that can hold and transmit water. They are a function of the subsurface rock and soil structure which depends on geological history
Why are the residence times of water between stocks matter?
The shorter the residence time, the more quickly the water will return to equilibrium if we disturb it.
If pollutants are stuck in a stock of water that has a long residence time it means that those pollutants are likely to remain there.
The longer the residence time, the more time it takes for the stock to replenish itself making it a nonrenewable rource if we extract water faster then it is replaced
Is water a closed or open system on earth?
It is a closed system on earth but if it gets polluted or ends up in the ocean, it is unstable for most purposes
Watersheds
A watershed is an area of land where all the water, whether surface or groundwater, drains into a common body of water, like a river, lake, or ocea
What are human impacts on the water cycle?
Land use change: (Deforestation, Urbanization , agriculture )
Explain how density of water varies with temperature and 2 reasons that this behavior is environmentally significant?
Water density increases as temperatures cool reaching its maximum at 4 degrees celsius, after that density decreases because the water turns to ice that float, protecting aquatic life below and driving ocean currents that regulate the earth's climate.
Explain the difference between specific heat capacity and latent heat of vaporization, and why water’s high value of each is significant.
Water’s specific heat capacity measures the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of water and because warming water abosrbs energy and cooling water releases it it helps regulate earth temperatures.
Water’s high latent heat of vaporization refers to the amount of energy needs to make water change states ( from liquid to gas or liquid to solid) and this is important because it enables the transport of water and energy throughout the globe which helps regulates temperatures
What is the largest stock of freshwater on Earth? What is the largest easily accessible stock of freshwater on Earth?
The largest stick of freshwater is in glaciers/ ice caps. The most accessible stock of freshwater is ground water.
In which stock does water have the longest average residence time? In which stock does it have the shortest?
Water in the atmosphere has the least residence time ( A week and this makes sense because it rains!) Deep groundwater and oceans have the longest residence time
What information would need to be included on a map to draw the watershed of a river? Explain. Why do watersheds matter?
To draw a map of a watershed you have to have the locations of bodies of water, rivers and streams because where they all connect is where there is a watershed. Watershed matter because they make water more easily accessible making them a backbone of our water resources.
How do deforestation and urbanization each affect flows in the hydrologic cycle?
Deforestation ( cutting down trees and destroying forest) reduces transpiration ( water from plants) which leads to reduced precipitation ( less rain) and reduced infiltration ( less water that gets absorbed by trees) leads to increased runoff ( water flows on the surface whihc can lead to flooding
Urbanization ( turning land into cities) means there is less soil for water to soak in causing more runoff meaning there is less water going into the air ( through plants or trees)
Why does water use matter?
Because many places don’t have enough water meaning it can lead to drought (Short term effect) or climate related issues ( Long term effects)
Consumptive vs Non consumptive use
Non consumptive refers to water that is returned to the body from which it was taken at the same quality ( meaning it can be reused) while consumptive use refers to water that is not available for reuse in the same location.
What are the impacts of excessive groundwater extraction?
Declining groundwater levels,Saltwater incursion, Land subsidence ( Cities are sinking!!)
What are the strategies singapore is using to slove its looming water crisis?
Import water, Desalination( Extracting salt from saltwater), Rainwater capture and storage, NEWwater ( Reuse of waste water)
Desalination
The process of extracting salt from saltwater to create freshwater and a brine concentrate. Mostly done in reverse osmosis, meaning high pressure water through filters
Explain the difference between consumptive and non-consumptive water use.
Give an example of each and explain why they fall into that category.
Consumptive water is when water is used up or lost in the process and cant be reused easily right away Example: Watering crops, water is soaked up by the soil, plants or evaporated. It cannot be reused.
Non consumptive water use refers to water that is used but not used up and can flow bak into the environment or be easily recycled and used again. Example: Hydroelectric power ( using water to make electricty) after the water goes through the turbine it continues to flow downstream making it available for other uses
Why is water storage an important component of managing water supply? (Relate this to natural characteristics of the hydrologic cycle.)
Water storage is important because it helps mage our water suplly byt balancing water availability throughout the year. If we have water storage then water from runoffs have a place to go, leading to less floods.
Explain what saltwater intrusion is and how human activity directly and indirectly makes it worse
Saltwater Intrusion is when salt water mixes with freshwater in underground aquifers or surface water sources. If we extract groundwater faster than it has time to replenish, saltwater will be able to intrude more quickly.
What are some of the actions that Singapore has done to address water scarcity that might be difficult for other countries to replicate? Explain
Singapore has turned to Desalination and NEWwater and others to adress water scarcity. Desalination takes a lot of money and and substantial energy imputs and this might be difficult for developing countries.
Potable vs Non Potable
Non Potable refers to uses of water that do not require it to be safe for drinking.
The capture and treat stormwater Facility in Santa Monica collects run off ( water that is not soaked up by anything) and they reuse tis water as a way to reduce water demand and improve water quality
How are having decentralized systems useful for recycling water for non potable uses?
Because of decentralized systems ( a system where water is distributed across multiple locations rather then being concentrated in a single point) water used in kitchens, showers or laundry all get stored in a surge tank and that water is used to water gardens, wash cars or flush toilets
What are the 2 pathways of pollution? Why is this important?
Non- point sources ( Contamination from different sources) and point sources ( contamination from a single direct source) and this is important because it tell us the difference in concentration of pollution, we are able to identify and measure it as well as control it.
What are the types of pollutants that are not directly harmful to human health?
Nutrients ( Source: Anima or human waste, fertilizer), Effects: Algae growth( toxic organisms)
Sediment ( Sources: Erosion), Effects: Increased turbidity, Disrupts some aquatic organisms
Heat ( Source: Cooling processes) Effects : Disrupts aquatic organisms
Debris( Source: Blow across land or thrown into waters), Effects: Entrapment and injury/death to wildlife
Infectious agents ( Source: Animal or human waste), Effects ( Disease or death)
Organic chemicals (Source: Petroleum leaks), Effects: Toxic, bioconcentrate
Inorganic chemicals ( Source: Industry, Acid rain), Effects : Diverse health impacts
Pollution from out pipes example ( Flint Michigan)
Corrosion occured when the city switched to more acidic water from flint river and didd’t treat the water according to regulation
Types of pollutants that are directly harmful to human health
Organic Chemicals (Sources: Petroleum leaks, industry ) Effects: Toxic
Inorganic Chemicals ( Sources: Industry, Acid Rain) Effects : Diverse health impacts including neurological effects
Pharmaceuticals ( Flushing of prescription medication), Effects: Known effects on reproductive systems of frogs and fish not wll known by humans yet
Infections agents ( Source: Animal or human waste) Effects :Death,Diseases
What are strategies for reducing pollution and risk?
Natural purification Process: Physical Process ( Dilution, Sedimentation, Filtration)
Chemical Process: Reaction or Aeration
These strategies seek to expand or mimic natural purification processs
Regulating point source pollution
Clean water Act ( 1972): Prohibited the release of pollutants from point sources into navigable waters without a permit
Why are combined sewer ( Point source) overflows horrible and what are strategies to reduce sewer overflows?
Combined sewers overflows is when due to heavy rains or snow melt sewer tanks are overflowing with untreated sewage into water wats carrying nutrients, sometimes even pharmaceuticals or infectious agents
Strategies: Separating storm and sewage lines, Increase capacity of combine sewer, Build an overflow storage tank
Green vs grey infrastructure when reducing pollution in a changing climate
Grey infrastructure are pipes, tunnels or pumps, Green Infrastructure are nature based solutions
Goal: Increase green infrastructure to reduce flooding and pollution
Reality: Heaveier rains causing more combined sewer overflows
Strategies to reduce nonpoint pollution
Restore Wetlands, Plant more plants at the edges of rivers ( Riparian Buffers)
Strategies for addressing water pollution
Reducing the ampunt of waste at its source, Treating water before its discharged, Cleaning up polluted waters
Cleaning up polluted Waters
Restoring wetlands: Absorbs nutrients, breaked down pollutants, proceeds habitats
Cleaning up floating pollutants by applying dispersant at surface ti disperse oil within water
Removing pollutants from channel bed
Legally: Safe Drinking water act (1974) which required the monitoring of drinking water quality
Explain the difference between point and non point sources of water pollution and given an example of each. Why is it harder to regulate and reduce nonpoint sources?
Non point sources are sources that are distributed whole point sources refer to 1 specific source. That being said because non point sources are distributed there is no one source that we can concenrtate our efforts on reducing pollutants making it hard to regulate
Point sources: Factories that release pollutants like chemicals
Non Point sources: urban Run off
Explain how “ improved water source” and “Sanitation” are diffrent and how they are related. to eachother?
A improved water source refers to water supply that is safe and reliable for humans to consume because the focus is on providing safe water from water that had other pollutants ( not waste) while sanitation refers to the management of human waste and the disposal of waste materials both are key to preventing waterborne diseases
Explain how nitrogen in the water indirectly affect human health even though it is not directly harmful?
Nitrogen in low concentrations are not directly harmful but it can cause long term health effects like cancer,
Describe how heavy rainfall can lead to untreated sweage ending in a lake or river?
Heavy rainfall could potentially lead to overflowing sewers that could spill into water ways if there is a combined sewer system which would end up in lakes or the rivers through the underground water system.
Describe 2 ways that vegetation can reduce water pollution?
By drinking in the water, plants can filter pollutants from stormwater runoff before it hits any rivers of streams.
They can also reduce soil Erosion and Sediment pollution, the roots of plants bind soil together preventing it from being washed away which stops sediments from being wash away as well ( clay or organic matter)
Describe the different clean up strategies for a pollutant that is less dense than water ( it floats) and ones that are denser then water ( it sinks)
For pollutants that float on water, planes can disperse a solution that helps break down the pollutant into smaller droplets that can be dispersed throughout the water. They can also use Booms as a way to keep the pollutant contained to a certain area
For pollutants that sink, We can use equipment that can scoop or vacuum up the polluted sediment and we can transport it out of the water
Describe an example of how trying to clean up water pollutants can lead to an increase in air pollution.
For pollutants that float above water, an option is to burn them ( if they are highly flammable) so they can especially burn off the pollutant but doing so can release particulate matter in the air which can increase air pollution.
Flood related vocabulary
Flood - When a body of water overflows its normal location and inundates an area of land that is usually dry
Floodplain: The are of land that will be underwater in specific magnitude flow ( Depends on differences in elevation)
Recurrence Interval: expected time interval for a given condition to be equalled or exceeded based on the probability of occurrence ( 100 year flood is an even that has a 1/100 chance of occurance in a year) we are using past streamflow data from pervious years to project into the future
What are the 3 causes of floods?
Rivers overflow their banks
Rain overwhelms the drainage system
Coastal water overflows onto land
What are different “Hard” Solutions that are used to help with flooding?
Dams
Leeves ( Walls built alongside rivers or around critical facilities to reduce risk of flooding) When Levees fail the damage can be huge because since the depth is greater the more water will come rushing in at a very alarming rate
How can flooding occur inland?
Flooding can occur due to overflowing rivers ( Fluvial Flooding) or it can be due to heavy rainfall ( Urban flooding)
How can flooding occur on coast?
It can be caused by high tides or extreme weather events ( Hurricanes)
What causes rivers to overflow?
Heavy total rain fall; the more rain the less the river can hold
Snow Melts or ice jams: When it rains or it is warm ice melts and ice jams can suddenly release
Flash Floods- Short duration and high intensity rain
What causes coastal flooding?
Storm surges, and land elevation and sea level ratio.
What are the benefits and cons of floods?
Benefits: Deposit fertile soil, recharges ground water and create fish and wildlife habitat
Cons: Damage to buildings, los of human and animal life, Crop damage,
Strategies to Reduce Flood Risk
“Hard” Solutions: Structures like dams (Provide storage capacity)and levees
Levees are walk built alongside rivers or around critical facilities to reduce risk of flooding
“ Soft” Solutions: Policy, managment
Bioretention areas ( Rain Gardens)
Sunken area designed to collect rainwater from rooftops
Permeable pavement
Allows rainwater and melting snow to infiltrate to soil underneath
Planter Boxes
Boxxed bioretention that collect and absorb runoff from streets, sidewalks and parking lots
Green Roofs
Roofs covered in vegetation to capture and absorb rainwater
Mitigating coastal floods
Structural solutions: Barrier islands or reefs, Flood walls, Raising Roads
Non structural solutions: Wetlands
What are 3 different causes of flooding along the coast? What are causes of flooding in cities, away from a river?
Causes for coastal flooding: High Tides, Coastal Erosion, Storm surges
Causes for flooding in cities: Heavy Rain ( Run off from drainage systems),
Describe a situation in which a levee reduced flood damage and one in which it increases flood damage
A Levee is when you choose to build walls around your house via soil so they are protected from flooding however if they fail and the water is higher then the levee it can cause rapid and worst flooding since it is a deep space.
Explain what can cause flooding to occur on a day it is not raining.
Flooding can occur due to poor drain systems, high tides, storm surges.
Energy VS Power
Energy: Ability to do work
Energy Units: Joules, Quads, Kilowatt
Power: Rate of energy production or consumption ( Energy / Time)
Power Units: Watt, ( J/S)
What are the 4 Energy system components?
Energy Resources( Primary) - Energy forms that exist in nature (coal,Oil)
Energy Currencies ( Secondary energy)- Created from primary energy to provide useful services ( Electricity, gasoline)
Energy Services- Things people wants/need ( Heating, lighting)
Energy Storage; Enables us to use Energy at a later time ( Batteries)
Energy Efficiency
Def: The same or better service using less energy
Conversion efficiency: how well energy is converted from one form to another ( Useful energy output/ energy input)
Energy Stocks and Flows
We (US)are mostly using natural gas and oil for our energy compared to before when they largely used wood and coal. Globaly we are using all 3 ( Coal, oil and natural gas)
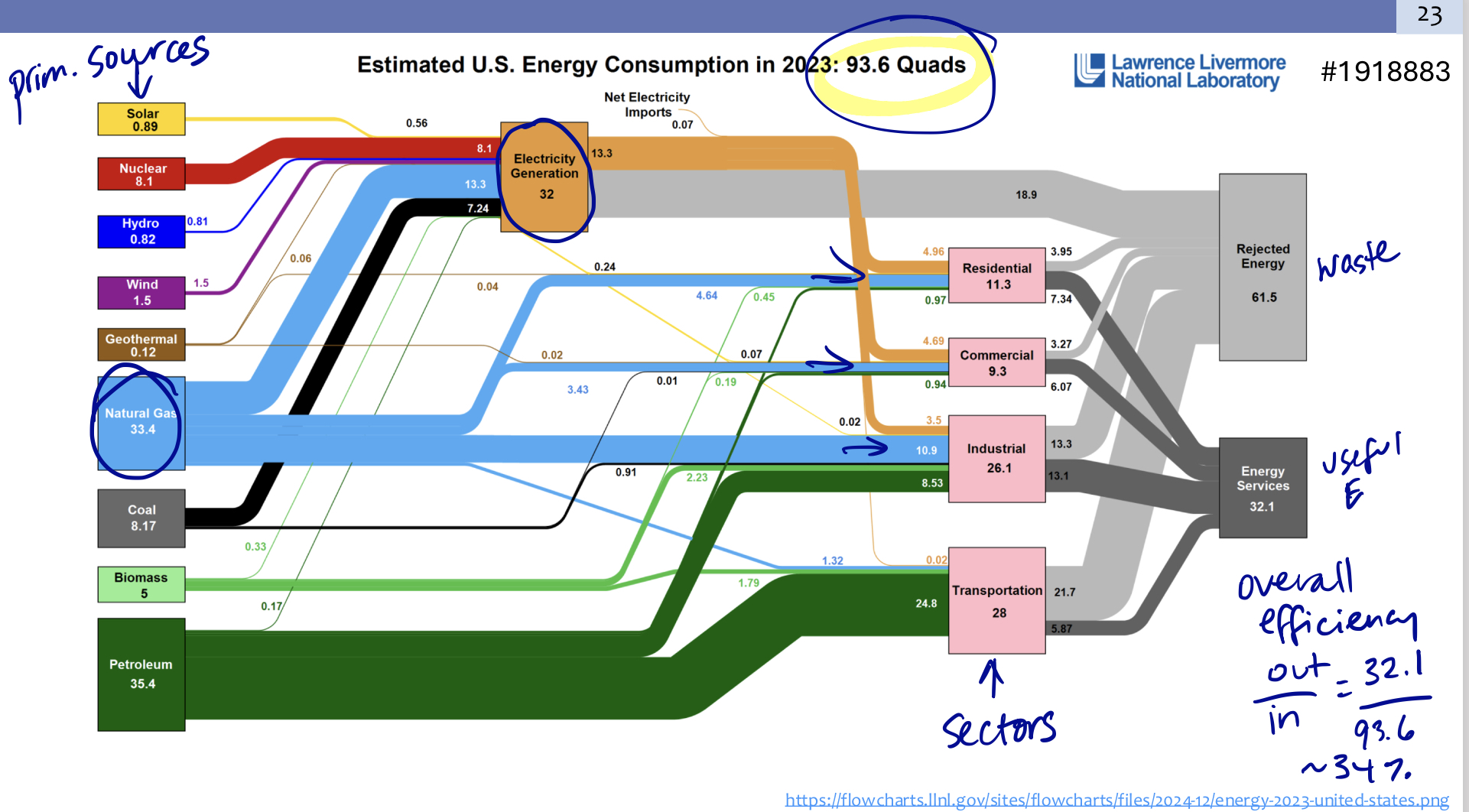
What is the estimated US Energy consumption and what what are the different sectors.
93.6 Quads, ( Residencial, Commercial, Industrial, Transportation)
What makes an energy source ideal?
Accessible, Abudant, Affordable, Secure, Clean and Just
Energy Density
Def: the amount of energy that can be stored or released per unit of mass or volume
Units; Million joules/ L 9 Per volume) or Million j/kg ( Per mass)
What is Coal?
How is it found?
Where is it found?
How do we use it?
What are its advantages?
Disadvantages?
Coal is made from the remains of plants that accumilate in wetlands or swamps and over time the material gets buried and the pressure produces coal
Finding coal is found based on location
We deep mine or soft mind if we are closer to the surface
We use it to generate electricity
It is cheap
Enviromental pollution
Are fossil fuels a larger part of the mix for total ( Primary) energy yuse or for electricity generation?
They are largely use for electricity generation because we mostly use natural gas and oil seeing as it has less enviromental impact
Interpret the Sankey diagram
Since coal is made from a biological material ( biomass) why is it not considered a renewable resource?
Since coal is made from plant remains that take millions of years it exceeds human lifespans making it a non renewable source
Hydropower
How does Hydropower generate electricity?
Dam blockes river to create river to create a reservoir and control flow through turbines
As water pins turbines inside of the dam they generate electricity
Wind Power
Wind turns the turbine and generates electricity
Solar Power
Through solar panels the suns energy is converted to electricity
Geothermal for space heating and cooling
Geothermal for Electricity
Underground pipes absorb energy from the ground and run it through a heat exchanger. This can be done all around the world
One works in areas with very high subsurface temperatures due to local geology
Minor Technologies
Concentrated Solar thermal- The use of mirrors reflecting sunlight to create heat which create hot steam that is turned to electricity
Tides, Waves and Moving water
What are the advantages of using renewable energy technology?
Minimal Greenhouse gas emmsions
Minimal Health Impacts
Low to minimal water use
Affordable
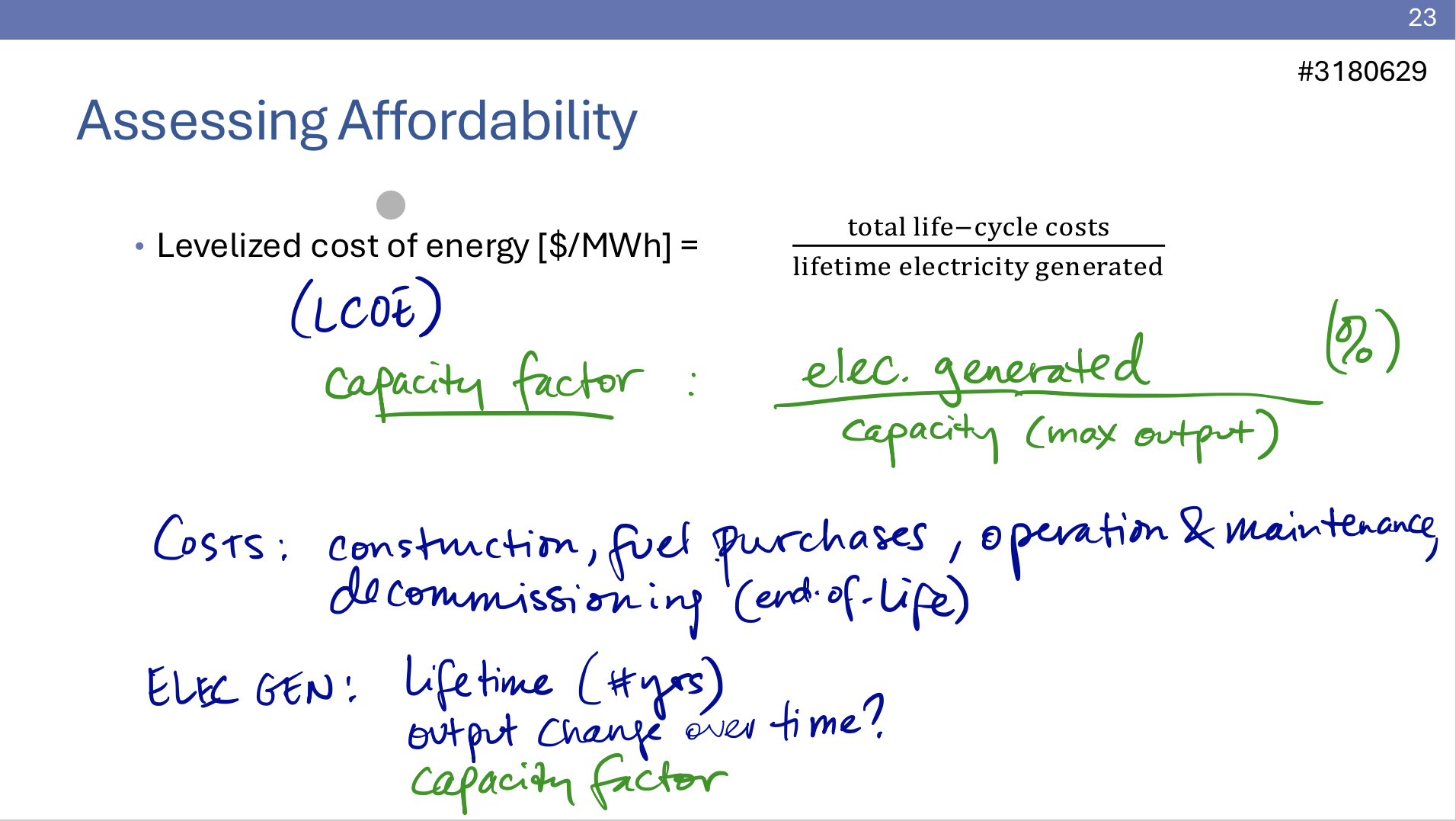
Assessing Affordability for renewable energy technology
Levelized Cost of Energy= ( Total Life- Cycle cost)/ ( lifetime electricity generated)
Capacity factor : (Electricity Generated/ Capacity
Challenges of Renewables
Storage
Land
Minerals
Speed and Scale