Topic 3 - Modelling
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Conceptual Modelling
originates from the mind --> main purpose is to outline the principles, processes and basic functions of a design/system
What is Conceptual Modelling used for?
communicate new ideas unfamiliar to people --> doesnt contain a lot of detail of how the product works --> more focused on introducing a new method of thinking
What do conceptual models have?
Contain all information required to describe a potential design solution.
Simulate the physicality of the design, functional features, performance, aesthetics.
Allow designers to get a feel for how well the design meets the original design brief, specifications and user needs.
Planning and communication (conceptual models)
Eg: MRT Map --> meant for clients/investors/building team --> helps them understand the layout
Mind mapping/brainstorming (conceptual models)
meant for the design team, yourself and other individuals --> showcases the concepts of the design
CAD visualisation (conceptual models)
meant for clients/buyers/investors --> visual representation of the final product
Conceptual modeling tools and skills
presentations
graphs/charts
diagrams
concept sketches
sketches to explain function
physical models to explain function/use
Advantages (conceptual models)
allows you to be creative + innovative with the design (w/o the restraints of technology)
save time in the design cycle --> no false leads
Client input into developing models
Testing
examines the product requirements
Disadvantages (conceptual models)
Performance --> models may not be representative of final product
Functionality --> models are not always able to replicate the product in use
Predictions --> model may not provide indications of the final product (materials, performance, interaction with the environment)
Tangible
perceptible by touch
Intangible
unable to be touched or grasped; not having physical presence
Graphical Modelling
used to communicate design ideas --> can be 3D or 2D --> can be orthographical, rendered, produced by hand/digitally)
What is it used for? (Graphical Modelling)
- Preview Ideas
- prove concepts
- develop iterations/improvements
- detect errors
- ergonomic assessments
- make client presentation
2D and 3D Graphical Models
the easy nature of sketching provides the designer with great flexibility (only paper + pencil needed)
3D sketches
- provides designer with a sense of form
- may need specific training and knowledge to produce (esp w/ CAD ones)
- easily communicate ideas with other stakeholders
2D sketches
allows designers to isolate details and structural features
Annotations
accompany drawings to improve communication of information
What do annotations do?
helps record fleeting thoughts, clarify obscure details, note alternatives, and record thoughts about particular features
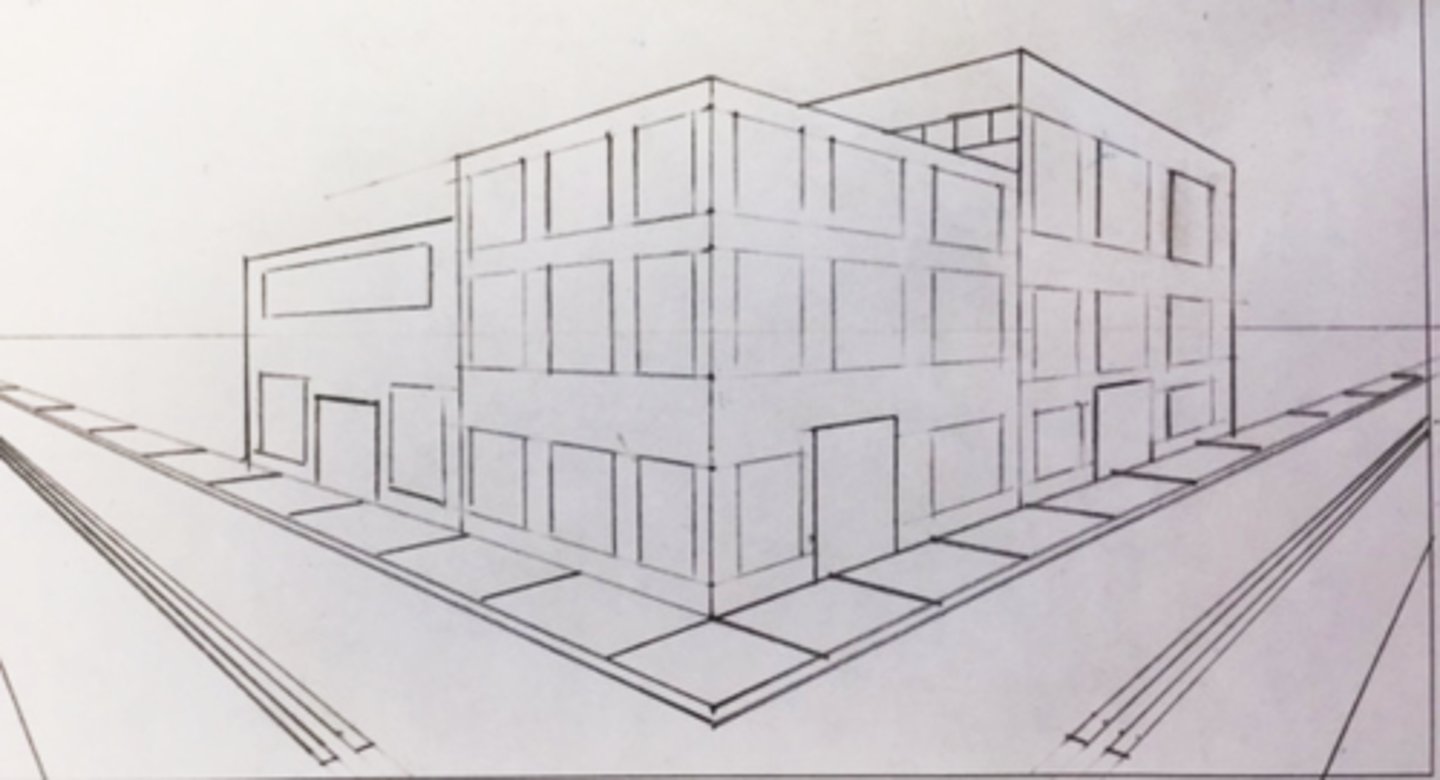
Perspective drawing
creates an illusion that the drawn objects size gets smaller as it retreats from the fixed viewpoint --> can be one-point, two-point, or three-point --> objects get smaller the further it is from the viewer
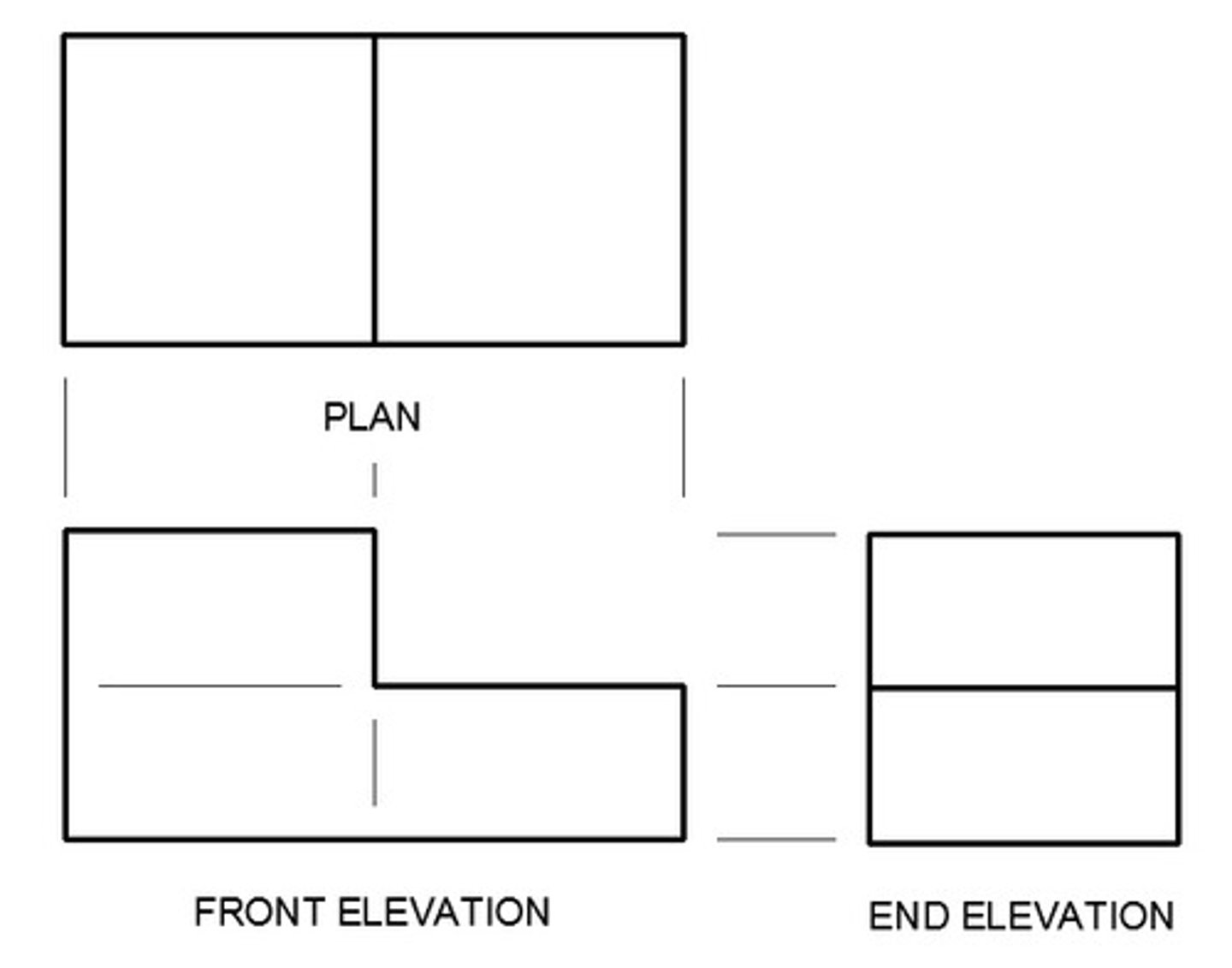
Projection/Orthographic Drawings
uses "line of sight" that are always perpendicular to the viewing plane --> produces a projected image --> forms of drawings are named depending on the positioning of the object
Scale Drawings
constructed to a specific ratio relative to the actual size of the product/space --> Commonly used ratios (reduction) are 1:5, 1:10, 1:20, 1:50, 1:100, 1:200, 1:500, 1:1000, 1:2000 and 1:5000.
Sketching
quickly shows ideas, modifies concepts, allows communication with outside and inside design teams at the earliest stage of the design process
Transitional Period (Between sketching and formal drawings)
Isometric and perspective drawings are used (late stage design process) --> used to communicate near complete design proposals to clients or marketing staff --> close to what the final design will look like
Formal Drawings
Technical drawing styles (engineering/orthographic) are used in the manufacturing stage to define the actual size, fit, finish and appearance of the final product --> Conveys significantly more information
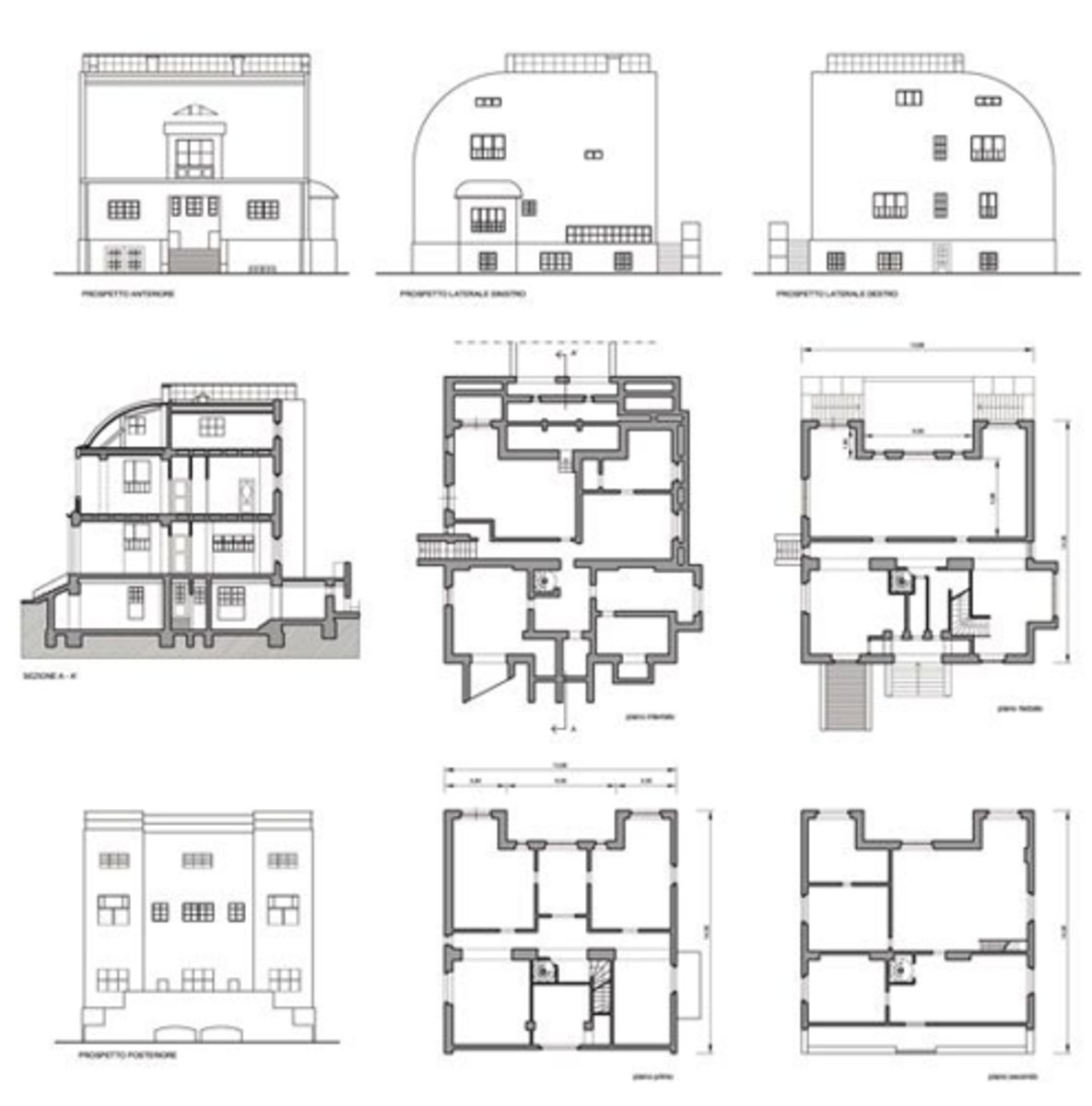
Parts and Assembly Drawings (what u get from fusion)
orthographic projections that communicate the functional detail of the design by indicating the size + relative position of all parts --> has a "parts list" --> can also be an exploded isometric
Physical Modelling
Three-dimensional, tangible representation of a design/system

What is Physical Modelling used for?
further development, analysis, and evaluation of a product
Purposes of Physical Modelling
makes it easier for the client to understand the product + get feedback on the aesthetics --> potential users sn also test the product in order to offer feedback regarding size, ergonomics, and functions
How can Physical Modelling be done/created?
usually a cheaper material that replicates the properties of the (potential) final material is used
Examples of materials for Physical Modelling
- Cardboard
- balsa wood
- acrylic
- high density polyurethane (HDP)
- moulding silicone
- urethane
- clay
- polymorph
Scale Modelling
version of the product that is bigger/smaller --> all dimensions have been ratioed + accurately modeled
Why is Scale Modelling used?
quick + inexpensive way for designers to visualise space, considering the relationship between parts of a product
Positives of Scale Modelling
gives a good understanding of the products --> flexible to our needs --> speeds up process (cheaper, faster to make)
Full Size models
model that is a proper representation of the actual dimensions
Aesthetic prototypes/models
may be a physical/CAD model --> utilised to access the appearance/visual appeal of a design --> looks not function
mock-up model
not functional, showcases the different parts --> typically full-sized

mock-up vs. functional prototype
Mock-up:
- full scale
- doesnt use the final materials
- produced to find design flaws (at their earliest stages)
- doesnt have functionality
- there can be multiple
Functional Prototype:
- includes functional aspects
- looks + feels like a real product --> one-off production
- changes are still able to be made
- marketing departments can start advertising campaigns, showcasing the product (pre-manufacture)
Instrumented Models
mainly used for testing --> provides quantitative data for analysis --> typically full-sized + utilises similar products as the final --> cant give user feedback

What do Instrumented Models do?
provides verification (checks that the idea is correct) and validity (checks that the function is correct)
example of Instrumented Models (Keyboard)
records the actions of the users and provides data on how often keys are used and number of errors the user makes (numbers of times the backspace is pressed)
Advantages (Instrumented Models)
-designers/manufacturers can test the concepts in near to real scenarios
- designers/manufacturers can present their ideas --> easily understood by users/clients
- testing the product in realistic scenarios --> quantitative + qualitative data
- can test + get feedback on ergonomics
- can be utilised to predict behaviours
Disadvantages (Instrumented Models)
- Can take time and be very expensive to set up
- certain skills may be needed to produce the correct type of model
- users would have to interact with the model in-person --> travelling issues
- may not work like the final product (esp if final is complex)
- may not be made of the same material as the final product
CAD
the generation, creation and analysis of a design/system using computer software
2D CAD
- operates on an x and y axis --> flat drawing
- design constructed using basic shapes
- made using softwares such as illustrator and fusion 360 (sketch mode)
- laser cutter
why is 2D CAD used?
helps you understand the measurements of the product --> comes second to 3D model
3D CAD
- produces solid/surface representations of objects that can be further manipulated
- material properties allows for virtual testing of physical + engineering properties
- can be used to make aesthetic focused models
- object can be viewed from all angles
- 3D printer + made on an x,y and z axis (fusion 350/solid works)
Surface Models
More about the shape and form of the OUTSIDE of the model --> what it looks like --> aim is to get as realistic as possible
Solid Models
Contains most of the geometric (weight, thickness) info of all CAD models --> have detailed EXTERIORs and INTERIORS --> format used for rapid prototyping
Bottom-up modelling
creates each part independently and then assembled later
top-down modelling
starts with the "outer shell" then does reverse engineering --> makes the parts so that they FIT the outer shell
What is the purpose of CAD?
- communicate products to stakeholders, users, clients, and design team
- functional analysis (design team)
- shows how the product is assembled (manufactured)
- test aesthetics
- basically data collection so that you can improve the overall product
- CAD to CAM
Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
any type of testing that a CAD model goes through and is evaluated based on the results --> pressure test, thermal dynamics --> used to predict IRL situations --> diminishes the need for multiple physical models
Virtual Prototyping
software driven modelling process that simulates products + environments by mimicking IRL behaviours/situations --> uses solid + surface models
what is Virtual Prototyping used for?
used in development, testing and assessments of products
CAD modelling methods
motion capturing
animation
virtual reality (VR)
digital humans
Motion Capturing
captures human motions, useful to test prototypes
Animations
used to understand floor plan/space --> work envelope --> good to see moving parts (understand how they work) --> design the space effectively to meet expectations of manufacturers, clients, or users
virtual reality (VR)
a virtual space --> cannot change the environment (its static) --> used to explore environments --> people cant interact, only look around --> needs HAPTIC TECHNOLOGY! to do this --> allows user to manipulate the environment

haptic technology
enables systems to interact with users through the sense of touch --> creates physical sensations in digital environments, such as vibrations, motions, or temperature changes, allowing users to navigate digital interfaces more engagingly

digital humans
digital version of anthropometric data --> can simulate if a product can suit a human ergonomically --> can find issues within the design that could endanger an actual person

Data modelling
the organisation of data within a computer/program --> organised through a variety of databases, models, or templates
What is Data modelling used for?
allows users to access info in different ways --> info includes data records that have no relationships w each other --> flat file takes up less space than hierarchical models
statistical modelling
the use of computer programs to collect, combine and present statistics --> common use can be seen through weather/climate predictions
Advantages of CAD
- can be done anytime, anywhere --> feedback can also be given at any time (no travelling needed)
- less resources used --> only need laptops and CAD software (faster --> can find mistakes and change them immediately)
- can create both 2D and 3D representations easily
Disadvantages of CAD
- complicated (learnability) --> steep learning curve + software is always updating --> skills need to evolve as the app does
- software can be expensive
Rapid Prototyping
production of a physical model of a design using 3D CAD data
Manufacturing Techniques
Additive
Subtractive
Shaping
Joining
additive
adds parts of the design bit by bit to create the final design

subtractive
taking a big lump of something/a material and removing it bit by bit to create the final design. Eg. Clay/Roman statues
Shaping
the use of molds/moulds
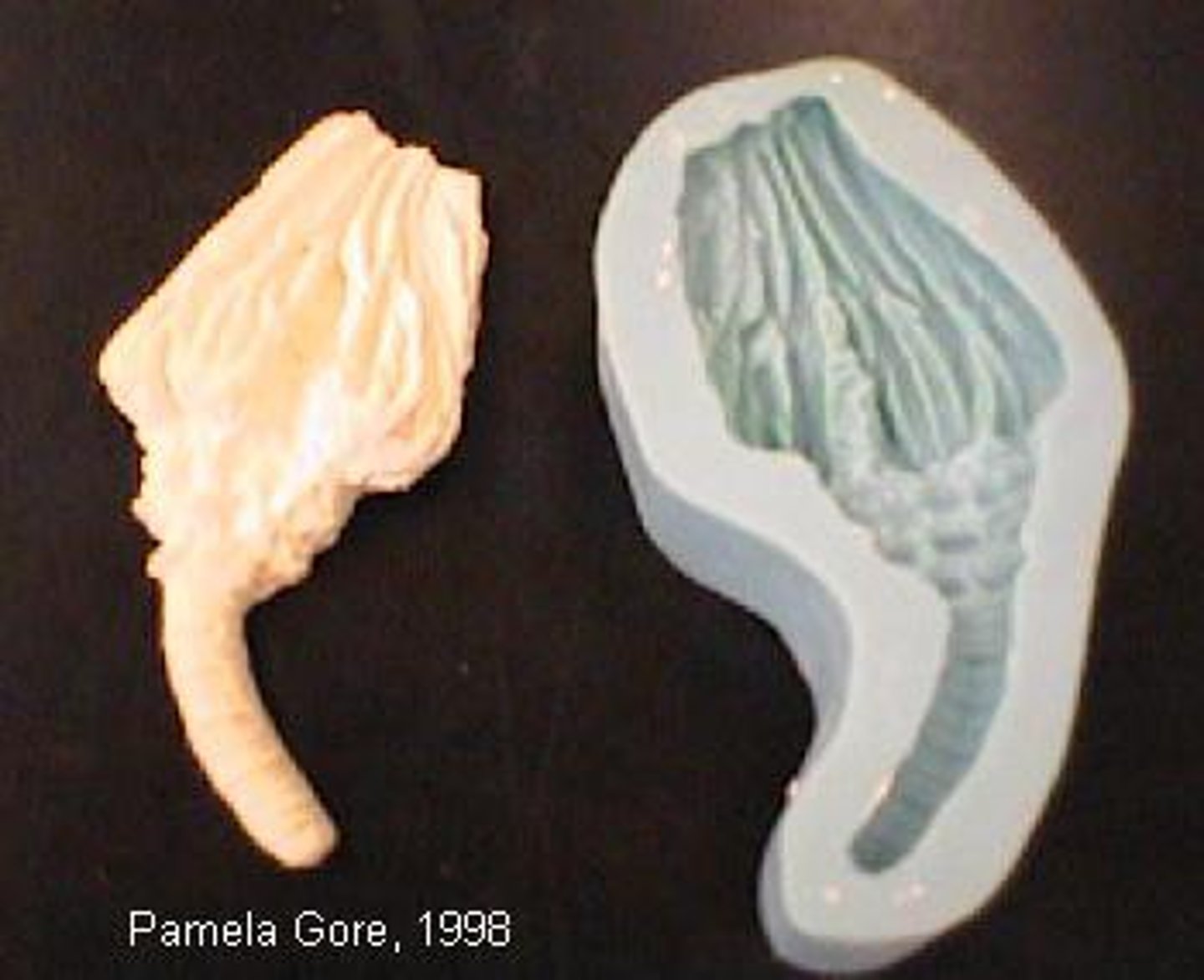
joining
screws, joining techniques/methods
Types of Rapid Prototyping (all are 3D printing)
Stereolithography (SLA)
Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM)
Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Stereolithography (SLA)
curing layers of photopolymer (light sensitive liquid plastic) to make a part of a product --> needs finishing + supports
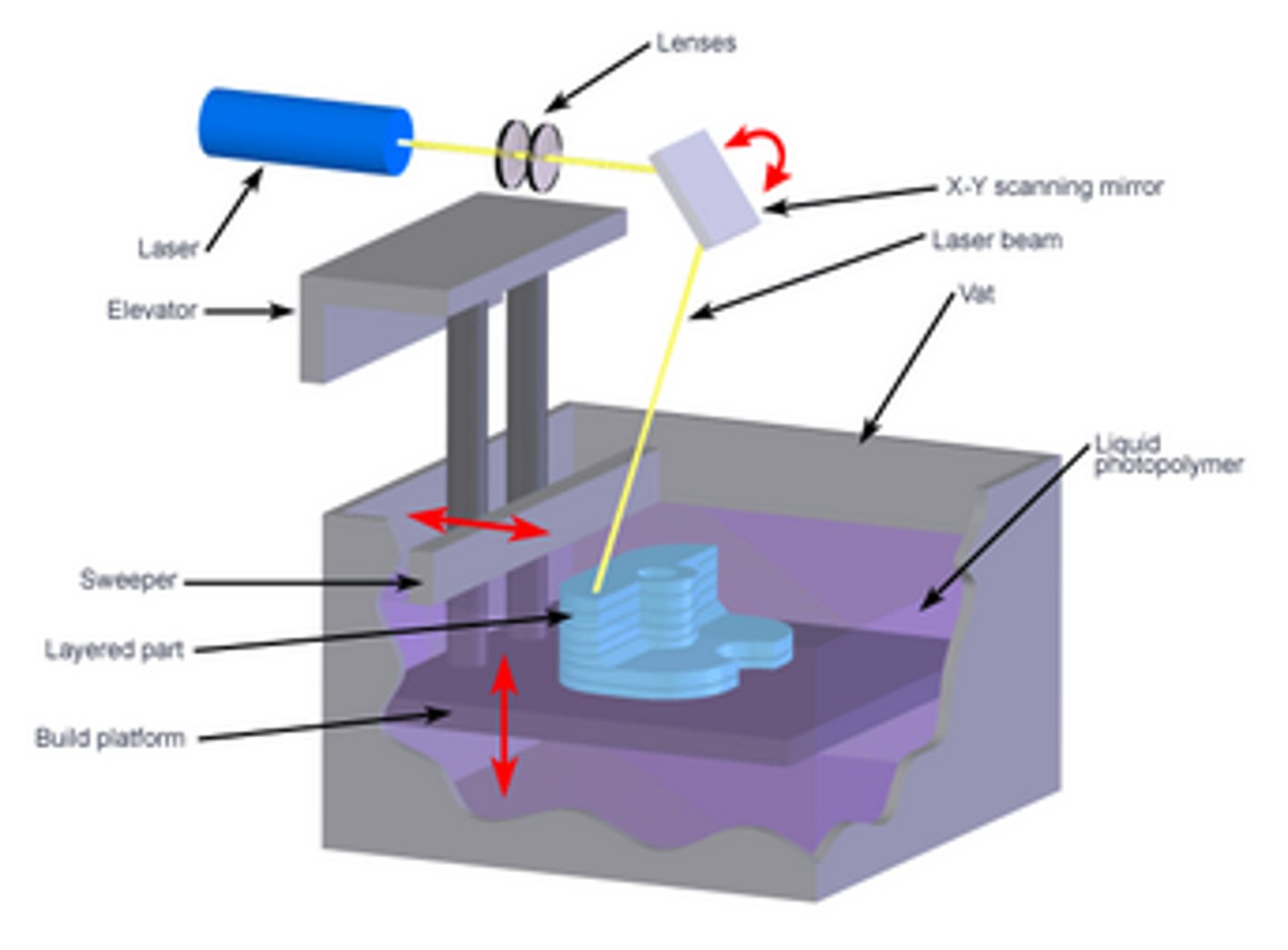
Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM)
utilises adhesive coated paper, plastic, metal or thin pieces of wood and laminates as a 3D printing medium --> sheets of materials are glued together, layer by layer and cut into using a knife/laser cutting --> needs minimal finishing but need support
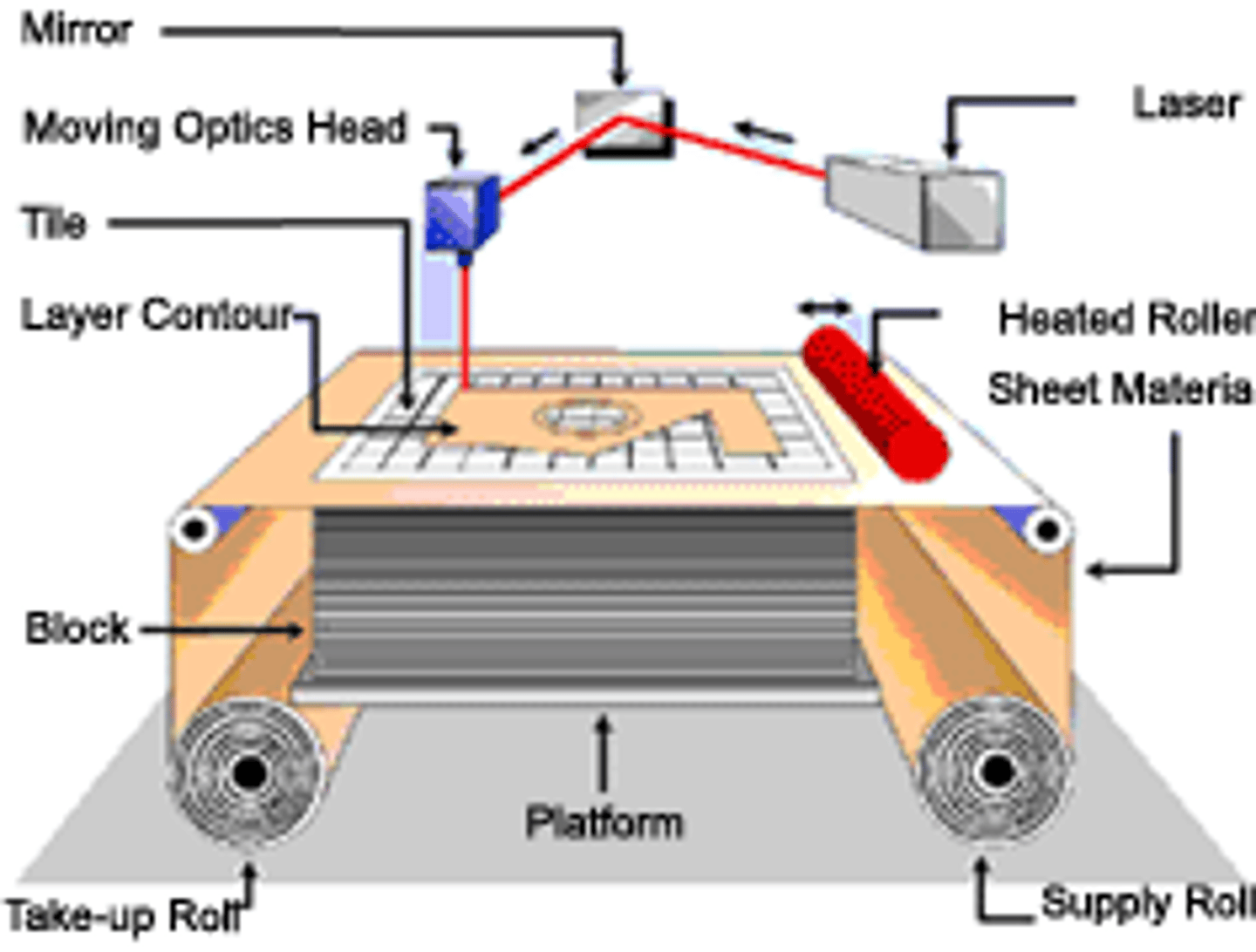
Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM)
additive manufacturing --> uses filaments (needs to be thermoplastics) + layering --> filament is hard and then warmed up to be malleable --> needs finishing + supports (its the type of 3D printing used in our school)
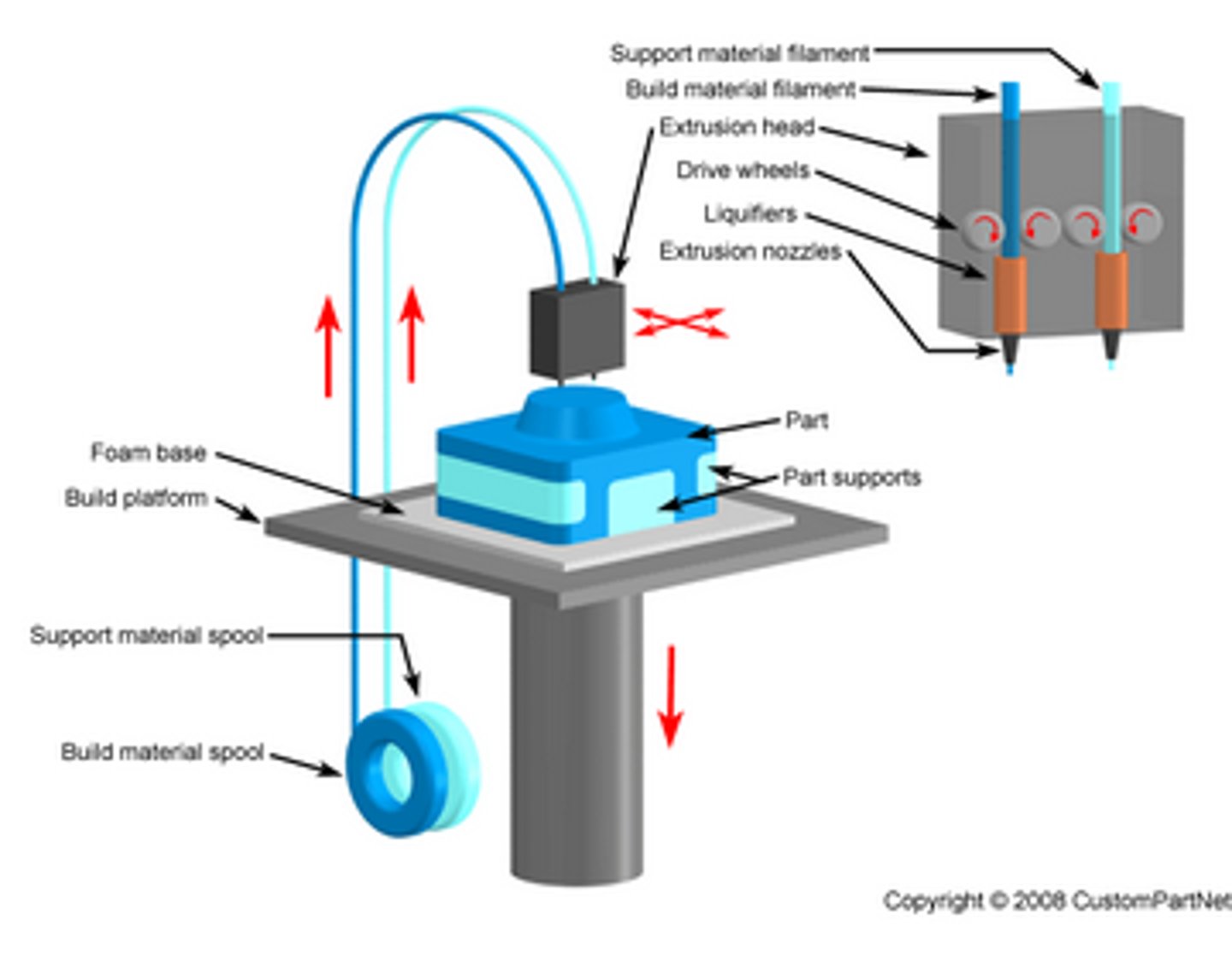
Types of thermoplastics for Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM)
ABS, PLA, TPU, PETG
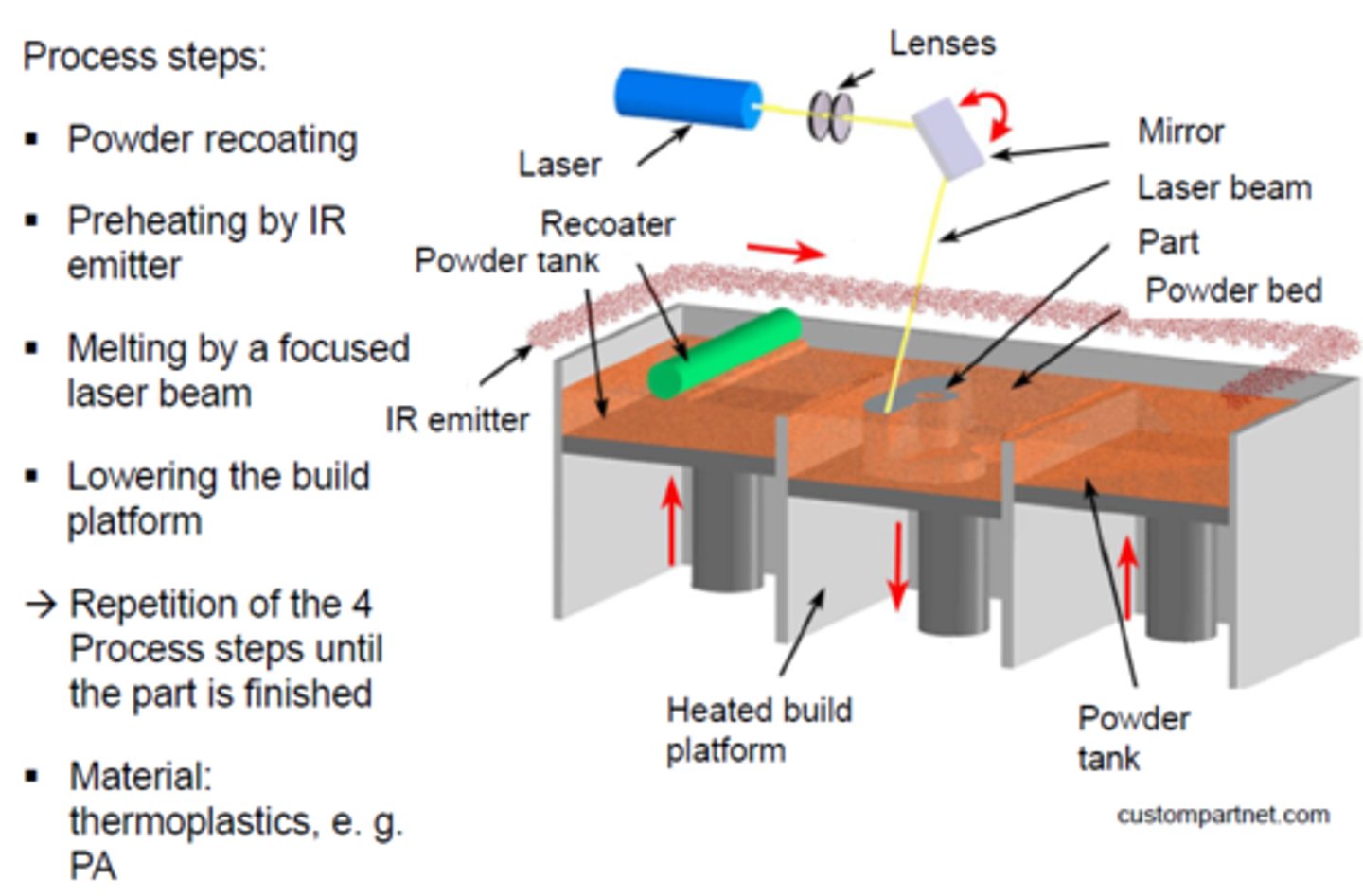
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
additive process --> high power lasers are used to bind powered material together into a solid structure --> doesnt needs supports but needs minimal finishing
Advantages of Rapid Prototyping
- cost --> a complicated model can be made at a low cost)
- speed --> makes a complicated model really fast --> cuts down development time
- staffing --> only need one person of staff for the product (they js need to draw the CAD)
- No physical effort
- more accurate dimensions if the CAD is good
Disadvantages of Rapid Prototyping
- quality --> model may not be able to represent the quality of real products
- fixed costs --> machinery can be expensive to buy
- range of materials --> not all materials can be rapid prototyped