311 Midterm 1
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
75 vocabulary flashcards covering key terms, people, movements, works, and institutions from Renaissance to Neoclassicism.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What was the primary function of guilds during the Renaissance for craftspeople?
served as associations of craftspeople that protected members’ economic interests and regulated their respective trades
Apothecaries
providers of pigments and materials to artists, linked to the Physicians and Pharmacists guilds
Apprentices/master relationships
> apprentices have to mimic the style of the master
> master reveals all their techniques in return
Newton
> Isaac Newton, 1687 treatise established gravitation and the three laws of motion
> influences Enlightenment
Louis XIV
> 1600s French king, “Sun King”
> Palace of Versailles
> major arts patron who centralized power
> established Royal Academy of Painting and Sculpture
Palace at Versailles
> Louis XIV royal palace - transformed hunting lodge
> he was very paranoid, forced everyone under one roof to consolidate power and monitor everything
> L’etat c’est moi - all art there was about state, reflecting power of king
Royal Academy of Painting and Sculpture (France)
> 1648 institution prioritizing figure drawing
> studied from nude models and classical sculptures
> painting only in private studios to promote “intellectual” style
L’état c’est moi
Louis XIV’s declaration meaning “I am the state.”
Prix de Rome
> prestigious art competition
> winners get to go to academy in Rome to live, work, study for 4 years
Puritanism
> colonial American ethos valuing modesty, influenced attitudes toward art and dress (restrictions to clothing)
> believed indulgences led to hell, but rich thought piety and prosperity could be compatible
Limner
early American portrait painter who relied on engravings and word-of-mouth
Grand Manner
portrait style that fills the canvas and signals the sitter’s status with class markers (clothes, colors, pets)
History Painting
genre depicting historical or mythological scenes with moral messages
Portrait Painting
focused on the likeness and status of individuals
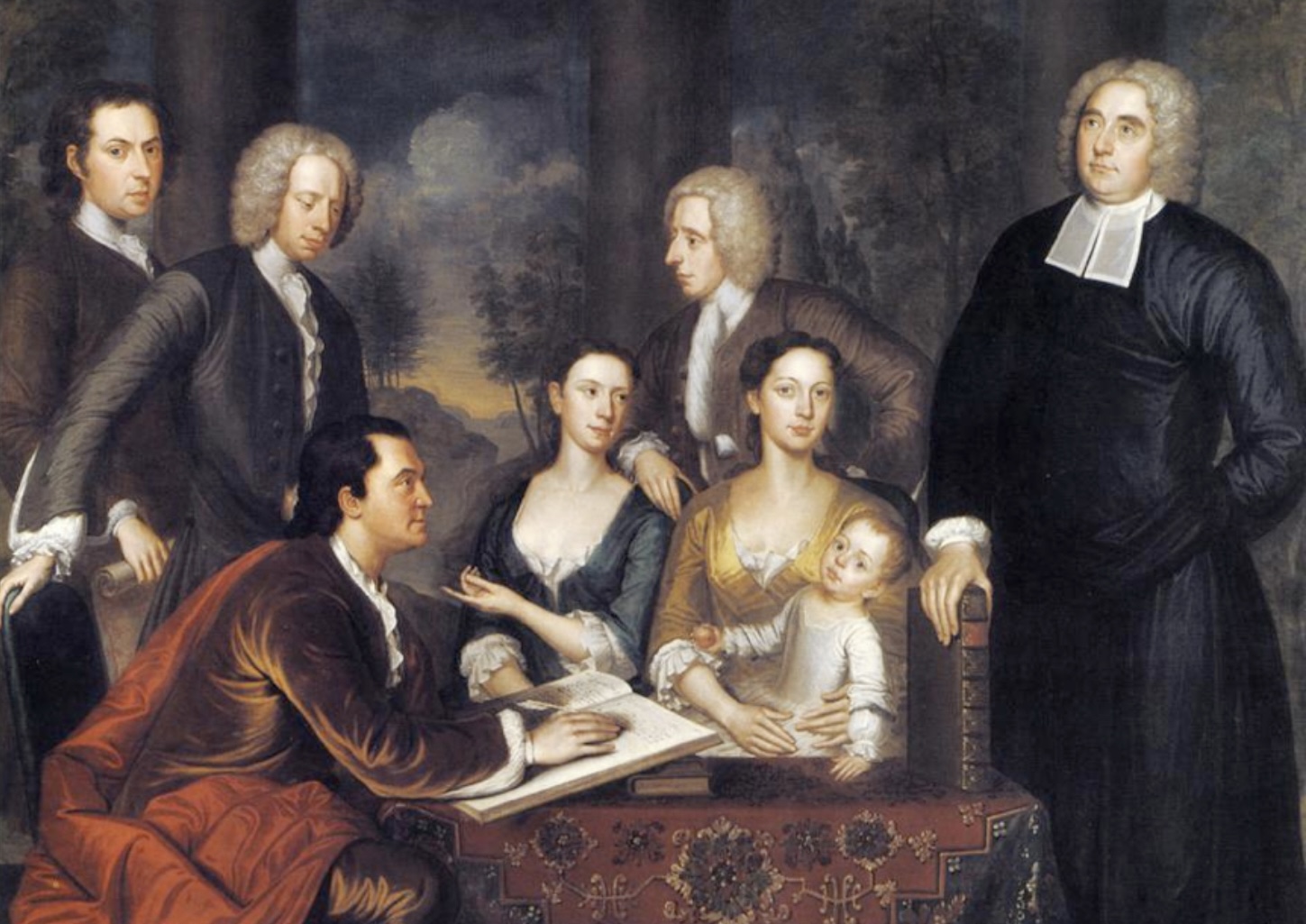

The Bermuda Group, 1729
John Smibert - group portrait in Boston
> Grand manner painting
> eight life-sized figures with Arcadian landscape
> “major aesthetic bombshell”
John Smibert
> American painter who imported European training and supplies to Boston
> top of his profession - competent painter
> brings copies of old master paintings
Prince Demah Barnes
> first African American slave painter who became a professional portraitist
> disrupts power dynamic of slave and the white (had to look directly at his master)
Joshua Johnston
> documented free African American professional painter, born slave but freed
> worked in Baltimore with abolitionist community; 80 works
> untrained “folk/naive” artist - decorative/utilitarian style
John Singleton Copley
> important colonial painter, moved to Europe
> started as portrait painter then moved to history painting
> provide for colonial elites, known for stagecrafts - “persuasive fiction”
> portrayed people as they are but clues to their status/hierarchy
> introduced to engravings and mezzotints from step father (artist)
> made his own anatomical drawings from medical books
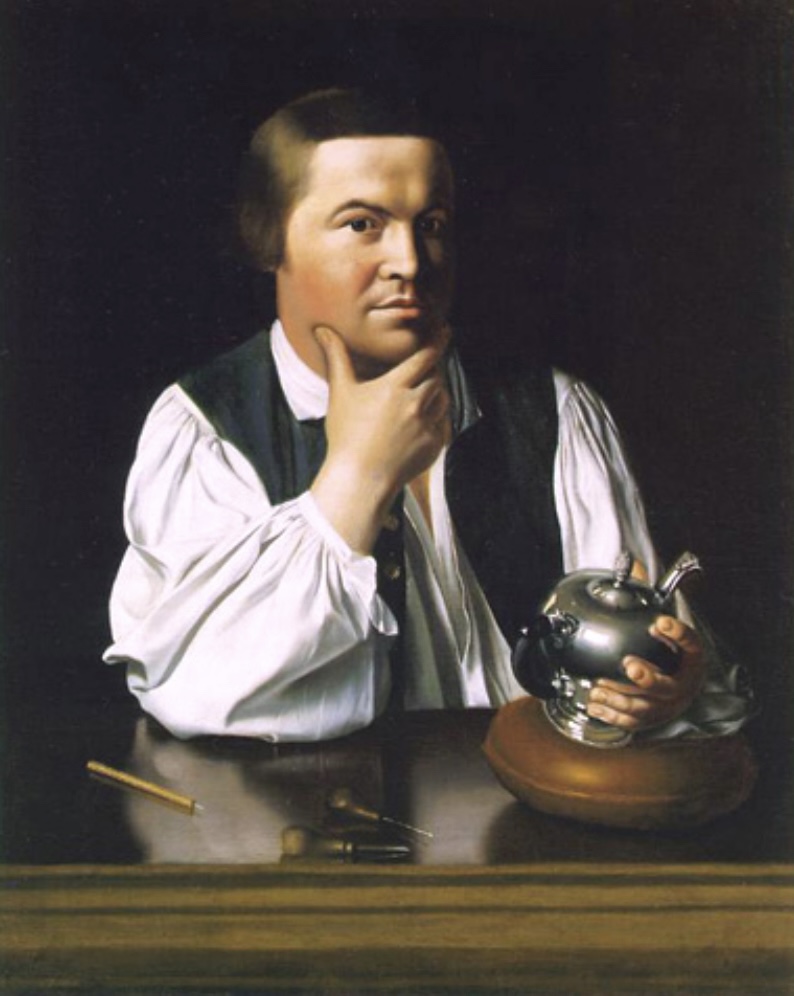

Paul Revere, 1768
John Singleton Copley
> political painting of a silversmith: Boston Tea Party and Stamp Tax
> subject of portraits; notable colonial figure.
> Copley usually stayed away from politics

Death of General Wolfe, 1770
Benjamin West - history painting
> Seven Year War (French vs England) depicting Wolfe’s death in battle
> scene is romanticized, unlikely everyone would gather around him on battle field to watch him die)
> figures painted with contemporary clothing
> Iroquois scout painted to show painting nude
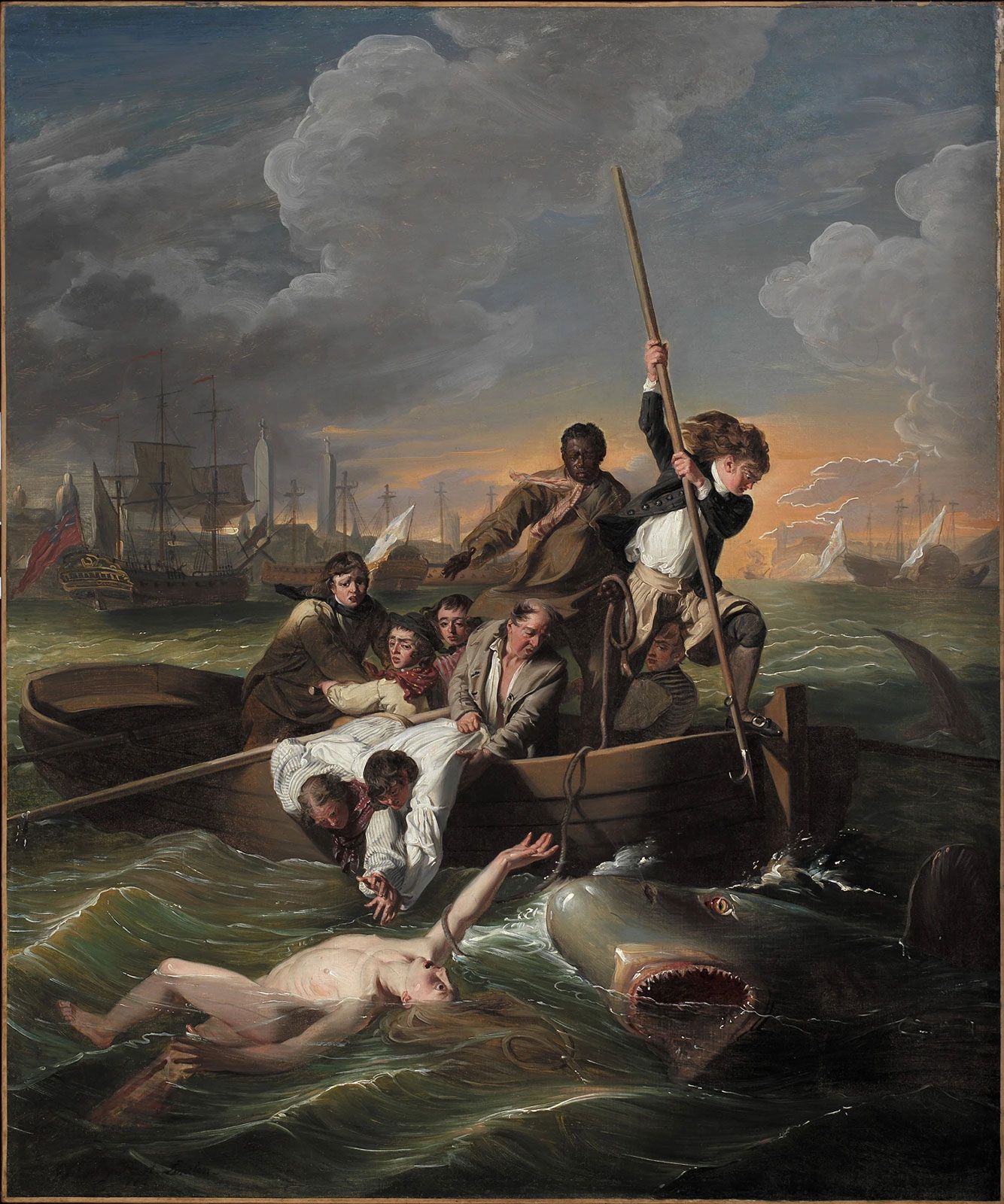

Watson and the Shark, 1778
John Singleton Copley - contemporary history painting
> shark attack, based on true story
> he faced new challenges: shark (he never saw a shark), water, numerous action figures (movement), nude
> minor historical event to great historical significance
> references to Raphael’s St George slaying the dragon
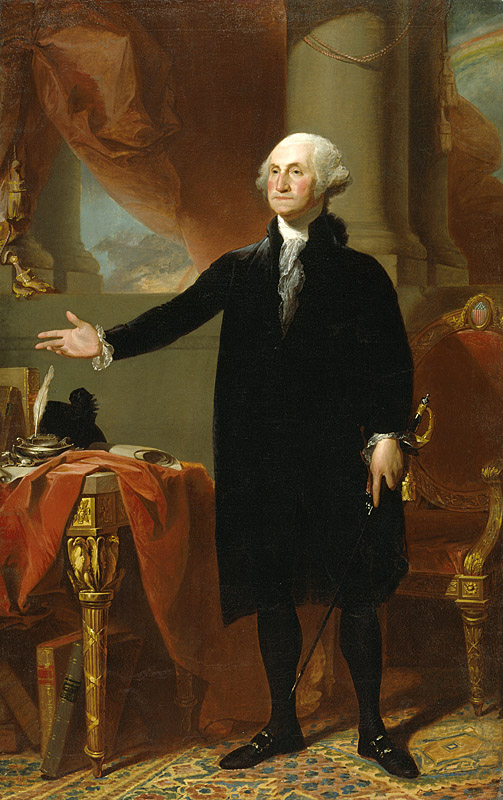

Lansdowne Portrait, 1796
Gilbert Stuart
> grand portrait of Washington in a state-like pose
> commissioned for Marquis (British subject) - British respected Washington
> Washington depicted as leader and president, not king/emperor
did not want to be seen as monarch
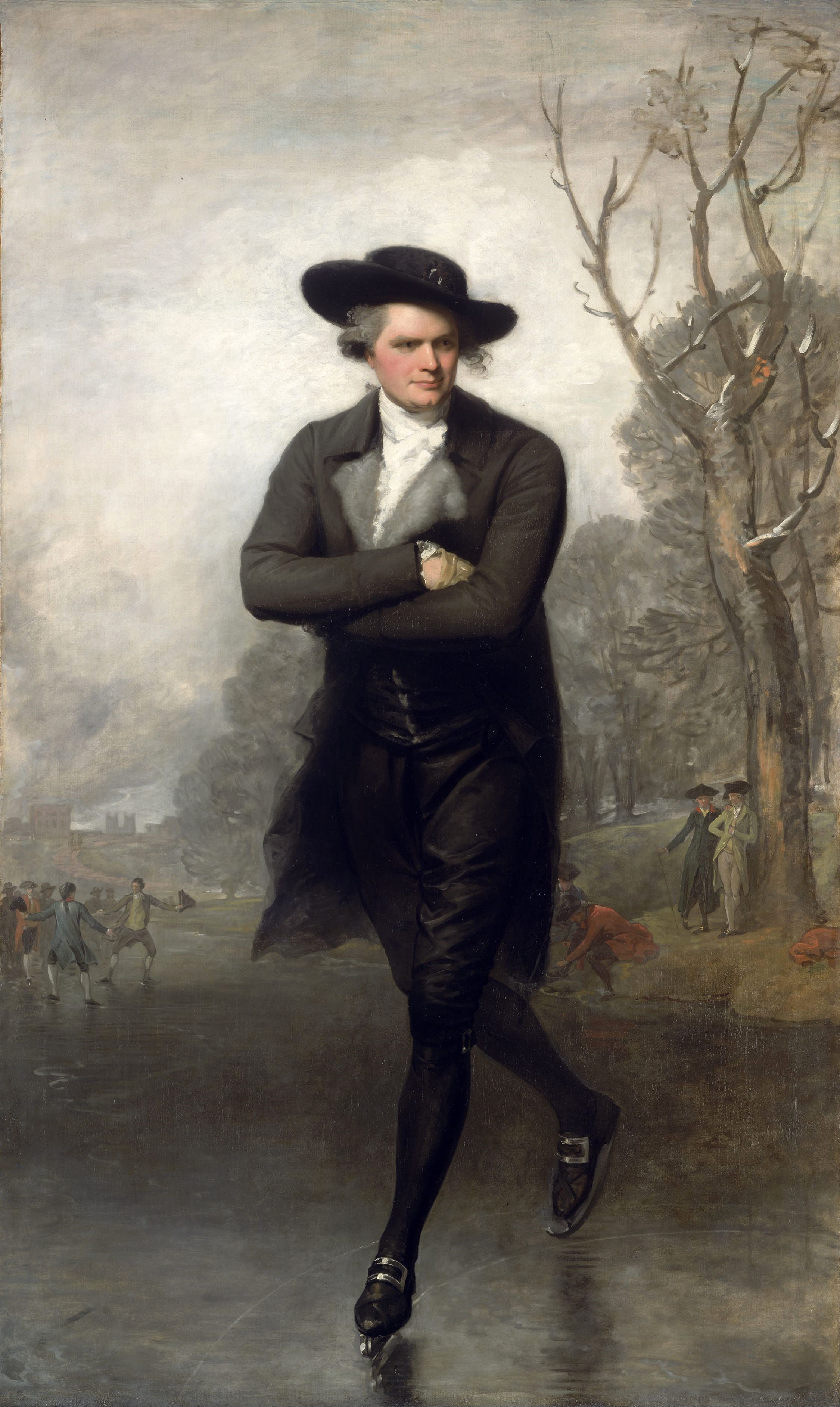

The Skater, 1782
Gilbert Stuart - Grand Manner portrait
> this launched his career in London
> created new category of figure painting
> couldn’t do full sized portraits
Gilbert Stuart
> American portraitist
> known as Washington painter
> not interested in history painting
> difficult personality; liked to spend $$, led him to debt and exiled from London and Dublin = goes back to America and becomes Washington’s painter
John Trumbull
> American painter known for large history canvases for the U.S. Capitol
> pupil of Benjamin West
> series on the Revolutionary war: 8 compositions, 4 large commissions to Capitol
Benjamin West
> American history painter who rose in Europe and became Royal Academy president
> friendship with King George III
> Neoclassical artist
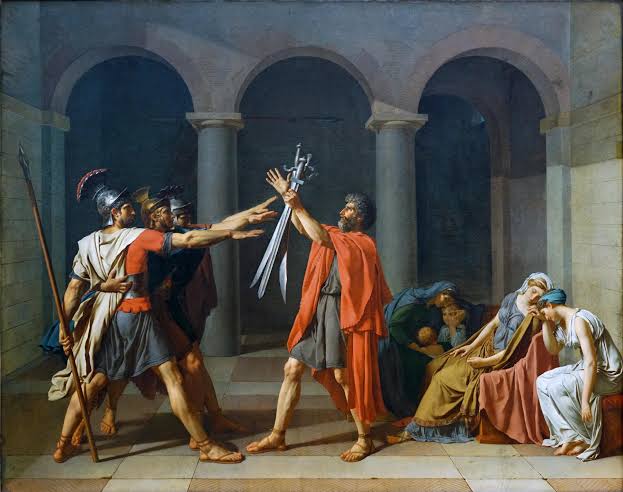

The Oath of the Horatii, 1784
Jacques Louis David
> Neoclassical history painting about civic virtue: devotion to state over family
> royal commission of devotion to king but David created this moment
> 3 bros fight to death, father in mid (symbolizes acceptance of fate with resolve), sis/wives sit behind
> 3 arches, 3 part story
> David depicts men as strong, intellectual and women as weak, emotional
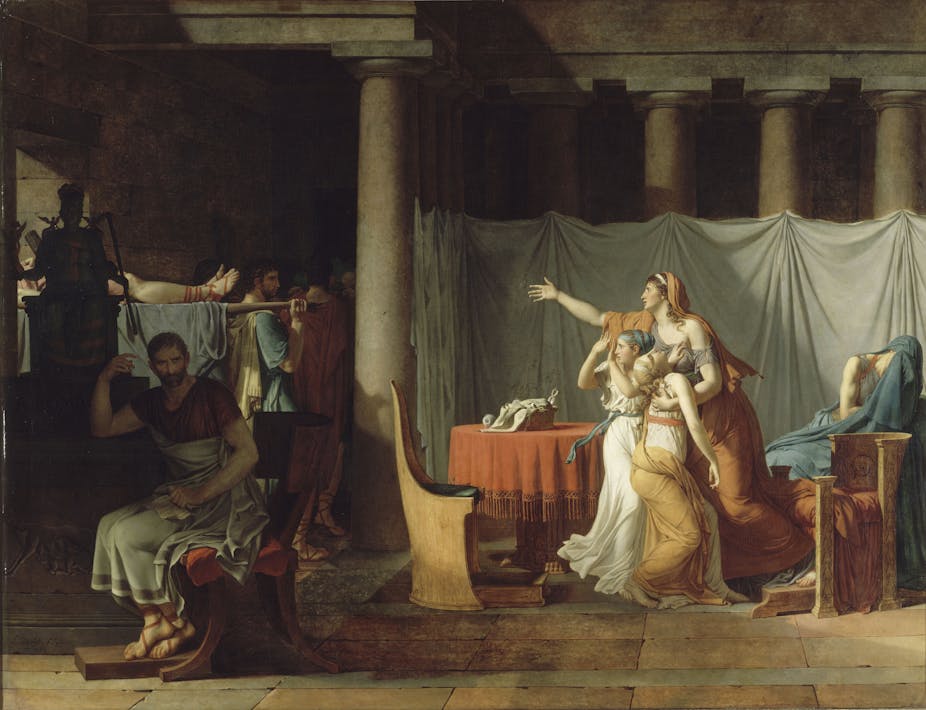

Brutus and the Bodies of his Sons, 1789
Jacques Louis David
> painting showing duty to the state over family
> Story: Brutus signs for execution of sons, sits with contemplation - state over family. tragedy seen in women
> changed subject to domestic aftermath; not historically accurate
> ironic because he is part of revolution
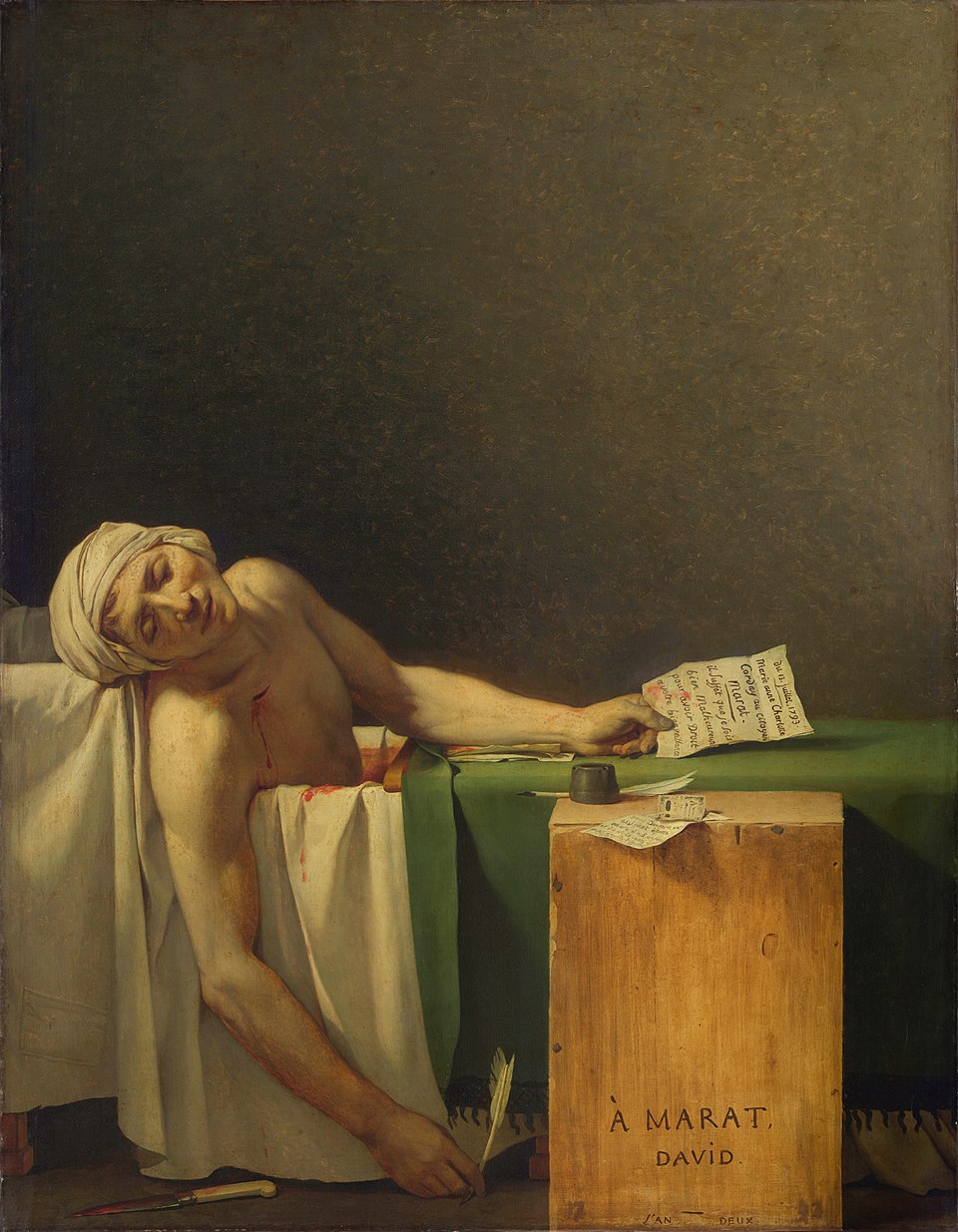

The Death of Marat
Jacques Louis David
> political martyrdom painting of the Revolution’s figure, Jean Paul Marat
> has skin condition, takes medicinal bath, he’s stabbed by Royalist
> sets David on path to become minister for propaganda for Revolution
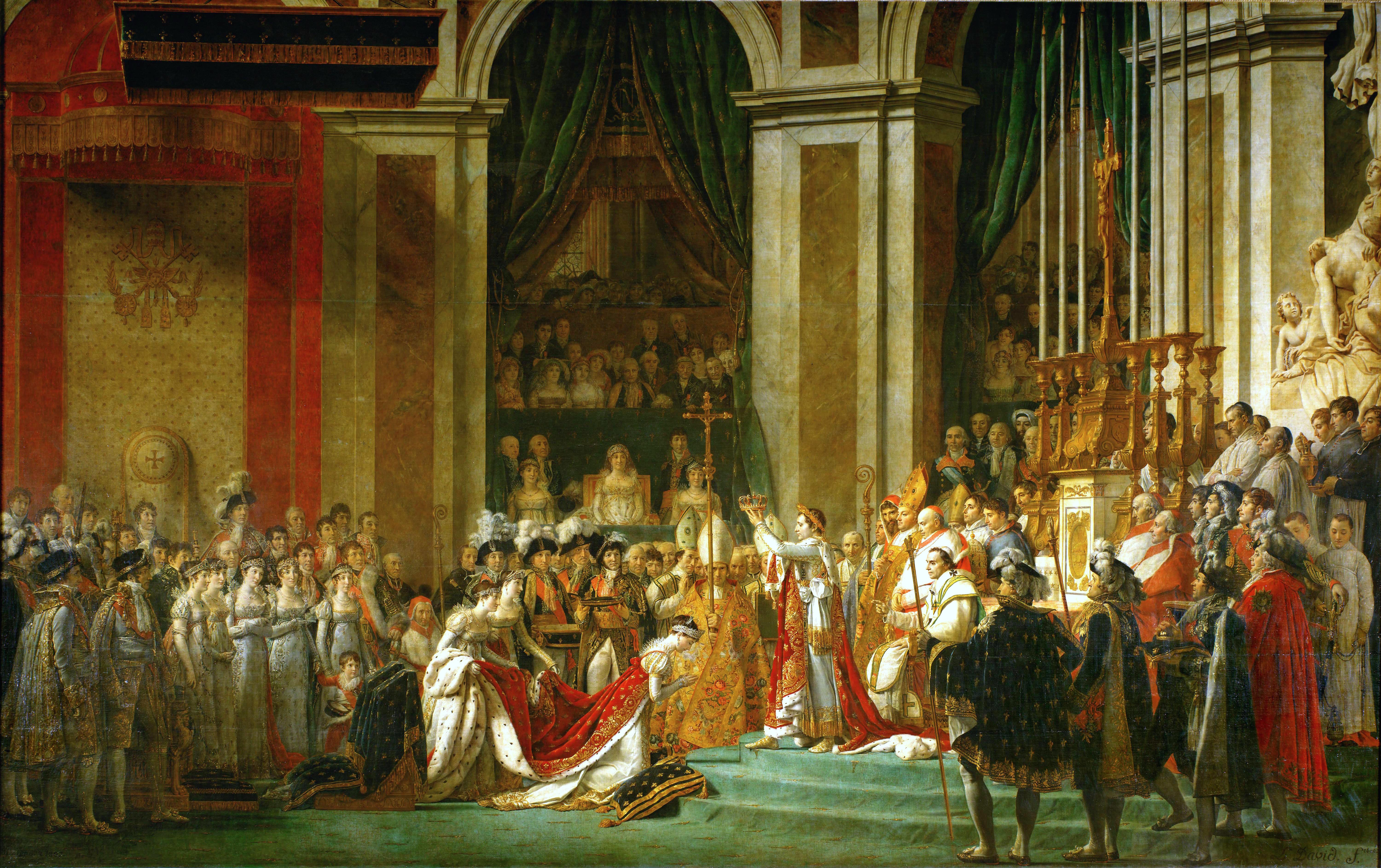

The Coronation of Napoleon, 1804
Jacques Louis David
> great propaganda piece depicting Napoleon’s coronation as emperor, not his coronation but his wife’s
> crowns his wife, Josephine, himself - declares himself higher than church
> painted his mother but she didn’t attend
> seen at Musee Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte
> French military leader and emperor who became a central subject of propaganda
> David, Ingres, Gros painted pieces of him
> looted art from other countries he invaded = stealing someone’s cutlure/history
Jean Auguste Dominique Ingres
> French Neoclassical painter known for portraits and elongated forms
> student of David
> wins Prix De Rome 1801, doesn’t go till 1806
> wants to be a history painter, flops after Napoleon is overthrown and goes back to portraits
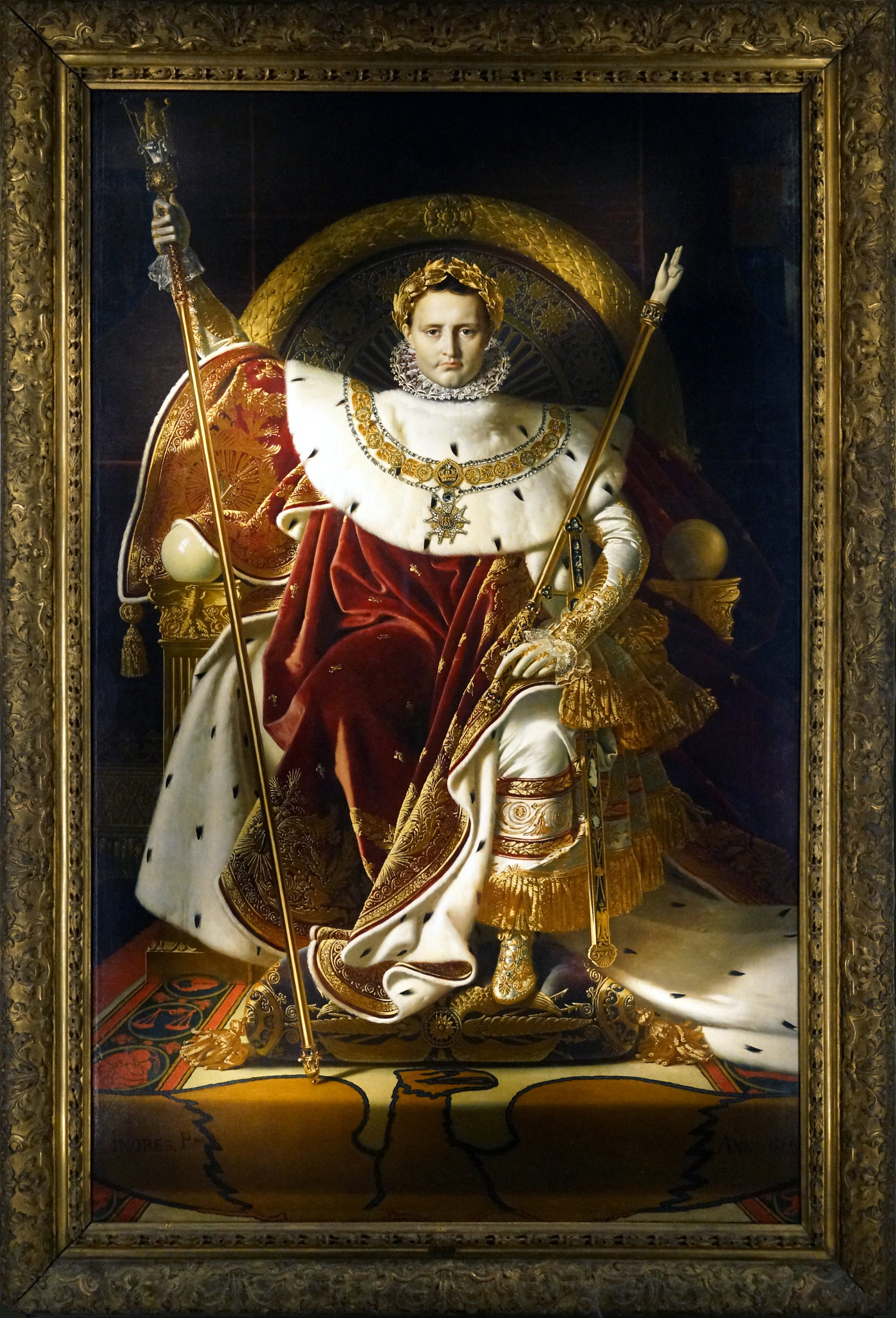

Bonaparte on the Imperial Throne, 1806
Jean Auguste Ingres
> painting portraying Napoleon as imperial ruler
> Napoleon stole from Van Eyck, Ghent Altarpiece
steals art in Europe for Musee Napoleon, Louvre
> creates halo in back, appears as divine ruler
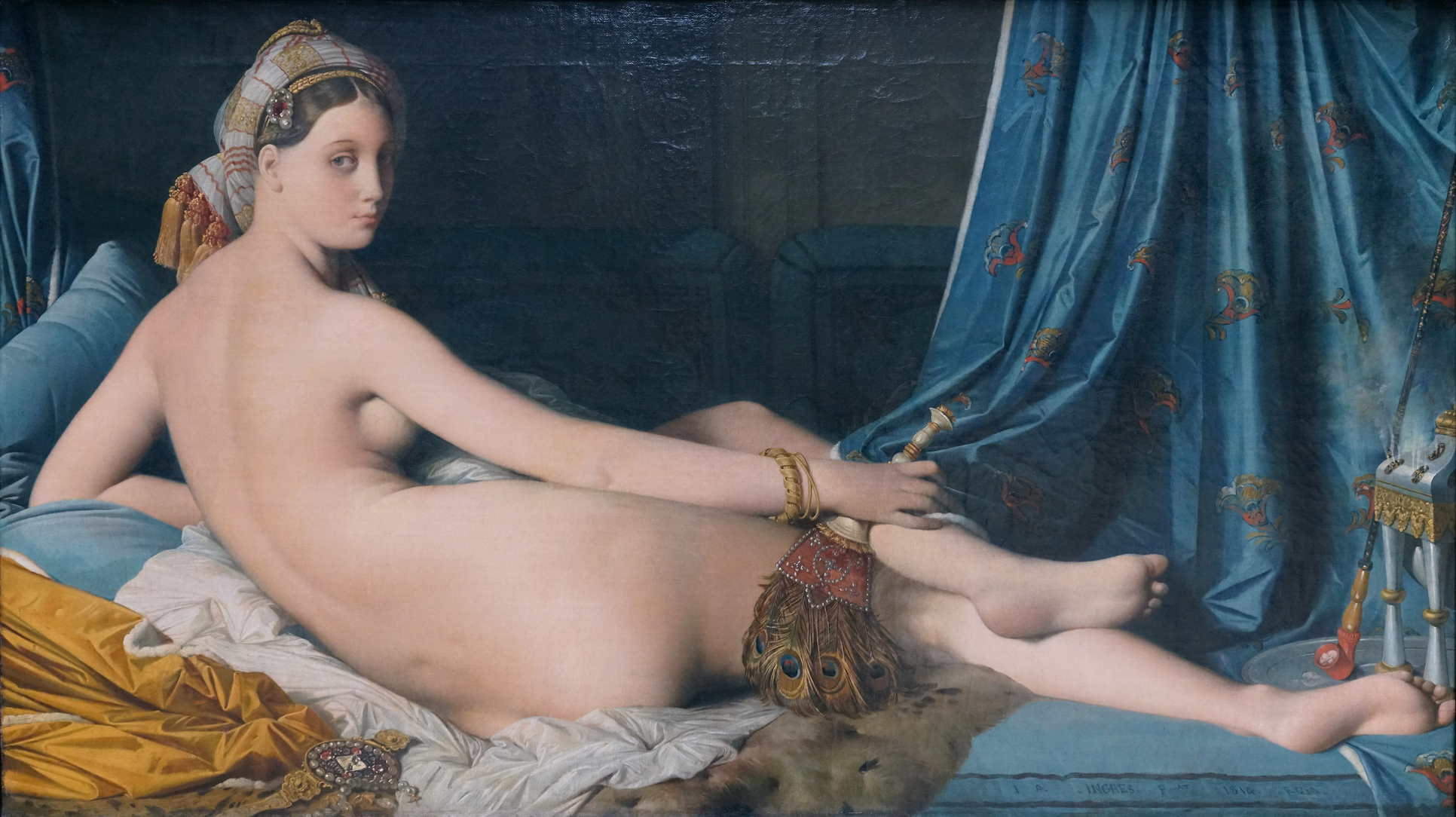
La Grand Odalisque, 1814
Jean Auguste Ingres
> Orientalist painting with an elongated spine
not received well because of body proportions
> odalisque - member of royal harem, they would be dressed modestly
> male fantasy meant for male gaze
Orientalism
Western representation of the Middle East and Turkey as exotic and romanticized
Antoine-Jean Gros
> student of David
> painted Napoleonic propaganda, notable for exotic subjects
> he rejected austerity of neoclassicism
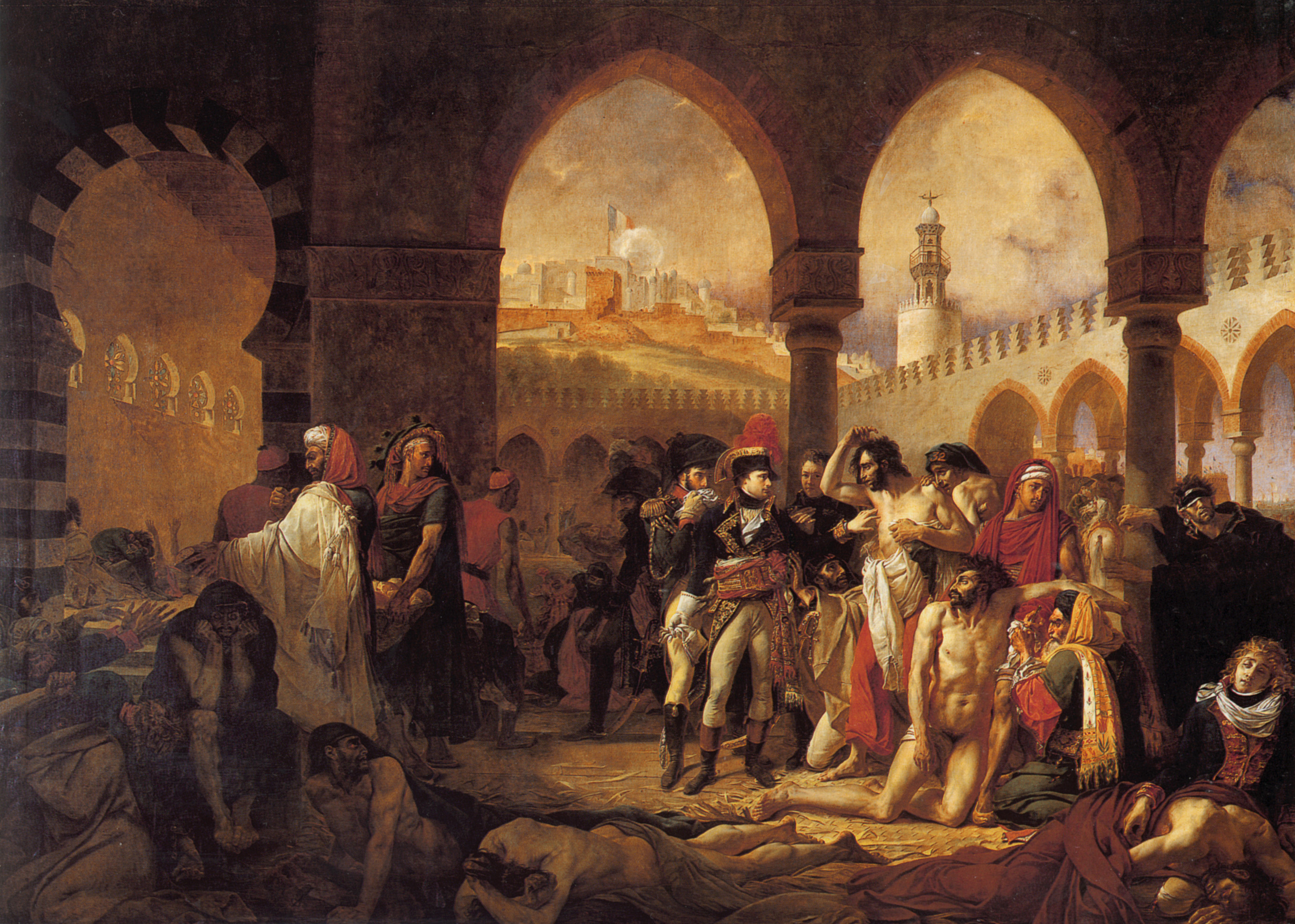

Napoléon Visiting the Plague Victims at Jaffa, 1804
Antoine-Jean Gros
> painting showing Napoleon amid plague victims in Jaffa
> power propaganda piece - show Napoleon is immune to disease and compassion as he visits ill soldiers
> unsure if scene is real, highly unlikely; he probably had everyone there killed
> exotic Islamic architecture
Jacques-Louis David
> leading Neoclassical painter, royal propagandist and later Republican figure
> legitimizes contemporary history: style remains the same but subject matter changes, dismantling Academy and Salons
> competed in Prix De Rome 4 times, loses 3 years in a row, held huge grudge against the academy
> part of Jacobin group - “minister of the arts”
> Napoleon’s first painter
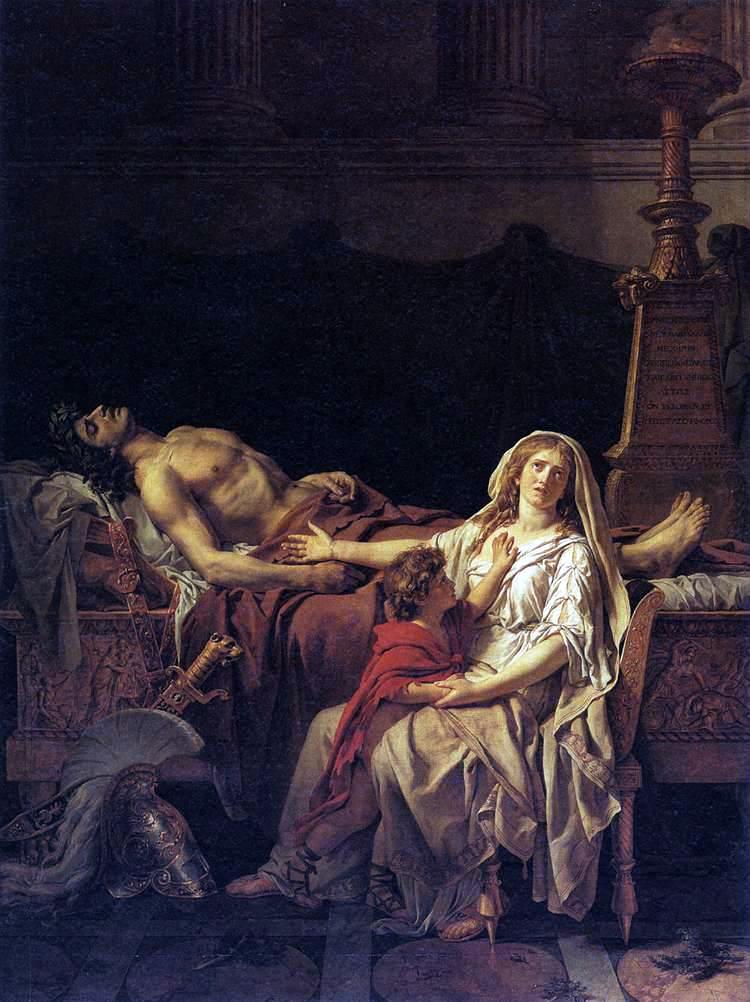

Andromache Mourning Hector
David’s 1780 Neoclassical piece addressing loss and stoicism.
Antoine Watteau
Rococo artist who developed the fête galante
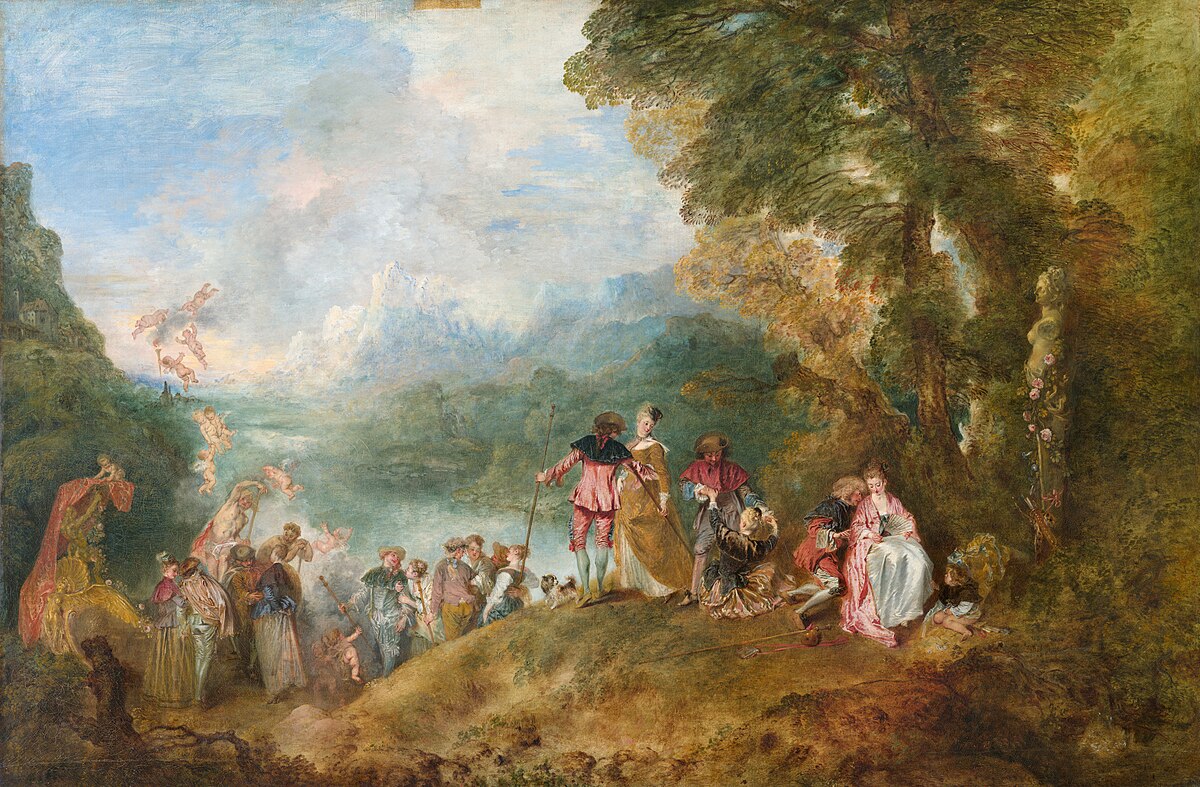

Embarkation for Cythera, 1717
Antoine Watteau
> Rococo painting illustrating lovers’ leisure
> reception piece into Academy
> Cythera = island of eternal youth and love
> reflects amorous outings
Fête galante
> Rococo genre of aristocratic, amorous outdoor scenes popularized by Watteau
> “celebration/party for the rich”
> erotic/sexual undertones
Francois Boucher
> Rococo painter, First Painter to the French King
> painted king’s mistress, resembling her as Venus
> director of Royal Academy
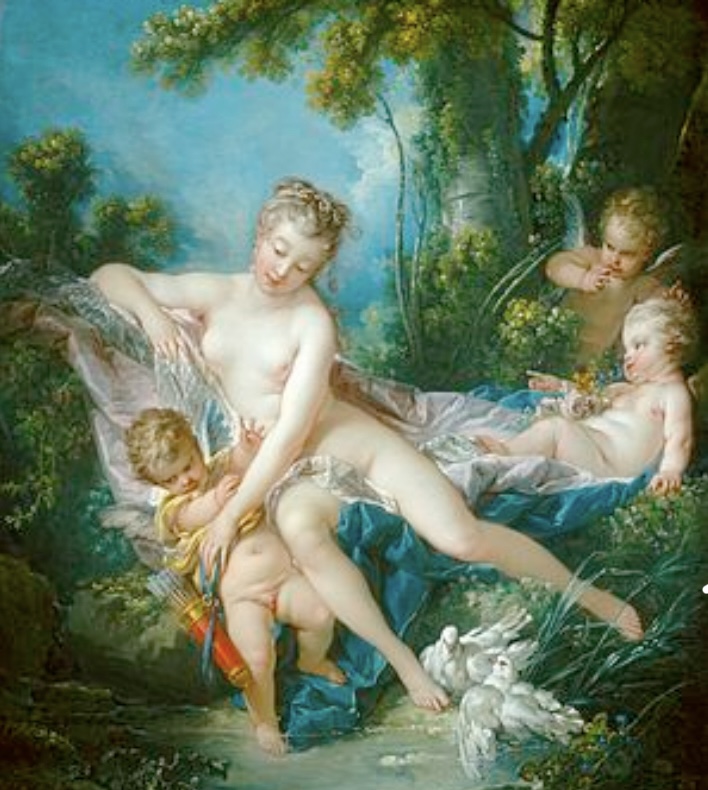

The Bath of Venus, 1751
Francois Boucher
> painting of the goddess Venus, emblematic of Rococo charm
Jean-Honoré Fragonard
> Rococo painter who bridged private commissions with Enlightenment ideas
> started out as academic painter then historical painter, won Prix De Rome
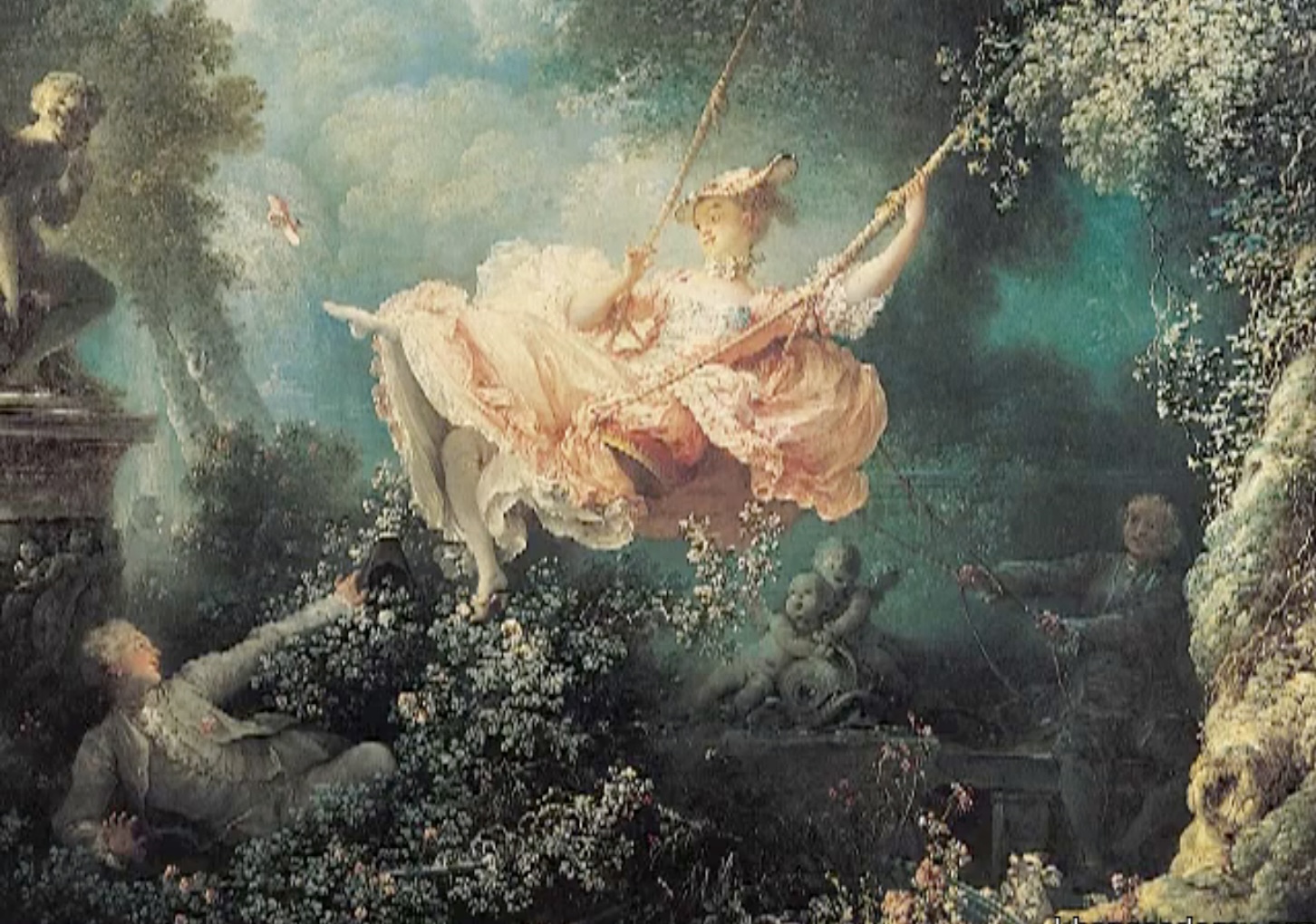

The Swing, 1760
Jean Honore Fragonard
> Rococo painting of intimate, playful excess
> commissioned by man who wanted image of him and his mistress
> symbolizes idleness and fickleness, women swinging between suitors
Nicolas Poussin
17th-century French classicist painter; epitome of academic classicism.
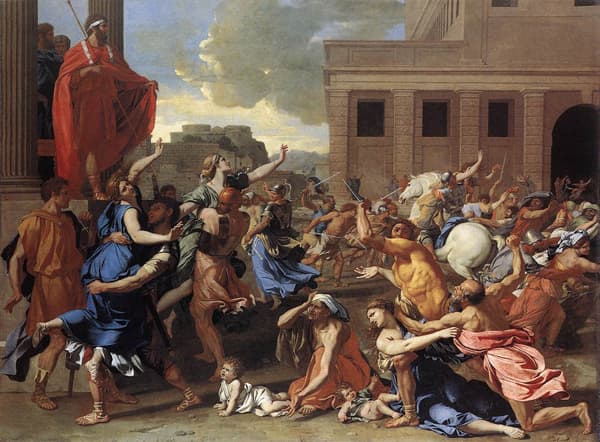

Abduction of the Sabine Women
Poussin’s painting illustrating classical myth in a preferred Neoclassical mood.
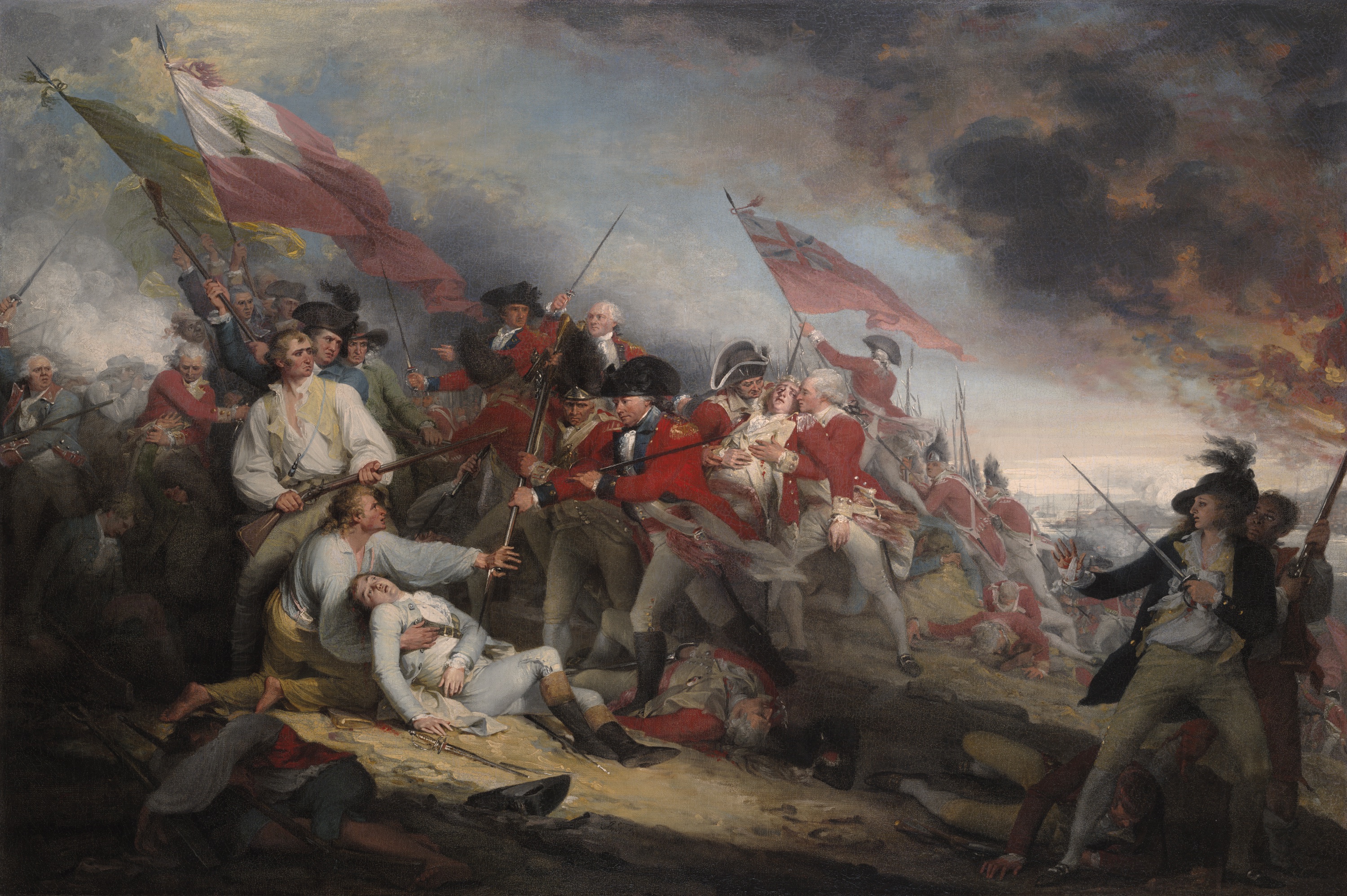

Death of Warren at Bunker Hill
Trumbull’s composition commemorating a Revolutionary War moment.
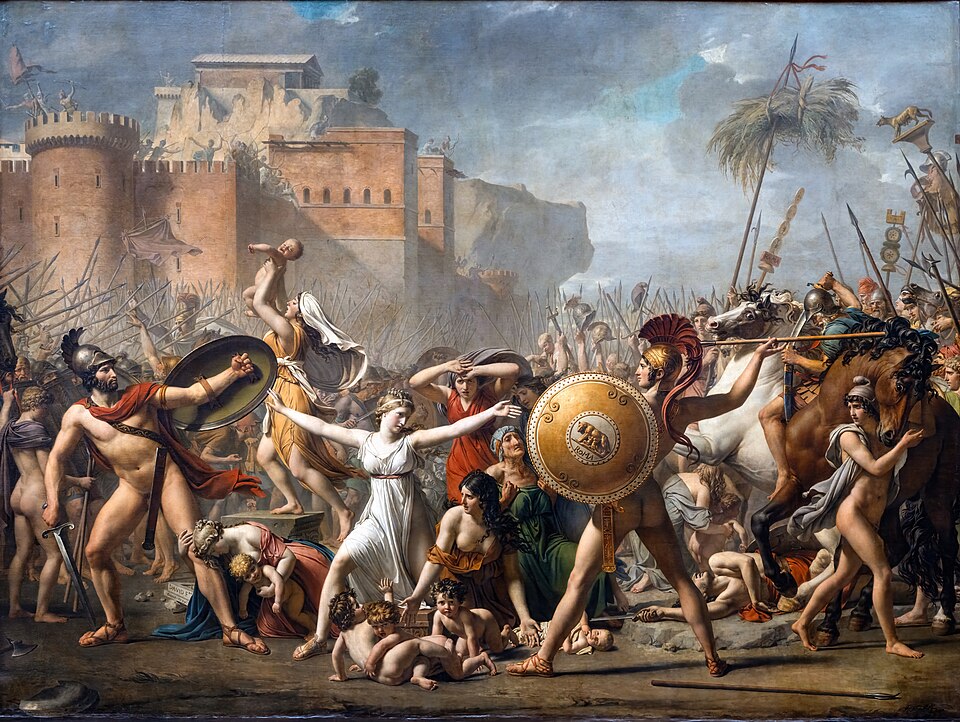

Interventions of the Sabine Women, 1795-99
Jacques Louis David
> painting of reconciliation and the Sabine myth
Jean Baptise Greuze
Enlightenment painter known for sentimental moral subjects
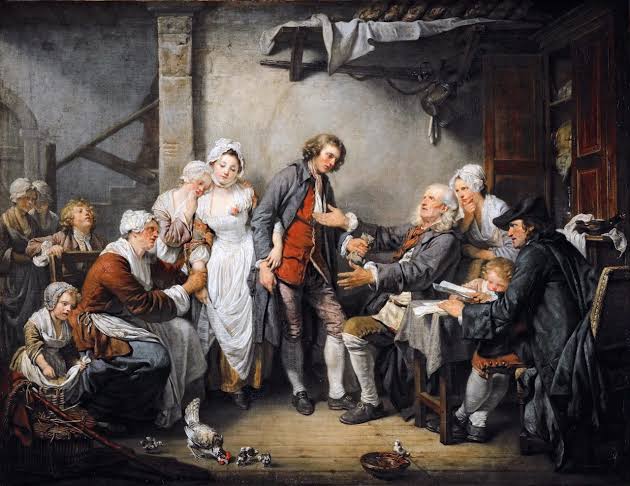

The Village Bride, 1761
Jean Baptise Greuze
> promoted moral virtue in rural life, a simple marriage for love
> NEOCLASSICAL
Jean-Baptiste-Siméon Chardin
Genre painter during Enlightenment, focusing on simple domestic life and moral realism
Denis Diderot
> French Enlightenment philosopher, art critic
> co-edited the Encyclopedie
Encyclopedie
extensive Enlightenment encyclopedia compiling knowledge across disciplines
Johann Winckelmann
> first modern art historian
> championed Greek classical ideals - Greek art was the epitome
> helped spread Neoclassicism
Elgin Marbles
Greek sculptures from the Parthenon; bought by Lord Elgin and housed in the British Museum
Pompeii and Herculaneum excavations
Mid-18th-century discoveries that sparked renewed interest in antiquity
The Grand Tour
elite European itinerary to Paris, Italy, and Greece; fueled neoclassical taste
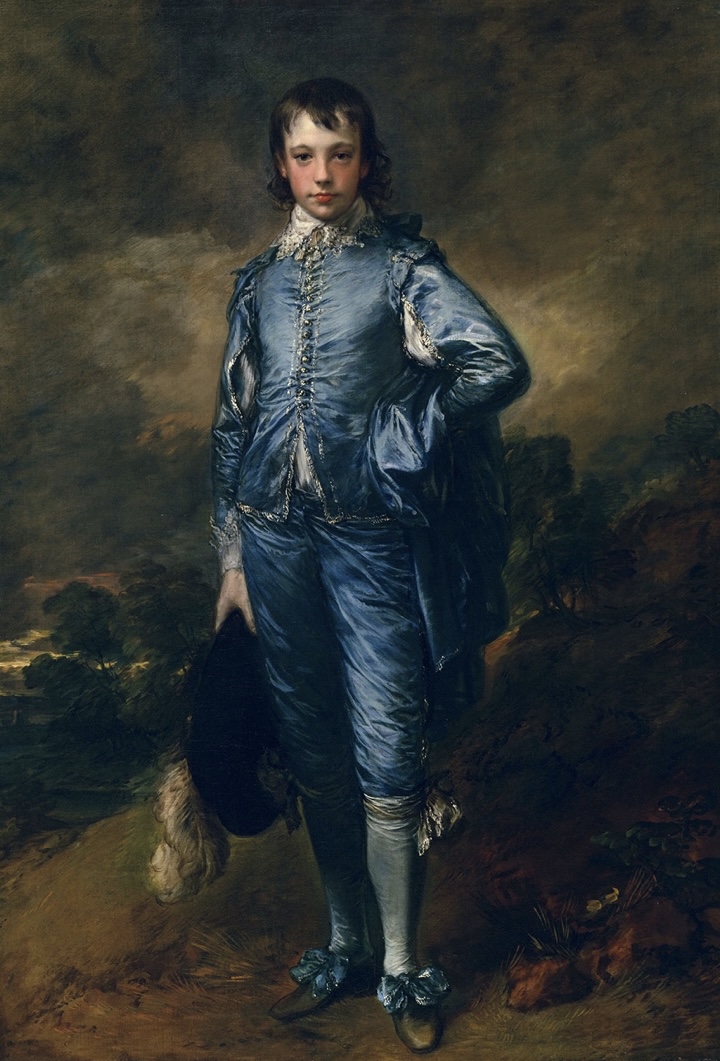

The Blue Boy, 1770
Thomas Gainsborough
> Grand Manner: figure takes up entire picture
> clothing & color = class marker
> confident posture, gives knowledge of his position
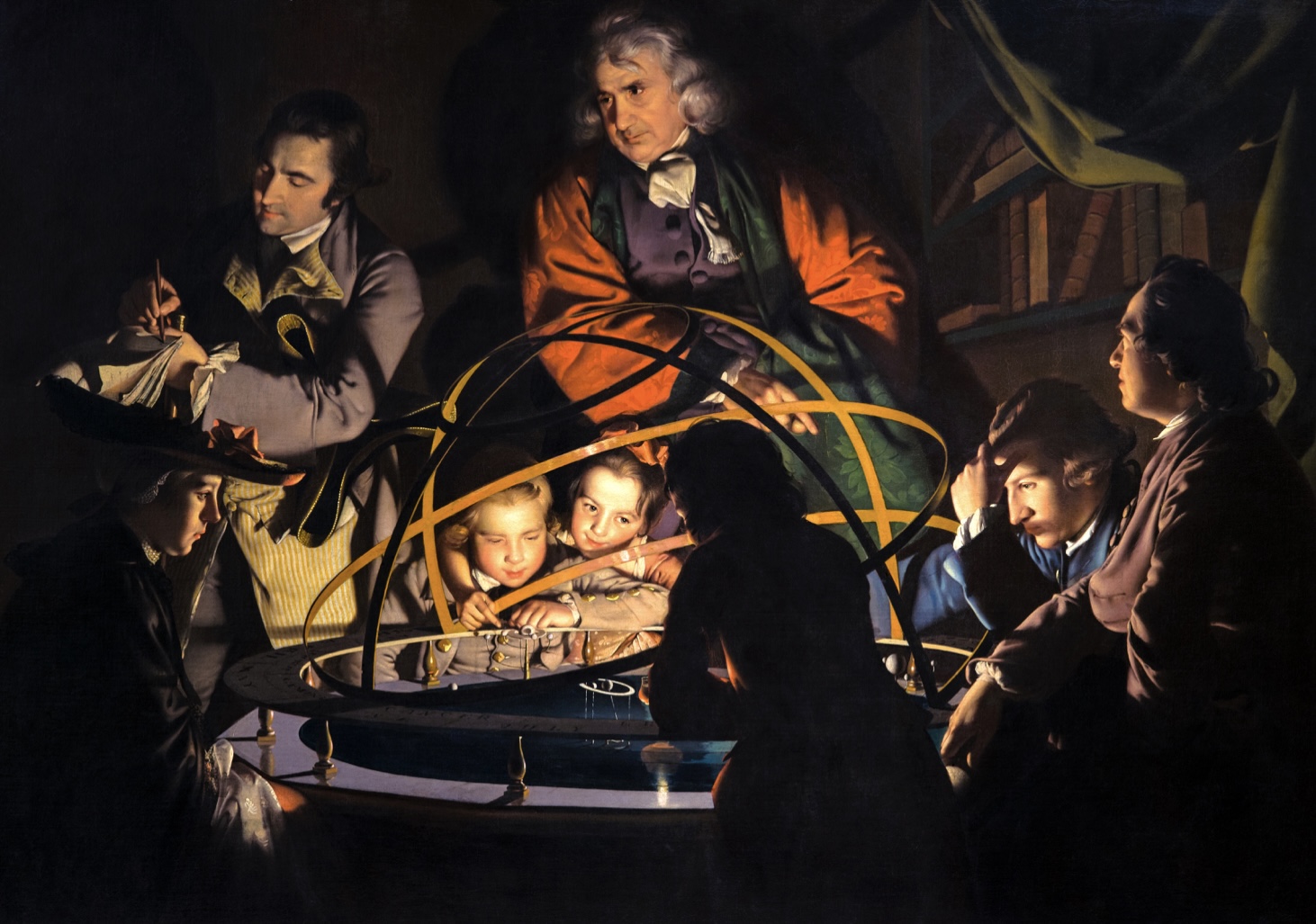

A Philosopher Lecturing on the Orrery, 1766
Joseph Wright of Derby
> showcasing an Enlightenment era scientific lecture on a mechanical model of the solar system
> dramatic light = metaphor for knowledge
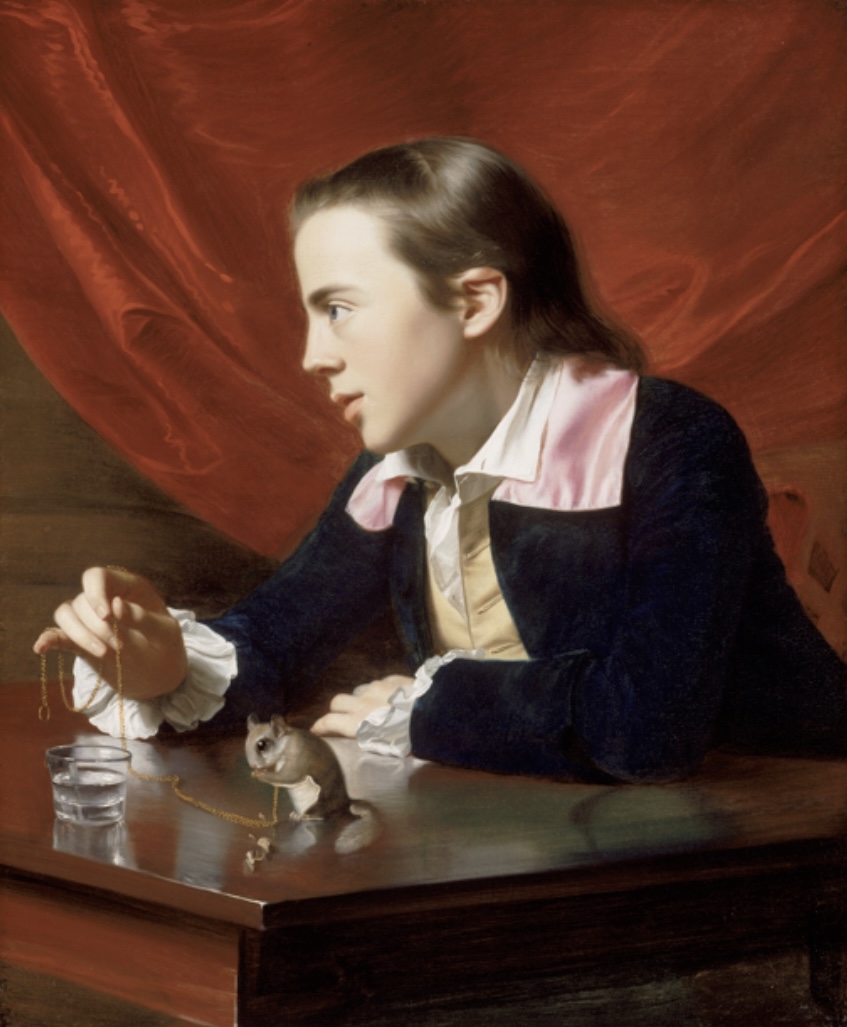

Boy With a Squirrel (Henry Pelham), 1765
John Singleton Copley
> depicting his half-brother
> pet squirrel = patient character
> painted while Copley was still in colonial America, is told by Rey
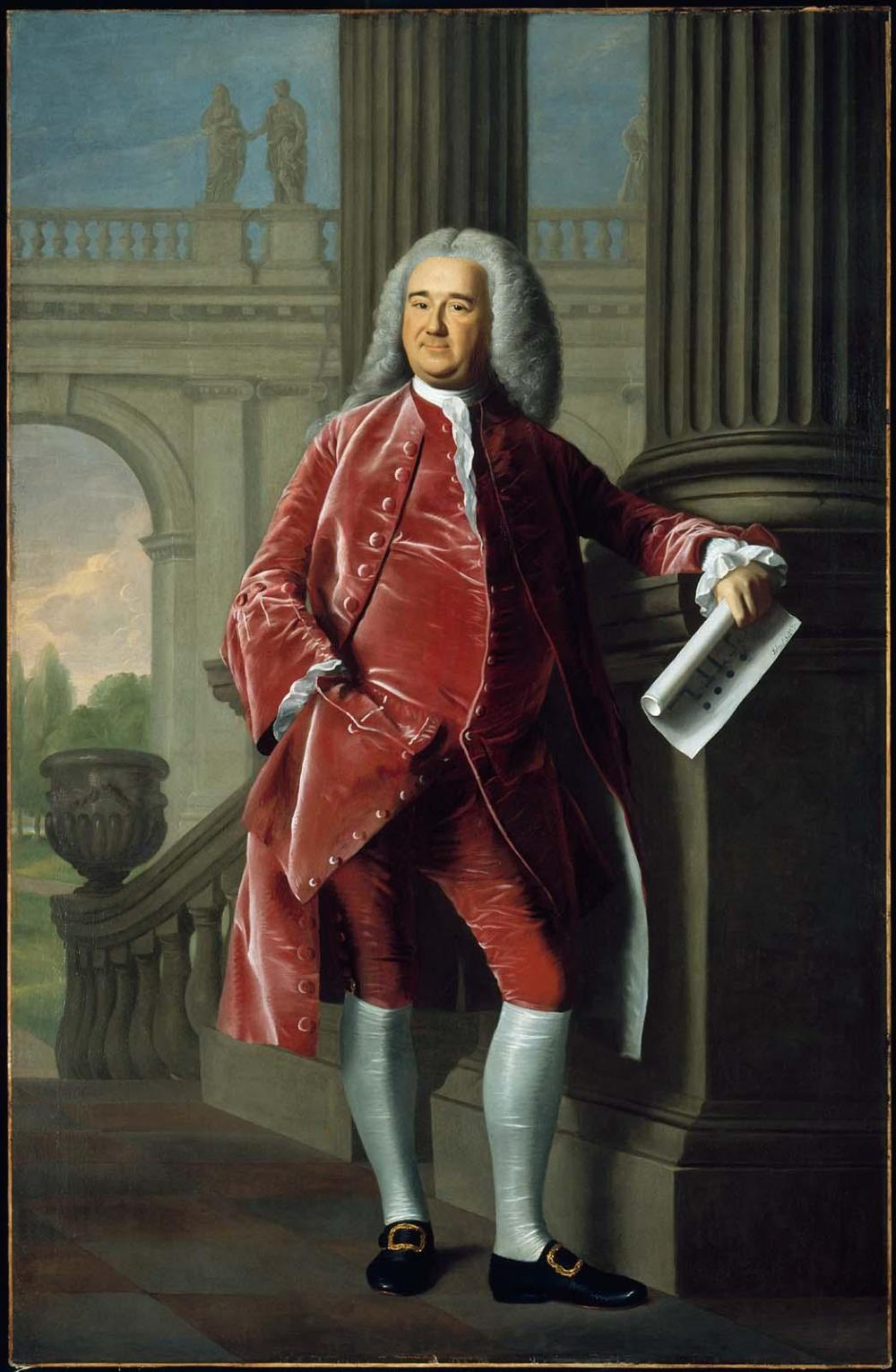

Nathaniel Sparhawk
A 1735 portrait by John Smibert, depicting the colonial magistrate Nathaniel Sparhawk.
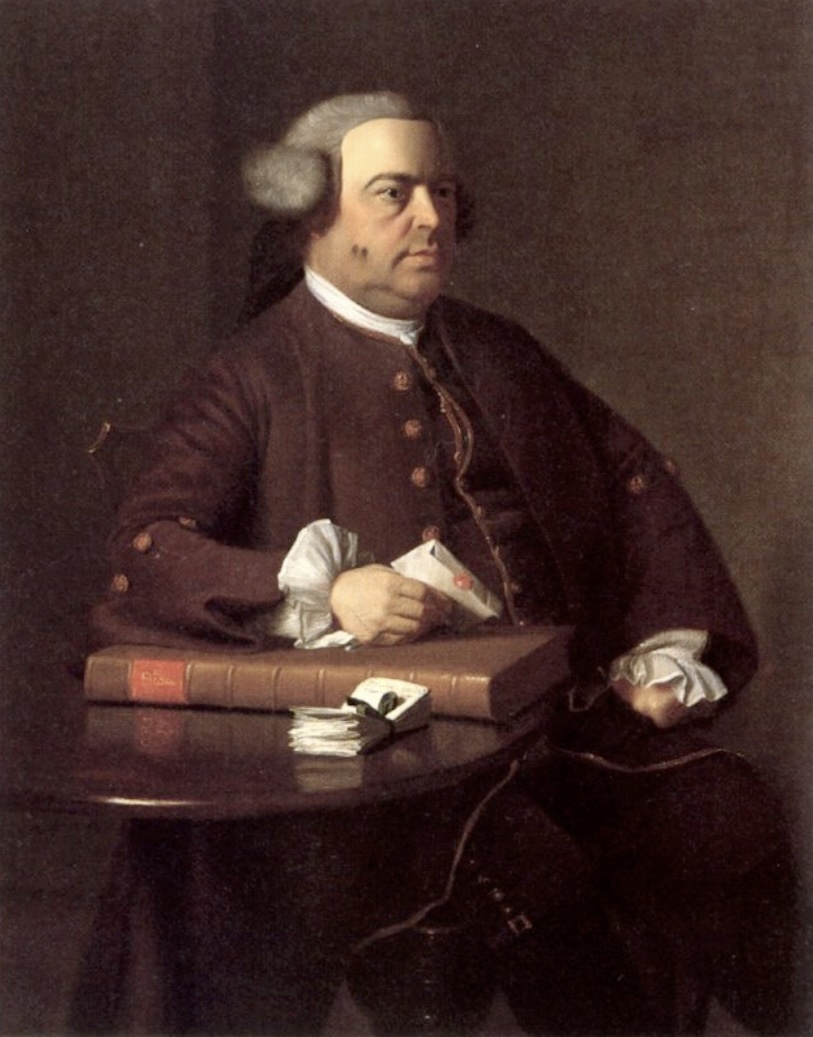

Nathaniel Allen
A colonial American portrait from the mid-18th century, attributed to various artists, often reflecting the limner style.

Mary and Elizabeth Royall
A 1758 portrait by John Singleton Copley, depicting the daughters of wealthy Boston merchant Isaac Royall, showcasing Copley's sharp detail and realism.
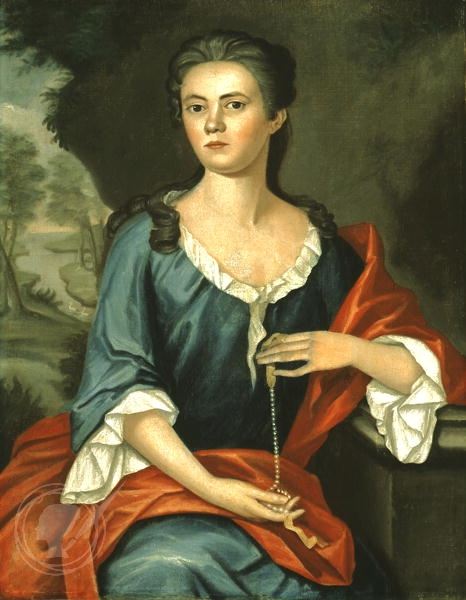

Mrs. Joseph Mann
Also known as 'Mary Mann', a 1753 portrait by John Singleton Copley, noted for its depiction of a prominent colonial woman.
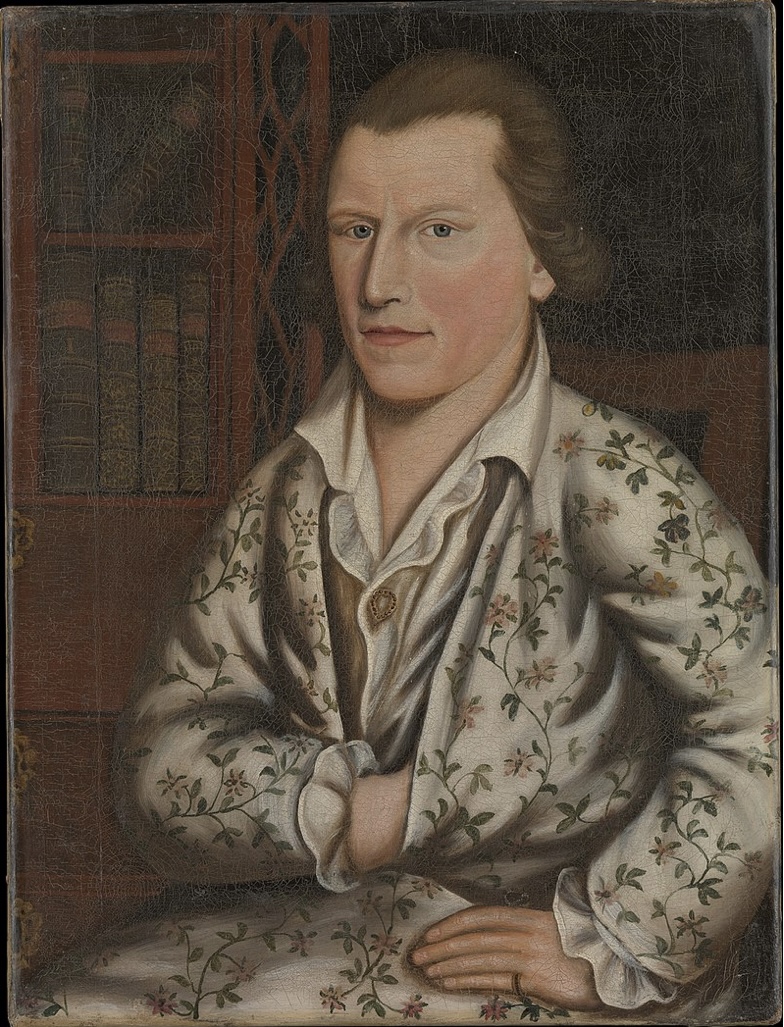

Portrait of William Duguid
A c. 1730s portrait by John Smibert, representing the Scottish surgeon William Duguid.
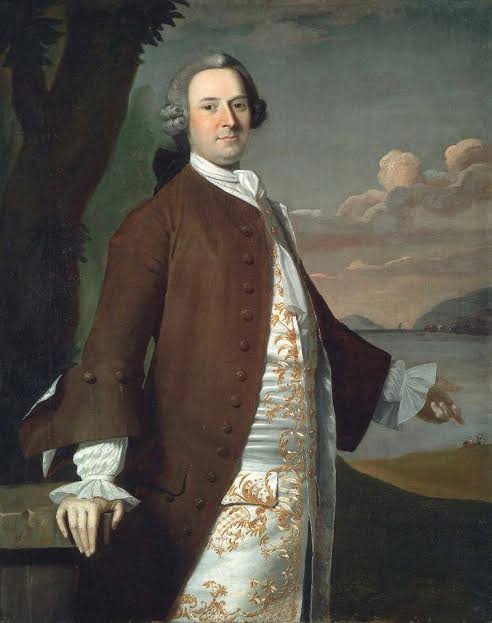

Isaac Winslow
A 1774 portrait by John Singleton Copley, depicting the affluent Boston merchant and loyalist Isaac Winslow, known for its psychological depth.
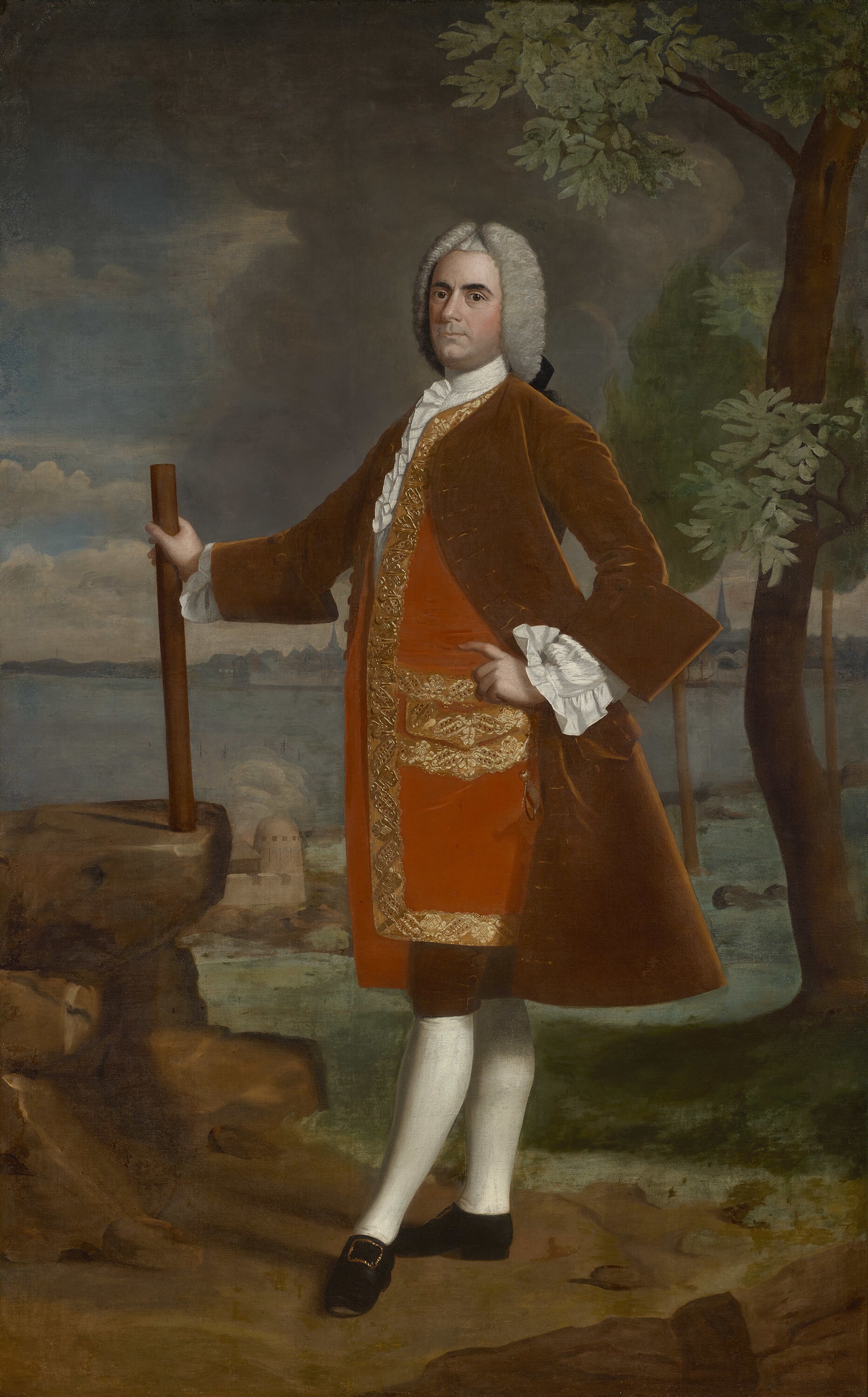

General Samuel Waldo
A 1758 portrait by Joseph Blackburn, showcasing the prominent colonial military leader and land speculator General Samuel Waldo.
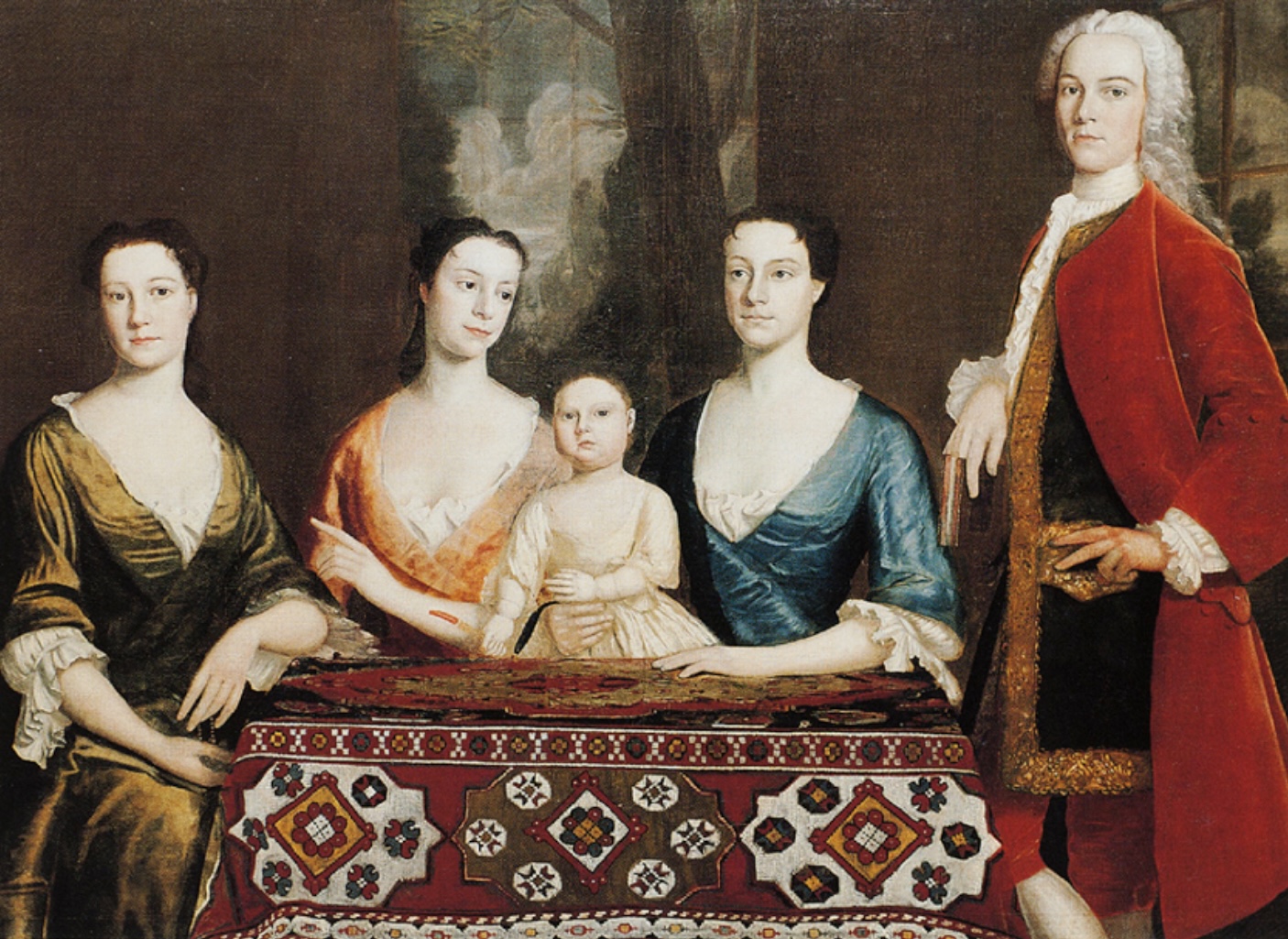
Isaac Royall and Family
A significant 1741 group portrait by Robert Feke, depicting the wealthy Isaac Royall and his family, considered a masterpiece of colonial American art.
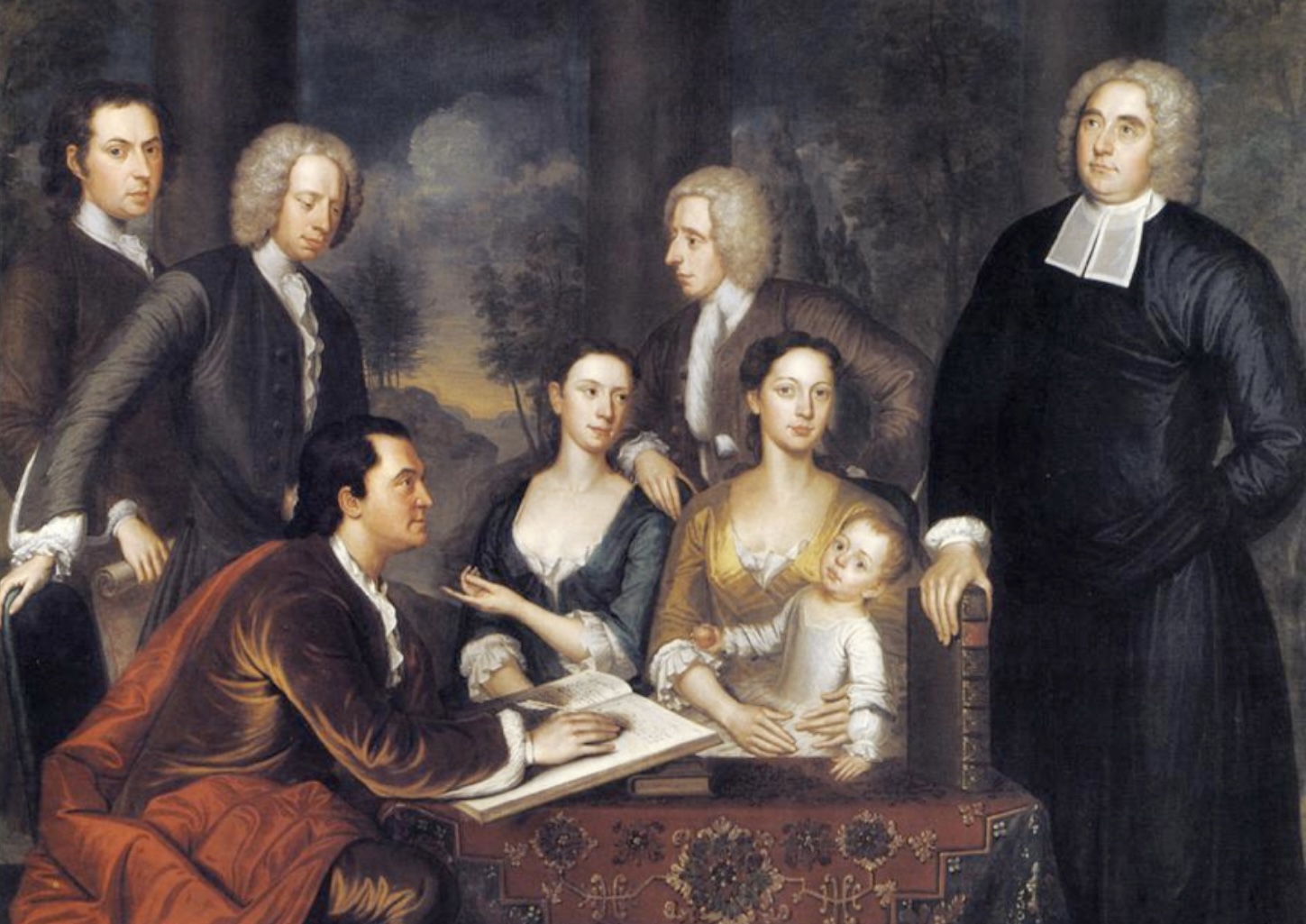

The Bermuda Group: Bishop Berkeley and His Family
A 1729 portrait by John Smibert, specifically depicting Dean George Berkeley and his entourage in anticipation of their unfulfilled Bermuda mission, a key work in early American art.
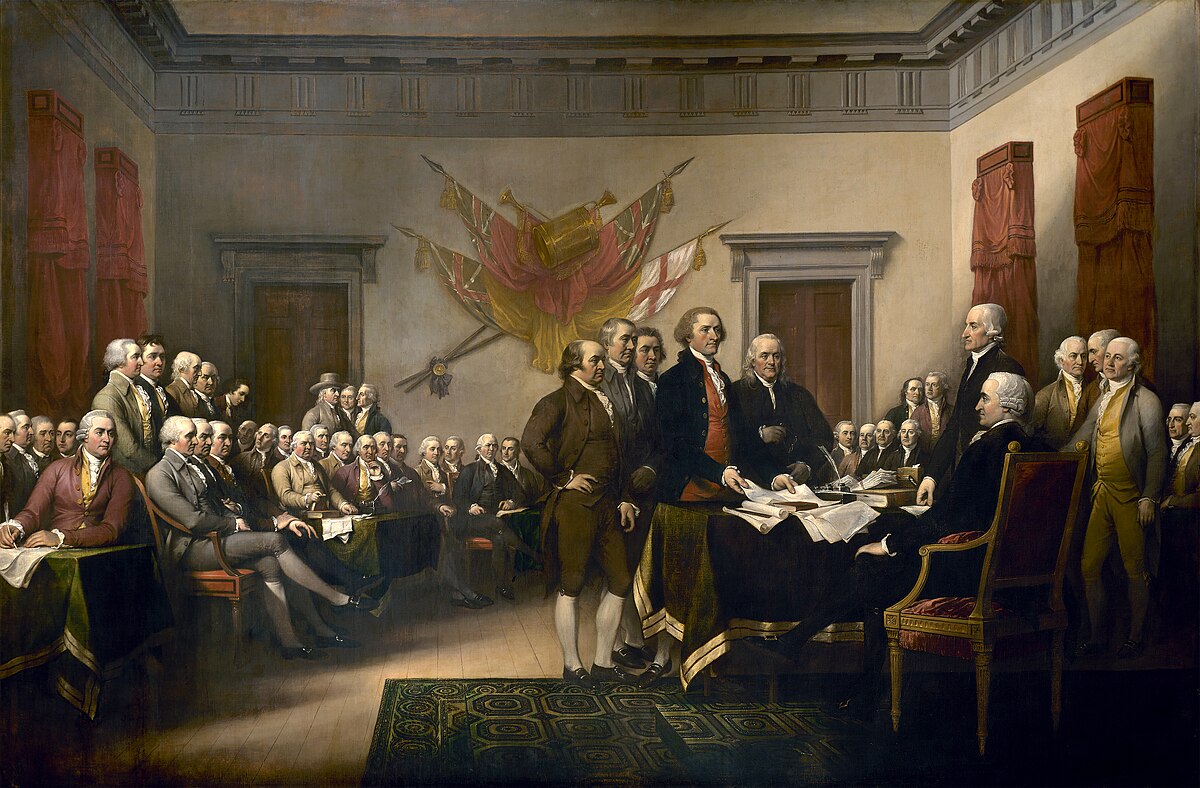

Declaration of Independence
A large-scale 1817 history painting by John Trumbull, depicting the presentation of the Declaration of Independence in 1776, housed in the U.S. Capitol Rotunda.
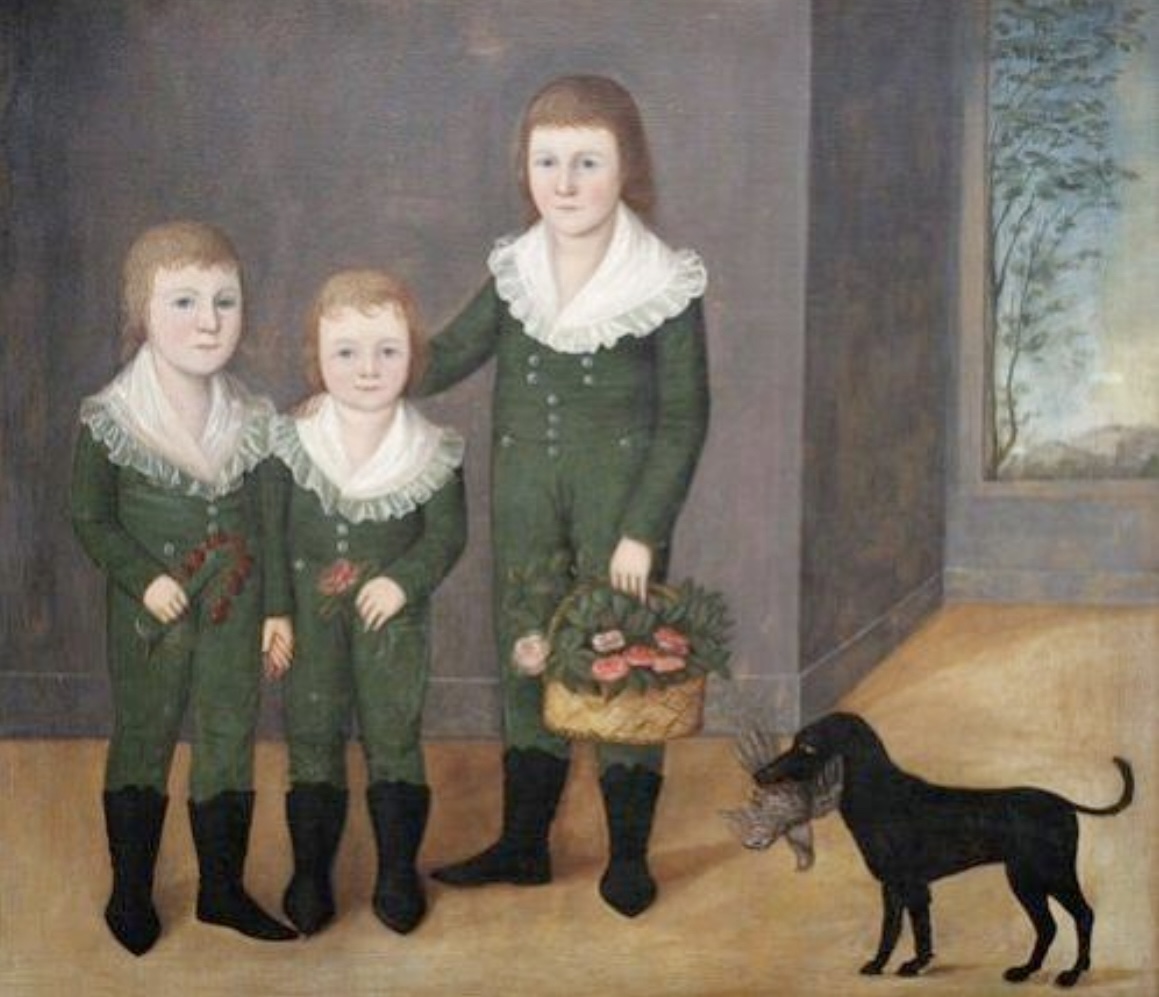

Westwood Children
A c. 1779-81 group portrait by Ralph Earl, depicting the children of the Westwood family, characteristic of American colonial painting.
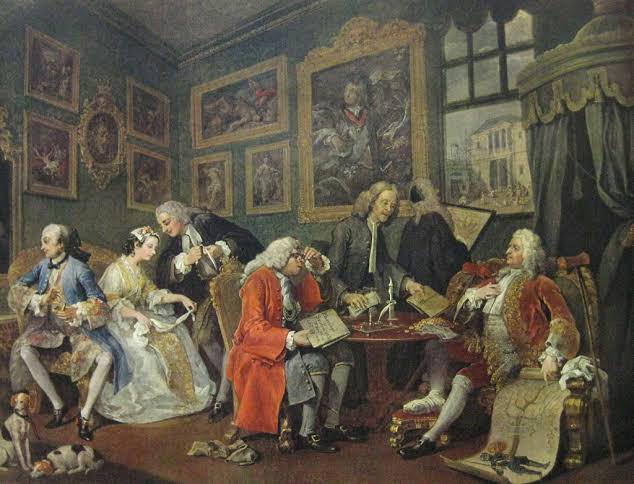

The Marriage Contract
The first painting in William Hogarth's 'Marriage A-la-Mode' series (1743), a satirical depiction of arranged marriages in 18th-century England through moral realism.
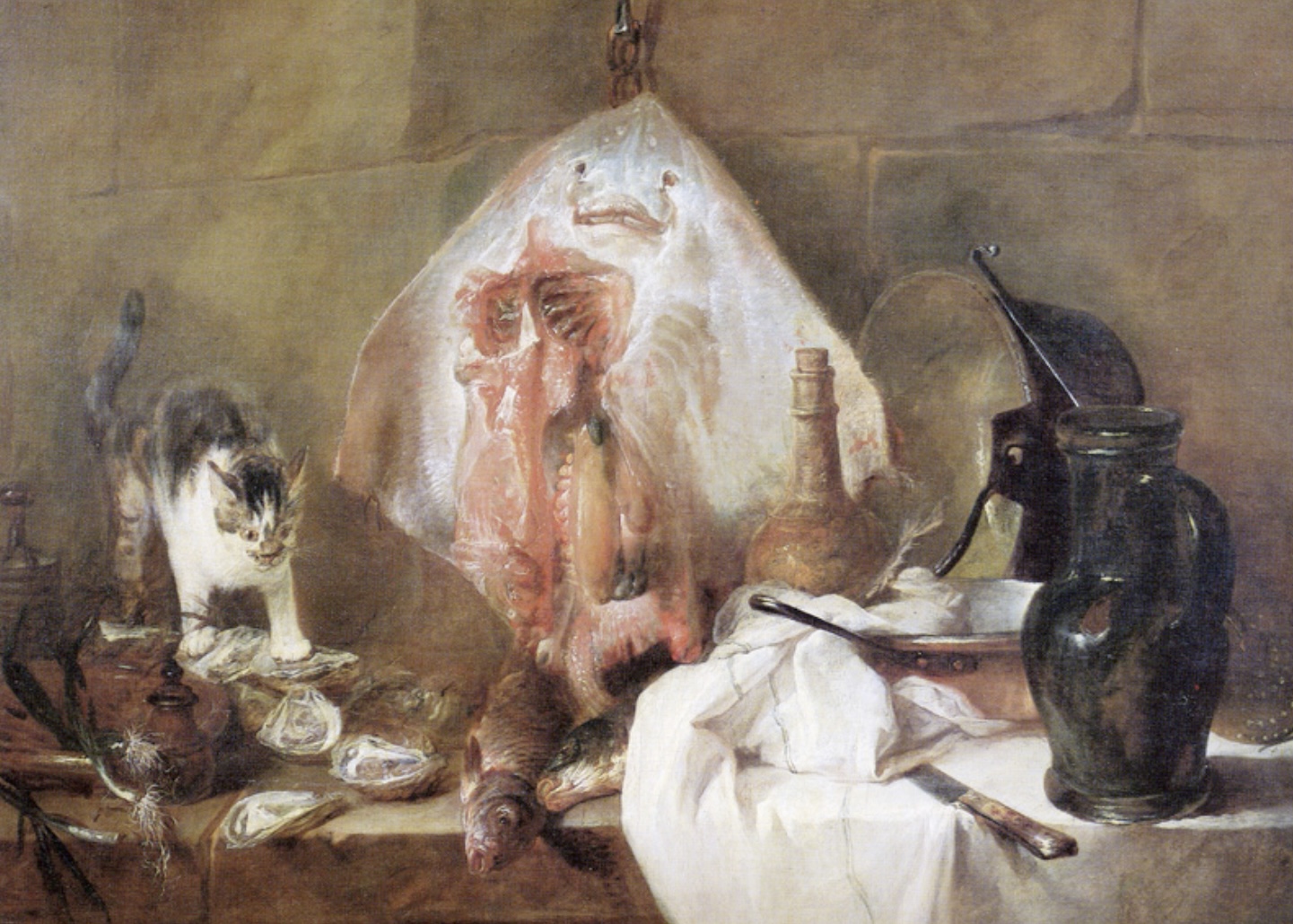

The Ray
Also known as 'La Raie', a 1728 still life by Jean-Baptiste-Siméon Chardin, celebrated for its masterful depiction of textures and light using a marine animal.
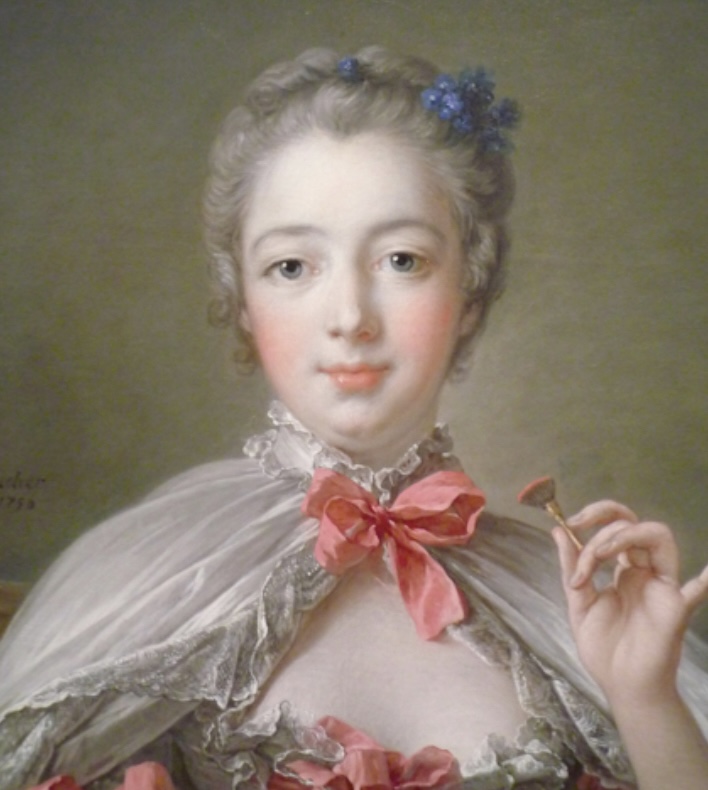

Madame de Pompadour
A prominent patron of the arts and King Louis XV’s chief mistress, famously depicted in Rococo portraits by artists like François Boucher and Maurice Quentin de La Tour, symbolizing the era's elegance.
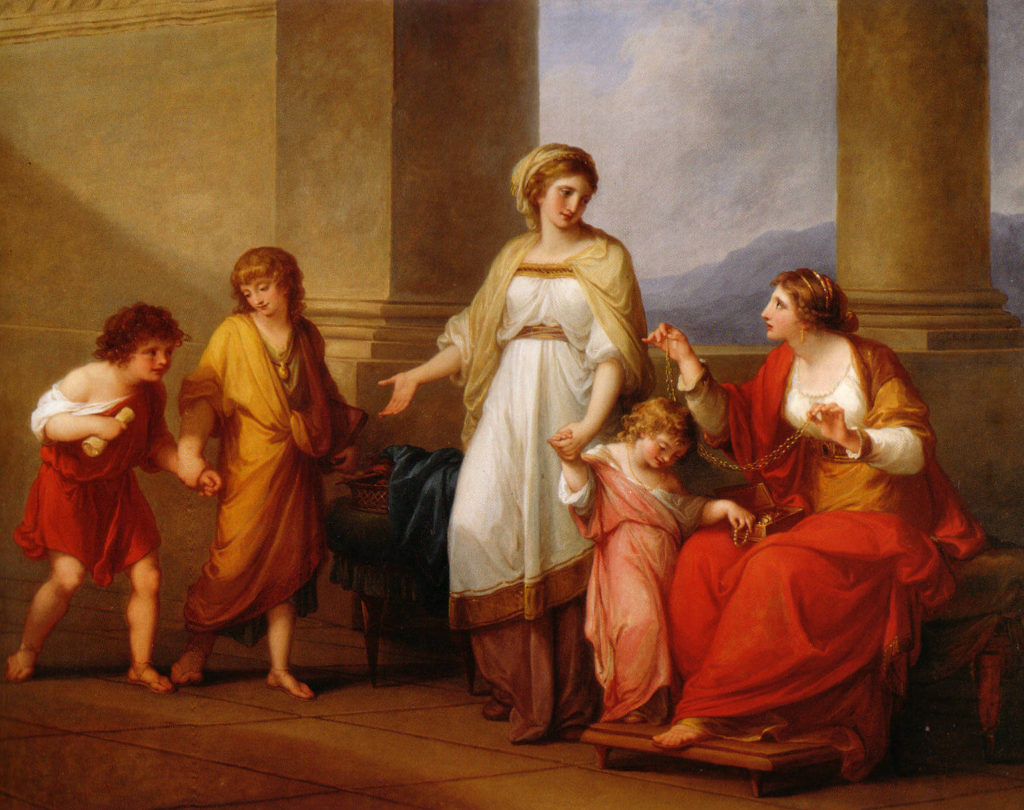

Mother of the Gracchi, Pointing to Her Children as Treasures
A 1785 Neoclassical painting by Angelica Kauffman, illustrating the Roman Cornelia presenting her children as her true 'jewels' or 'treasures,' embodying civic virtue.

Death of Socrates
A 1787 Neoclassical masterpiece by Jacques-Louis David, depicting the philosopher Socrates choosing to drink hemlock rather than renounce his beliefs, emphasizing stoicism and moral uprightness.
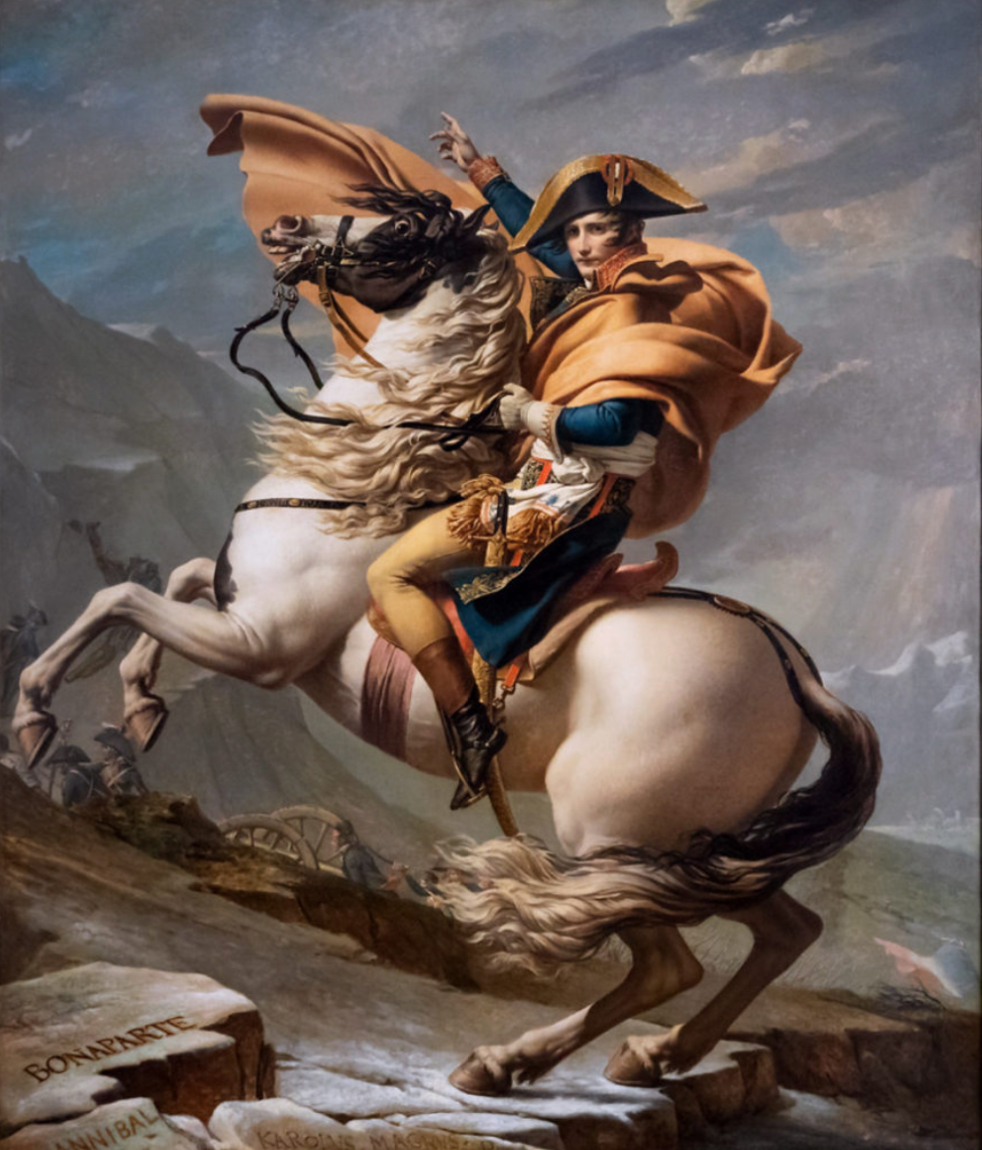

Napoleon Crossing the Alps
A series of iconic 1801 portraits by Jacques-Louis David, showing Napoleon leading his army across the St. Bernard Pass, serving as powerful propaganda for his leadership.

Marie Antoinette With Her Children
A 1787 portrait by Élisabeth Louise Vigée Le Brun, depicting the Queen and her children in a more natural, maternal light, aiming to improve her public image.
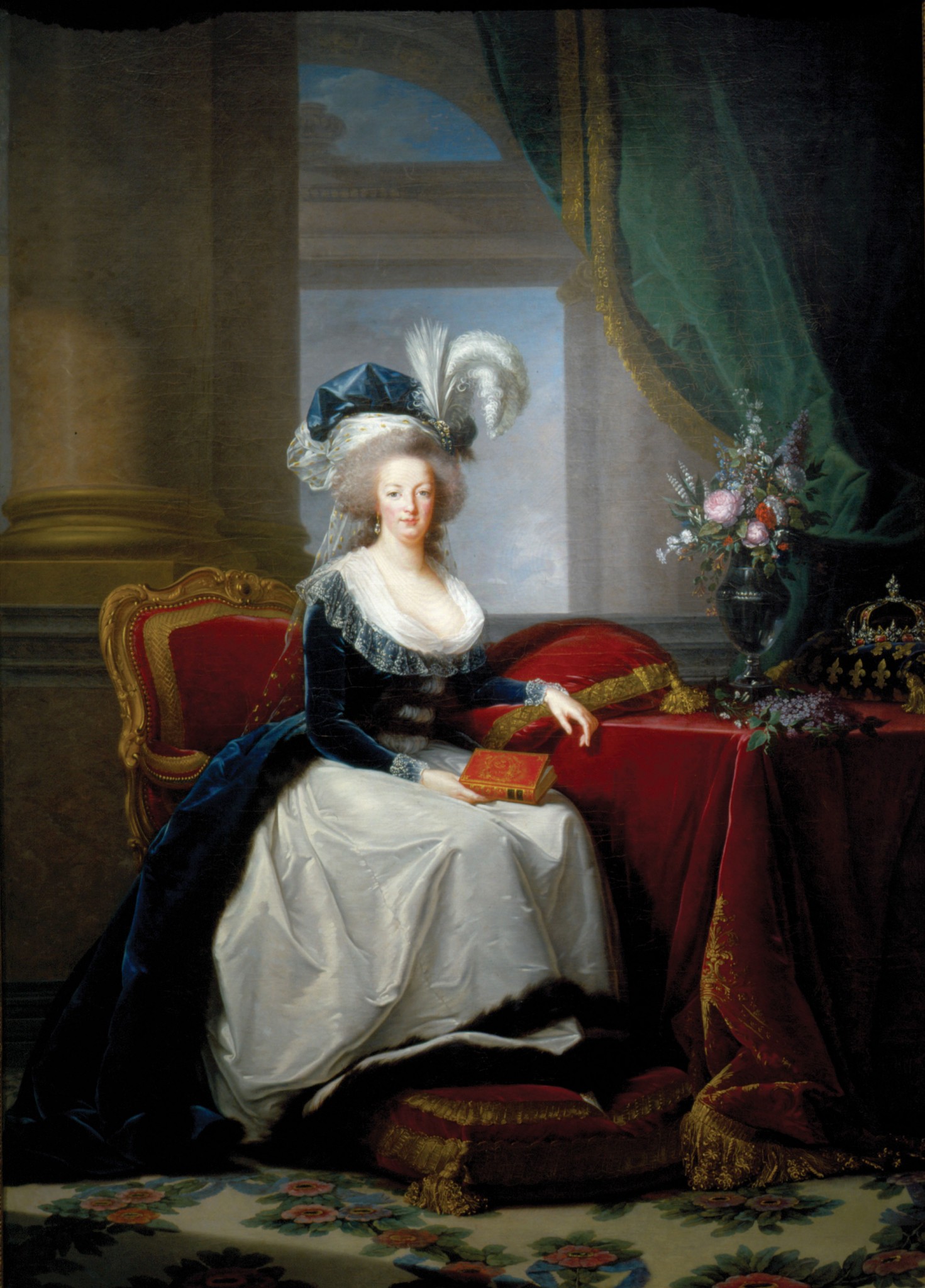

Marie Antoinette
The last Queen of France before the French Revolution, frequently portrayed by Élisabeth Louise Vigée Le Brun in numerous royal portraits that documented her life and reign.
Hierarchy of Genres
History painting
Portraiture
Genre painting
Lanscapes
Still Life Painting
Standards of Royal Academy of Painting and Sculpture
based on academies in Rome and Florence
use of perspective and foreshortening
naturalistic coloring
no trace of brushstrokes - smooth surfaces