Year 10 Science Genetics and Biotechnology
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Female reproductive system
The system of organs in females—including the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina—responsible for producing eggs, enabling fertilisation, and supporting the development of a baby during pregnancy
Male reproductive system
The organs in males—including the testes, vas deferens, prostate, and penis—that produce, store, and deliver sperm for fertilisation
Gametes
Sex cells (sperm in males, eggs in females) that carry half the number of chromosomes (haploid) and combine during fertilisation
Zygote
The single cell formed when a sperm fertilises an egg; it contains a full set of chromosomes and begins dividing to form an embryo
Embryo
An early stage of human development following the zygote stage, lasting until about eight weeks after fertilisation
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
DNA
A double-helix molecule that stores genetic instructions used in the development, functioning, and reproduction of living organisms
RNA
Ribonucleic Acid; a single-stranded molecule that helps carry out instructions from DNA to build proteins in cells
Amino acids
Small molecules that are the building blocks of proteins, linked together in specific sequences based on genetic instructions
Proteins
Large, complex molecules made of chains of amino acids, created using instructions from genes, and responsible for most functions and structures in living organisms
Adenine
A base 'A' that pairs with 'T'
Cytosine
A base 'C' that pairs with 'G'
Guanine
A base 'G' that pairs with 'C'
Thymine
A base 'T' that pairs with 'A'
Backbone of DNA
The sugar-phosphate structure that forms the sides of the DNA ladder, providing stability and support for the bases
Genes
Sections of DNA that carry the instructions for making proteins, which determine traits and functions in the body
Chromosomes
Structures found in the nucleus of cells, made of DNA and proteins, that carry genes—the instructions for an organism's traits and functions. Humans have 23 pairs.
Nucleus
The cell's control center that contains chromosomes and directs all cell activities through gene expression
Allele
Different forms of the same gene that can result in different traits, such as eye colour or blood type
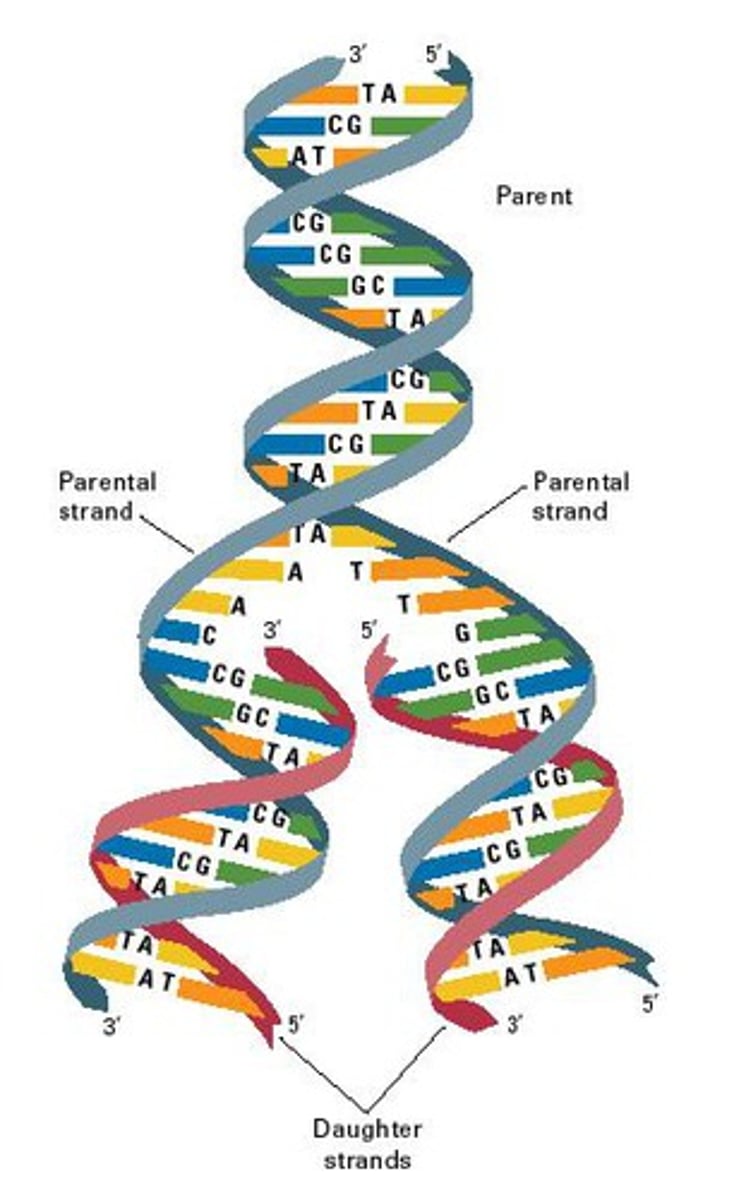
Replication
The process of making an exact copy of DNA before a cell divides, ensuring each new cell has identical genetic material
Mutation
A change in the DNA sequence that may result in a new trait, be neutral, or cause disease; mutations can be inherited or caused by environmental factors
Substitution
A mutation where one base in the DNA sequence is replaced with another, changing the order and the function

Deletion
A mutation where one or more bases are removed from the DNA sequence, changing the order and the function

Insertion
A mutation where one or more extra bases are added into the DNA sequence, changing the order and the function

Mitosis
A type of cell division that produces two genetically identical diploid body cells, used for growth and repair
Meiosis
A special type of cell division that produces four genetically unique haploid gametes, each with half the usual number of chromosomes
Diploid
A cell that has two sets of chromosomes, one from each parent
Haploid
A cell that has only one set of chromosomes, such as gametes
Prophase
The first stage of cell division where chromosomes appear and the nucleus starts to break down
Metaphase
The stage of cell division where chromosomes line up in the center of the cell, preparing to be separated
Anaphase
The stage where chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite ends of the cell
Telophase
Two new nuclei form, and the cell starts to split into two
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism, represented by the alleles it carries (e.g., Bb or TT)
Phenotype
The physical or observable traits of an organism, such as height, eye colour, or blood type
Dominant gene
An allele that is always expressed in the phenotype, even if only one copy is present (e.g., B in Bb)
Recessive gene
An allele that is only expressed in the phenotype when two copies are present (e.g., b in bb)
Homozygous
Having two of the same alleles for a gene (e.g., TT or tt)
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a gene (e.g., Tt)
Gregor Mendel
An monk known as the father of genetics who discovered the basic principles of heredity through experiments with pea plants
Genetic modification
The direct manipulation of an organism's DNA to alter its characteristics, often by inserting genes from another species
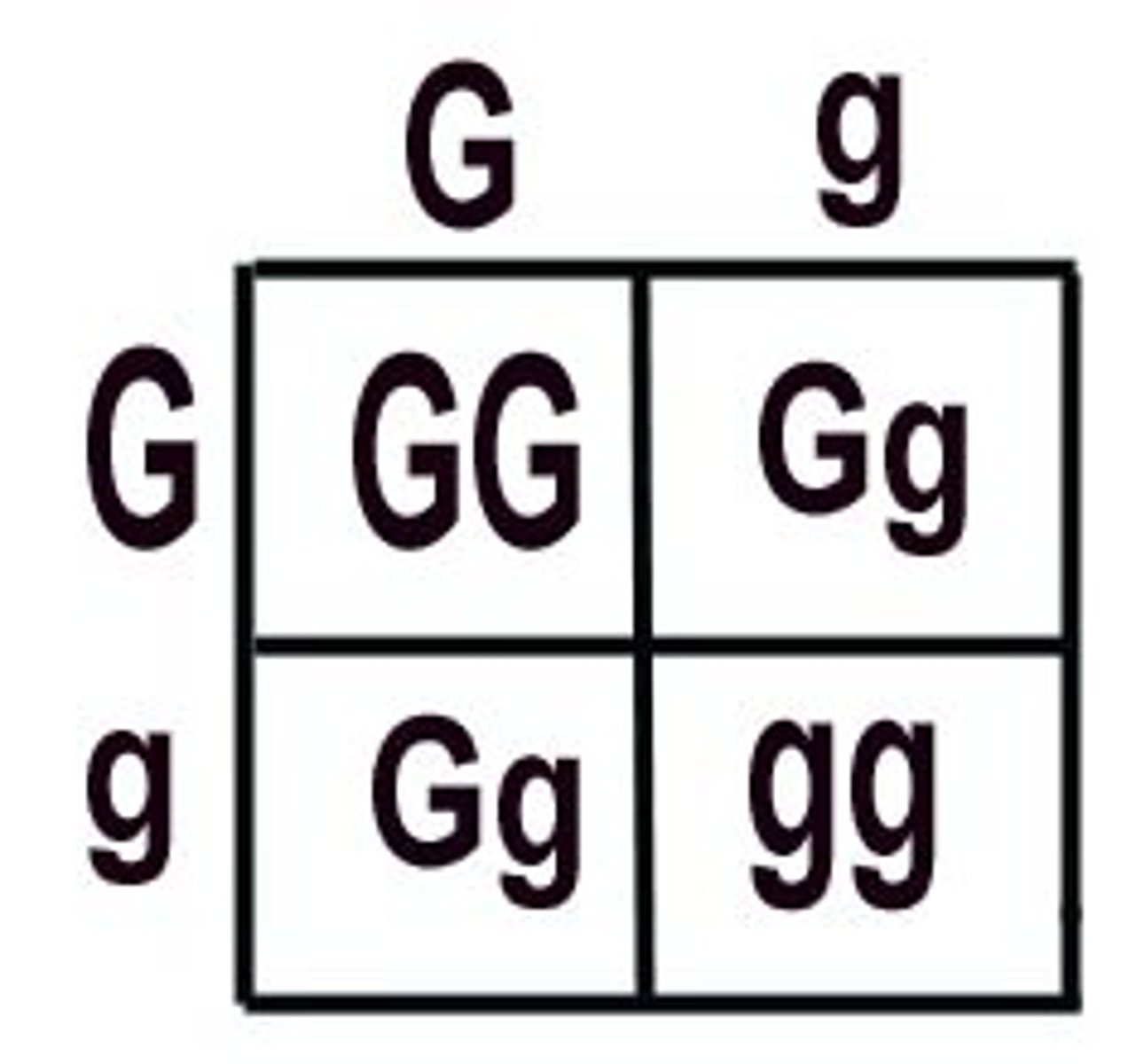
Punnet Squares
A diagram used to predict the probability of offspring inheriting certain alleles based on the genotypes of the parents, with a 1:2:1 ratio in genotype and a 3:1 ratio in phenotype
Biotechnology
The use of living organisms, cells, and biological systems to develop products or solve problems in medicine, agriculture, and industry
Genetically modified organism (GMO)
An organism whose genetic material has been altered using biotechnology to express desired traits, such as pest resistance or faster growth
Bioethics
The study of ethical issues in biology and medicine, including topics like genetic modification, cloning, and medical consent