5.10 humoral adaptive immunity & B lymphocytes
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
humoral vs cell mediated immunity (target)
humoral immunity acts primarily against extracellular pathogens
cell mediated immunity acts primarily against intracellular pathogens
plasma B cells
secrete antibodies specific to the infection, each plasma cell can only produce one type of antibody, short lived
memory B cells
remain in the lymphatic tissue to remember the antigen for future infections
clonal selection in B cells
APCs display foreign antigens on their MHC-II markers and bind to specific complementary cells in the lymph nodes
clonal expansion in B cells
the differentiation and proliferation of B cells into plasma cells and memory B cells
steps in activation of humoral adaptive immunity
B cells undergo clonal selection
helper T cells that bind to the antigen release cytokines (interleukin) to activate specific B cells
B cells undergo clonal expansion (activated by clonal selection and helper T cells)
plasma cells and memory B cells are produced
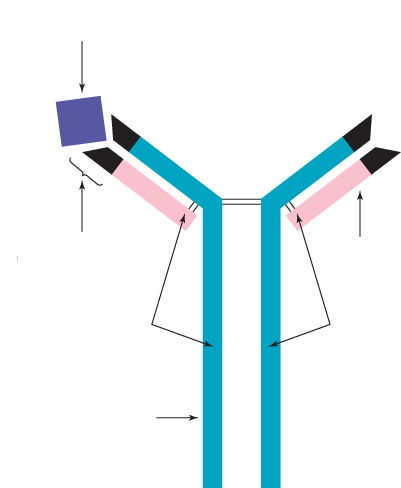
antibody structure
constant regions
variable region (antigen-binding site)
light & heavy chains
quaternary structure
both sides identical
antibody function
precipitation
inflammation
agglutination
neutralisation (of pathogens and toxins)
opsonisation
precipitation
antibodies bind to soluble antigens, making them insoluble
causes antigens to precipitate out of solution, creating a solid more visible to the IS
occurs due to cross-linking between antigens and antibodies
inflammation
antibodies can trigger the release of histamine, causing inflammation
can also activate a complement cascade
agglutination
antibodies bind to surface antigens on pathogens to form antigen-antibody complexes
causes pathogens to clump together and become more visible to the IS
neutralisation (of pathogens and toxins)
antibodies bind to toxins, venoms and surface antigens on pathogens, neutralising them via a coating and preventing them from binding to cell surface receptors
opsonisation
antibodies bind to surface antigens on pathogens to form antigen-antibody complexes and tag the pathogen for destruction
activates phagocytes and complement proteins, leading to the pathogen’s destruction