the urinary system
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
what are the 3 things urinalysis can do?
screen for diseases
detect infections
diagnose a medical condition
why is pee yellow?
it contains urochrome, a yellow pigment
functions of the urinary system
removes waste from the blood
maintains concentrations of water and electrolytes
regulates pH and blood pressure
maintains homeostasis!
urine is __% water
95
urinary system structures
two kidneys, ureter, bladder, and urethra
function of kidneys
filter blood
function of ureters
transport urine from kidneys to bladder
function of bladder
stores urine
function of urethra
transports urine outside of the body
the kidneys are positioned ________, meaning they are located behind the ______
retropeironeally
peritoneum
what is the inner area of the kidney called?
renal medulla
what is the outer shell of the kidney called?
renal cortex
what is the medial side of the kidney?
renal sinus
what supplies the kidneys with blood?
renal arteries and veins
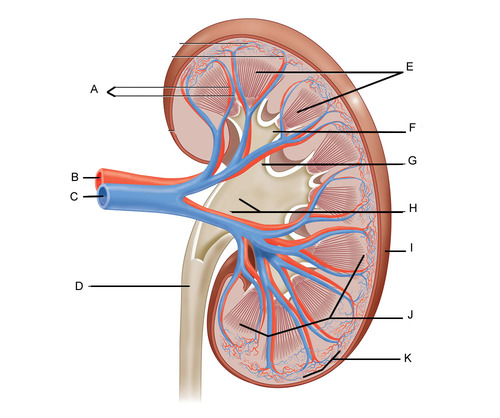
label!
A) renal vessels
B) renal artery
C) renal vein
D) ureter
E) renal pyramid
F) minor calyx
G) major calyx
H) renal pelvis
I) renal capsule
J) renal medulla
K) renal cortex
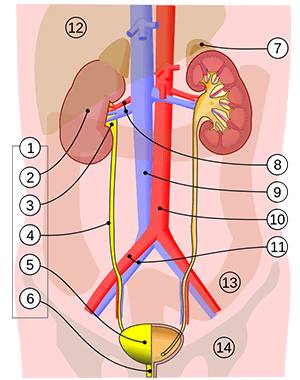
label! (only 2-6 and 8-10)
///
kidney
renal pelvis
ureter
bladder
urethra
///
renal artery and vein/renal vessels
renal vein
renal artery
renal arteries attach to ______
aorta
renal veins attach to ______
inferior vena cava
what process removes substances from the blood?
diffusion
what is the resulting liquid of blood filtering containing the waste called?
the filtrate
each kidney has 7-18 ______
renal pyramids
what is the functional unit of the kidney?
nephron
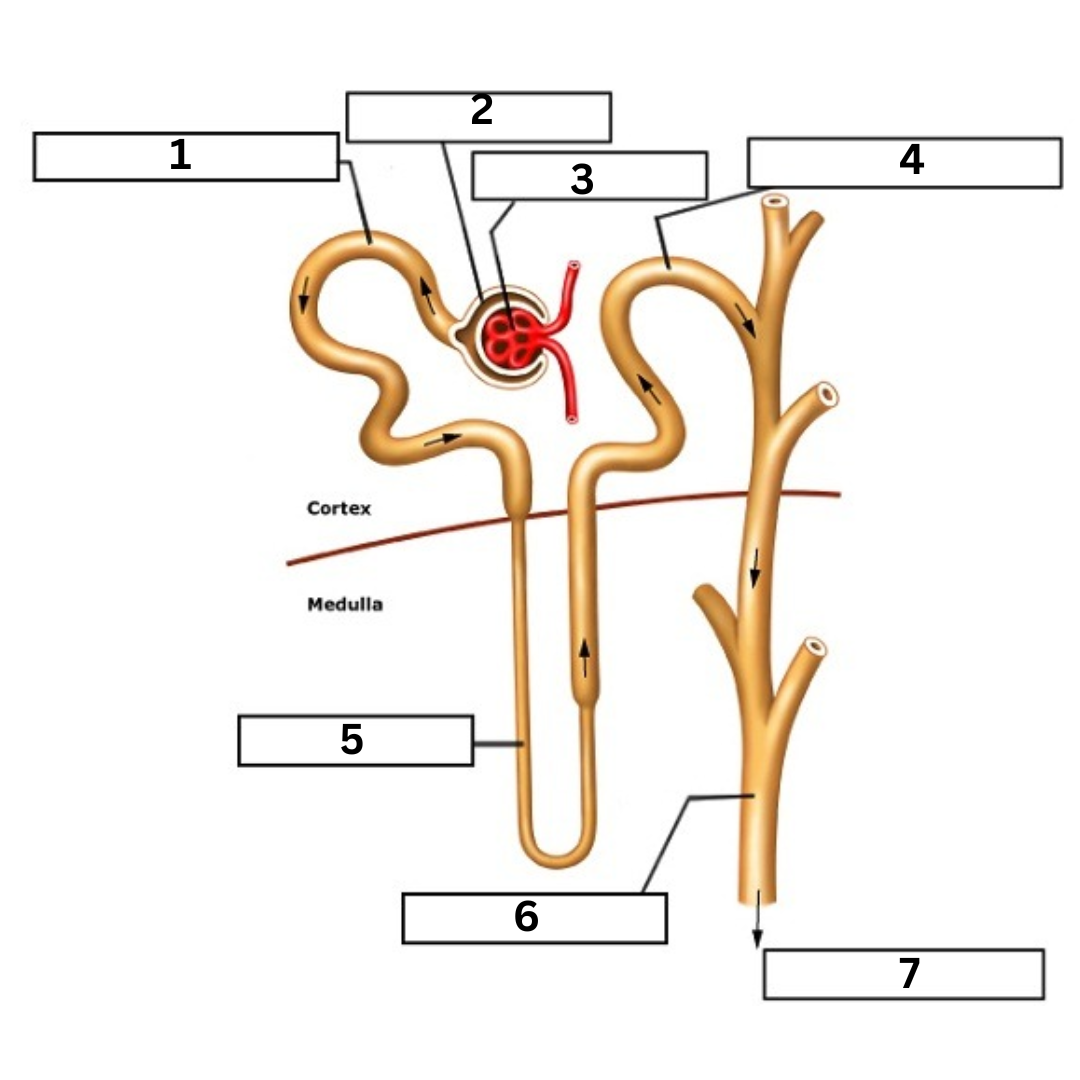
label!
proximal tubule
bowman’s capsule
glomerulus
distal tubule
loop of henle
collecting tubule
to ureter, then bladder
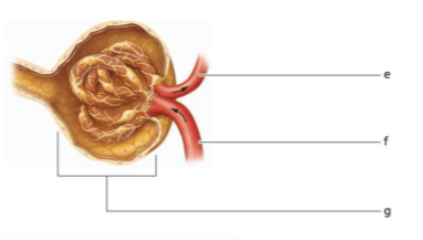
label!
e) efferent arteriole
f) afferent arteriole
g) glomerulus
what is the first step in urine formation?
glomerular filtration
in glomerular filtration, the glomerulus filters _____ and small substances from the _____ plasma. then it transports it into the glomerular _____ as glomerular _____. _____ _____ allows the movement of fluid out of the glomerulus and into the glomerulus capsule.
water
blood
capsule
filtrate
hydrostatic pressure
what is the 2nd step of urine formation?
tubular reabsorption
during tubular reabsorption, _____ filtered substances are transported from the _____ to the _____
useful
filtrate
blood
what is the 3rd step of urine formation?
tubular secretion
during tubular secretion, additional _____ from the _____ are moved from the _____ capillaries into the renal _____
wastes
blood
peritubular
tubule
filtrate flow chart
bowman’s capsule/glomerulus → proximal tubule → loop of Henle → distal tubule → collecting tubule/duct
what does secretion do?
removes substances from blood and collects as urine
what does absorption do?
moves water, glucose, and other substances back into blood
how many nephrons in a kidney roughly?
1 million
what is urea produced by?
the breaking down of proteins
what does erythropoietin increase?
rbc production
what is another term for urine elimination?
micturition
what muscle controls urination
detrusor muscle
what is the urethra?
a tube that carries urine out of the bladder to outside of the body
what are inserted into the bladder to drain urine?
catheters
what is inserting a catheter called?
catheterization
what do kidney stones form from?
minerals like calcium, oxalate, uric acid
what is the common name for cystitis?
bladder infection/UTI
what causes cystitis?
e. coli enters bladder/kidneys
is cystitis more common in men or women? why?
women - shorter urethra allows bacteria to spread easier and reach bladder
what are the symptoms of cystitis?
frequent need to urinate
pain in abdomen
burning sensation when peeing
cloudy urine with an odor
what increases risk of bladder cancer?
smoking
how does a person live without a bladder?
they have a bag attached to them that collects the urine instead of a bladder
what is the fancy name for prostrate enlargement?
benign prostrate hyperplasia
how does prostrate enlargement affect urine output?
it slows it
what does an overactive bladder cause?
urgent sensations to pee
what is incontinence?
inability to control urination
what is duplicated ureter?
two ureters drain into bladder rather than a single one
what is used to clean blood when the kidneys have failed?
dialysis
when there is no compatible kidney available, a kidney _____can be used
exchange