Edexcel IGCSE Biology - Food Production
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
what do plants need?
light, carbon dioxide, minerals, water
what environments can be used to enhance crop growth?
glasshouses/polythene tunnels
why are glasshouses used to increase crop yield?
protect crops from harsh weather conditions
carbon dioxide levels can be controlled/enhanced - using a paraffin heater (photosynthesis)
easier to protect crops from diseases and pests
artificial light can be provided in winter and at night (photosynthesis); crops can be grown all year round
temperature can be controlled (enzymes) with a heater in winter
heat is trapped from the sun to increase temperature
water supply can be controlled
why is it beneficial to control/enhance carbon dioxide concentration and temperature in a glasshouse for crop yield?
increase the rate of photosynthesis in the crops (no longer limiting factors)
this means that the crops will grow bigger and faster so yield will increase
also means crops can be grown all year round
what are fertilisers?
chemical substances which contain supplementary minerals for plant growth
why are fertilisers used?
when crops grow they take up minerals from the ground
when crops are harvested, they are not replaced
fertilisers replace these missing minerals
this means that crops have the minerals required for growth (and then some) so they can grow more and crop yield increases
what minerals do fertilisers usually contain?
nitrates, phosphates and potassium
why do plants require nitrates?
they are components of amino acids in plants which are required for growth
why do plants require phosphates?
they are required for respiration and root growth
why do plants require potassium?
to help enzymes required for photosynthesis and respiration
what is pest control?
utilisation of pesticides or biological control to prevent insects eating the plants
what is a pesticide?
a chemical that kills pests, but not crops
what types of pesticide are there?
insecticide
fungicide
herbicide
what is biological control?
using animals who are natural predators/parasites/disease causing organisms of pests to kill them - either encouraging current organisms or introducing new ones
what are the advantages of pesticides?
protect crops and increase yield
easy to use
work quickly
cheap
what are the disadvantages of pesticides?
pests can become resistant
you have to reapply them regularly
can damage other wildlife
bioaccumulation - can run into streams
can be poisonous to humans in large quantities
what are the advantages of biological control?
no harmful chemicals
avoids resistance
can target specific species
long lasting - don’t need reapplication
what are the disadvantages of biological control?
disrupt food webs
predators themselves can become a problem
may not be specific enough - eat wrong organism
take a longer period of time to work
may not adapt to surroundings
may not be wholly effective
what is yeast?
a single-celled fungi - microorganism
what is the main use of yeast in food production?
fermentation to produce bread or alcohol
what reaction does yeast perform that makes it suitable for bread/alcohol production?
anaerobic respiration
what is the word equation for anaerobic respiration of yeast?
glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide
what is the useful product of anaerobic respiration for bread production?
carbon dioxide
why is the production of carbon dioxide by yeast useful in bread production?
when the dough is left to rise, the yeast respire aerobically at first
when all the oxygen is used up, the yeast respire anaerobically producing carbon dioxide bubbles
these bubbles expand, causing the bread to rise
in the oven, these bubbles expand more making the bread rise further
ethanol is burnt off in oven
what ingredients have to be a part of bread dough in order for it to rise?
carbohydrates
they are broken down into sugars which act as fuel for the yeast
practical: describe how to investigate anaerobic respiration by yeast in differing conditions
dissolve sugar in boiled water
mix yeast with sugar solution in a boiling tube
add a layer of oil on top to stop oxygen reacting, to ensure only anaerobic respiration takes place
connect the boiling tube to a test tube of water
count the number of bubbles produced over a set time
you can alter the conditions to investigate:
temperature - water bath
concentration of sugar solution
pH - use buffer solution
what reaction does yoghurt making use to make yoghurt?
fermentation - anaerobic respiration
what bacteria is used in yoghurt making?
lactobacillus
what does lactobacillus do?
breaks down lactose in milk to form lactic acid
describe the process of yoghurt making
all equipment is sterilised to kill unwanted microorganisms
milk is pasteurised at 85C for 15 secs to kill any unwanted microorganisms
the milk is cooled to 40-45C so lactobacillus can be added without being denatured
the mixture is incubated at this temperature for several hours to allow lactobacillus to convert lactose to lactic acid,
this lowers the pH of the mixture and denatures milk proteins so the y coagulated and yoghurt thickens
stir and cool the yoghurt to 5C so flavourings and fruit can be added
what container is used to grow microorganisms on a large scale?
a fermenter
what liquid does a fermenter contain?
culture medium in which microorganisms can grow and reproduce
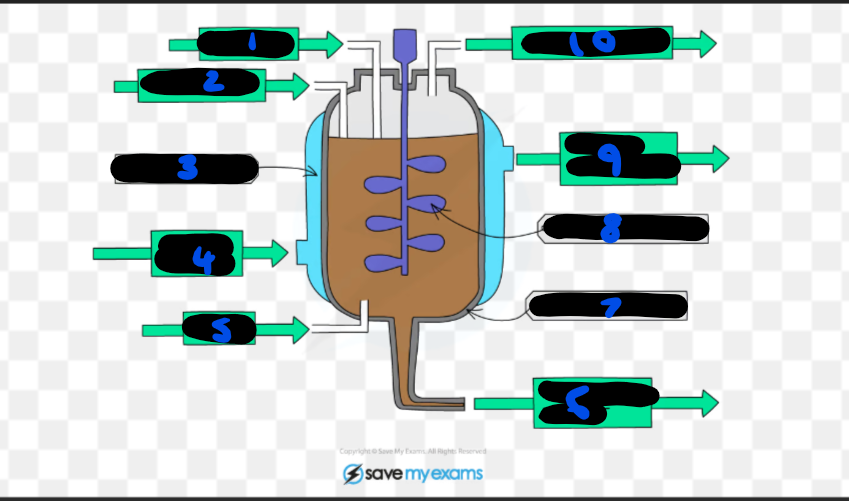
label this fermenter
would also have a pH probe and thermometer
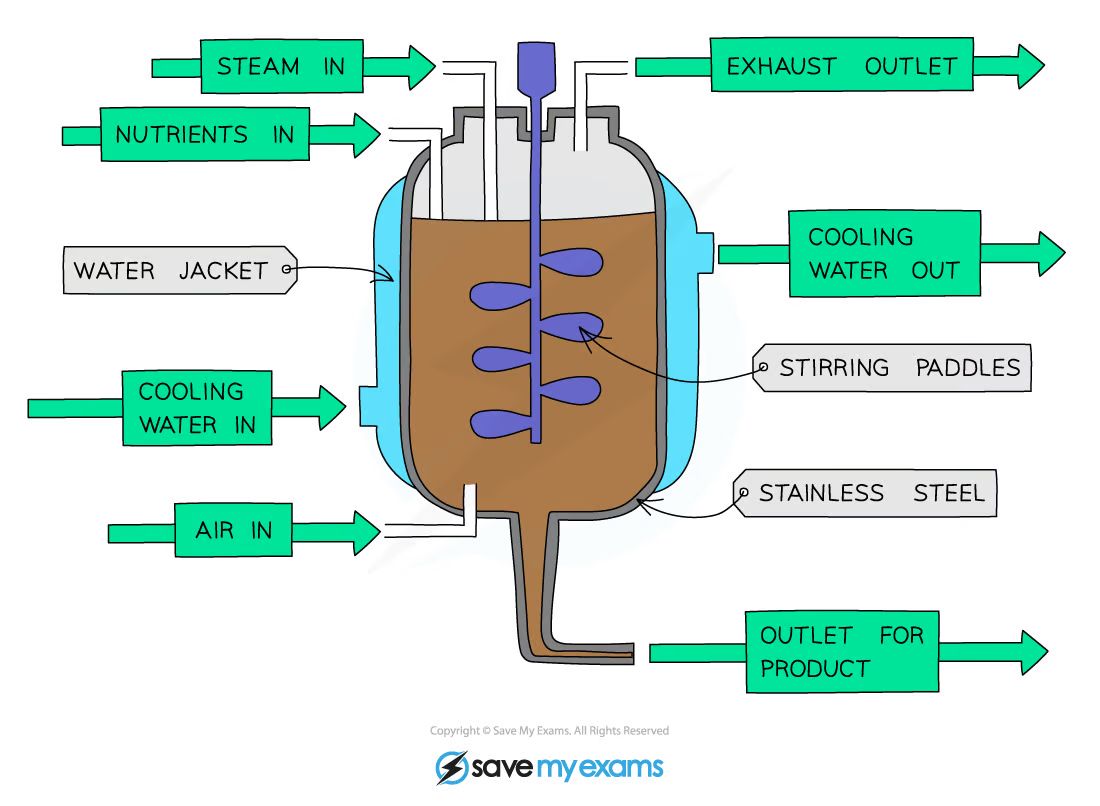
how are nutrients provided for growth?
in the culture medium
why is the pH monitored and controlled?
to ensure it is at the optimum level for microorganisms and enzymes to work efficiently so the rate of reaction is highest
why is the temperature monitored and controlled?
to ensure it is at the optimum level for microorganisms and enzymes to work efficiently so the rate of reaction is highest
water jacket ensures that it doesn’t get too hot
why are there stirring paddles?
to ensure that the nutrients, oxygen, temperature, pH and microorganisms are distributed evenly, increasing yield as microorganisms can always access everything they need
why is oxygen provided?
to ensure that aerobic respiration can take place if necessary (if it is not required then no oxygen is allowed in)
why does the fermenter need aseptic conditions?
to prevent unwanted microorganisms from growing and contaminating the product; prevents competition
why are fish farmed?
to combat the increased demand for fish which leads to overfishing
it also insures short food chains which mean less energy loss
fish is high in protein and low in fat so a good food
what methods are used in fish farming?
maintenance of water quality
control of intraspecific predation
control of interspecific predation
controlling pests and diseases
controlling feeding
selective breeding
describe maintenance of water quality
fresh water is constantly moved through the area
the water is filtered to remove waste and harmful bacteria to prevent disease
this also prevents eutrophication
describe control of intraspecific predation
predation between fish of the same species
fish are separated by age, gender and size to prevent this
describe control of interspecific predation
between different species of animal
fish are kept in cages to prevent birds/other animals eating them
this also means that they move less and thus use up less energy
describe controlling pests and diseases
due to close conditions these can spread easily
antibiotics are fed to fish regularly and pesticides are sprayed to try and prevent this
however this can lead to resistance or other nearby animals can eat them
describe controlling feeding
fish are fed regularly in small amounts to prevent overeating and food wastage
fed a high protein diet - pellets made from other smaller fish
this is to maximise how fast and how big they grow
describe selective breeding
fish can be selectively bred to produce fish with ideal characteristics - faster growing, less aggressive