Stars, Black Holes, Galaxy
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is the main composition of a star?
A. Rocks and metals
B. Gas and plasma
C. Ice and dust
D. Solid hydrogen
B. Gas and plasma
Stars are mostly hydrogen and helium in a superheated state called plasma.
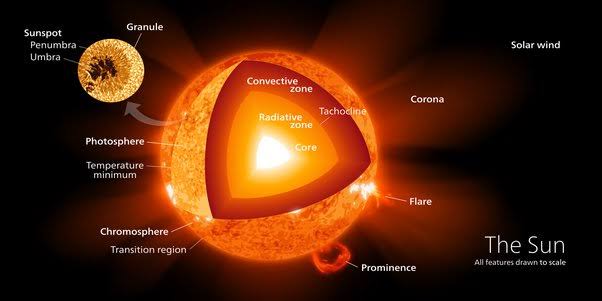
Where does a star get its energy?
A. Combustion
B. Friction
C. Nuclear fusion
D. Gravitational collapse
C. Nuclear fusion
Fusion converts hydrogen into helium in the core, releasing massive energy.
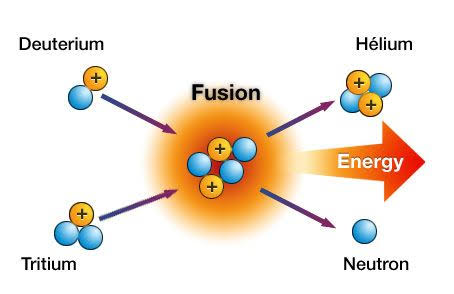
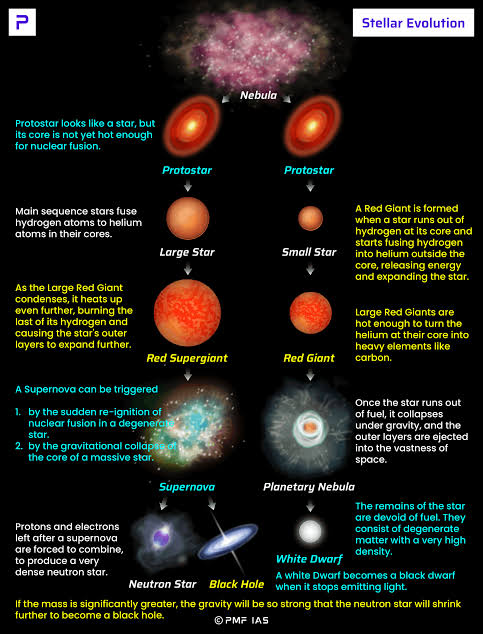
What’s the correct sequence in a massive star’s life cycle?
A. Protostar → Main Sequence → Red Giant → White Dwarf
B. Protostar → Main Sequence → Red Supergiant → Supernova → Black Hole
C. Nebula → Brown Dwarf → Supernova
D. Main Sequence → Planetary Nebula → Neutron Star
B. Protostar → Main Sequence → Red Supergiant → Supernova → Black Hole
A supernova is:
A. A collapsing black hole
B. A cloud of cosmic dust
C. An exploding dying star
D. The birth of a galaxy
C. An exploding dying star
A supernova releases huge energy and spreads heavy elements into space.

What exactly is a black hole?
A. A hole in space
B. A dark star
C. A collapsed star with extreme gravity
D. A planet with no light
C. A collapsed star with extreme gravity
Forms after a supernova if the core is massive enough. Not even light escapes.
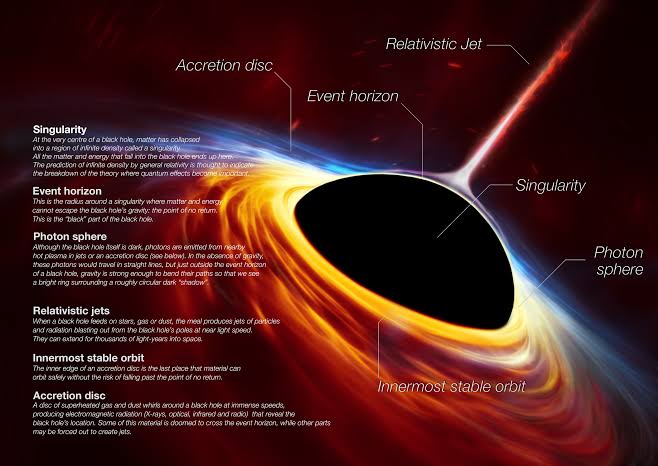
In a black hole, the event horizon refers to:
A. A spinning disk
B. A burst of energy
C. The point of no return
D. The outer gas layer
C. The point of no return
Once crossed, nothing can escape the black hole’s gravitational pull.

Stars are formed from:
A. Planet collisions
B. Supernova explosions
C. Nebulae
D. Meteors
C. Nebulae
Stars form from clouds of gas and dust called nebulae, where gravity pulls matter together.

A galaxy is:
A. A collection of solar systems only
B. A star
C. A group of stars, gas, dust, and dark matter
D. A space between planets
C. A group of stars, gas, dust, and dark matter
Galaxies hold billions of stars and other celestial bodies, held together by gravity.

The Milky Way is classified as what type of galaxy?
A. Irregular
B. Elliptical
C. Spiral
D. Dwarf
C. Spiral
It has spiral arms and a central bulge; our Solar System is in one of the arms.

What force holds galaxies together?
A. Magnetism
B. Pressure
C. Dark energy
D. Gravity
D. Gravity
Gravity is the dominant force that binds stars and systems within galaxies.
Which of the following is NOT a typical star type?
A. Red Giant
B. White Dwarf
C. Blue Moon
D. Neutron Star
C. Blue Moon
Blue Moon isn’t a star type; it’s just a rare full moon.

A white dwarf is:
A. A baby star
B. A collapsed core of a medium star
C. The same as a black hole
D. A ball of plasma
B. A collapsed core of a medium star
Remains after a red giant sheds its outer layers.

A neutron star forms when:
A. A small star goes nova
B. A massive star collapses but not into a black hole
C Two galaxies collide
E A star becomes a planet
B. A massive star collapses but not into a black hole
Super dense, and may spin rapidly (pulsars)

What does the H-R diagram show?
A. Planet orbits
B. Galaxy shapes
C. Star brightness vs temperature
D. Moon phases
C. Star brightness vs temperature
It plots stars by luminosity and surface temp; shows star evolution.
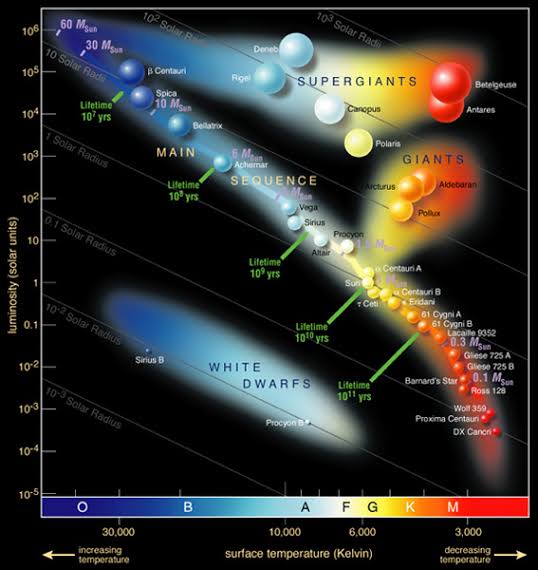
Main Sequence stars are in which phase?
A. Birth
B. Mid-life, fusing hydrogen
C. Dying
D. Collapsing
B. Mid-life, fusing hydrogen
Stars like the Sun are stable and converting hydrogen to helium.

A quasar is:
A. A mini black hole
B. A quiet galaxy
C. A bright, active galactic nucleus
D. A type of come
C. A bright, active galactic nucleus
Powered by a supermassive black hole eating matter rapidly.

Gravitational lensing occurs when:
A. A telescope zooms in
B. A black hole spins
C. Light bends around a massive object
D. A star explodes
C. Light bends around a massive object
Gravity curves space, bending light. Proof of massive objects like black holes.
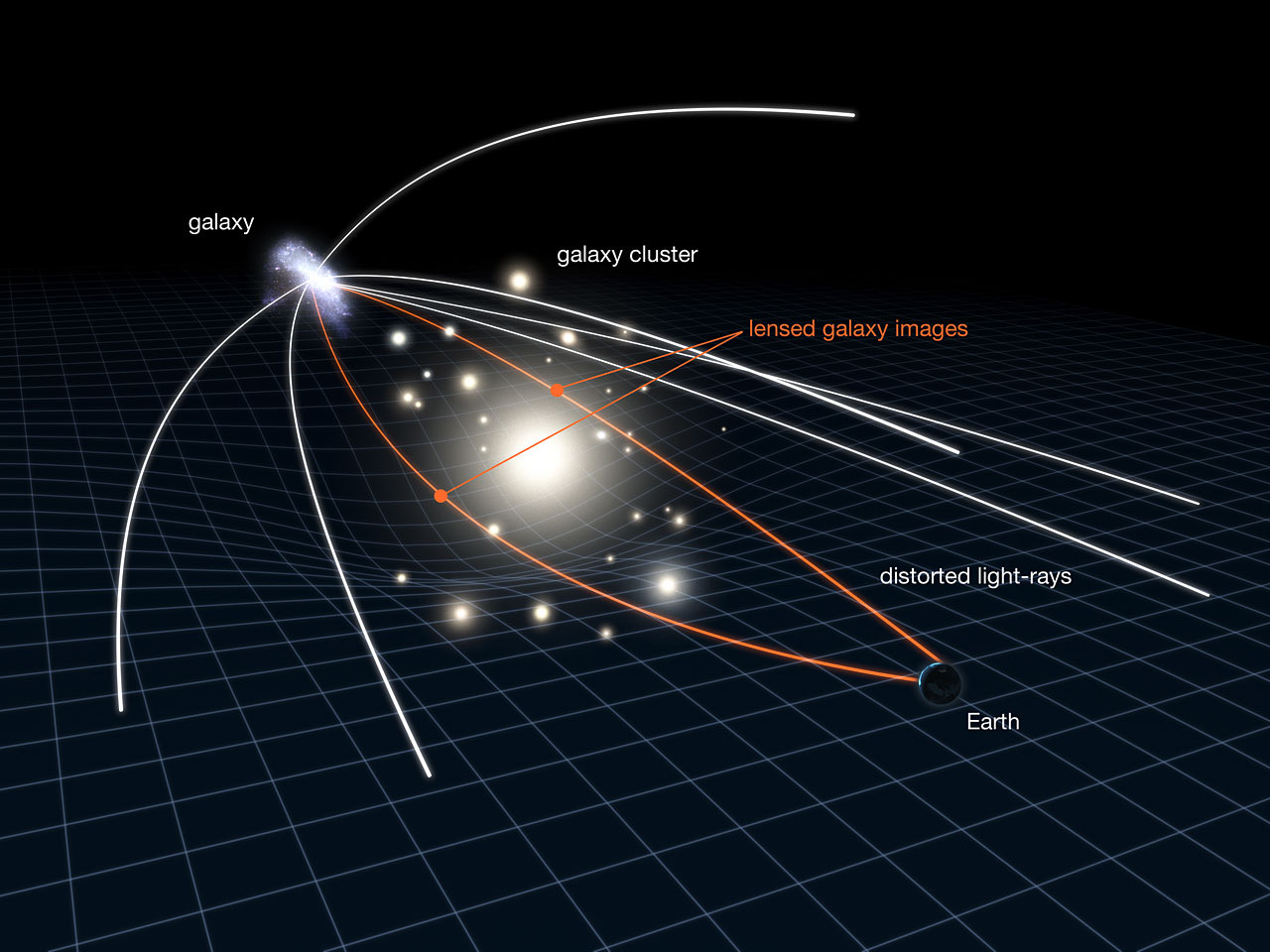
Which is NOT evidence of a black hole?
A. X-ray bursts
B. Stars orbiting “nothing”
C. Gravitational lensing
D. Seeing a dark sphere
D. Seeing a dark sphere
We can’t see black holes directly—they’re invisible. But we see their effects.

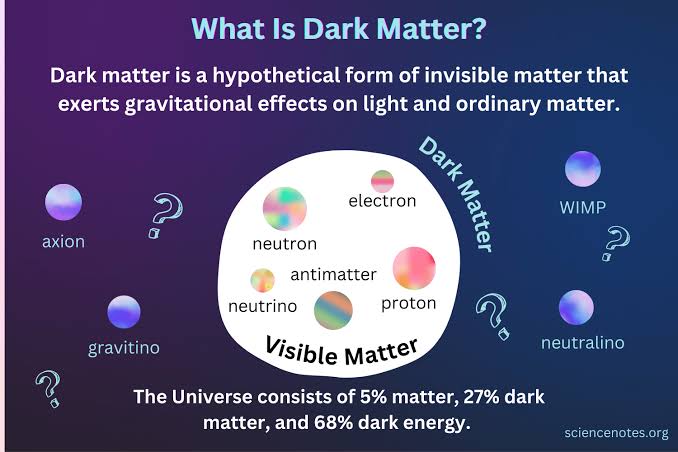
Dark matter is:
A. Anti-gravity
B. Light-absorbing gas
C. Invisible matter with gravity
D. Black hole material
C. Invisible matter with gravity
It doesn’t emit light, but affects how galaxies rotate and form.