Therapeutic Exercise stretching & strengthening
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
different types of exercise
flexibility (ROM), strengthening, aerobic (cardiovascular)
what is the goal of rehabilitative?
Goal is to improve deficits that impact occupational performance
ROM exercises (stretching)
-increases the resting length of the muscle
-single joint muscle: joints should be positioned opposite of the muscle's action
-multi joint muscle: muscle must be lengthening over all joints simultaneously
-Balance ROM exercises with positioning strategies
How long do you hold a ROM exercise for?
Hold 15-60 seconds
what is AROM (active)?
client moves actively

What is AAROM (Active Assisted)
active assisted ROMOTP assist client to achieve full range
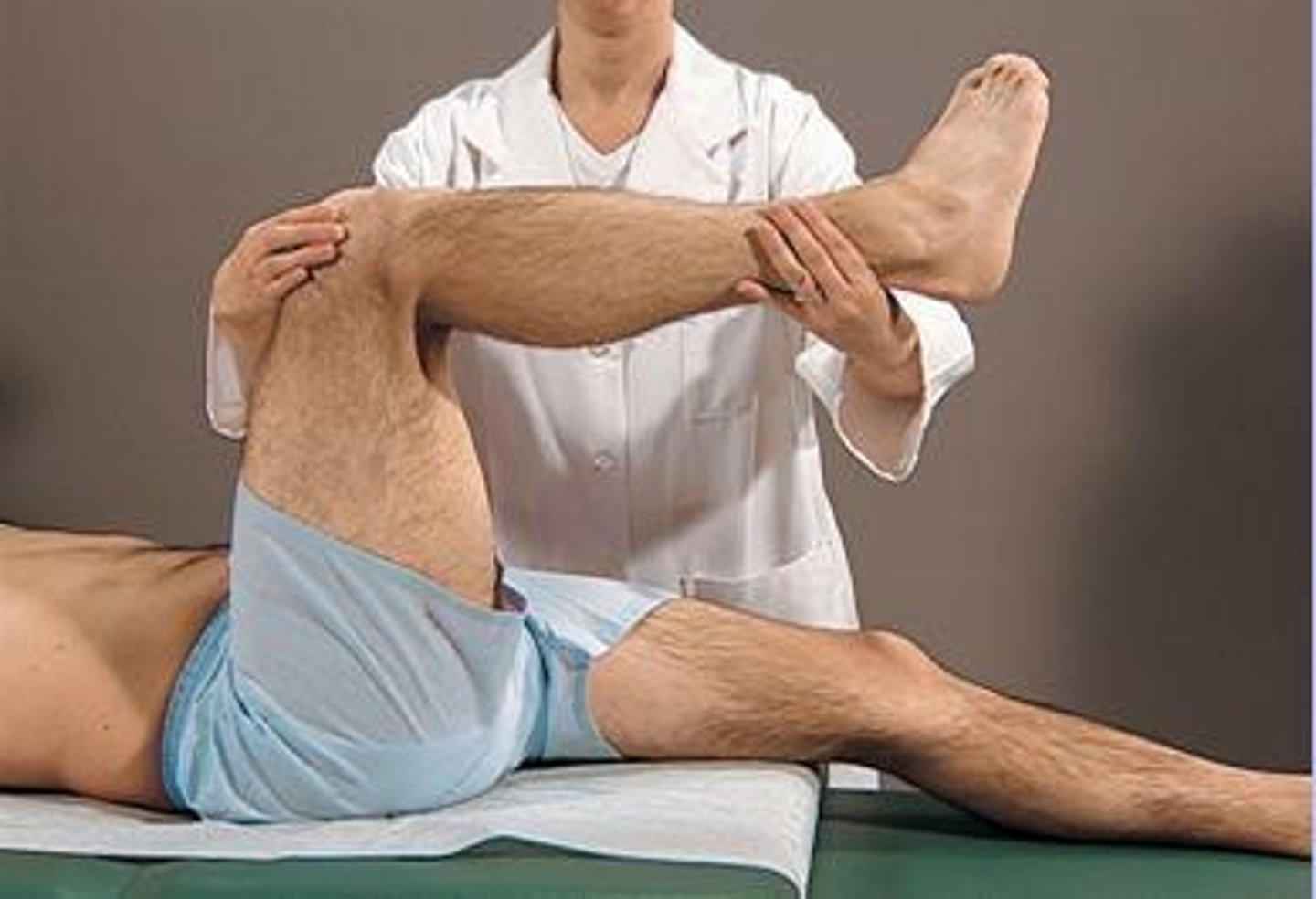
what is PROM? (passive)
OTP moves the client through the ROM passively
what is the neuro application of AROM
client moves actively. can maintain ROM or be strengthening in weak individuals.
what is the neuro application of AAROM
client requires assist to achieve full ROM (typically due to weakness)
what is the neuro application of PROM
cleint unable to move limb and OTP completes exercises to maintain ROM
what is the ortho application of AROM
client safe to activate their muscles and move independently
what is the ortho application of AAROM
client can complete ROM with support to maximize range
what is the ortho application of PROM
therapist must move limb b/c client is unsafe to activate muscles (often due to surgical repair) OR client is clear for therapist to apply pressure to increase ROM
isometric contraction
muscle attachments do not move
gravity is not a factor
fixed speed and resistance
no joint motion

concentric contraction
muscle attachments move closer together (muscle shortens)
movements occur against gravity (raising motion)
variables speed, fixed resistance

eccentric contraction
muscle attachment move farther apart
movement occur with gravity (lowering motion)
decelerates movement caused by gravity
fixed speed variable resistance
closed chain
exercises where the distal end of the extremity is fixed to a stationary object (or surface)
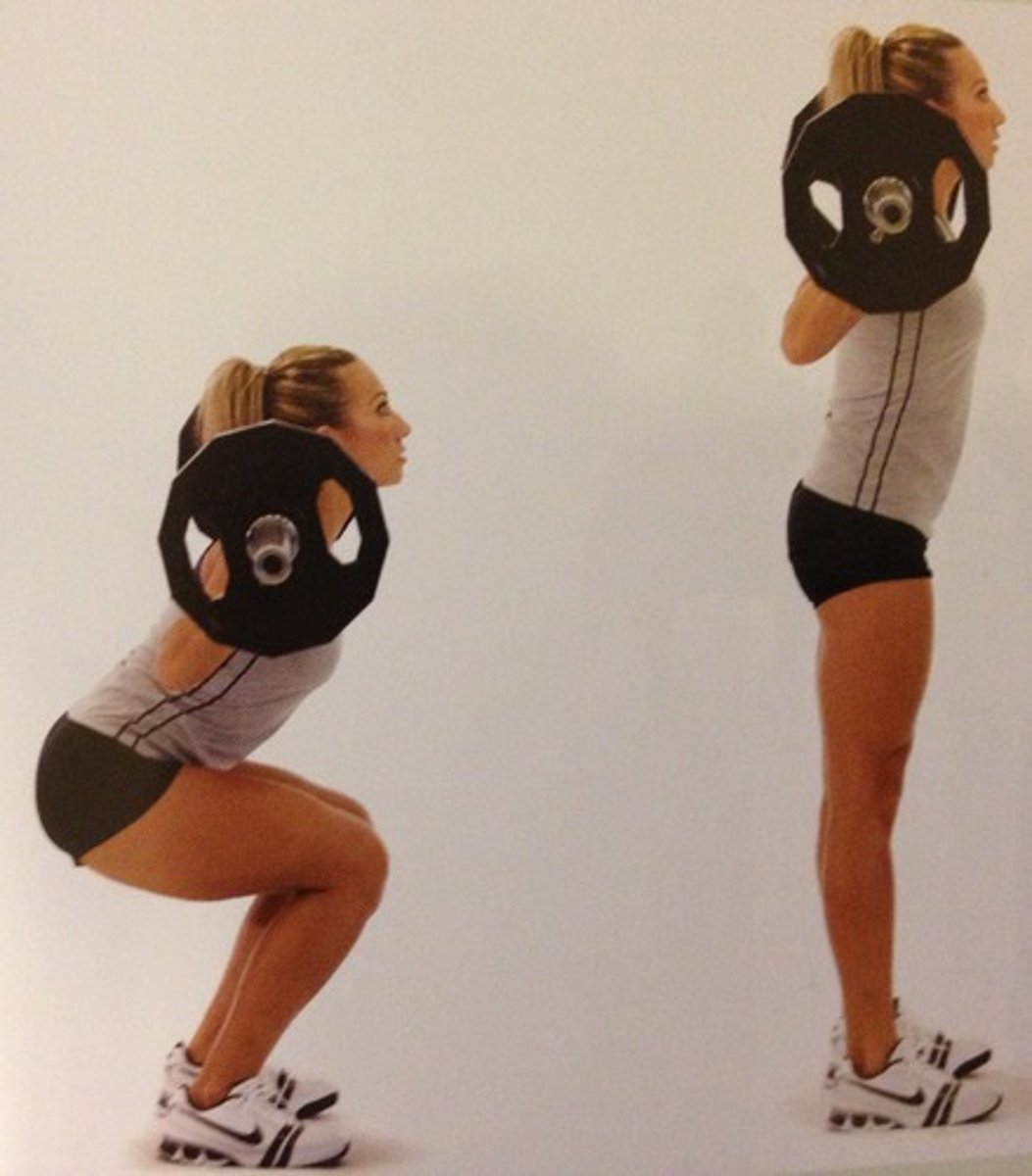
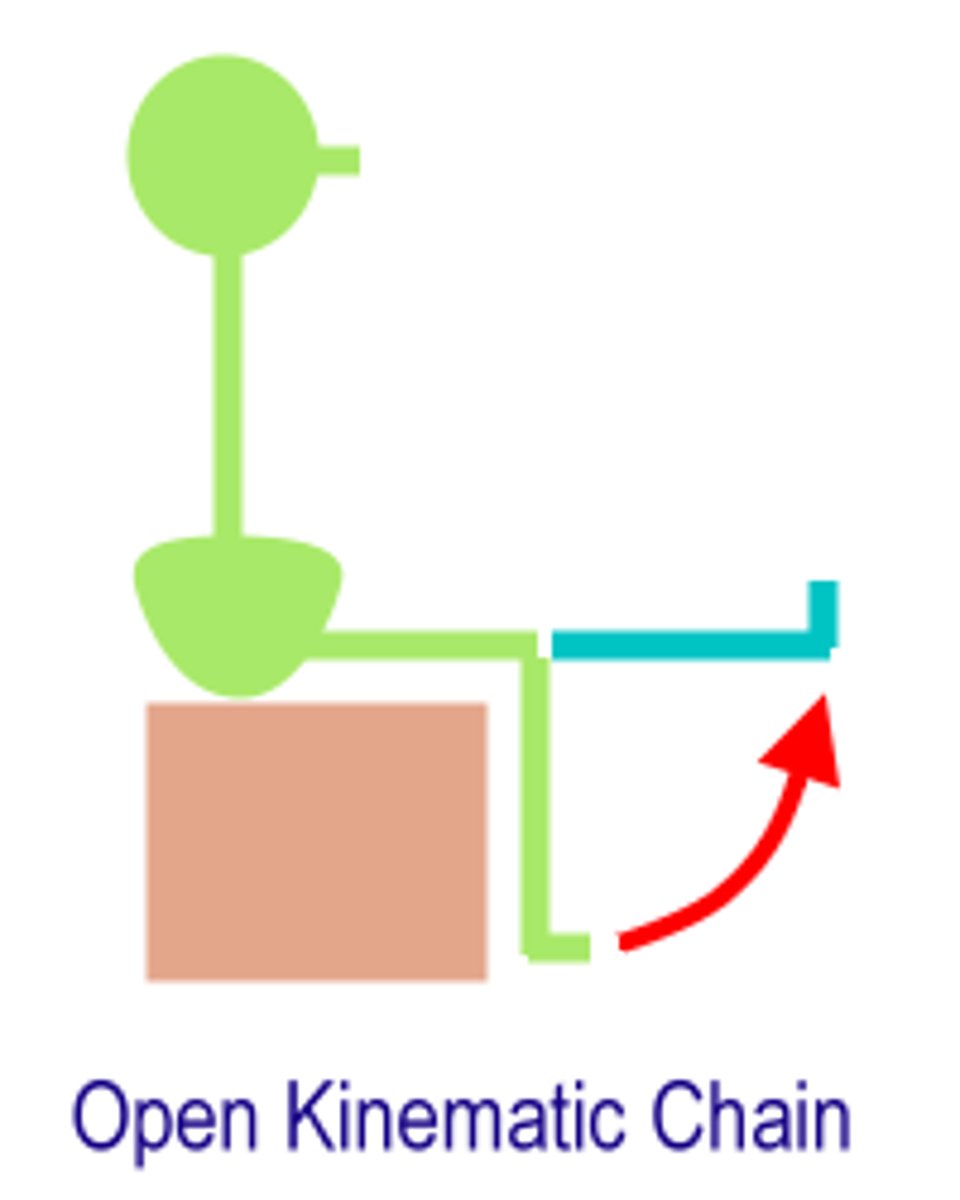
open chain
allows the distal end of the extremity (chain) to move freely
endurance
designed to increased stamina lower intensity or resistance over more time or reps

strength
designed to increase strength higher resistance over fewer reps; (sets of 3x10)

what do you consider when deciding how much resistance to use for a patient?
MMT results, age, PLOA, clinical observations, pt feedback
what are isometric exercises?
tightening contractions with minimal joint movement
strengthening the muscle in only one position, so good for building stability and not dynamic strength
scapulohumeral rhythm
beyond 30 degrees flexion, the scapula and humerus move at a 1:2 ratio. full flexion or abduction of the shoulder involves approximately 60 degrees scapular rotation and 120 degrees flexions
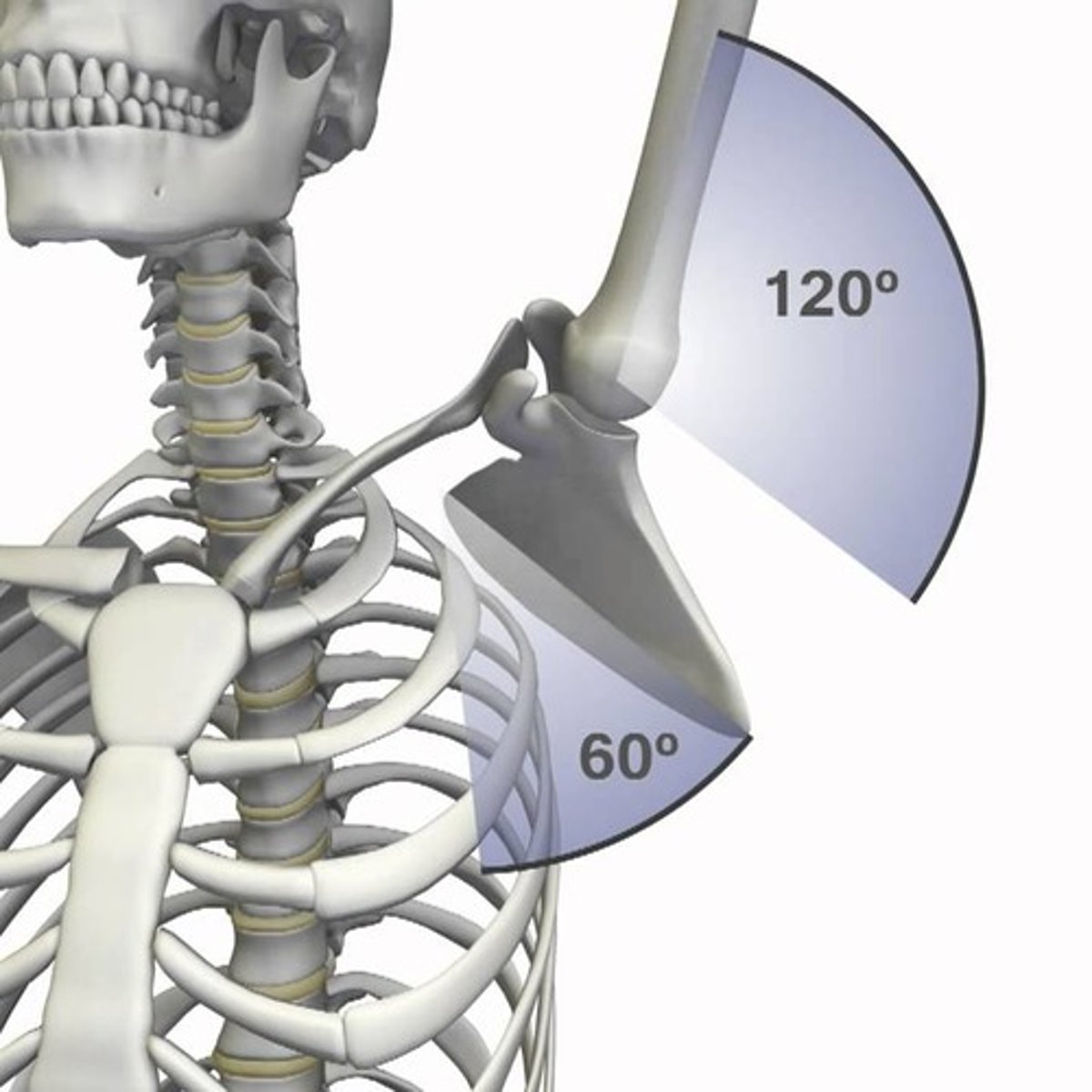
What is subacromial impingement?
Compression of the soft tissues between acromion and humeral head
what is the goal for exercise?
30 mins 5 days a wk of moderate intensity exercise