Anatomy Exam 1
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Not done
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What is Homeostasis? Why it is important for living systems
Homeostasis is the ability of an organism to maintain a consistent internal environment, or “ steady state”. It is important because it can normalize blood sugar regulation.
General steps of a negative feedback loop.
Mechanism that reverses deviation from the set point
Ex: Temperature regulation, Blood Sugar Regulation.
Positive feedback and when/where it occurs in the body
The stimulus is reinforced to continue in the same direction until a climactic event occurs
Ex: Childbirth contractions, Breast Feeding, Blood Clotting.
Atom and the roles of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons.
Atoms is the smallest quantity of an element
Protons is positive charge
Neutrons is no charge
Electrons is negative charge
Atomic number, Mass number, and Charge State from Subatomic particles
Atomic number, Protons, and Electrons are bottom left number of Element.
Mass number is top left number of Element
Neutrons if top left minus bottom left.
Atoms, Ions, Isotopes, Molecules, and Compounds
Atoms is smallest quantity of an element. It composed of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons.
Ions is an atom with an electric charge Positive and Negative. Cation when ion with positive. Anion is ion with negative charge
Isotopes is same element but different mass number. (the bottom left number)
Molecules is 2 or more atoms bonded together (same element)
Compounds is composed of two or more different elements joined by Chemical Bonds
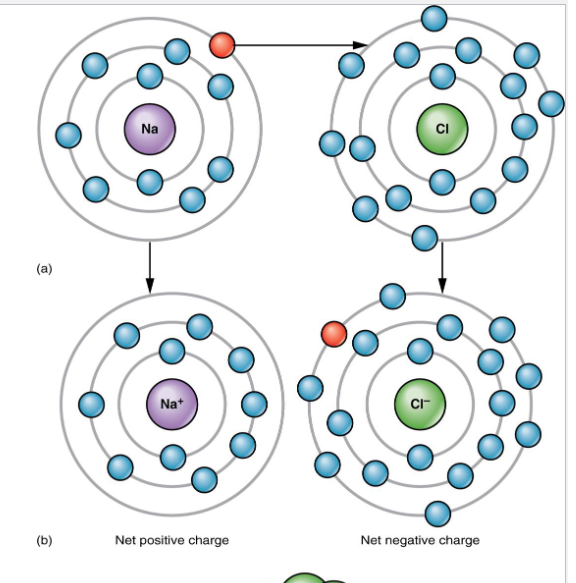
Ionic Bonds
The ongoing close association between ions of opposite charge (give electron away)
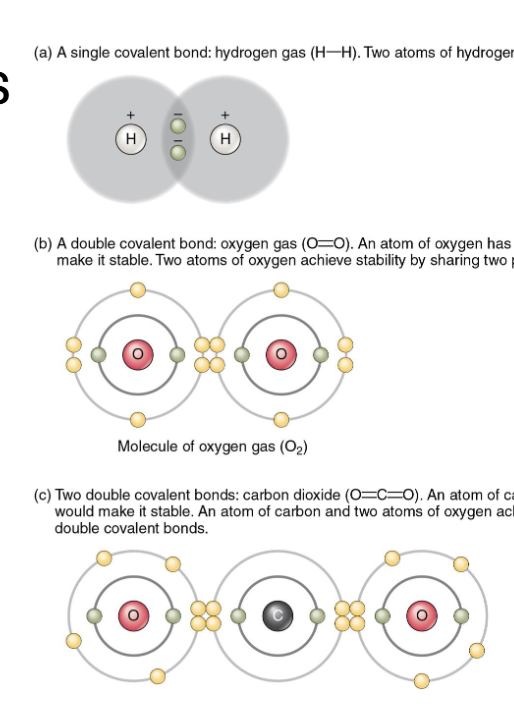
Covalent Bonds
Share electrons in a mutually stabilizing relationship
Stronger than ionic bonds (strongest attach)
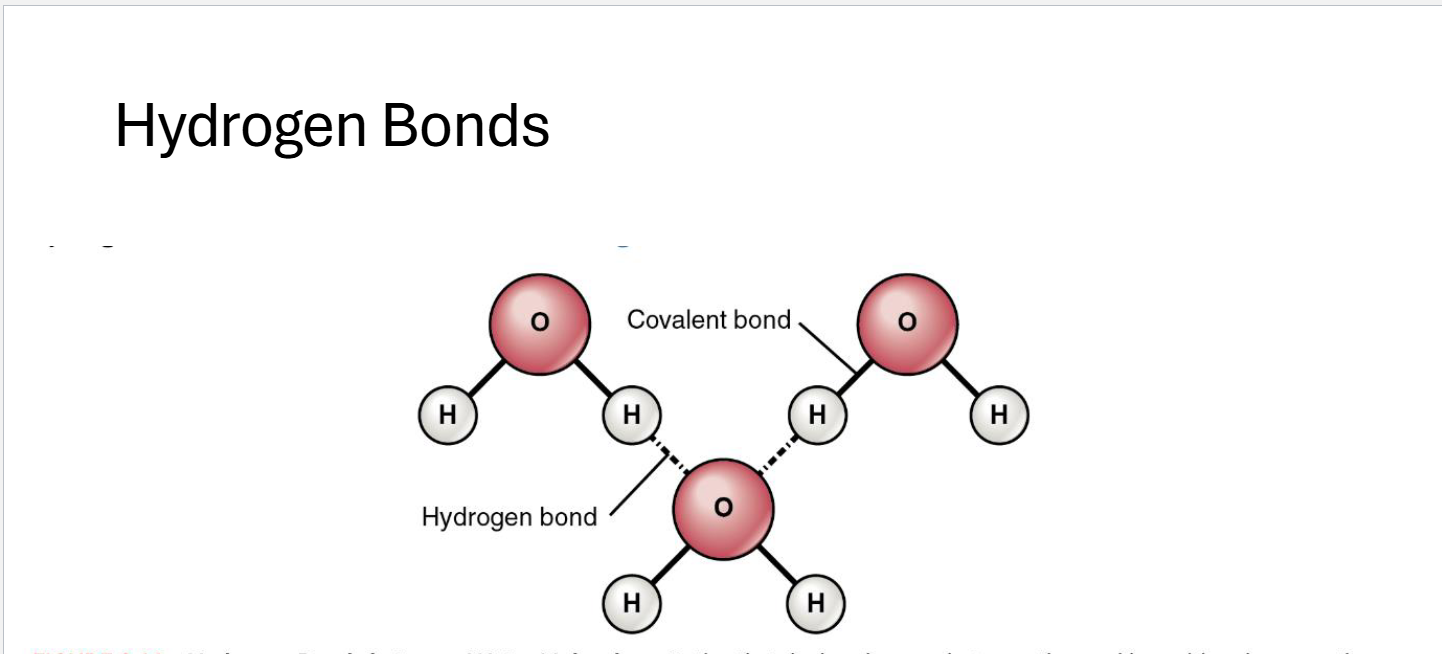
Hydrogen Bonds
Weak Negative (-) oxygen attach to weak Positive (+) of hydrogen fro covalent bonds
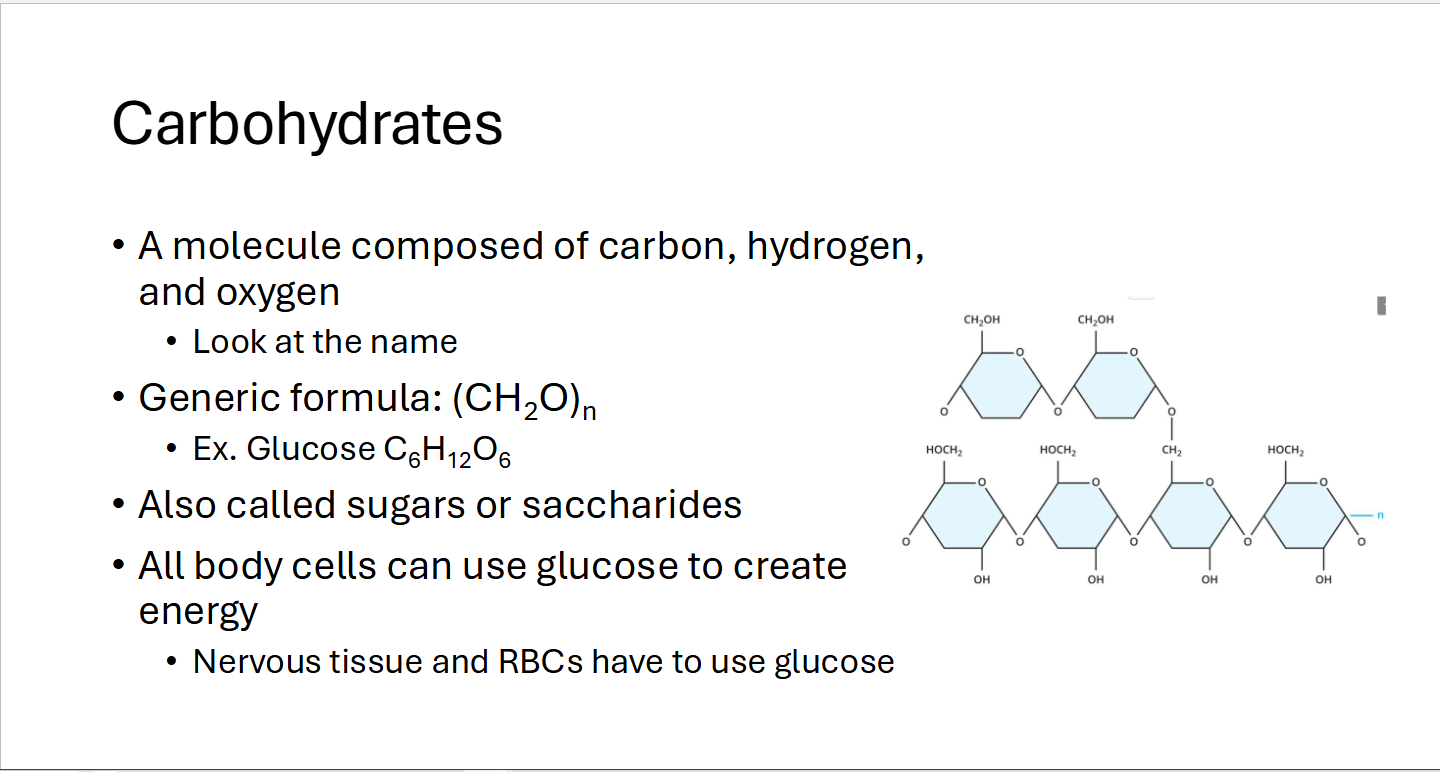
Carbohydrates
Molecule composed of Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), and Oxygen (O)
Generic formula: CH2O
Also called Sugars or Saccharides
All body cells can use glucose to create energy
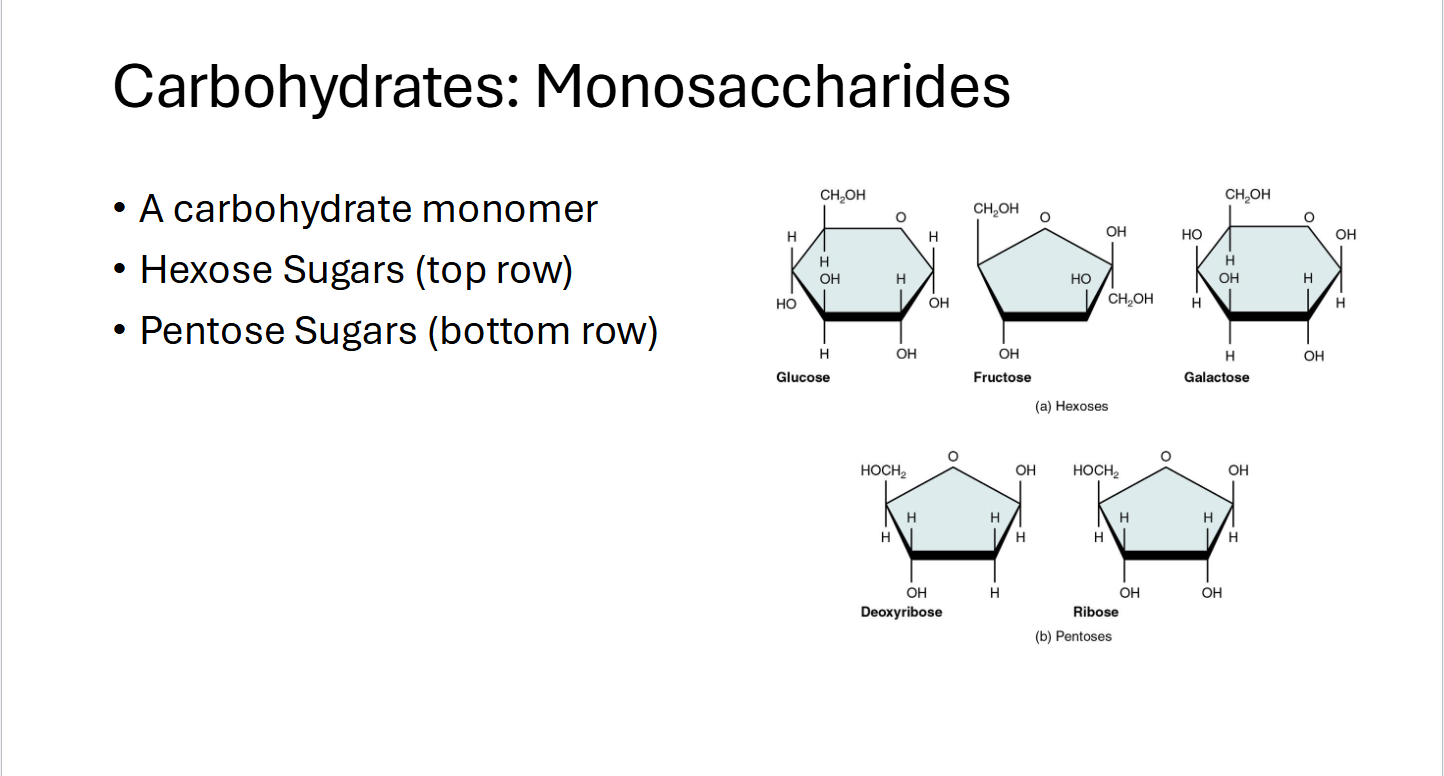
Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides
A Carbohydrate monomer
Hexose sugars (Top rows)
Pentose Sugars (Bottom row)
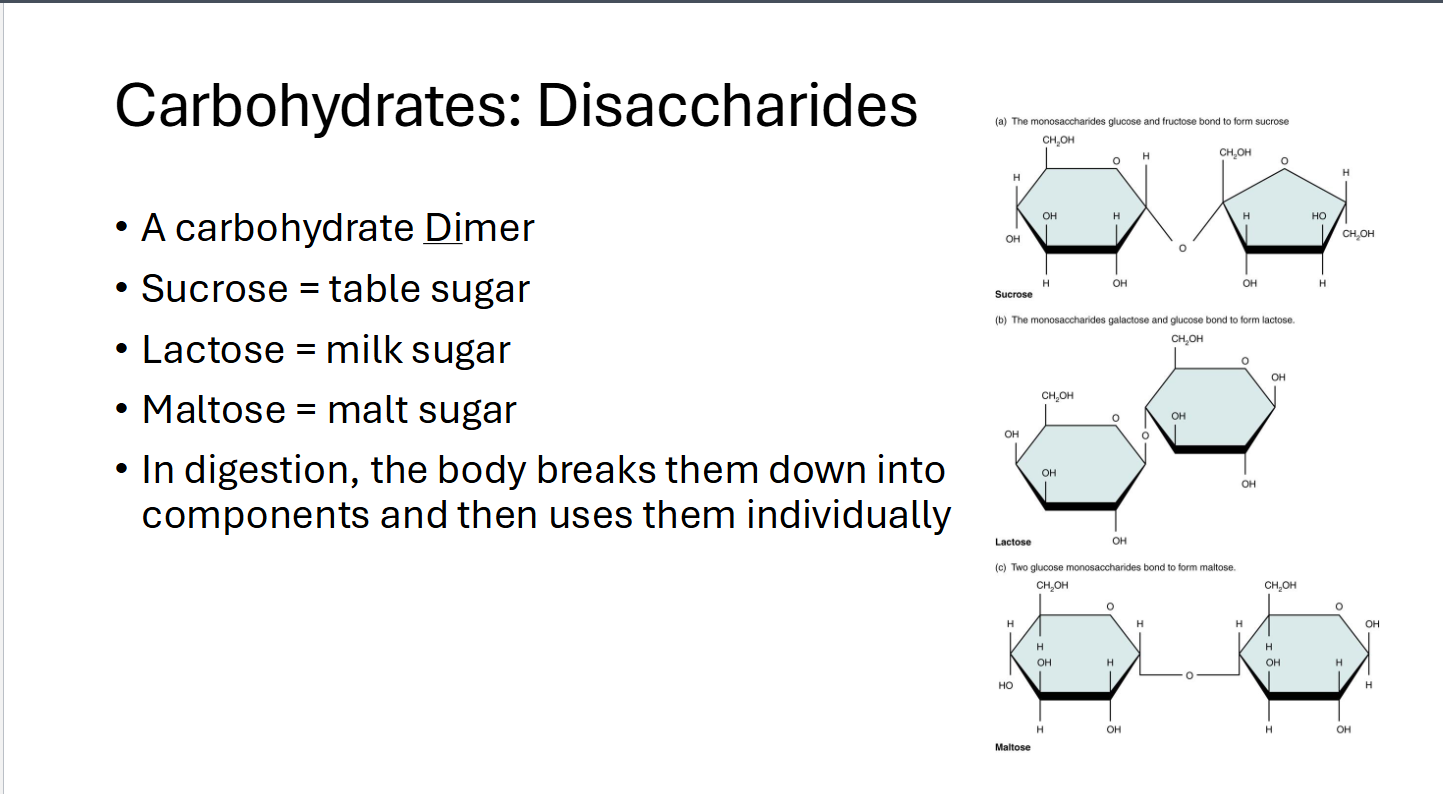
Carbohydrates: Disaccharides
A Carbohydrate Dimer
Sucrose = table sugar
Lactose = milk sugar
Maltose = Malt sugar
Body breaks them down into components and then uses them individually
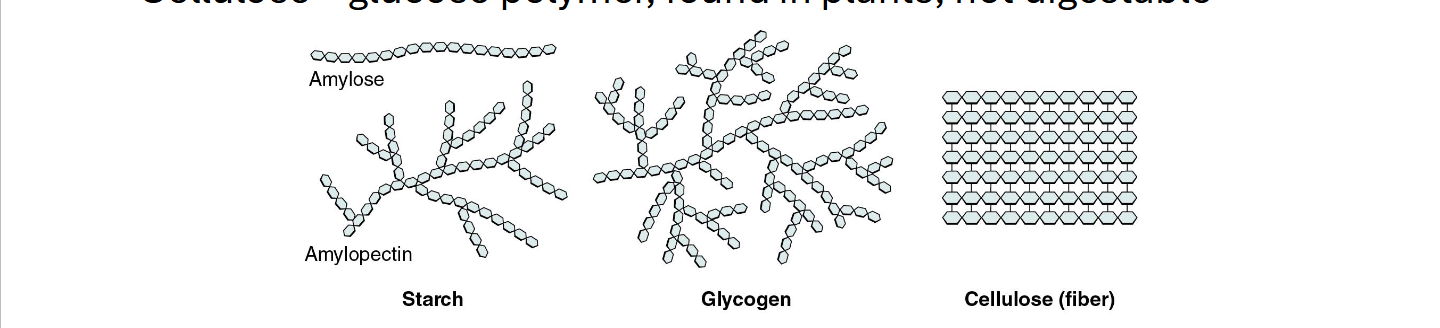
Carbohydrates: Polysaccharides
Can be thounsands of monosaccharides
Starches - Glucose polymers, found in plants, easy to digest
Glycogen - Glucose polymers, found in animals, how we store glucose in our bodies
Cellulose- glucose polymer, found in plants, not digestable
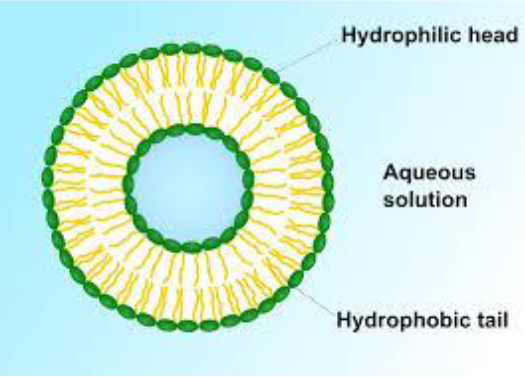
Lipids
Made of mostly hydrocarbons, few oxygen atoms
Non polar; hydrophobic
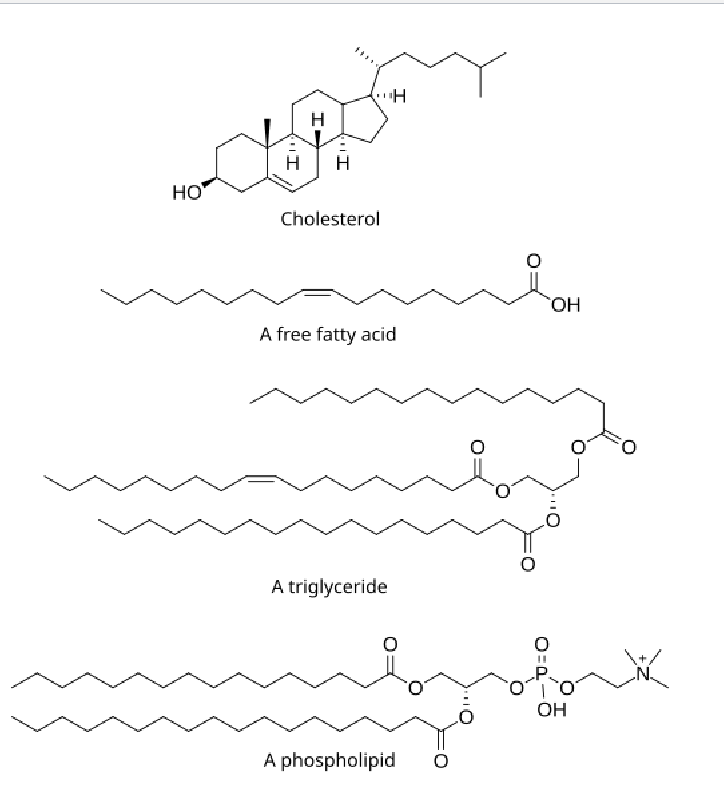
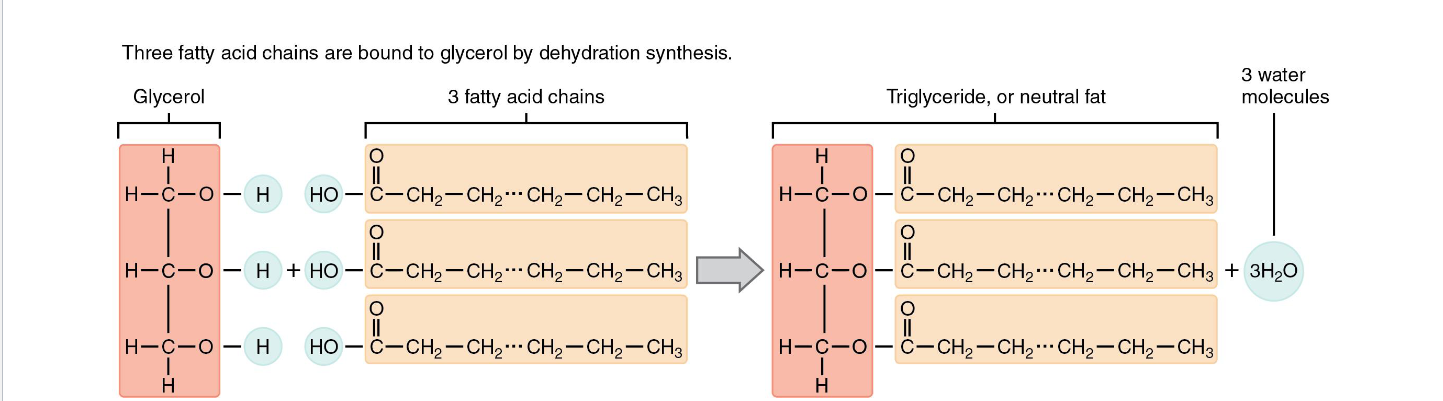
Lipids: Triglycerides
Glycerol + 3 fatty acid chains
Major source of fuel for body
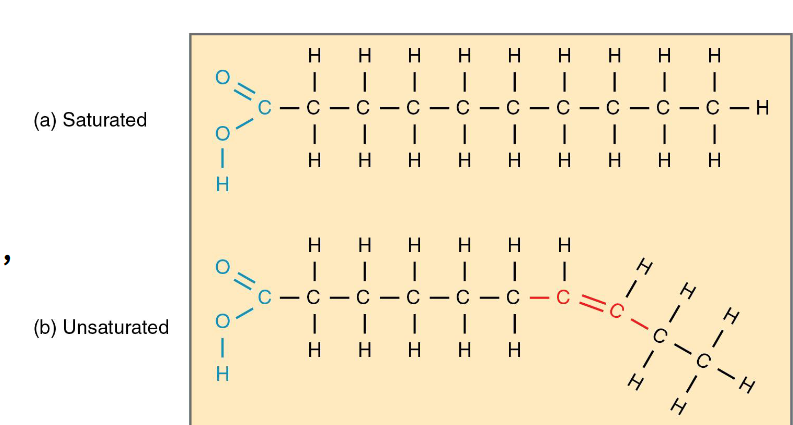
Saturated and Unsaturated Fats
Saturated: no double bonds maximum number of hydrogen atoms ( pack together tightly)
Unsaturated: one double bond , forms a kink (cannot pack together tightly)
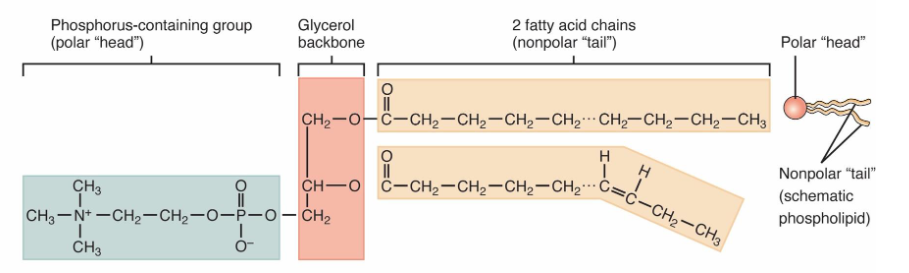
Lipids: Phospolipids
Phosphate group + Glycerol + 2 fatty acid chains
The phosphorous head is polar, the fatty acid chains are non-polar
Amphipathic
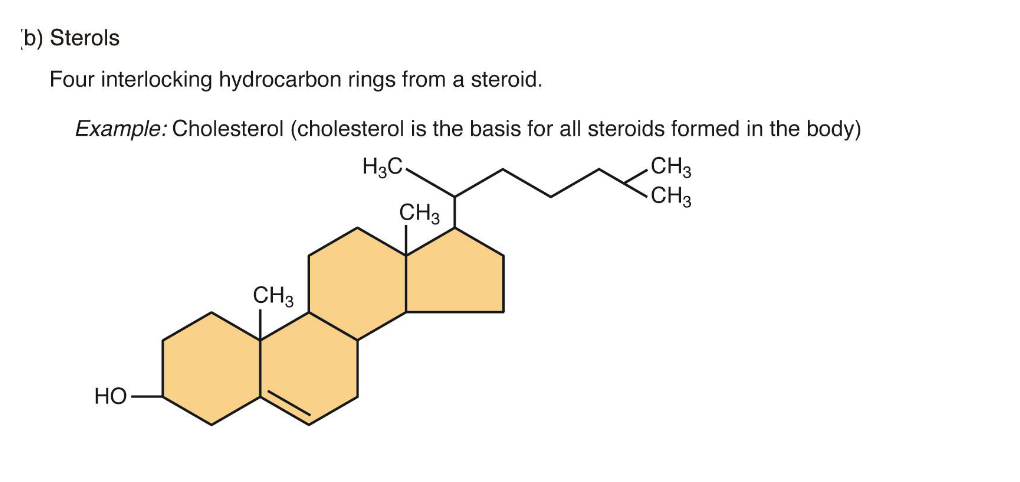
Lipids: Steroids
4 Hydrocarbon rings bonded to a variety of other atoms and molecules
Protein
Monomer: Amino acids
Polymer: Polypeptide or protein
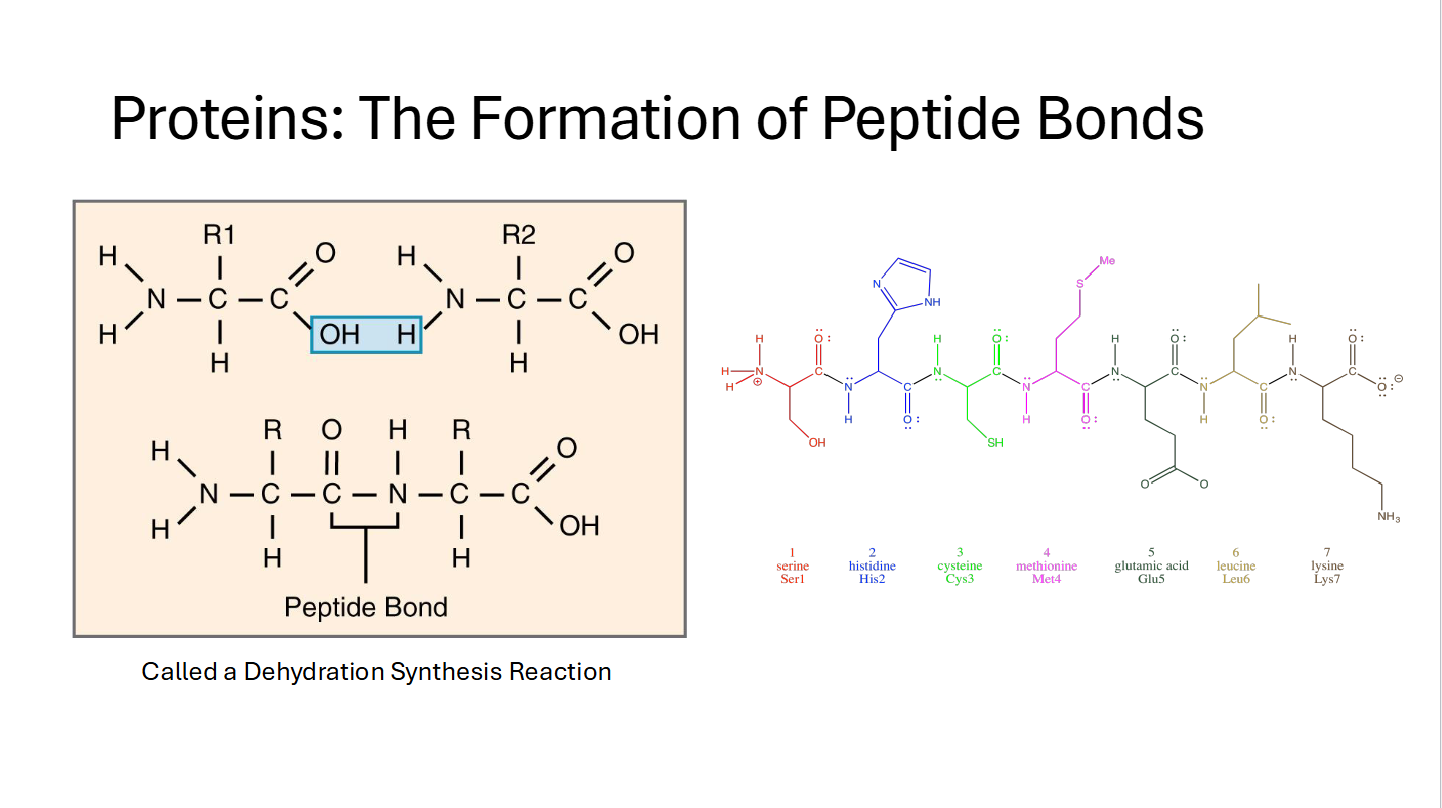
Peptide Bond
Found in all tissues and organs
N-Terminus and C-terminus
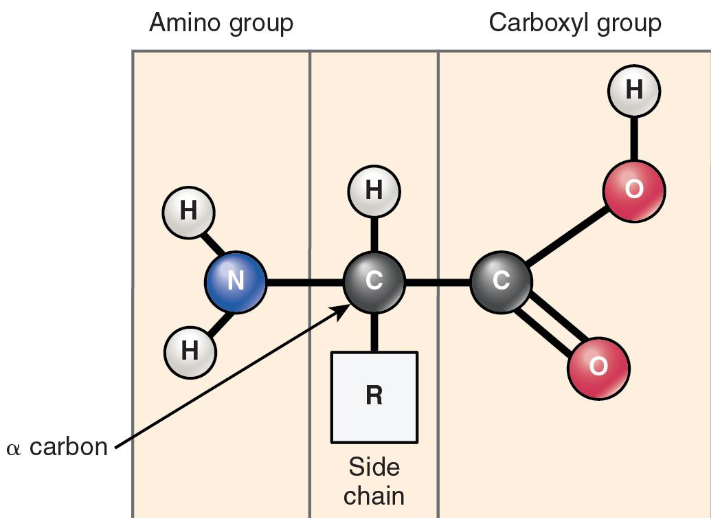
Protein: Structure of an Amino Acid
Central carbon atom
called alpha carbon
An Amino group
Carboxyl group
Hydrogen
Variable group
Proteins: The Formation of Peptide Bonds
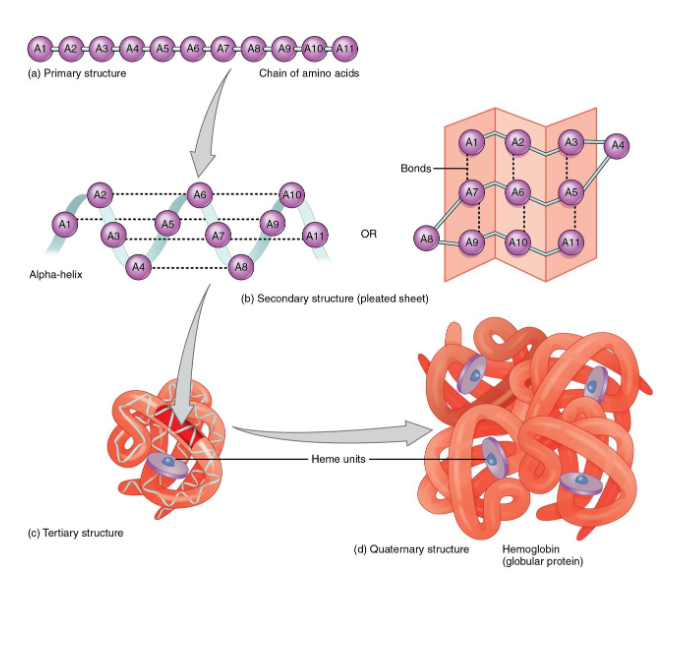
Proteins: Form= Function
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Quaternary
Factors that affect protein folding: (Denature)
Temperature
pH
Salt
ETC
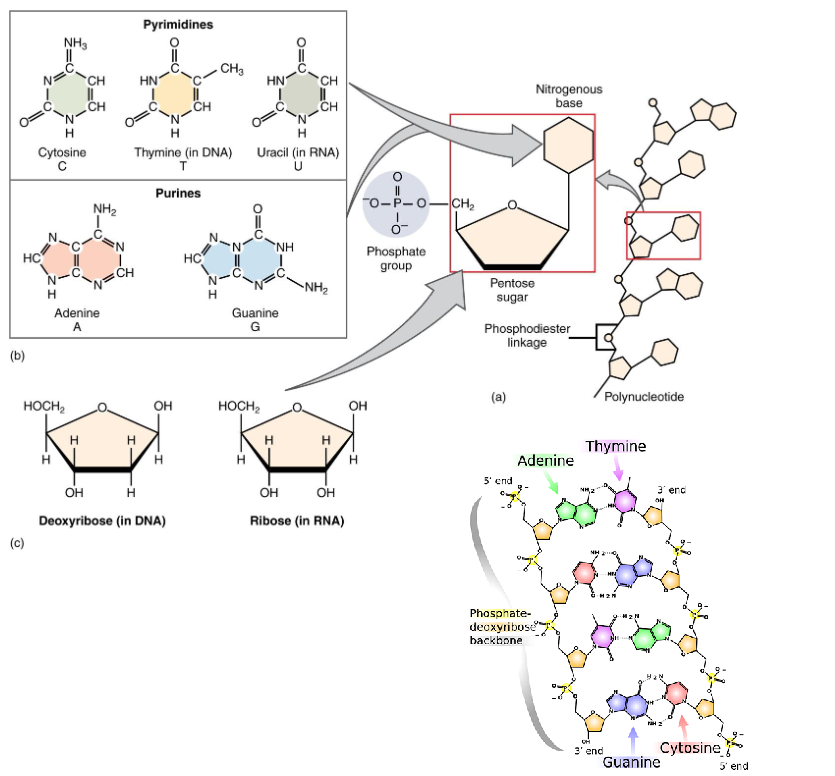
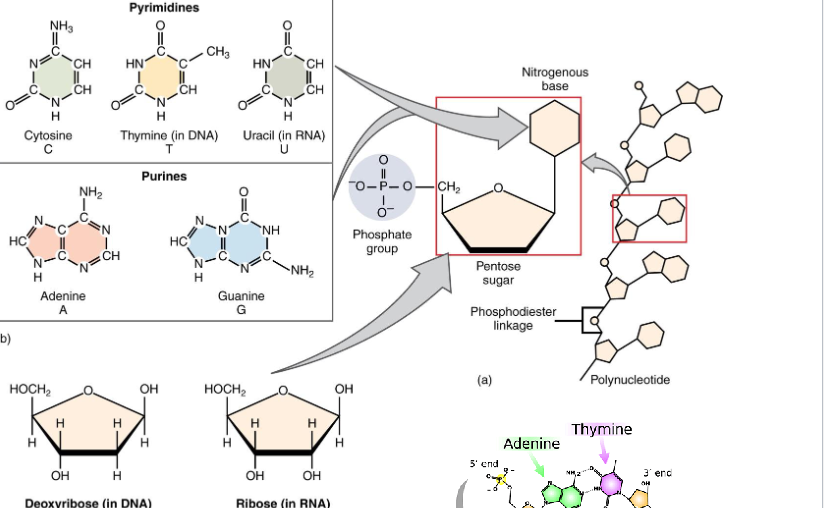
Nucleic Acids
Monomer: Nucleotide
Polymer: Nucleic Acid
DNA and RNA
5’ and 3’ Ends
3’- CGGGTCACGTAC- 5’
RNA: 5’ GCCCAGUGUATG 3’
DNA: 5’ GCCCAGTGCATG 3’
Pentose Sugars
The Nucleus
Stores DNA
Regulates gene expression
Nucleolus creates Ribosomes
Nuclear envelope with pores
Chromatin versus Chromosome
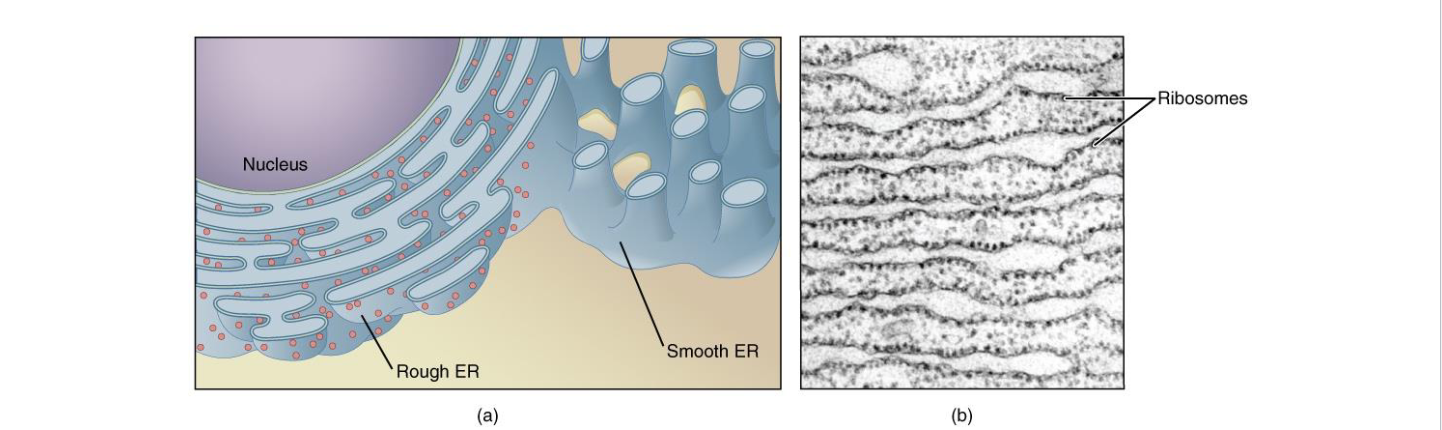
Rough ER
Covered in Ribosomes giving it a rough/bumpy appearance
Synthesis of membrane proteins or secreted proteins
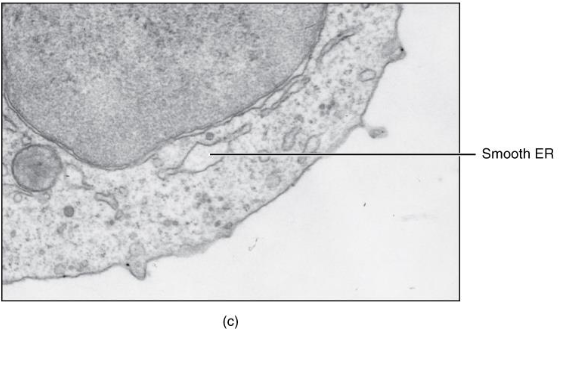
Smooth ER
Lipid synthesis
Steroid Hormone Synthesis
Stores Ca2+
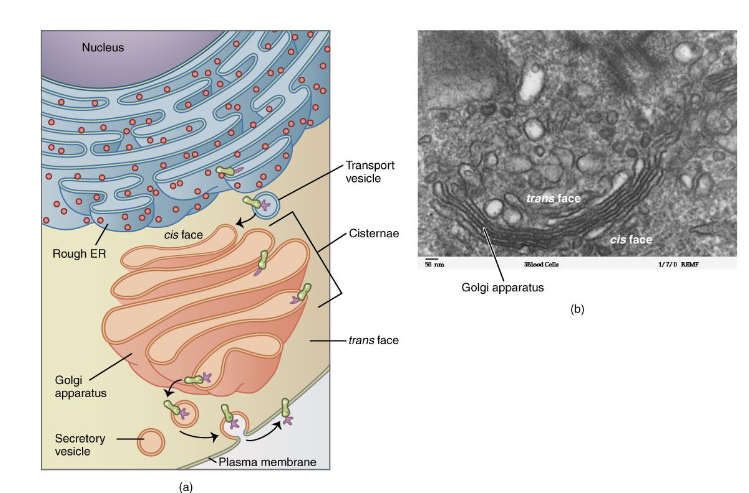
Golgi Apparatus
Stack of Flattened discs
Look like stack of pancakes
Sorts, Modifies, and ships proteins made in Rough ER
Cis-Face ————> Trans-Face
Vesicles
Membrane-Bound transport vehicles
Transport materials between the above organelles and the plasma membrance
Lysosomes
A Specialized vesicle
Contains enzymes that break down and digest unneeded cellular components
In some immune cells they breakdown foreign materials like bacteria
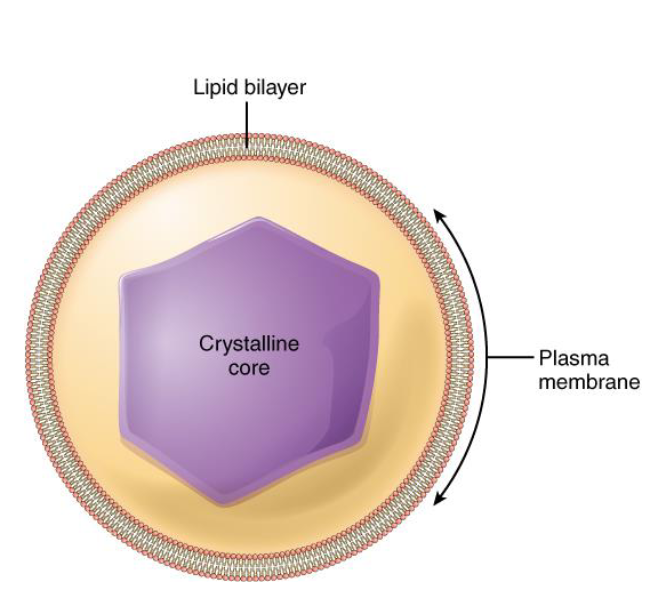
Peroxisomes
Membrance-bound organelle that contains mostly enzymes
Lipid metabolism
Chemical Detoxification through Peroxide
Complicated chemistry
The Plasma Organelles
Cholesterol
Scattered throughout hydrophobic regions
Strengthens Membrance
Stabilize Membrane at extreme temperatures
Lipid and protein components
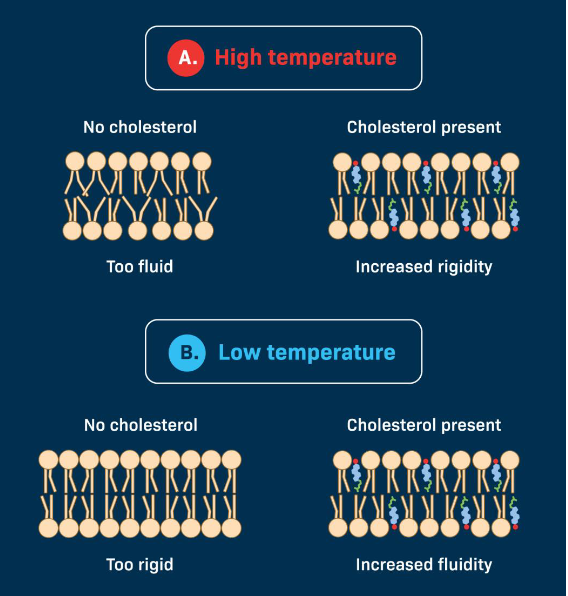
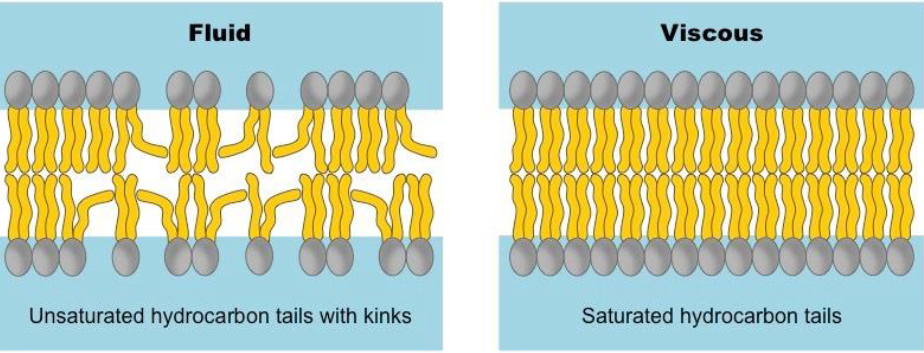
Factor Affecting Membrane Fluidity
Saturated (more solid; less fluid)
Unsaturated (more fluid; distribution of unsaturated tails matters too)
Length of tails
Cholesterol
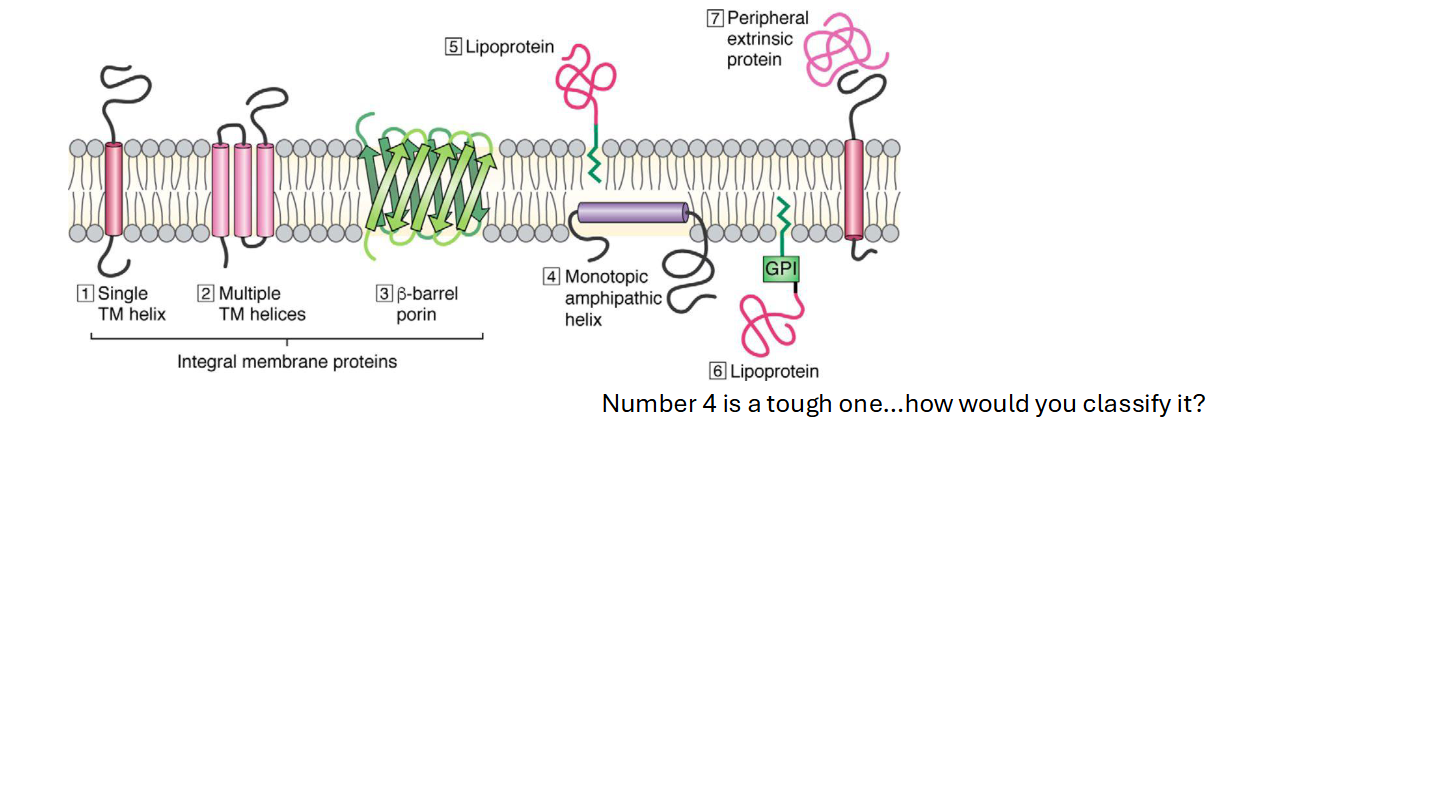
The Plasma Membrane (Protein Components)
Integral Proteins
Embedded in the plasma membrane
Peripheral Proteins
Closely associated to the plasma membrane
Plasma membrane (Funtion)
Physical Barrier: establishes flexible boundary, protects cellular contents, and supports cell structure. Phospholipid bilayer separates substances inside and outside the cell
Selectively Permeable Boundary: Regulates entry and exit of ions, nutrients, and waste molecules through the plasma membrane
Electrochemical Gradients: Establishes and maintains an electrical charge difference across the plasma membrance
Communications: Contains receptor that recognize and respon to molecular signal
The cell Cycle
Interphase- cell is not dividing
G1
S
G2
Mitosis