Week 2 Economics - Demand and Supply
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Objectives - variables that influence the demand for goods and supply, supply of goods and services, explain how equilibrium in a market is reached, and illustrate on a graph, use demand and supply graphs to predict changes in prices and quantities.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Ceteris paribus condition
when analysing the relationship between two variables like price and quantity, other variables must be held constant.
define quantity demand
the amount of a good or service a consumer is willing and able to buy at a given price.
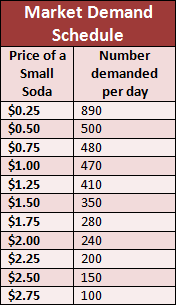
define a demand schedule
A table showing the relationship between the price of the product and the quantity of the product demanded.
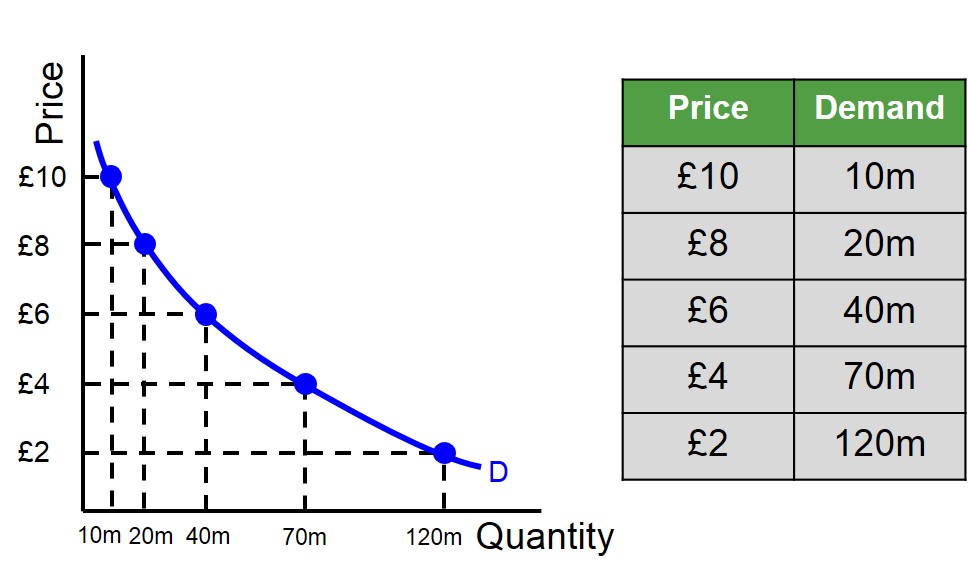
define a demand curve
a curve that shows the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product demanded.
Define a market demand
the demand of a good or service by all consumers.
the law of demand
holding everything else constant
when the price of the product falls, the quantity demanded increases.
when the price of the product rises, the quantity demanded decreases.
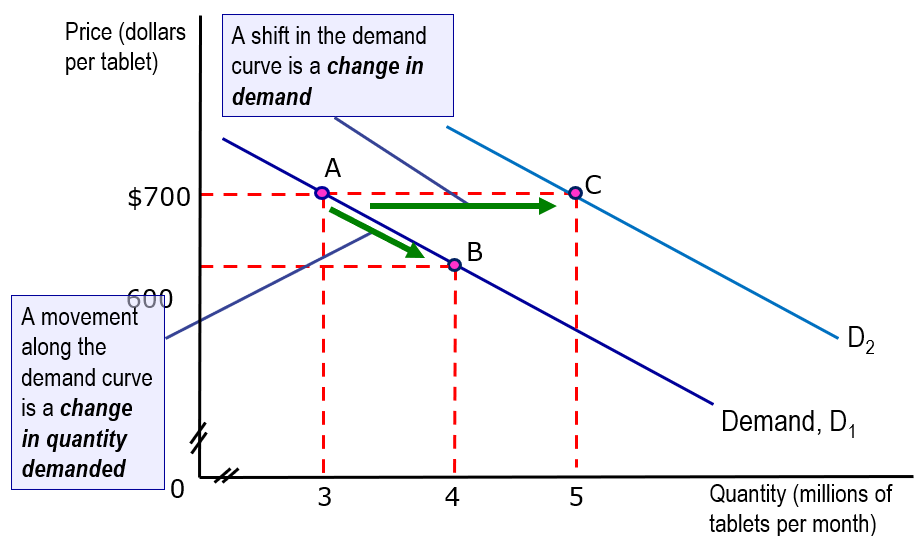
changes in quantity demanded
change in the quantity demanded = change in the quantity of a product that people plan to buy, which results from a change in the price of a good.
e.g., as the price of tablets fall, the quantity demanded increases
Change in demand
change in demand is a change in he quantity that people plan to buy when any influence other than the price of the good changes,
a change in the demand means that there is a new demand schedule and a new demand curve.
change in demand curve
when demand decreases, the demand curve shifts leftwards from D1 to D3
When demand increases, the demand curve shifts rightwards from D1 to D2.
Variables that affect market demands
income
price of related goods
tastes/preferences
population and demographics; number of buyers
expected future prices
Change in demand (income)
a normal good is a good for which the demand increases if income increases, and demand decreases if income decreases.
an inferior good is a good for which demand decreases if income increases, and demand increases if income decreases.
change in demand (prices of related goods - substitutes)
a substitute is a good that can be consumed in place of another good. e.g., applas and oranges are substitutes.
the demand for a good (apple) increases, if the price of one of its substitute increases (orange)
same for decreasing
change in demand (prices of related goods - compliments)
a compliment is a good that is consumed with another good. like millk and cereal.
the demand for a good increases (milk), if the price of its compliments fall (cereal).
the demand for a good decreases, if the price of its compliments rise.
Change in demand (number of buyers)
the greater the number of buyers in a market, the larger is the demand for any good.
Change in demand (taste/preferences)
taste/preferences change when people are better informed, new goods become available, season, trend, fashion.
change in demand ( expected future prices)
a rise in the expected future price of a good increases the current demand for that good.
a fall in the expected future price ofa good decreases the current demand for that good.
a change in demand vs change in the quantity demanded.
change in demand refers to a shift in the demand curve. occurs due to a change in the variables, other than the products own price, that affect the demand.
a change in the quantity demand refers to the movement along the demand curve as a result of the change in the product’s price.