CORE ORGANIC
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/49
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
1
New cards
What is the functional group of an alcohol?
\-OH
2
New cards
What is the general formula for alcohols?
CₙH₂ₙ₋₁OH
3
New cards
How do you name alcohols?
hydroxy-, -ol
4
New cards
What kind of intermolecular forces do alcohols have?
hydrogen bonding
5
New cards
Why do alcohols have hydrogen bonding?
the OH bond is highly electronegative
6
New cards
How do alcohols’ melting and boiling point compare to hydrocarbons of similar carbon chain lengths?
higher melting/boiling points
7
New cards
Why do alcohols have higher melting and boiling points as hydrocarbons of similar chain length?
hydrogen bonding is stronger than London forces
8
New cards
Are alcohols soluble in water?
soluble in short chains - hydrogen bonding with water
insoluble in long chain - non-polarity of CH bond takes precedence
insoluble in long chain - non-polarity of CH bond takes precedence
9
New cards
What is a primary alcohol?
the C with the -OH group is bonded to one other Carbon atom
10
New cards
What is a secondary alcohol?
the C with the -OH group is bonded to 2 other carbon atoms
11
New cards
What is a tertiary alcohol?
the C with the -OH group is bonded to 3 other carbons
12
New cards
What forms when you partially oxidise a primary alcohol?
aldehyde -CHO
13
New cards
What conditions are needed to partially oxidise a primary alcohol?
* dilute H₂SO₄
* potassium dichromate(VI) / Cr₂Kr₂O₇
* distill product as it’s produced
* gentle heating
* potassium dichromate(VI) / Cr₂Kr₂O₇
* distill product as it’s produced
* gentle heating
14
New cards
What is the equation for the partial oxidation of ethanol?
CH₃CH₂OH + \[O\] → CH₃CHO + H₂O
15
New cards
What forms when you fully oxidise a primary alcohol?
carboxylic acid, -COOH
16
New cards
What conditions are needed to fully oxidise a primary alcohol?
* conc. H₂SO₄
* K₂Cr₂O₇
* reflux
* strong heat
* K₂Cr₂O₇
* reflux
* strong heat
17
New cards
What is the equation for the full oxidation for ethanol?
CH₃CH₂OH + 2\[O\] → CH₃COOH + H₂O
18
New cards
What forms when you oxidise a secondary alcohol?
ketone
19
New cards
What conditions are needed to fully oxidise a secondary alcohol?
* conc. H₂SO₄
* potassium dichromate (VI)
* strong heating
* potassium dichromate (VI)
* strong heating
20
New cards
What is the equation for the oxidation of propan-2-ol?
CH₃CH(OH)CH₃ + \[O\] → CH₃COCH₃ + H₂O
21
New cards
Is it possible to oxidise a tertiary alcohol?
no
22
New cards
What is a dehydration reaction?
a reaction in which water is lost to form an organic compound
23
New cards
What are the products of a dehydration reaction with alcohol?
alkene and water
24
New cards
What conditions are required for the dehydration of alcohols?
* conc. H₂SO₄
* conc. H₃PO₄
* 170°C
* conc. H₃PO₄
* 170°C
25
New cards
What products are formed in halide substituition with alcohol?
haloalkane and water
26
New cards
What conditions are needed for an alcohol to form a halogenoalkane?
* NaX
* H₂SO₄
* heated under reflux
* H₂SO₄
* heated under reflux
27
New cards
What are haloalkanes?
saturated organic compunds that contain carbon atoms and at least one halogen atom
28
New cards
Are haloalkanes soluble in water?
no
29
New cards
Why aren’t haloalkanes soluble in water?
C-H bonds are non-polar, not compensated for enough by C-X bond polarity
30
New cards
Do haloalkanes have a polar bond?
Yes, halogen has a higher electronegativity than C
31
New cards
Which intermolecular forces do haloalkanes have?
permanent dipole-dipole, London forces
32
New cards
What causes an increase in the boiling point of a haloalkane?
* increased carbon chain length
* halogen further down group 7
* halogen further down group 7
33
New cards
How would the mass of a haloalkane compare with the mass of an alkane of the same chain length?
greater (halogen mass > carbon mass)
34
New cards
What is the most important factor in determining halogen reactivity?
strength of the carbon-halogen bond
35
New cards
What would bond polarity suggest the order of reactivity of haloalkanes would be?
C-F would be the most reactive (most polar)
36
New cards
What does bond enthalpy suggest the order of reactivity of haloalkanes would be?
C-I would be the most reactive (lowest bond enthalpy)
37
New cards
What is a nucleophile?
electron pair donor
38
New cards
What are some examples of nucleophiles?
\:OH⁻, :CN⁻, :NH₃⁻, :Cl⁻
39
New cards
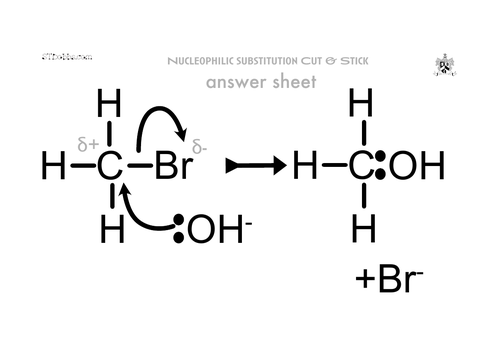
What is nucleophilic substituition?
a nucleophile donates a lone pair of electrons to a C⁶⁺ atom and the ⁶⁻ atom is replaced by the nucleophile
40
New cards
What is hydrolysis?
reaction in which water is a reactant
41
New cards
Which reactant often produces hydroxide ions for hydrolysis?
water/H₂O
42
New cards
What fission does water undergo to produce OH⁻?
heterolytic
43
New cards
What are CFCs?
chlorofluorocarbons (haloalkanes containing only C, Cl, F)
44
New cards
What is the problem with CFCs?
catalyse the breakdown of ozone in the atmosphere (via free radical substituition)
45
New cards
What is the main function of the ozone layer?
provides protection from harmful UV rays
46
New cards
Does ozone protect in all layers of the atmosphere?
no, in the troposphere it contributes toward photochemical smog
47
New cards
How do CFCs break down the ozone layer?
free radical substituition
48
New cards
What is the overall equation for the decomposition of ozone?
2O₃ → 3O₂
49
New cards
What is the initiation step for the breakdown of ozone?
Cl₂ → 2Cl∙
50
New cards
What are the propagation steps for the breakdown of ozone?
1. Cl∙ + O₃ → ClO∙ + O₂
2. ClO∙ + O₃ → 2O₂ + Cl∙