ID Lecture 4: Intro to Antimicrobial Agents and Antimicrobial Resistance | Quizlet
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Beta-lactams MOA
bind in the site of PBP to prevent crosslinking of peptidoglycan (cell wall synthesis inhibitors)
Quinolones MOA
inhibits DNA topoisomerase to prevent DNA replication (DNA replication inhibitors)
Tetracyclines MOA
prevents bacterial protein synthesis by inhibiting the 30S subunit (protein synthesis inhibitor)
Macrolides MOA
prevents bacterial protein synthesis by inhibiting the 50S subunit (protein synthesis inhibitor)
Bacteria can develop antibiotic resistance through what major mechanisms?
1. Limit intake
2. Active export
3. Inactivation or modification of the drug
4. Alteration of antibiotic targets
5. Target bypass
Intrinsic resistance
organism is inherently not susceptible to the antibiotic due to factors like the antibiotic size, characteristics, biofilm production, etc.
How do gram-positive bacteria gain intrinsic resistance?
they have a thick, heavy crosslinked, and hydrophilic peptidoglycan cell wall
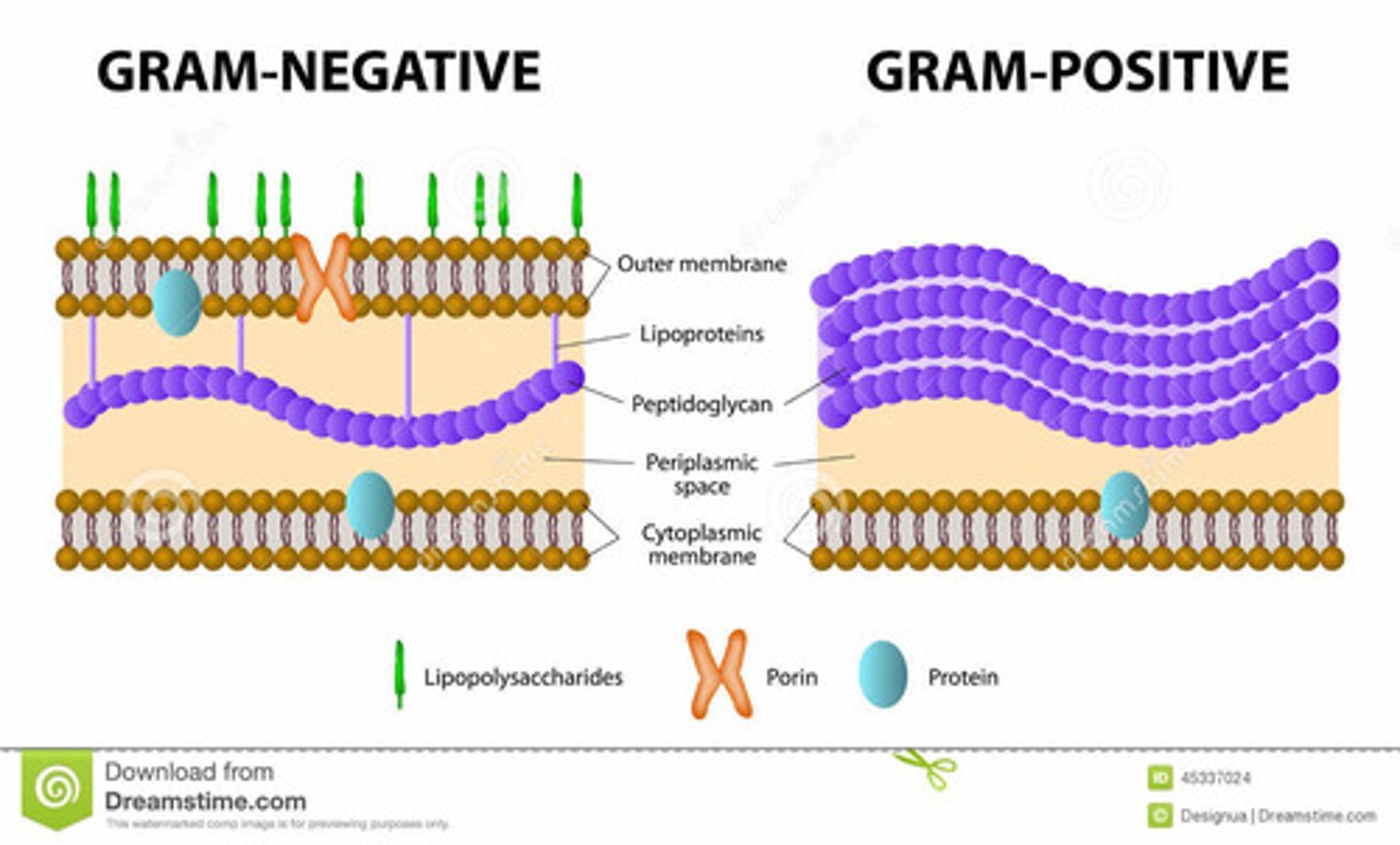
How do gram negative bacteria gain intrinsic resistance?
they have an outer membrane with porin channels that allow for entry of hydrophilic molecules - preventing LARGE molecules from entering
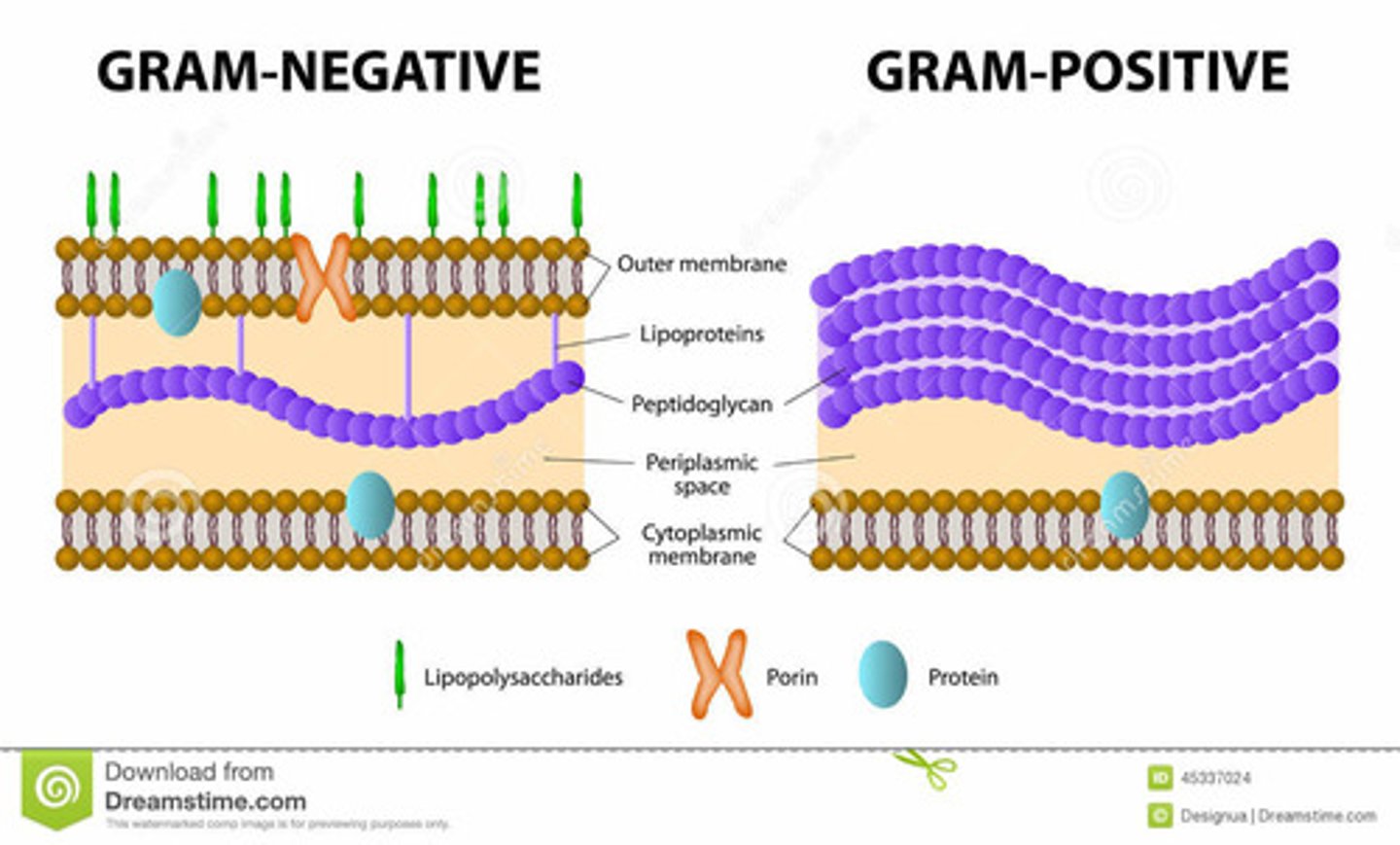
Which antibiotic molecules are good for gram negative bacteria?
small hydrophilic molecules
Which antibiotic molecules are good for gram positive bacteria?
small and large molecules
How do bacteria limit intake of antibiotics?
reduced membrane permeability and decrease number of porin channels
Active export mechanism of resistance
enhanced export by energy-dependent efflux pumps
Inactivation or modification of the drug
enzymes that destroy or modify the antibiotic
Alteration of antibiotic targets
amino acid substitutions or post-translational modifications prevent the antibiotic from binding to its target
Target bypass
bacteria develop alternate pathways or overproduce the target so that it takes more of the antibiotic
Can bacteria have multiple mechanisms of resistance?
Yes
How is antimicrobial resistance acquired?
Mutations to genomic DNA
Horizontal gene transfer
What are the different types of horizontal gene transfer?
Transformation
Conjugation
Transduction
How do point mutations cause antibiotic resistance?
single mutations increase resistance by a little - but they add up if a bacteria has multiple mutations
What is required for horizontal gene transfer?
mobile genetic elements (MGE)
What are mobile genetic elements?
genetic material that can move around within a genome or that can be transferred between species
Ex: plasmid, transposon, gene cassette, or phage
Transformation
dead bacteria that release their genetic elements into the environment so that living cells can uptake it
What do bacteria need in order to uptake genetic elements from the environment?
competence
Conjugation
MGE's get transferred through a pilus from the donor cell to the recipient cell
Transduction
virus transfers genetic material from one bacterium to another
What are the mobile genetic elements?
Plasmids
Gene cassettes
Transposons
Phages
Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)
the lowest concentration of antimicrobial that inhibits growth of bacteria in vitro
Zone diameter (ZD)
the diameter of bacterial killing around an antibiotic infused disk
Breakpoints
determed by the FDA and CLSI to know if the MIC or ZD is sufficient for clinical use
Can susceptibility breakpoints change?
yes - especially as resistance increases
MIC > breakpoint
resistant
MIC < breakpoint
susceptible
MIC = Breakpoint
Intermediate