Raster Surfaces
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
raster surfaces are
continuous
why are raster surfaces continuous
each grid cell has a z-value
what are some examples of terrestrial surfaces? statistical surfaces?
terrestrial
DEM
slope
aspect
precipitation
statistical
population density
crime rates
density of animals in area
spatial interpolation
predicts values for cells in a raster from a limited number of sample data points
what are some data types we can interpolate
elevation
rainfall
air quality
noise levels
how is a continuous surface calculated
from point data
what is interpolation the estimation of
the z value (height) of a surface at unsampled data based on known surrounding z values
what bounds the continuous surface
a mask or extend
4 more common spatial interpolation methods
trend
local
global
IDW
spline
Natural neighbours
is trend an approximate or exact interpolation method
approximate
trend is a _____ surface
polynomial
what happens with global polynomial interpolation
creates a surface that represents gradual, coarse-scale trends and is useful for capturing long-range patterns
is local variation captured in global interpolation
NO
which tool uses global polynomial interpolation
trend
what is a first order global polynomial
a single, flat plane (a linear function) to all data points to model
what is the goal of a polynomial
minimize error of prediction
when is global interpolation used for
large scale patterns
1st order polynomial vs 2nd order polynomial vs 3rd order polynomial
1st - linear polynomial
2nd - one bend
3rd - two bends
does trend pass through actual measured points
not normally - inexact interpolation
what does trend use to fit the interpolation
least squares regression
what should be true about the points above and below the trend best fit line
should be the same below and above it
when should local polynomial interpolation be used
when you have data that exhibits short-range variation
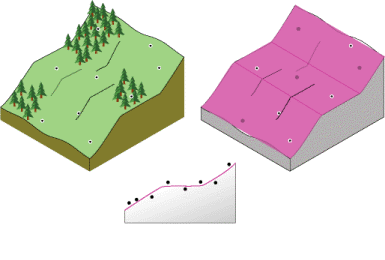
IDW interpolation method
estimates cell values by averaging the values of sample points in neighboring cells
in IDW what is the relationship between point weight and distance
as the distance from a point increases, its weight decreases
what are TWO conditions that must be met before using IDW
samples are relatively evenly distributed
surface characteristics do NOT change across the landscape
what are variables of IDW
nearest neighbour
fixed radius
barriers
power
contrast nearest neighbour and fixed radius in IDW
nearest neighbour - integer value defining the MINIMUM number of points to be used for interpolation
fixed radius - distance in map units where all input points in the specified radius will be used for interpolation
what are barriers
barriers - specify location of linear features known to interrupt the surface continuity
what do barriers NOT have
z values
examples of barriers
fences, railways, cliffs
what do barriers do to the interpolation
the selected input points for the interpolation MUST be on the SAME side of the barrier as the current processing cell
which interpolation method can use barriers
IDW
spline
kriging
what must a power be
a positive, real number
what is a common power value
is 2
what happens by defining a higher power option
more emphasis can be put on the nearest point = nearby data will have MORE influence
will a higher power result in a more or less detailed surface
more detail
what happens in IDW with a higher power
a less smooth and more "spiky" interpolation with higher peaks and deeper valleys
what are some issues with IDW
min and max values must be sampled or variation will be missed
surface will NOT go exactly through the sampling points
spline
the bending and stretching of a surface to pass through ALL measured points
what can spline result in
a surface that captures BOTH global trends and local variation
how does spline estimate values
mathematical function that MINIMIZES the change in slope
what are two conditions of spline
surface must pass exactly through the data points
surface must have minimum curvature = minimum change in slope
what type of points is spline a good choice for
points without abrupt changes in values
what are the spline variables
regularized spline - higher weights = smoother surface
spline with tension - higher values = coarser surface
number of points - more points = smoother the surface
when to use IDW or spline?
IDW
the variables being mapped decreases in influence with distance
spline - the variable is smooth, continuous surface that does NOT have large variability over short distance
what does natural neighbours use twice
Thiessen polygons
where is the polygon boundary in nearest neighbours
between grid cell and nearest sampling point
which interpolation provides the best looking surface
nearest neighbours
what are Thiessen polygons
each defines an area of influence around its sample point so any location inside the polygon is closer to that point than any other
when is nearest neighbour most appropriate
sample data points are distributed with uneven density

spline
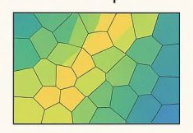
nearest neighbour

trend
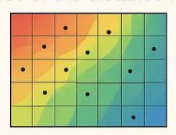
IDW