Honors Chem Lap 3
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ughh fudge this smh
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What element is found in period 3, Group 2A?
a. carbon
b. magnesium
c. boron
d. oxygen
b. Magnesium
What element is found in period 4, Group 8A?
a. barium
b. manganese
c. krypton
d. carbon
C. Krypton
Which of the following pairs of elements would have similar properties?
a. aluminum & silicon
b. oxygen & helium
c. lithium & magnesium
d. chlorine & bromine
d. Chlorine & bromine
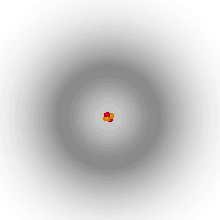
Which model is this?
Quantum Mechanical Model, modern description of atom
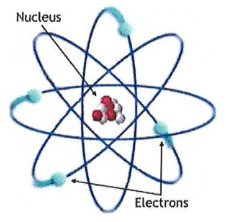
How about this model?
Rutherford’s atomic model, electrons orbit the nucleus
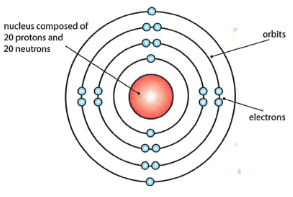
What is this one?
Bohr’s atomic model, places electrons in fixed energy levels
A quantum of energy in the form of light is called a(n)
a. neutron
b. cloud
c. photon
d. alpha particle
c. Photon
Which electron transition results in the emission of energy?
a. n = 3 to n = 4 c. n = 1 to n = 2
b. n = 1 to n = 3 d. n = 2 to n = 1
d. n = 2 to n = 1
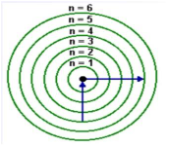
Which electron transition results in the absorption of energy?
a. n = 3 to n = 2 c. n = 2 to n = 3
b. n = 2 to n = 1 d. n = 4 to n = 3
c. n = 2 to n = 3
Energy levels correspond to ____________ on the periodic table.
a. periods
b. groups
c. elements
d. columns
a. Periods
According to Dr. Neil deGrasse Tyson, an understanding of quantum mechanics is the entire foundation of
our ____________ revolution.
a. agricultural
b. cultural
c. democratic
d. technological
d. Technological
The electron cloud is a 3D shape that the electron is traveling within and shows where the electron is
likely to be found
a. 10% of the time
b. 50% of the time
c. 90% of the time
d. 100% of the time
c. 90% of the time
When each electron has its lowest possible energy, the atom is in its
a. excited state
b. highest energy level
c. ground state
d. unstable state
c. Ground state
Atomic orbitals are three dimensional, and like fuzzy clouds with no sharp boundaries.
a. True
b. False
a. True
What shape is the p orbital?
a. sphere shape
b. p shape
c. dumbbell shaped
d. complex shapes
c. Dumbbell shaped
The maximum number of electrons in each energy level is equal to 2n². If n = 2, the maximum number of electrons is:
a. 2
b. 8
c. 18
d. 32
b. 8
What sublevel or sublevels are in the second energy level?
a. s
b. s, p
c. s, p, d
d. s, p, d, f
b. s, p
How many electrons can all three of the 2p orbitals hold?
a. 2
b. 4
c. 6
d. 10
c. 6
Which of the following orbitals is highest in energy?
a. 2p
b. 3d
c. 4s
d. 3s
b. 3d
If energy is added to an atom and an electron moves up to a higher energy level, it will
a. Stay there indefinitely in an excited state
b. Quickly emit energy to move back down to a ground state level
c. Continue to move up to a higher and higher energy level
d. Change into another type of atom
b. Quickly emited energy to move back down to a ground state level
Energy levels further away from the nucleus are closer together than the energy levels nearer the nucleus. Because of this, an electron requires ______ energy to move to a higher energy level the further it is from the nucleus.
a. more
b. less
c. the same amount
b. less
The Aufbau Principle states that electrons will occupy the levels and orbitals with the _______ energy first.
a. highest
b. lowest
c. potential
d. wave
b. Lowest
The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that each orbital can hold a pair of electrons that spin in:
a. an opposite direction
b. the same direction
c. no specific direction
a. An opposite direction
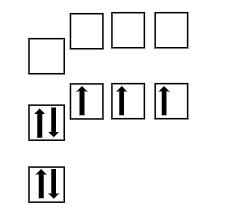
What is this?
The correct way to fill a 2p orbital with 3 electrons using Hund’s rule
Electrons will occupy a p-orbital only after
a. The previous s-orbital is empty
b. The previous s-orbital is half full
c. The previous s-orbital is completely full
c. The previous s-orbital is completely full
In the electron configuration 1s², what does the superscript indicate?
a. the energy level b. the orbital c. the number of electrons
c. the number of electrons
What does this orbital diagram represent?
Ground state of nitrogen
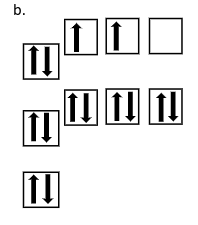
What does this other orbital diagram represent?
Ground state of silicon
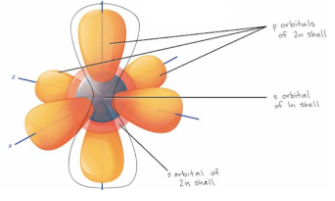
Given the following orbitals, which electrons, on
average, are more distant from the nucleus?
a. 1s
b. 2s
c. 2p
c. 2p
The electron configuration of carbon is
(6 electrons)
a. 1s1-2s2-2p6 c. 1s2-2s2-2p1
b. 1s2-2s2-2p2 d. 2s2-2p1
b. 1s2-2s2-2p2
The electron configuration of chlorine is
(17 electrons)
a. 1s2-2s2-2p6-3s2-3p6 c. 1s2-2s2-2p5
b. 1s2-2s2-3p7 d. 1s2-2s2-2p6-3s2-3p5
d. 1s2-2s2-2p6-3s2-3p5
Which element has the following electron configuration: 1s²2s²2p4
a. carbon c. nitrogen
b. oxygen d. fluorine
b. Oxygen
Which element has the following electron configuration: 1s22s22p63s23p1
a. aluminum c. nitrogen
b. chlorine d. neon
a. Aluminum
Which element has the following electron configuration: 1s22s22p63s23p63d64s2
a. calcium c. krypton
b. iron d. phosphorus
b. Iron
How many electrons are in the highest occupied energy level of neon, 1s22s22p6?
a. two
b. four
c. six
d. eight
d. Eight
Atoms of elements with the same number of electrons in their highest occupied energy level are found in the same
a. period
b. group
c. compounds
d. energy levels
b. Group
The excited state electron configuration for an element is 1s22s22p23s23p1 What is the element?
a. aluminum
b. magnesium
c. fluorine
d. potassium
c. Fluorine
An electron may drop all the way back down to the ground state in a single step, emitting a photon in the process, or it may drop back down to the ground state in a series of smaller steps, emitting a photon with each step.
a. true b. false
a. True
During the flame test lab, what was emitted by electrons as they dropped back down to ground state?
a. infrared energy
b. radiowaves
c. photons
d. gamma rays
c. Photons
During the flame test lab, why did the color of light observed when each substance was heated vary from one substance to another? Because each element has
a. a different number of electrons in the first energy level being promoted to higher energy levels
b. a different spacing of electron energy levels, so the possible electron transitions for each are unique
c. a different number of protons in the nucleus, causing an attraction to the electrons that is different for each
element
d. all of these
b. A different spacing of electron energy levels, so the possible electron transitions for each are unique
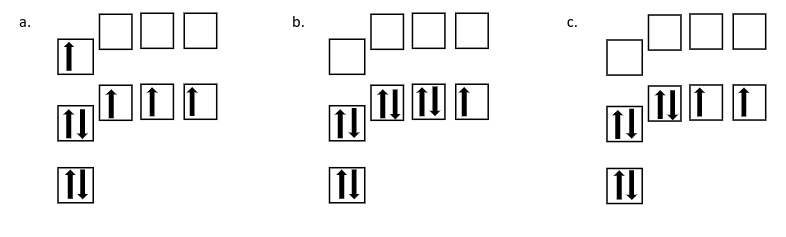
Which of the following orbital diagrams shows an excited state electron configuration?
A
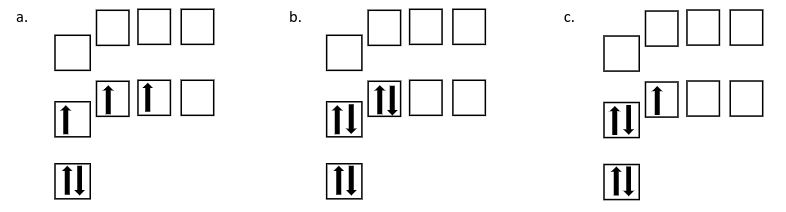
Which of the following orbital diagrams shows an excited state electron configuration for boron?
A
Which of the following would be the correct noble gas electron configuration for sulfur?
a. [Ne]3p4
b. [Ar]2p2
c. [He]2s22p63s23p4
d. [Ne]3s23p4
d. I no no type
Because building the 3d orbital requires a lot of energy, electrons actually go into the s orbital of the _______energy level before going into the third energy level. The periodic table reflects this exception by dropping the d orbitals
down a period.
a. second
b. third
c. fourth
d. fifth
c. Fourth
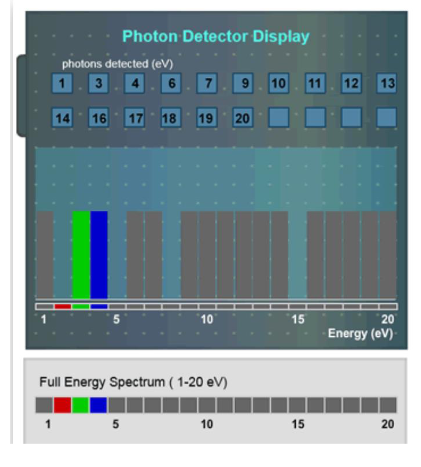
According to the spectrum seen below, which photons were absorbed by the element?
A. 2 eV, 4 eV, 7 eV, and 14 eV
B. 1 eV, 3 eV, 4 eV, and 6 eV
C. 2 eV, 3eV, and 4 eV
D. 2 eV, 5 eV, 8 eV, and 15 eV
D. 2 eV, 5 eV, 8 eV, and 15 eV
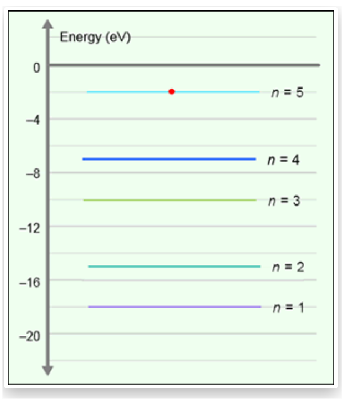
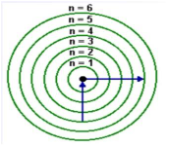
According to the energy level diagram below, what sequence of photons could be emitted from
an electron moving from energy level 5 to energy level 1?
A. 5 eV, and then 11 eV
B. 10 eV, and then 8 eV
C. 6 eV, 6 eV, and then 4 eV
D. All of the above
A. 5 eV, and then 11 eV