4.7- Organic Chemistry
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What is crude oil
Crude oil is a finite resource found in rocks.
Crude oil is the remains of an ancient biomass consisting mainly of plankton that was buried in mud.
Crude oil is a mixture of a very large number of compounds
What are the majority of compounds in crude oil
Hydrocarbons, mostly alkanes
What are hydrocarbons
Most of the compounds in crude oil are hydrocarbons, which are molecules made up of hydrogen and carbon atoms only.
What is a homologous series
Series of compounds with same general formula, same functional groups and similar chemical properties.
What are the prefixes for the first 4 members of a homologous series
meth-
eth-
prop-
but-
What is the general formula for the homologous series of alkanes
Cn H2n+2
What are the first 4 members of the alkane homologous series
Methane (CH4)
Ethane (C2H6)
Propane (C3H8)
Butane (C4H10)
Why can alkanes be described as saturated
They have only single bonds
Draw the displayed formula of ethane
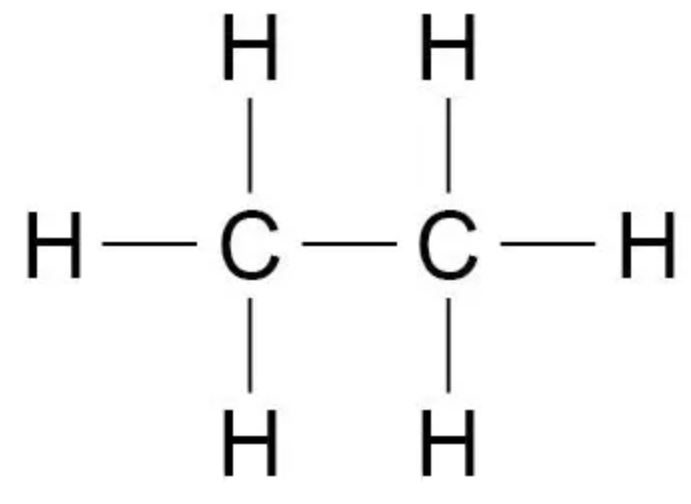
Describe how fractional distillation takes place
Crude oil is heated and vaporised.
Vapour rises up the fractionating column (tower).
The column is hotter at the bottom and cooler at the top.
Hydrocarbons cool as they go up the column and condense at different heights, as they have different boiling points.
Large molecules, high boiling points - collected at the bottom.
Small molecules, low boiling points - collected at the top.
This gives fractions- fractions which are groups of hydrocarbons with similar boiling points and similar number of carbon atoms (chain length)
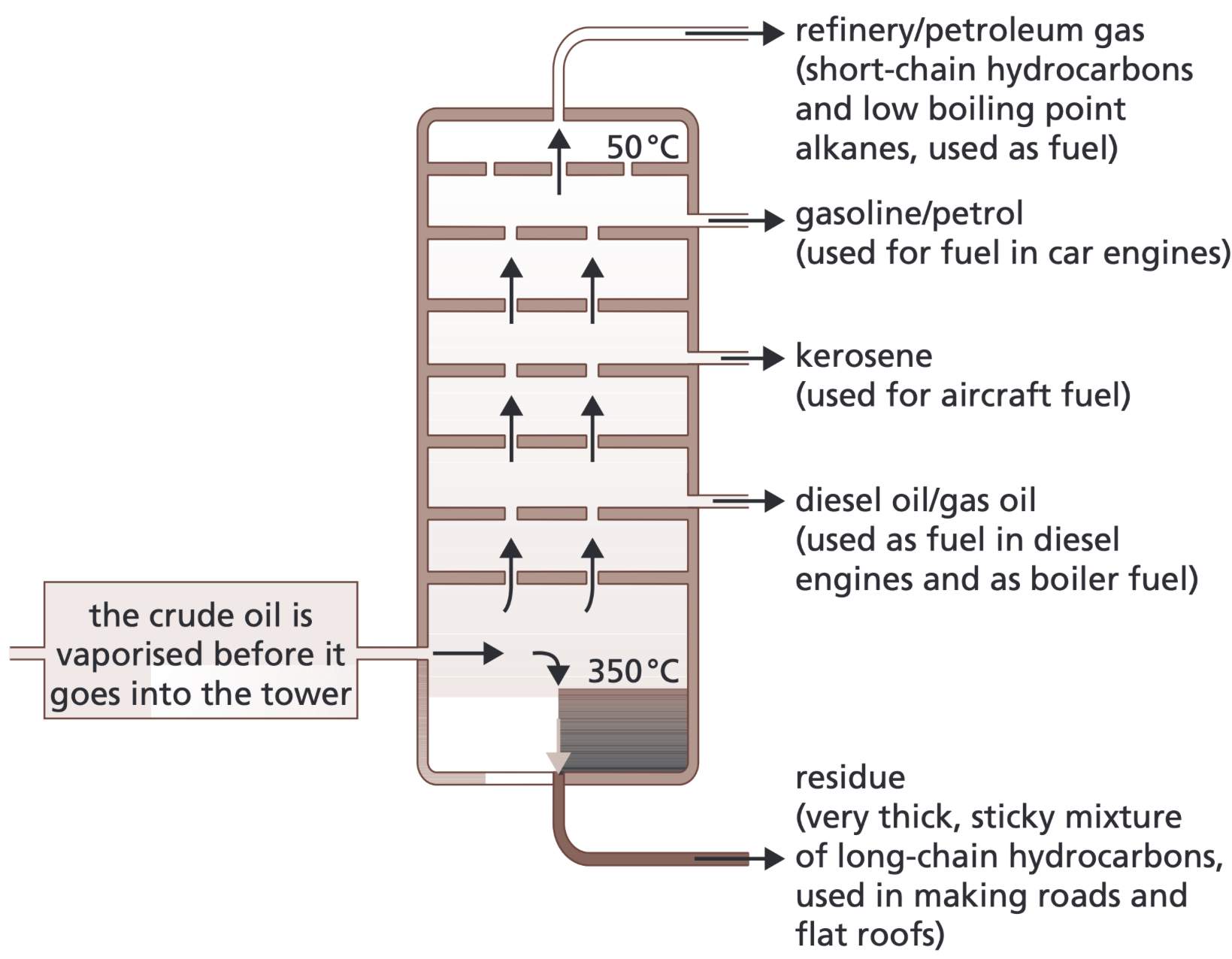
What types of products can be produced from crude oil
Many of the fuels on which we depend for our modern lifestyle, such as petrol, diesel oil, kerosene, heavy fuel oil and liquefied petroleum gases, are produced from crude oil.
Many useful materials on which modern life depends are produced by the petrochemical industry, such as solvents, lubricants, polymers, detergent
Why is there such an array of natural and synthetic carbon compounds
The vast array of natural and synthetic carbon compounds occur due to the ability of carbon atoms to form families of similar compounds.
Describe what happens to boiling point, flammability and viscosity when the chain length/ number of carbon atoms increases
Boiling point increases
Flammability decreases
Viscosity increases
What happens during complete combustion of hydrocarbons
Exothermic reaction
During combustion, the carbon and hydrogen in the fuels are oxidised
The complete combustion of a hydrocarbon produces carbon dioxide and water.
General equation:
hydrocarbon + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
What happens during incomplete combustion
Happens when there is insufficient oxygen for complete
Hydrogen and carbon are not fully oxidised
General equation:
hydrocarbon + oxygen → carbon + carbon monoxide + water
Why is cracking needed
To match supply and demand:
Many longer hydrocarbons produced from crude oil are far less useful, and so are in much less demand than supply (eg kerosene is used as aeroplane fuel, but not much else)
Many shorter, more flammable hydrocarbons are more useful so are in higher demand than supply (eg petrol and natural gas)
Cracking allows longer less useful hydrocarbons to be broken down into smaller more useful hydrocarbons ( a shorter chain alkane and an alkene)
Alkenes can be used to produce polymers and as feedstock in the petrochemical industry
What are the conditions needed for catalytic cracking
Catalytic cracking uses a temperature of approximately 550°C and a catalyst known as a zeolite which contains aluminium oxide and silicon oxide- the reactant also needs to be vapour
What are the conditions needed for steam cracking
Steam cracking uses a higher temperature of over 800°C, steam and no catalyst- the reactant also needs to be vapour
What is the test for alkenes
When added to bromine water, alkenes will turn it from orange/yellow to colourless
Alkanes will do nothing, it will remain orange/brown
What is the functional group of alkenes
C=C double bond
Why can alkenes be described as unsaturated
They contain a double bond
They contain two fewer hydrogen atoms than the alkane with the same number of carbon atoms
What is the general formula for the homologous series of alkenes
Cn H2n
What are the first 4 members of the alkene homologous series
Ethene (C2H4)
Propene (C3H6)
Butene (C4H8)
Pentene (C5 H10)
Why is there no methene in the alkene family
The functional group of alkenes is the C=C double bond, so only one carbon would not have this functional group, so wouldn’t be an alkene
Draw the displayed formula of propene
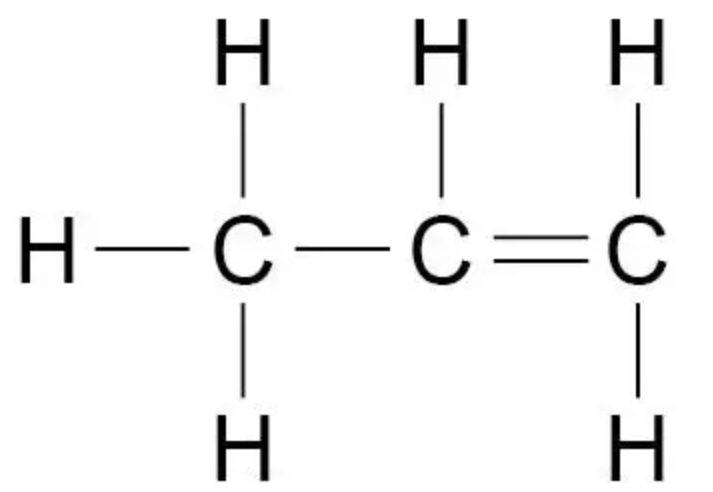
What is the importance of functional groups for reactions of organic compounds
It is the generality of reactions of functional groups that determine the reactions of organic compounds
What tends to happen with combustion reactions of alkenes
Alkenes react with oxygen in combustion reactions in the same way as other hydrocarbons, but they tend to burn in air with smoky flames because of incomplete combustion.
What would be produced from the reaction of ethene with steam (water)- hydration of ethene
Ethanol
(a catalyst, high pressure, and high temperature is needed and the ethene must also be a gas)
(the reaction is reversible)

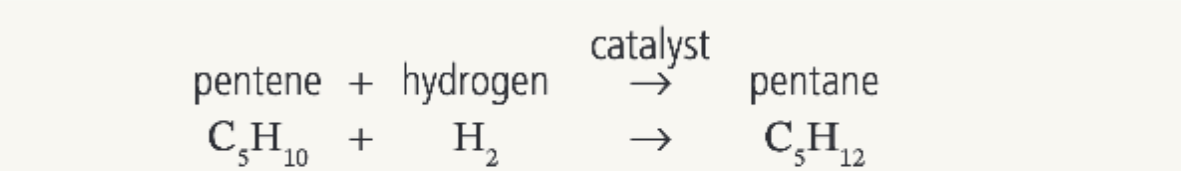
What would be produced from the reaction of pentene and hydrogen
Pentane
(60oC and nickel catalyst required)
What would be produced from the reaction of ethene and bromine water (this applies for any halogen)
Dibromoethane solution (colourless)

What is the functional group of the alcohol homologous series
-OH
What is the general formula for the alcohol homologous series
CnH2n+1OH
What are the first 4 members of the alcohol homologous series
Methanol (CH3OH)
Ethanol (C2H5 OH / CH3CH2OH)
Propanol (C3H7OH / CH3CH2CH2OH)
Butanol (C4H9OH / CH3CH2CH2CH2OH)
Draw the displayed formula for ethanol
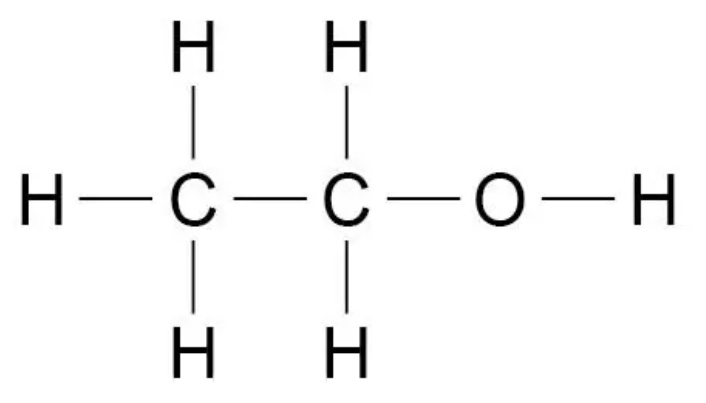
How can ethanol also be produced using fermentation of yeast
Glucose → Ethanol + Carbon dioxide
Takes a few days
Produces waste product (CO2)
30oC
Glucose in solution
Absence of air
What are some uses of alcohols
Methylated spirits (mixture of ethanol and methanol) can be used to remove permanent marker
Useful as solvents in products like perfumes, mouthwash and and aftershave
What is produced if an alcohol is dissolved in water
A neutral solution
Describe how alcohol burns in air
Used as fuel, is a biofuel
e.g CH3CH2OH + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O
Describe how alcohols react with sodium
Sodium effervesces (gives off a gas)
Less vigorous than with water
e.g. 2CH3CH2OH + 2Na → 2C2H5ONa + H2
Forms a sodium alkoxide (eg sodium ethoxide)
Describe how alcohols reacts with an oxidising agent (eg potassium dichromate (IV), or is left exposed to air and reacts with microbes in the air )
Reacts to form carboxylic acid
e.g. CH3CH2OH + 2[O] → CH3COOH + H2O
[O] = oxygen atoms from oxidising agent
What is the functional group of a carboxylic acid
-COOH
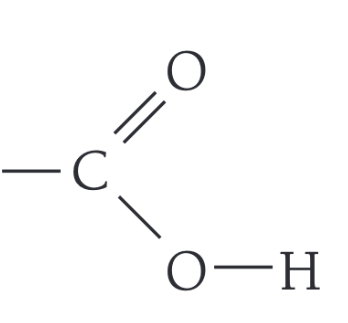
What are the first 4 members of the carboxylic acid homologous group
Methanoic acid (HCOOH)
Ethanoic acid (CH3COOH)
Propanoic acid (CH3CH2COOH)
Butanoic acid (CH3CH2CH2COOH)
Why can carboxylic acids be described as weak acids
They release H+ ions when dissolved in water (this makes them acids)
They only partially disassociate in water (this makes them weak)
The reaction for them dissolving in water:
e.g. CH3COOH (aq) ⇌ CH3COO-(aq) + H+(aq)
Have a higher pH than stronger acids with the same concentration
Describe how carboxylic acids react with carbonates
React in the same way as other acids to produce a salt, water and carbon dioxide
e.g:
2 CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COOHNa + CO2 + H2O
Salts produced have the -oate suffix, e.g ethanoic acid produces ethanoate salts and propanoic acid produces propanoate salts
Describe how carboxylic acids react with alcohol
React to produce an ester and water
Use sulphuric acid as the catalyst
e.g:
CH3COOH + CH3CH2OH → CH3COOCH2CH3
The reaction of ethanoic acid and ethanol produces the ester ethyl ethanoate
What is the functional group of esters
-COO-
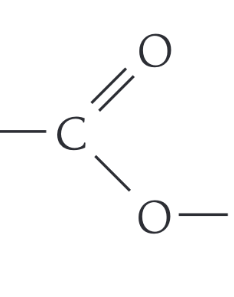
Draw the displayed formula of ethyl ethanoate
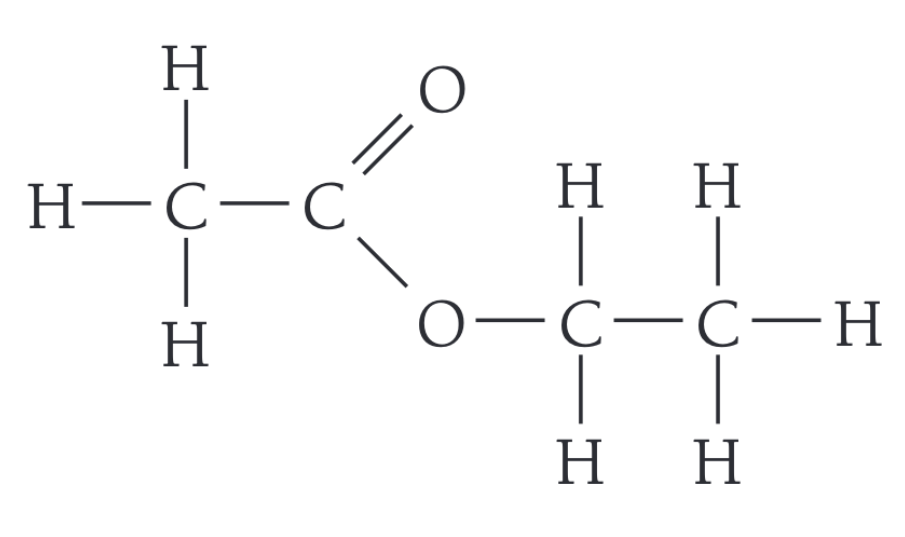
How do alkenes make polymers
By addition polymerisation
What happens in addition polymerisation
In addition polymerisation reactions, many small molecules (monomers) join together to form very large molecules (polymers).
In addition polymers the repeating unit has the same atoms as the monomer because no other molecule is formed in the reaction.
The double bond of the alkene breaks form a single bond in the middle, and bond to the other monomers on either side of it
Draw the equation for the polymerisation of ethene
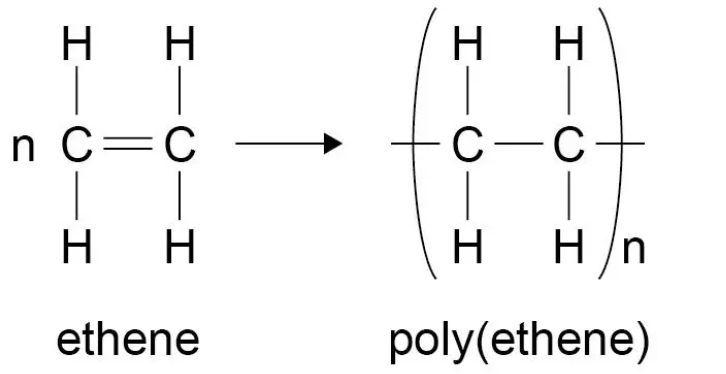
What are plastics made of
Very large covalently bonded molecules made of repeating units, called polymers
What are some uses of poly(ethene)
Transparent, used in many plastics, such as plastic bags, plastic bottles, dust bins, washing up bowls, and cling film
What happens in condensation polymerisation
Condensation polymerisation involves monomers with two functional groups. When these types of monomers react they join together, usually losing small molecules such as water, and so the reactions are called condensation reactions.
The simplest polymers are produced from two different monomers with two of the same functional groups on each monomer.
Describe how polyesters are made in condensation polymerisation
Made from the reaction of diols (eg ethanediol) and dicarboxylic acid (e.g ethanedioic acid)
Also makes water
The general formula is seen on the image
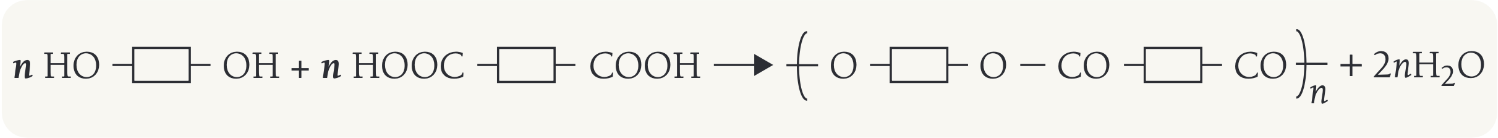
Draw the reaction of ethanediol and hexanedioic acid to produce poly(ethyl hexanoate)
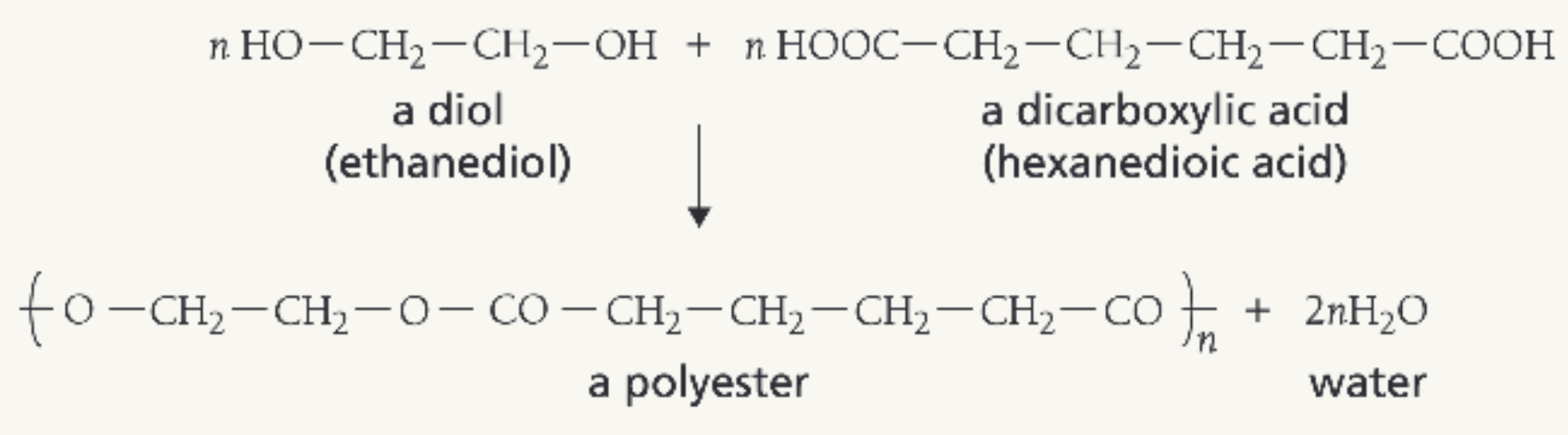
What are the uses of polyesters
Used in addition to cotton in clothes to strengthen them and reduce wrinkles
How many functional groups does each amino acid have
2- one acidic (the carboxylic acid group -COOH) and one basic (the amine group- NH2) an
What is the simplest amino acid- draw it

Draw the reaction of 3 glycine molecules reacting to form a tripeptide and water
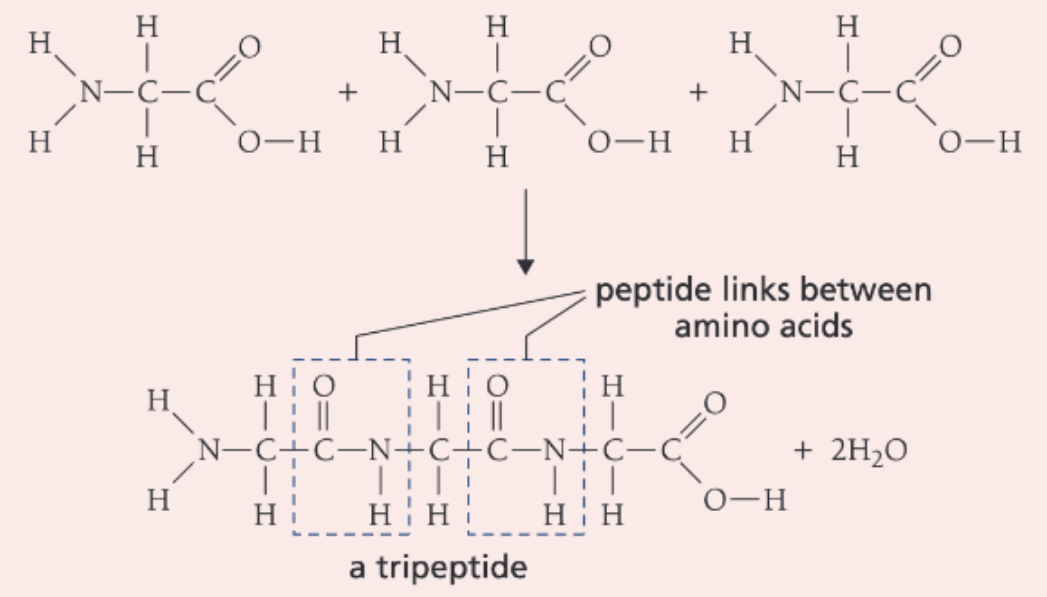
What are polypeptides
Polypeptides are polymers made of many amino acids, held together by peptide bonds
Proteins are polymers made of one or polypeptides
What is formed from the polymerisation of simple carbohydrates like glucose
Polymers like starch and cellulose, as well as water
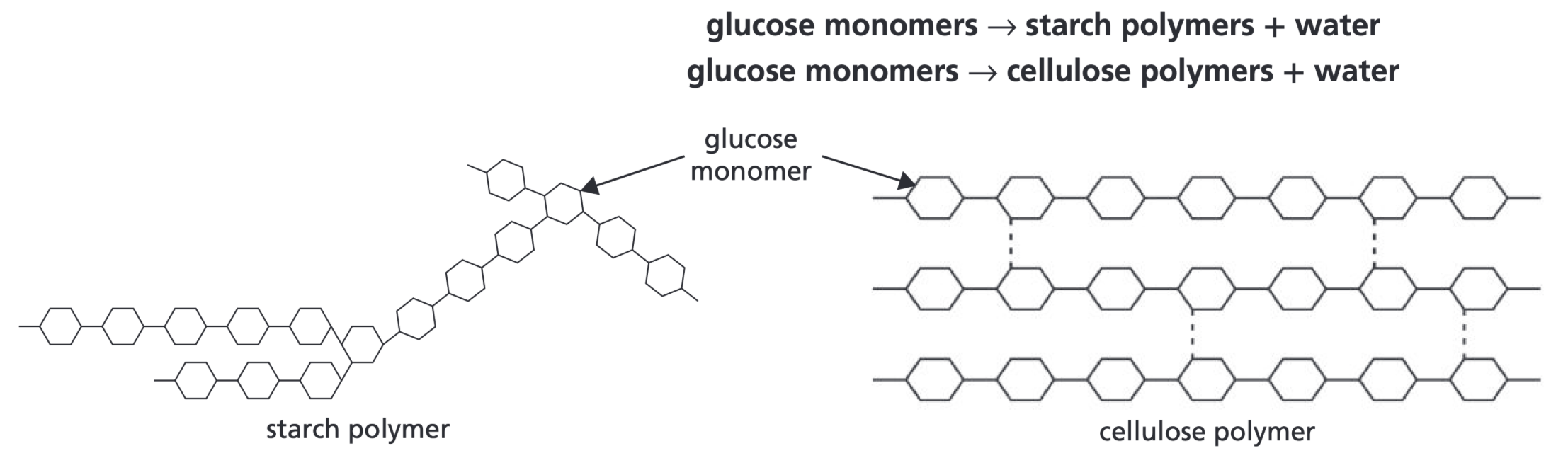
What is made from the polymerisation of amino acids

What is DNA
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a large molecule essential for life. DNA encodes genetic instructions for the development and functioning of living organisms and viruses. It is formed in condensation polymerisation
Most DNA molecules are two polymer chains, made from four different monomers called nucleotides, in the form of a double helix
What is DNA made of
Two polymer chains, each made of repeating nucleotide units
Each monomer (nucleotide) is made of one phosphate, one deoxyribose sugar, and one base