MKTG Final Exam
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Market Segmentation
Dividing a market into distinct groups based on characteristics to tailor products and marketing strategies.
SWOT Analysis
Evaluating a company's internal strengths and weaknesses, and external opportunities and threats to make strategic decisions.
Perceived Value
The worth customers assign to a product or service, often higher than its actual cost.
Positioning Statement
Describes how a brand differentiates itself from competitors in the minds of consumers.
Product Development
Process of creating new products or improving existing ones to meet customer needs and solve problems.
Branding
Establishing a unique identity for a product or service to differentiate it in the market.
Pricing Strategy
Plan that determines how a company sets prices for its products or services.
Promotional Elements
Various tools and tactics used to communicate with customers and promote products or services.
Media Types
Different channels used for advertising, such as TV, radio, social media, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
What are the 4 steps in the marketing process?
Research 2. Segmentation and positioning 3. the 4 Ps (product, price, place, promotion) 4. Sell the product
What are the business benefits for segmentation?
Identification of unfulfilled needs 2. Better product design 3. more targeted promotions 4. increased customer satisfaction
What are the customer benefits for segmentation?
Convenience and time savings 2. tailored products and services 3. relevant offers 4. Personalized experience
Why do marketers use targeted promotions?
Saves money and time
Why segment?
It brings value, it creates and delivers value.
Real Value
Actual cost
Perceived value
What customers think the value is (often higher than the real value, if its higher than the customers real value, they will buy).
What is SWOT and how is it used?
SWOT: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It is a current overview of where the company is at. Strengths and weaknesses are inside the company, and opportunity and threats are external. UNDERSTAND INSIGHTS AND TRADEOFFS
What are the different ways to segment markets?
Demographics, geographics, psychographics, behavioral. + usage, (needs, preferences, decision process)
Demographics
Basic characteristics: Gender, ethnicity, age, religion, education
Geographics
Physical location: Urban vs suburban, country / region
Psycographics
Personality
Behavioral
Customer behavior: Purchase behavior, usage.
Usage
Recency, frequency, loyalty, profitability. Target the most loyal and the most profitable (usually the same group)
Needs, preferences, decision process
Requires research, but if you know these, you can create the perfect marketing mix.
Needs
If you understand what they want, need, and how to go about it, you have to position your perceived value.
Targeting
How do you know which segments to target? You cannot target all segments. YOU CAN’T MARKET TO EVERYONE, IF YOU TRY, YOU WILL BE MARKETING TOWARDS NO ONE.
How do you know which segments to target?
Need to 1. evaluate attractiveness of each market segment 2. Selecting one or more segments to pursue. 3. Designing marketing programs to serve segments.
Criteria in selecting target segments?
Market size (needs to be large enough and profitable) 2. Expected growth (if it is small now, must expect growth) 3. Competitive position (less competition, more attractive) 4. Cost to reach (don’t waste money) 5. Company fit (segment should fit w/ company objectives).
Cost to reach
You don’t want to waste your money on promoting the wrong ways (white claw example) → needs to have growth.
Positioning
How you are perceived in the mind of you consumers.
Value formula
Value = perceived benefits - perceived costs
Value in marketing:
Marketing is understanding your consumers and delivering that perceived value. Value is all in the mind of the consumers.
What are the 4 elements to a positioning statement?
Defining the target market (who? when? where?)
The value (what value?)
The evidence (why and how?)
The competitive set (relative to whom?)
What happens if a company needs to reposition?
A company would reposition and then have to answer the question of what is the unique value that we are going to give to the customers.
Product
Anything that is offered to a market for consumption that satisfies a need. It provides value and solves a problem.
Characteristics of services?
intangibility (can’t touch)
Inseparability (simultaneous creation and consumption)
Inconsistency (Starbucks drinks can taste different)
Inventory (there isn’t really any inventory)
Steps in new product development process?
Strategy development
Idea generation
Idea screening
Business analysis
Product development
Test marketing
Product launch
Reasons for new product failures
Insignificant points of difference
Incomplete market and protocol before product development starts
Not satisfying a need on a critical factor
Bad timing
No economical access to buyers
Too little market attractiveness
Poor execution of the marketing mix: brand, name, package, price, promotion, distribution
Poor product quality
Example of new product failure
Google glasses → The market was not attractive; people didn’t see it as a need or a want. (Lesson: Think ahead about what failures you might encounter).
Points of difference
Attributes or benefits consumers strongly associate with a brand, positively evaluate, and believe they could not find to the same extent with a competing brand.
Points of parity
Associations that are not necessarily unique to the brand but may be shared with by others.
Product life cycle stages
Introduction (wanting to inform people on the product)
Growth (persuading people)
Maturity (reminding people about your product)
Decline (to phase out)
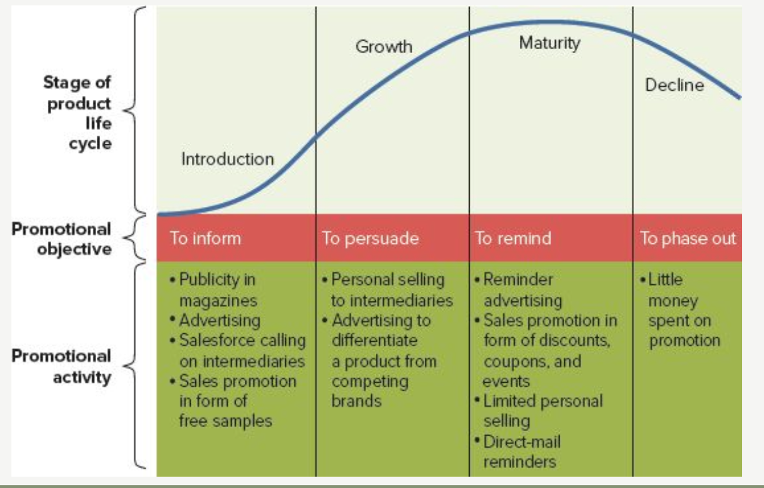
Maturity
How to get customers to engage: reminding tactic
Commercials/marketing serve to remind consumers that the product exists
More fun and exciting commercials
Consumers already know what the product is
Product life cycle in decline, what should we do?
2 choices
Discontinue brand
Repositioning: Change brand image to try and restart and make it successful again
(subways athletes instead of Jered)
Different types of products
High learning products
Low learning products
Fashion product
fad product
High learning product
Tesla, iPhone: People are reluctant because they don’t know enough about it; companies need to educate/guide consumers (tech)
Low learning product
Low involvement purchases, no worrying about buying it / how to use it (iPhone Face ID commercial)
Fashion product
Fashion is the one thing that comes and goes (trends)
Fad Product
Silly bands, fidget spinners: Super fast upwards but then can immediately decline.
Brand Equity
Added value a brand name gives beyond product benefits
gives brand competitive advantage
Consumers are often willing to pay a higher price for brand equity
Brand personality
A set of human characteristics associated with a brand name
What counts for branding?
Is how a brand is perceived in the eyes of customers. NOT how it is viewed by the company
Pricing equation
Pricing = perceived value, not real value
Why can brands like supreme charge $200 for a shirt?
Because supreme is perceived as high value and luxury, so it can charge high prices.
When do consumers purchase?
Consumers purchase when perception of value is greater than price. Customers care about value more than the price.
What are the 3 steps to cover before you decide your pricing strategy
What is the goal of the product or business
Conduct a through market pricing analysis. Similar to step 1, what’s your company’s position in the market? Think Tesla vs Walmart
Analyze your target audience.
Psychology of Pricing: Decoy effect
Common tactic at restaurants (it costs them nothing for a combo but we are willing to pay the few extra dollars)
Psychology of Pricing: Anchoring
Discount stores; They will slap a sticker over the original tag so you can see the original price, and how much you are saving.
Psychology of Pricing: fair and Switch
Black Friday. When you bring them into the store with super deals and they end up buying something else.
Communications
Process of conveying message to others. Requires source, message, channel of communication, receiver, encoding, and decoding
Integrated marketing communication
Designing marketing communications programs that coordinate all promotional activities to provide a consistent message across all audiences
Why promote?
Awareness
Information
Attitude (or image)
Call to action
Promotional Mix
The combination of one or more communication tools used to (1) inform prospective buyers about the benefits of the product, (2) persuade them to try it, and (3) remind them later about the benefits they enjoyed by using the product
Promotion decision process
Planning, implementation, evaluation
Inbound marketing
Consumer driven, timely, content rich, solution based. EX: Blogging, social media, SEO, Podcasting, Email blasts to approved lists
Outbound marketing
Marketer driven, disruptive, hard sell, product based. EX: Broadcast and print advertising, cold calling, telemarketing, trade shows, email blasts to purchased lists.
Product advertising
Focused on selling a product or service.
Pioneering (informational)
Competitive (persuasive)
Reminder