Schizophrenia – I
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is schizophrenia
a severe mental disorder characterized by disturbances in thought, perception, and behaviour. Symptoms may include delusions, hallucinations, and impaired functioning.
What are the 4 clusters of clinical symptoms of schizophrenia
Positive symptoms
negative symptoms,
Cognitive symptoms,
affective/mood symptoms
Explain the two main psychotic phenomena of positive schizophrenia symptoms
Hallucinations
Delusions
Seen in acute phase of the illness
Tend to respond well to treatment
Explain in detail hallucination phenomena of positive schizophrenia symptoms
Distortion in perception
Sensory perception in the absence of a sensory stimulus
Can occur in any of the 5 sensory modalities – auditory, visual, somatic, olfactory and gustatory
Most common type in psychosis: auditory hallucination
Examples:
Hearing voices from outside one’s head (even when the patient is alone)
Talking about the patient (3rd person’s voices)
Talking directly to the patient (2nd person’s voices)
Explain in detail delusion phenomena of positive schizophrenia symptoms
Distortion in thought content
Systematic, false, fixed belief held by the patient with absolute conviction, despite evidence to the contrary
Types: persecutory (most common in schizophrenia), reference, grandiose, erotomanic, somatic, thought insertion/withdrawal/control/broadcasting
Examples:
“My neighbour is trying to poison me”
“My movements are being monitored by cameras, wherever I go”
“I am immortal”
“I am the richest man in the world”
What other positive symptoms refer to schizophrenia
Disorganised thinking and speech
Characterised by frequent derailment or loose associations, invented words, tangential, incomprehensible speech
Grossly disorganised behaviour
Range from childlike silliness to unpredictable agitation – impairs tasks of daily living
Catatonic motor behaviour: decrease in reactivity to environmental events, to such an extreme that patients can maintain a rigid posture and resist effort to be moved
What are the negative symptoms referring to schizophrenia
Reflect a decrease, deficit or loss of normal functions
Considered to be restricted affect, avolition, anhedonia, and asociality
Manifestations include:
Social withdrawal and isolation
Dull or emotional blunting
Poverty of speech
Autism
▪ Seen in chronic phase of the illness
▪ Tend not to respond well to treatment
▪ Relate to long-term disability
What are the affective/mood symptoms referring to schizophrenia
Depression
Anxiety
To be distinguished from negative symptoms
▪ Related to suicide
▪ Treatable
What are the 7 core domains of cognition
Working memory
Attention/vigilance
Reasoning and problem-solving
Processing speed
Visual learning and memory
Verbal learning and memory
Social cognition
What are the two diagnostic criteria of schizophrenia
DSM-V
ICD-10-CM

what are endophenotypes
Endophenotypes in schizophrenia are measurable traits that connect genetic factors to the symptoms of the disorder. They are invisible signs of the condition that can be tested and may appear in both patients and their relatives.
Examples include impaired working memory, abnormal eye movement, and reduced attention—these traits are linked to the genetic causes of schizophrenia but are not direct symptoms like hallucinations or delusions.
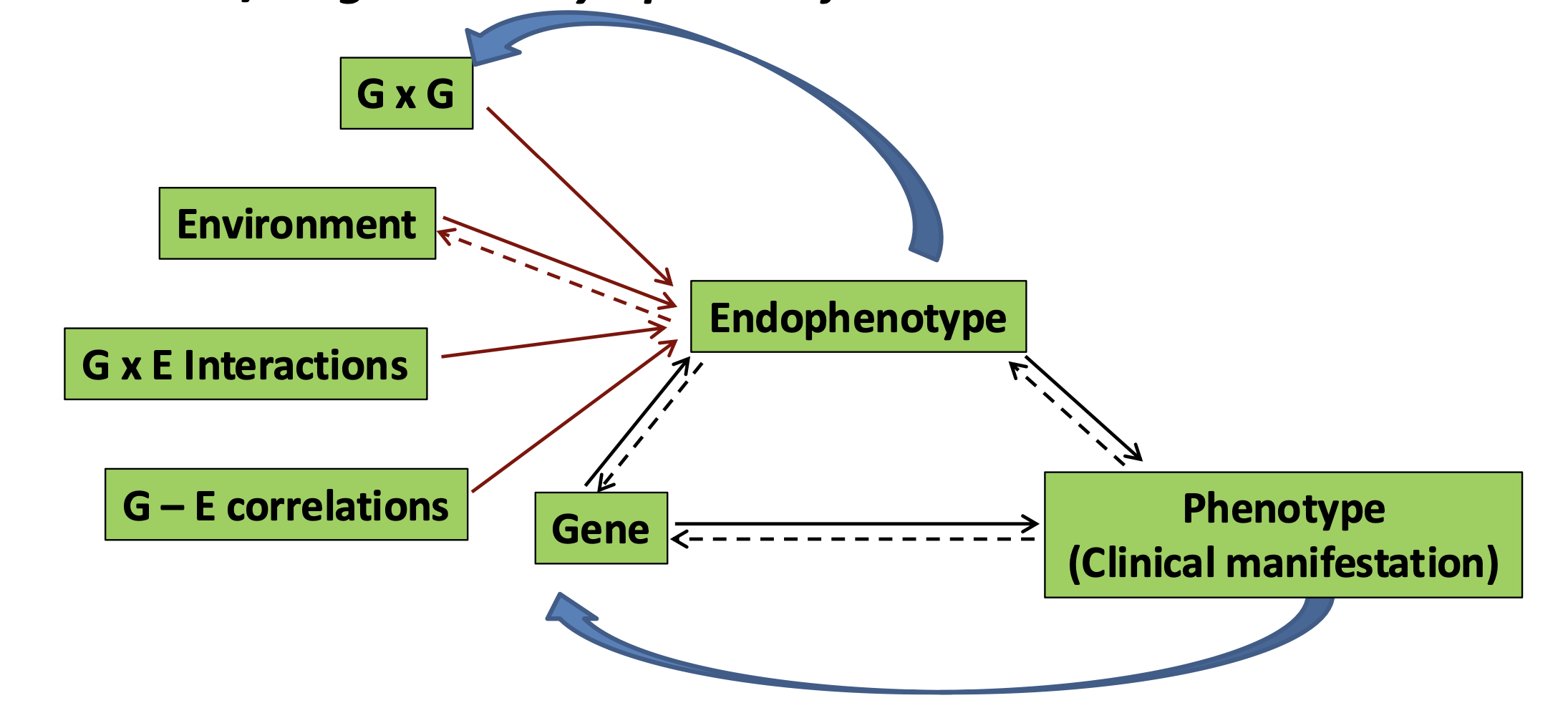
What are some criteria for endophenotypes
An endophenotype is associated with illness in the population
An endophenotype is heritable
An endophenotype is state-independent (manifest whether illness is active or in remission) but age-normed and might need to be elicited by a challenge
Within families, endophenotype and illness co-segregate
An endophenotype identified in probands is found in their unaffected relative at a higher rate than in the general population
An endophenotype should be a trait that can be measured reliably, and ideally is more strongly associated with the illness of interest than with other psychiatric conditions