Language and Thought
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Language Instinct
our language ability is an instinct that is the result of a biological arrangement in the brain
humans speak language cause we have the human brains
a prescholler’s tacit knowledge grammer is more sophisticated than the most state of the art computer lanagugae system
Language
system for communicating with others using signals that are combined according to rules of grammer and conveying meaning
grammar
set of rules that specify how units of laaguage can be combined to produce meaningful messages
Uniqueness of Human Langauge
use words to refer to intangible things
use lanaguge to name, categorize, and describe things to ourselves when we think
Phonemes
smallest unit of sounds that are recognizable as speech rather than as random noise
no meaning
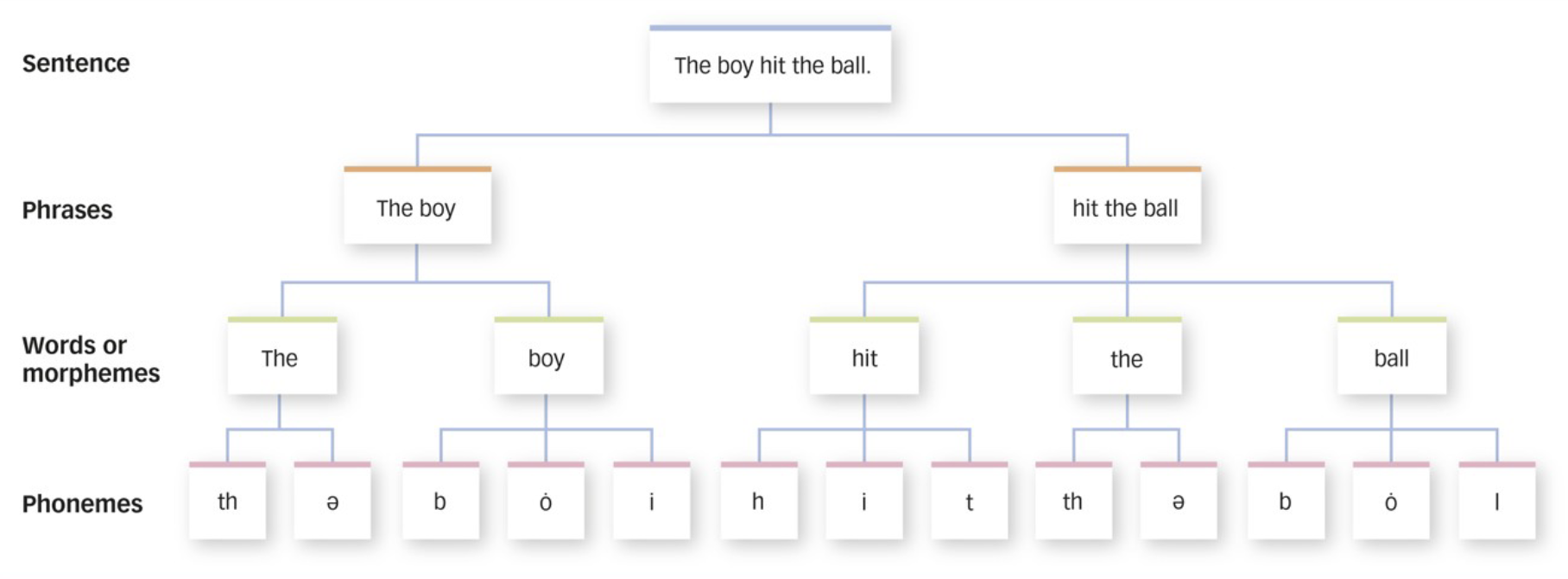
Phonological rules
set of rules that inidcate how phoneses can be combined to produce speech sounds
if these rules are broke, you get an accent
Morphemes
smallest units of languages that have meanings
Morphological Rules
rules that indicate how morphemes can be combined to form words
Content morphemes
refer to things and events (cat, dog)
Function morphemes
serves as gramatical functions such as tying a sentence together (and, or)
Syntactical Rules
rules that indicate how words can be combiend to form phrases and sentences
Meaning
Deep Structure - meanign of sentence
Surface structure - how the sentence is worded
Sentences with different surface strucutres can have the same deep structure
Langauge Development
children learn lanage at a quick rate
1 year old - 10 words, next 4 years knows 10,000 words
children make few errors when learning to speak
most are systematic (overapplyign rules)
Passive mastery develops faster than active memory
children understand langauge better than they speak it
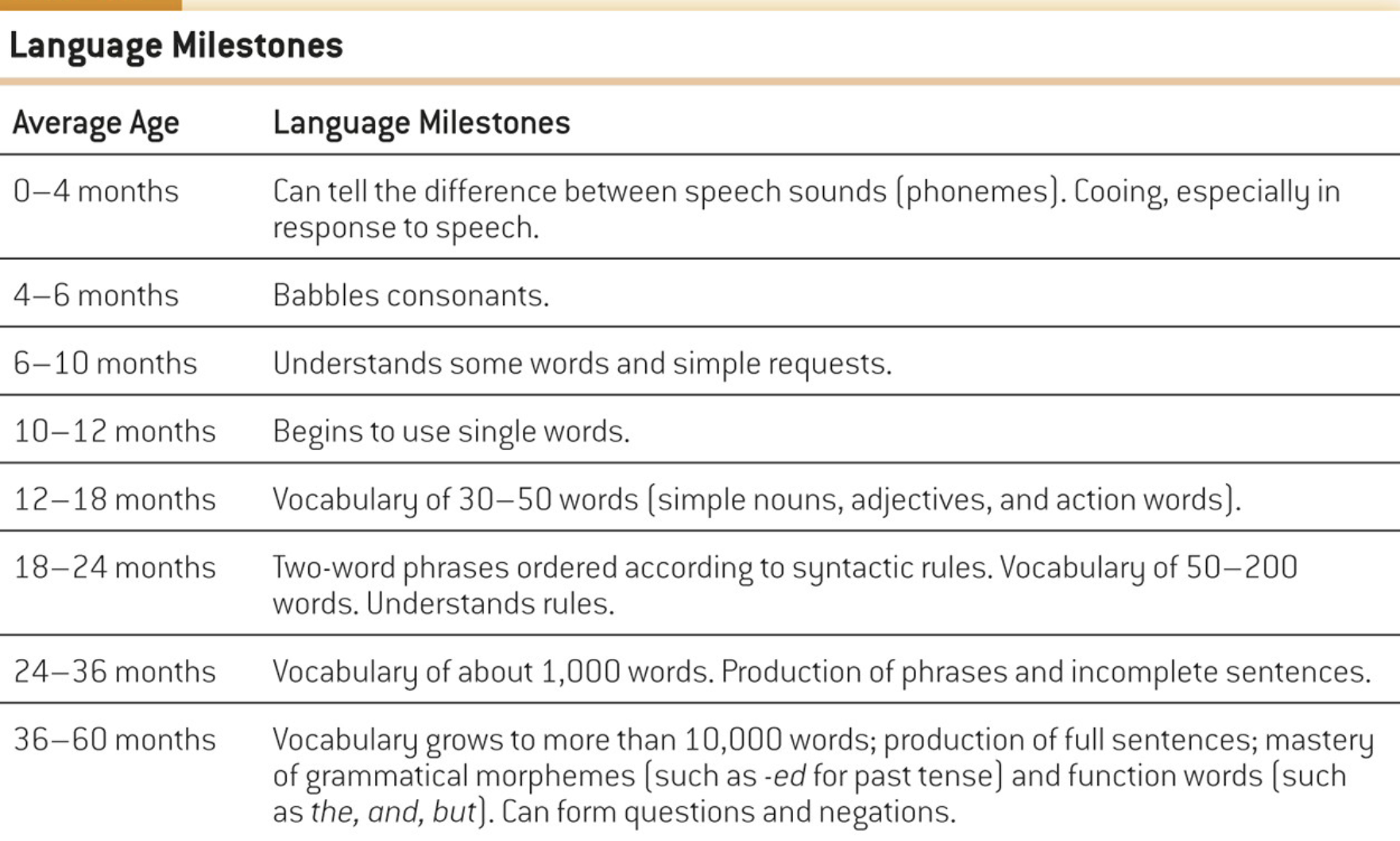
Language Milestones
at birth, infants can distinguish among alll the contrastign sounds that occur in human languages
within the first 6 months they lose this ability
after 6 months, they can only distinguish between contrasting sounds in the language they speak
Theories of Language Development
Behavorist
BF Skinner - learn language just like we learn anything else
through reinforcement, shaping, extinction and other principles of operant conditioning
Arguments against behavorist
parents dont spend time teaching children to speak grammatically
children generate more than they hear
errors children make are often overgeneralizations of grammatical rules
Theories of Language Development (Nativist)
Language development is best explained as an innate, biological capacity — something humans are born with rather than something we simply learn through reinforcement or imitation
Noam Chomsky
Nativist theory of language development, language learning capacities are built into the brain
Claimed that the brain is specialized to acquire language rapidly through exposure to speech.
Langauge Acquisition Device (LAD)
collection of processes that facilitate language learning
A hypothetical brain mechanism or collection of processes that makes language learning natural and automatic.
It enables children to infer grammatical rules from the language they hear.
It functions as the “mental engine” that drives language learning.
Theories of Language Development (Interactionalist)
although infants are born with the innate ability to acquire lanaguage, social interactions play a critical role in language
Linguisic relativity Hypothesis
language shapes the nature of thought
Benjamin Whorf
cited that Inuits have different words for snow, therefore he belied they think about snow differently from how we do
Language and Thought
the language of though in which knowledge is couched can leave nothign to the imagination because it is the imagination
Steven Pinker
language and thought are not the same thing.
He believes that language is simply a tool for expressing thoughts that already exist in the mind — not the source or structure of those thoughts.
Ambiguity
Proves have lanaguage and thoughts are seperate
one sentence can have 2 meanings, which shows that thoughts exists in a deeper mental code
Concept
mental representation that groups or categorizes shared features of related object,s events or other stimuli
Necessary condition
something that must be true of object to belong in the category
Sufficient condition
something that, if it is true of the object, orives it belongs in category
if German Shephard, then it is a dog
Family Resemblance Theory
members of a category have features that appear to be characterisitc of category members but may not be possed by every member
Prototype theory
psychological categories are best decibed as organized aroudn a prototype
Prototype
best or most typcial member of a category
for north americams, a prototyical bird would be a wren
Exemplar theory
we make category judgements by comparing new instances with stored memoreis for other instnaces of the category
you see a hariry 4 legged animal, you categorize it as a dog because it looks similar to a German Shephard

Types of Problems
Ill-defined problem, Well defined problem
Ill Defined Problem
one that doesnt have a clear goal or well defined solution path
Well defined problem
one with clearly specfied goals and clearly defined solution paths
Means Ends Analysis
process for searching foe the means or steps to reduce the differences between the current situation and the desired goal
Means Ends Analysis Process
analyze the goal state (desired outcome)
analze the current state (starting point)
list the differences between the current and goal state
reduce the list of differences by
direct means
generating a subgoal
finding similar problem with known solution
Analogical Problem Solving
solving a problem by finding similar problem with a known solution and applying that solutoon to the current problem
Creativity and Insight
how people solve problems in new or non-obvious ways — especially when typical thinking patterns or “mental sets” get in the way
Functional fixedness
tendency to perceive the functions of objects as fixed
process that constricts our thinking