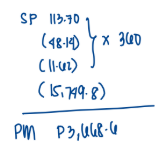ACYMANS3: Activity Based Costing
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
A(n)_______________ method first traces costs to activities and then to products.
a. Direct costing
b. Traditional costing
c. Absorption costing
d. Activity-based costing
d. Activity-based costing
A(n) _______________ method first traces costs to a department and then to products.
a. Direct costing
b. Traditional costing
c. Absorption costing
d. Activity-based costing
b. Traditional costing
Of the following, which is the best reason for using activity-based costing?
a. To keep better track of overhead costs
b. To more accurately assign overhead costs to cost pools so that these costs are better controlled
c. To better assign overhead costs to products
d. To assign indirect service overhead costs to direct overhead cost pools
c. To better assign overhead costs to products
A basic assumption of activity-based costing (ABC) is that
a. All manufacturing costs vary directly with units of production
b. Products or services require the performance of activities, and activities consume resources
c. Only costs that respond to unit-level drivers are product costs
d. Only variable costs are included in activity-cost pools
b. Products or services require the performance of activities, and activities consume resources
Design of an ABC system requires
a. That the job bid process be redesigned
b. An adjustment to product mix
c. That a cause-and-effect relationship exists between resource costs and individual activities
d. Both (b) and (c)
c. That a cause-and-effect relationship exists between resource costs and individual activities
ABC should be used in which of the following situations?
a. Single-product firms with multiple steps
b. Multiple-product firms with only a single process
c. Multiple-product firms with multiple processing steps
d. In all manufacturing firms
c. Multiple-product firms with multiple processing steps
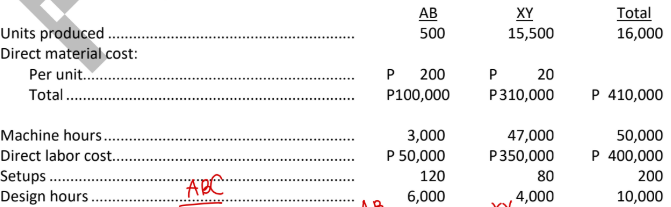
Company X produces two products, AB and XY, and uses a costing system in which all overhead is accumulated in a single cost pool and allocated based on machine hours. The company’s management has decided to implement ABC because a cost study has revealed significant amounts of overhead cost related to setup activity and design activity. The number of setups and the number of design hours will be the activity drivers for the two new cost pools, and machine hours will continue as the base for allocating the remaining overhead. Selected information follows for the company’s operations:
Overhead:
Setup-related ....................................................... P 250,000
Design-related...................................................... 350,000
Other.................................................................... 900,000
Total overhead..................................................... P1,500,000
a. Calculate the total and per unit costs reported for the two products by the existing traditional costing system.
AB
→ 240K total cost
→ 480 unit cost
XY
→ 2.07M total cost
→ 133.54 unit cost

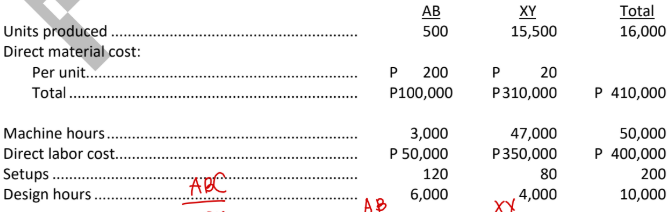
Company X produces two products, AB and XY, and uses a costing system in which all overhead is accumulated in a single cost pool and allocated based on machine hours. The company’s management has decided to implement ABC because a cost study has revealed significant amounts of overhead cost related to setup activity and design activity. The number of setups and the number of design hours will be the activity drivers for the two new cost pools, and machine hours will continue as the base for allocating the remaining overhead. Selected information follows for the company’s operations:
Overhead:
Setup-related ....................................................... P 250,000
Design-related...................................................... 350,000
Other.................................................................... 900,000
Total overhead..................................................... P1,500,000
b. Calculate the total and per unit costs reported for the two products by the ABC system.
AB
→ 564k total cost
→ 1,128 unit cost
XY
→ 1.746M total cost
→ 112.65 unit cost
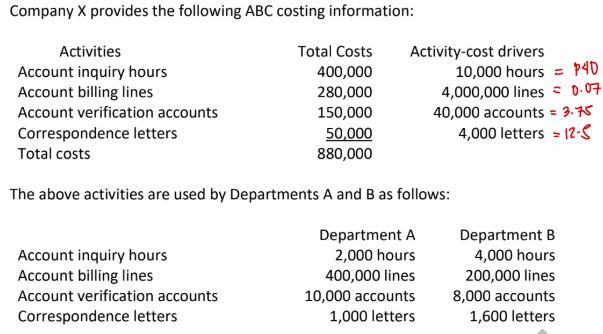
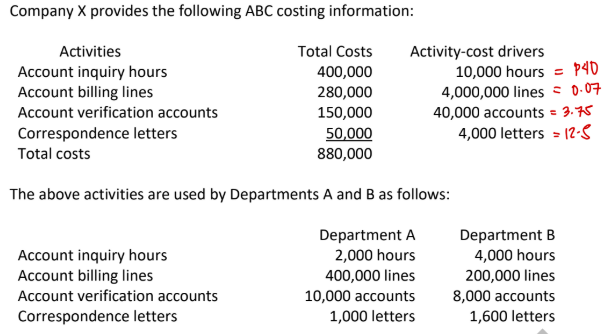
How much of the account inquiry cost will be assigned to Department A?
a. P80,000
b. P400,000
c. P160,000
d. None of the choices
a. P80,000
→ 40 × 2k = 80k
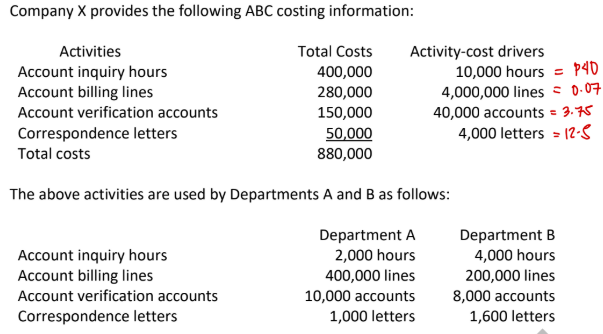
How much of the account billing cost will be assigned to Department B?
a. P28,000
b. P280,000
c. P14,000
d. None of the choices
c. P14,000
→ .07 × 200k = 14k
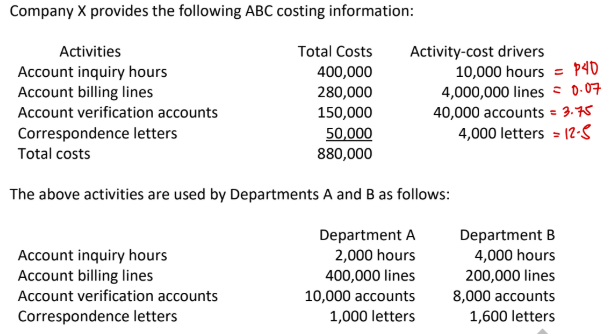
How much of account verification costs will be assigned to Department A?
a. P30,000
b. P37,500
c. P150,000
d. P10,000
b. P37,500
→ 3.75 × 10k = 37.5k
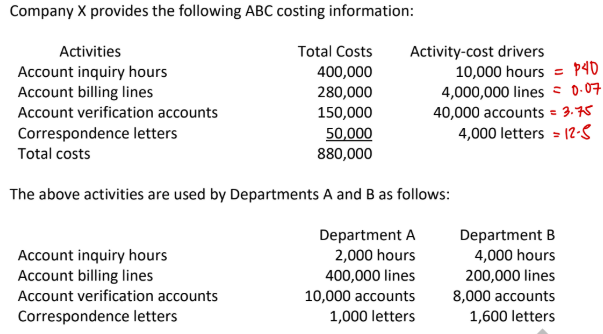
How much of correspondence costs will be assigned to Department B?
a. P1,600
b. P12,500
c. P50,000
d. P20,000
d. P20,000
→ 12.5 × 1.6k
How much of the total costs will be assigned to Department A?
a. P158,000
b. P80,000
c. P224,000
d. P880,000
a. P158,000
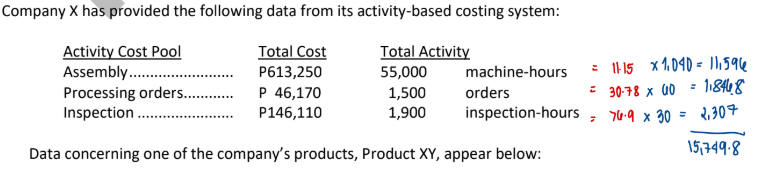
Data concerning one of the company’s products, Product XY, appear below:
Selling price per unit................................. P113.70
Direct materials cost per unit ................... P48.14
Direct labor cost per unit.......................... P11.62
Annual unit production and sales............. 360
Annual machine-hours.............................. 1,040
Annual orders ........................................... 60
Annual inspection-hours........................... 30
According to the activity-based costing system, the product margin for product ABC is:
a. P3,668.60