Unit 2 AP Chem (excluding the last two lessons)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
bonding
chemical bond formed between atoms or ions when electrons are transferred or shared
valence electrons
electrons that can be found in their outermost shell of the atoms. They are electrons used for bonding.
electornegativity
measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons
what does coloumbs law state
attractive force between charged particles increases with an increase in charge and decreases with an increase in the distance
why does electornegativity decrease down a column
as there is greater distance from the nucleus because there is more electron shielding
why does electornegativity increase as you move across a periodic table
because the protons increase, leading to a stronger nucleur charge which increases attraction
ionic bonding
a bond formed between 2 or more atoms or ions. Electornegativity difference is so great that the electornegative steals elctrons from the less electornegative
-very strong bonds
-tends to happen between nonmetals and metals but there are exceptions
electornegativity difference for an ionic bond to occur
greater than 1.7
covalant bonding
a bond formed between 1 atoms or ions. The lectronegativty difference is solow so the atoms share the electrons instead
-happens between onmetals
polar covalent
-stronger than nonpolar covalent
-electrons are shared unequally
-electornegativtiy difference between 0.5-1.7
nonpolar covalant
-electrons are shared equally
-weaker than polar covaltn
-
metallic bonding
-weakest bond
-formed between metallic substances
electonrs move freely between the different metallic atoms
-described as sea of electrons throughout metal
-free movement gives metals mettalic properties
held by cations that are allowed to be delocalized and move anywhere, creating coloumbic attraction
-this is why we cant use the periodic table column groups to predict the number of valence electrons as we don’t knwon which element are from any specific atom
single bond
single lone electron of one elemnet shares the single lone of another
examples: H2, HCl
triple bond
When 3 lone lectrons bond with the 3 lone pairs of another elemnt
Ex. N2
double bond
lone pair of elctrons of one element bond with the lone pair of another molecule
Ex. O2, CO2
lattice
lattice energy can be represented using a modification of Coloumbs law where the nergy is proprotional to the charges and inversely proportional to distance
-energy to sepreate ions is known as lattice energy
-lattice energy is defined as change in energy that occurs when has ions combine to form a solid
-all ionic bonds are polar and lattice structures
enthalpy
energy required when breaking a bond or the energy released when a bond is formed
also known as bond energy
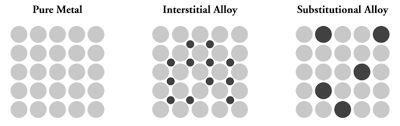
institial alloy
atoms added tot he metal that are small and fit in between metal atomsin the existing holes (interstices)
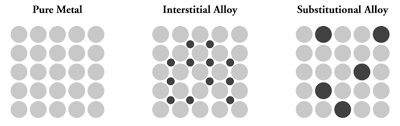
substitutional alloy
atoms have similar radii so they replace each other
lewis structure
shows a representation fo how the atoms connect to form in a molecule
resonance structure
one of several Lewis structures used to describe the delocalization of electrons within a molecule or polyatomic ion, where atoms remain fixed but electrons move between them, creating fractional bonds and charge
how to determine formal charge
-determine valence electrons
-substract the sum of the lone electrons and bonds connection to the atom
-to check it, sum for formal charges should add up to 0 for a molecule or add up to the charge of the polyatomic ion
how do covalnet bonds form
-at lowest energy state
-attraction between nuclei is greatest for shared electrons but repulsions between electrons and between nuclei is small
lattice sturcutre propoerties
-nonvolatile
-nonconductive unless they can be melted or dissolved into ions
-soluable in polar compounds
0insoluable in nopoplar compounds like oil