EOR: peds random pearls
1/263
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
264 Terms
top 5 causes of infant mortality
- birth defects
- preterm birth & low birth weight
- maternal pregnancy complications
- SIDS
- injuries
1 umbilical artery think....
congenital anomalies → renal
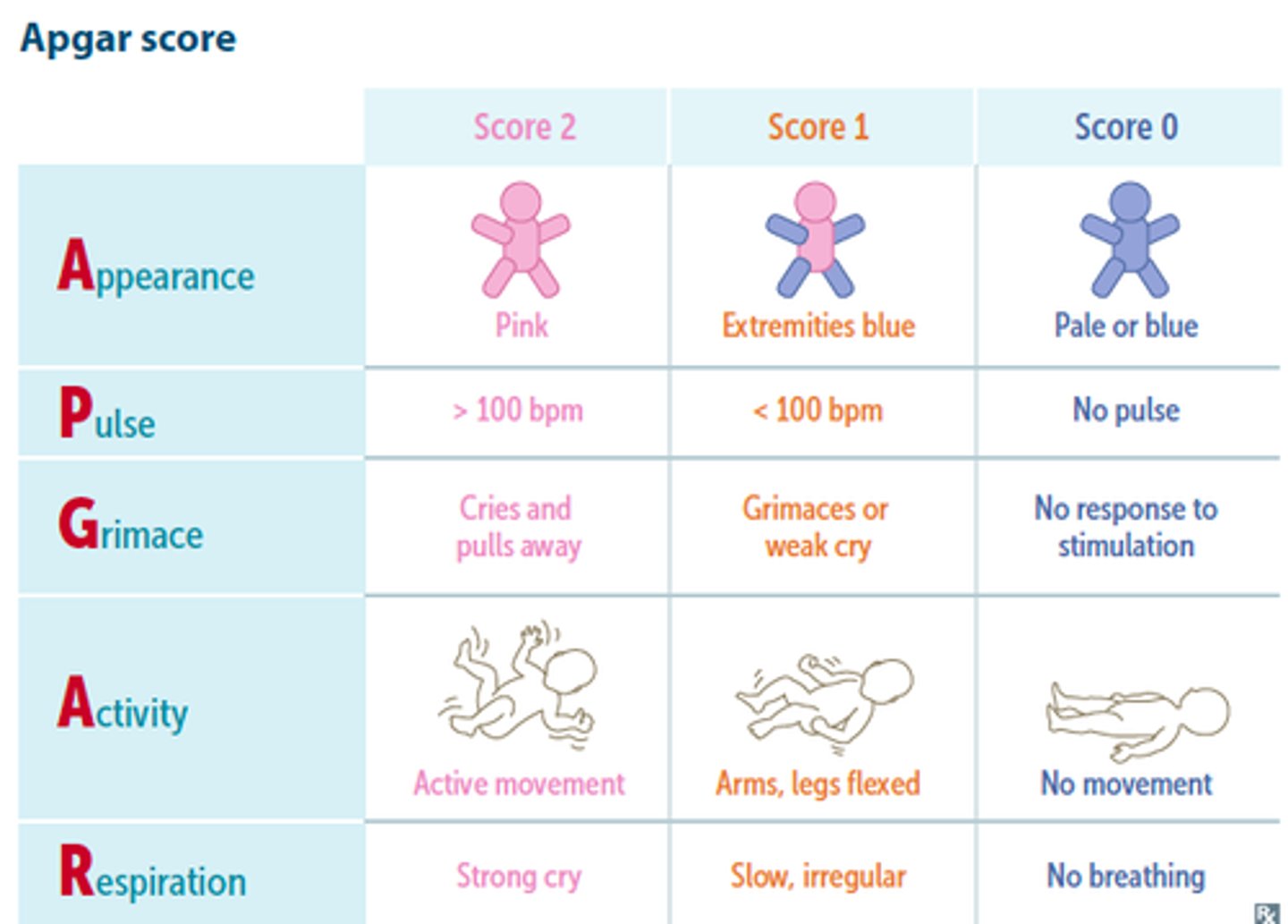
APGAR scoring
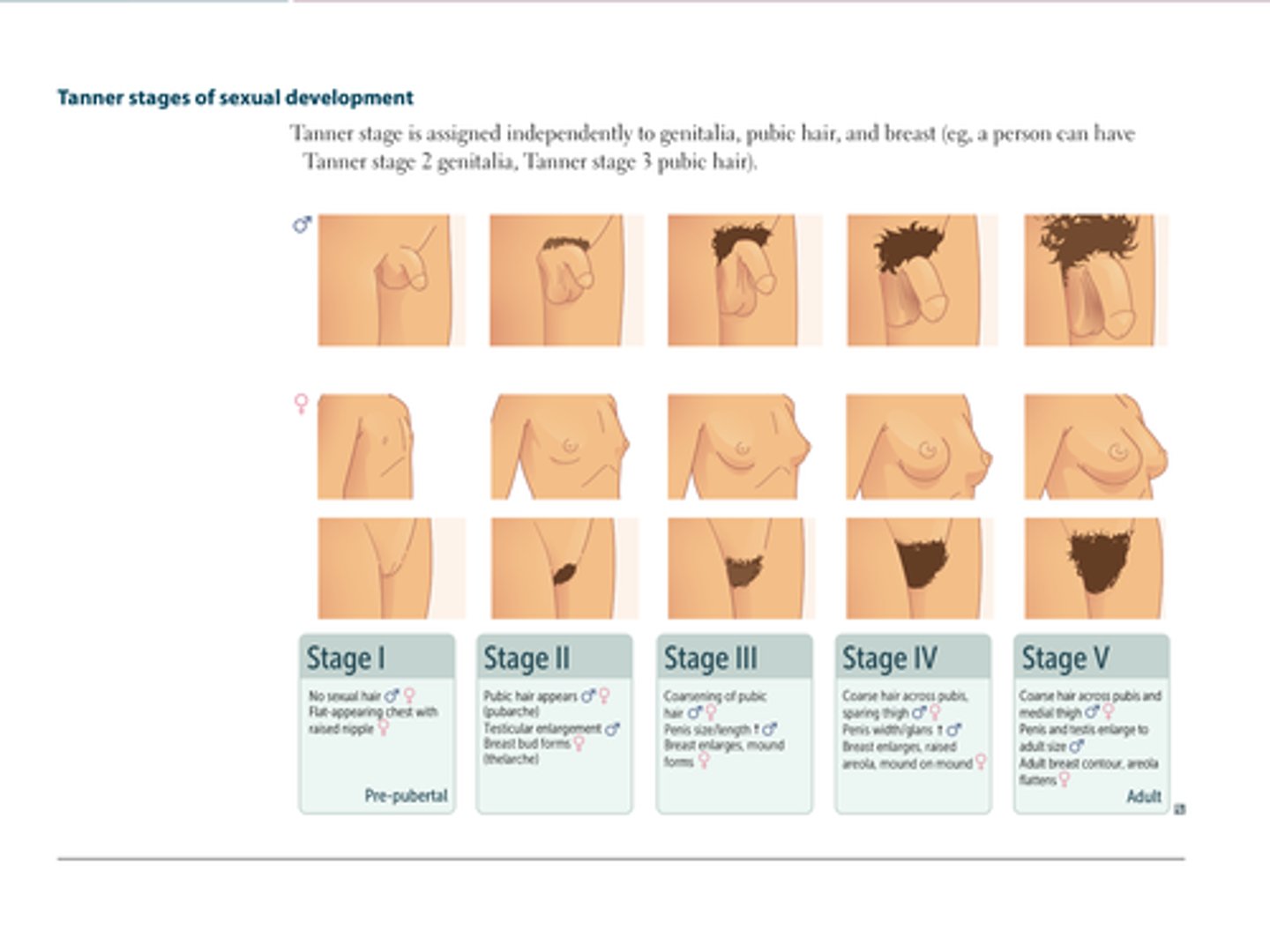
tanner stages
erythematous grouped papules/pustules that classically SPARES the vermillion border
perioral derm → topical pimecrolimus, metro, erythro or clinda
**PO abx if extensive
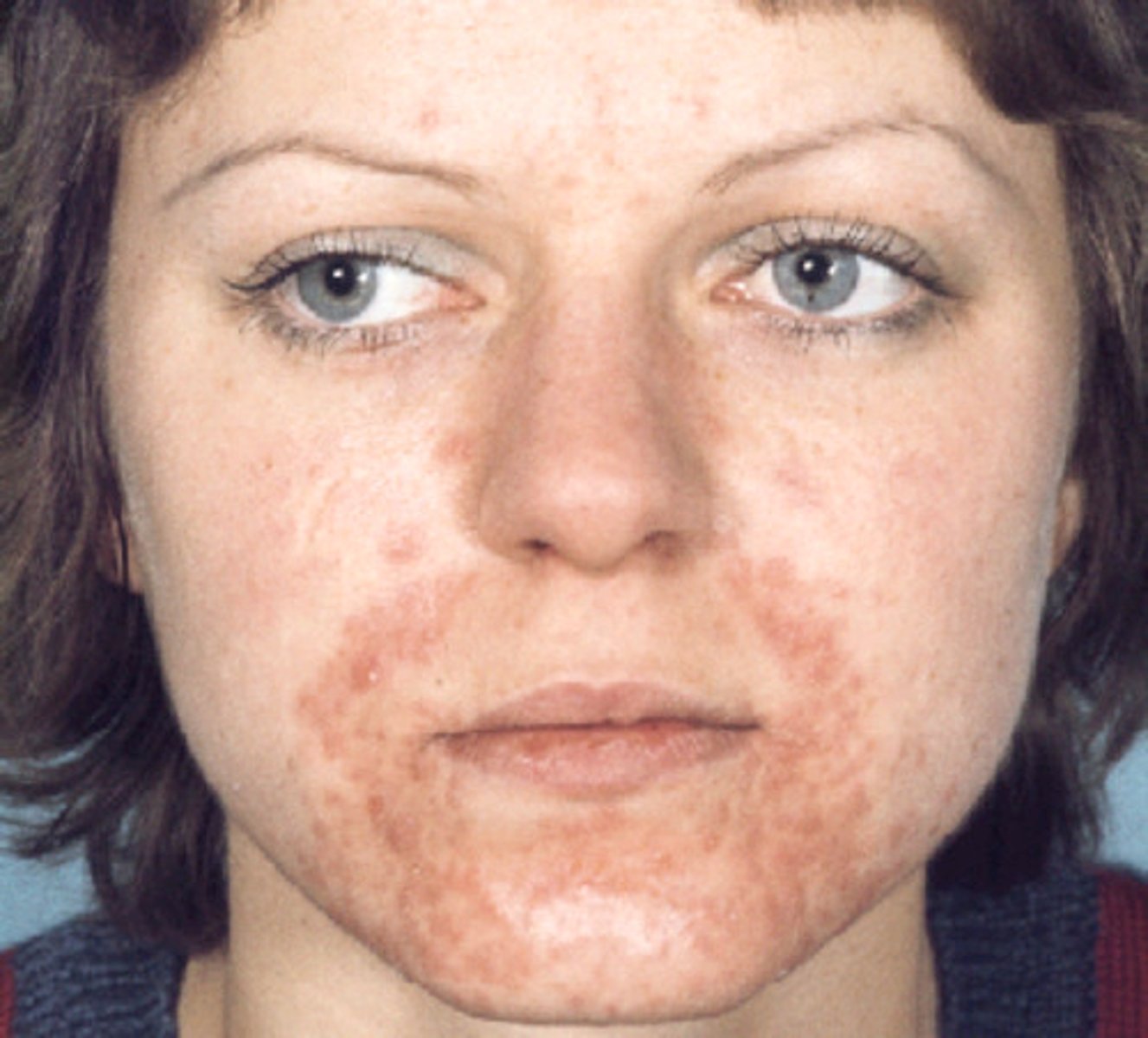
perioral derm risk factors
- women 20-45 y/o
- h/o topical steroid use
- fluoride toothpaste
- lip licking
- hormonal changes (OCPs)
- cinnamon gum
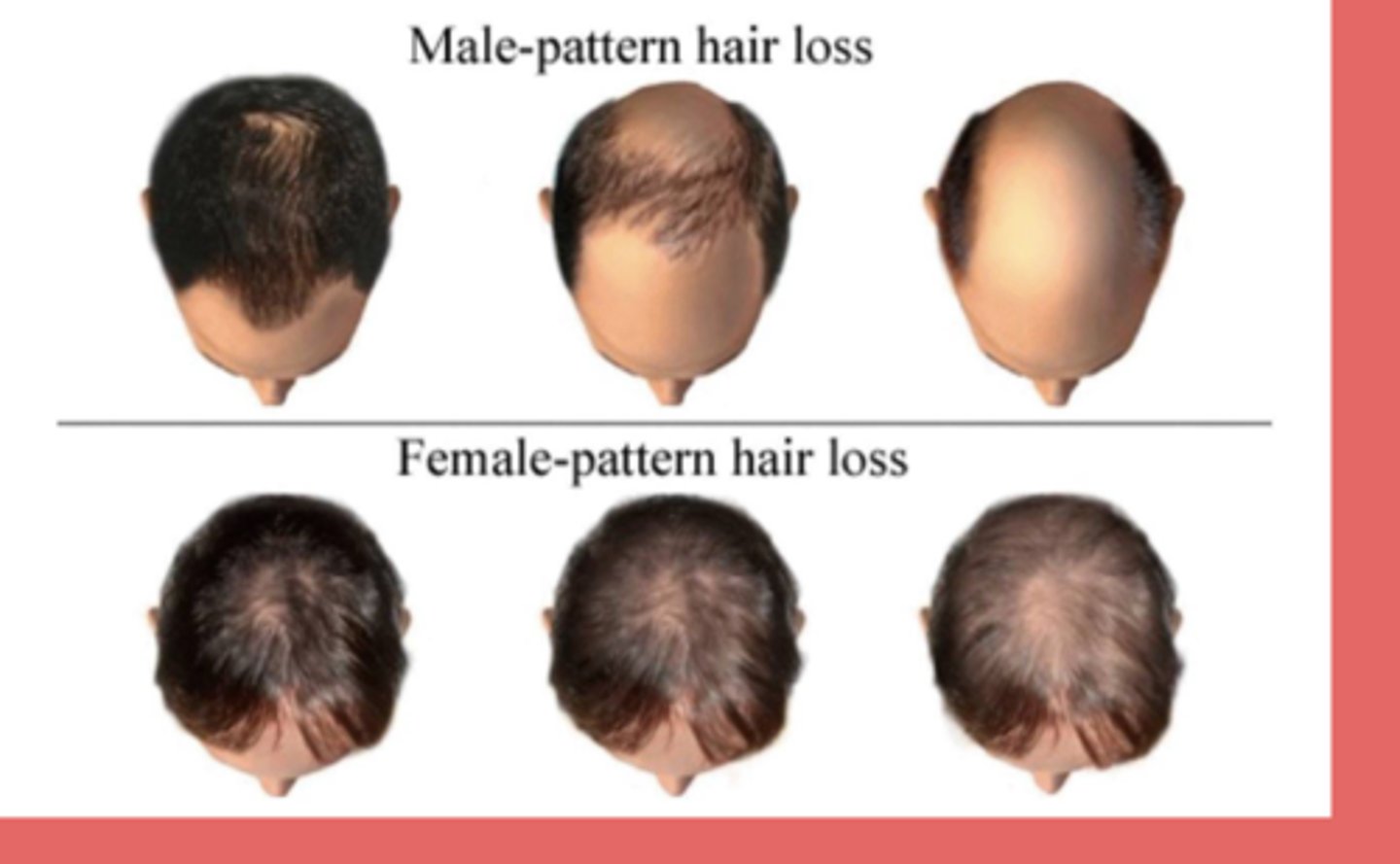
gradual progressive loss of terminal hairs on the scalp in a characteristic distribution
↓ anagen to telogen ratio
dermoscopy: miniaturized hair & brown perihilar casts
androgenic alopecia → MC type of hair loss in M&F
- males: bitemporal thinning & vertex scalp
- females: vertex scalp (doesn't affect frontal hairline)
DHT (key androgen) shortens the anagen phase
anagen = growth phase
telogen = resting phase
tx = topical minoxidil, PO finasteride, spiro
MOA of finasteride
5-a-reductase inhibitor → inhibits conversion of testosterone to DHT
category X med
disruption of the skin barrier due to filaggrin gene mutation & disordered immune response
atopic dermatitis
MC locations of atopic derm
infantile → scalp, cheeks, neck, extensor surfaces (crawling)
childhood → flexural areas (ACF, popliteal)
adolescence → flexural areas, hands/feet
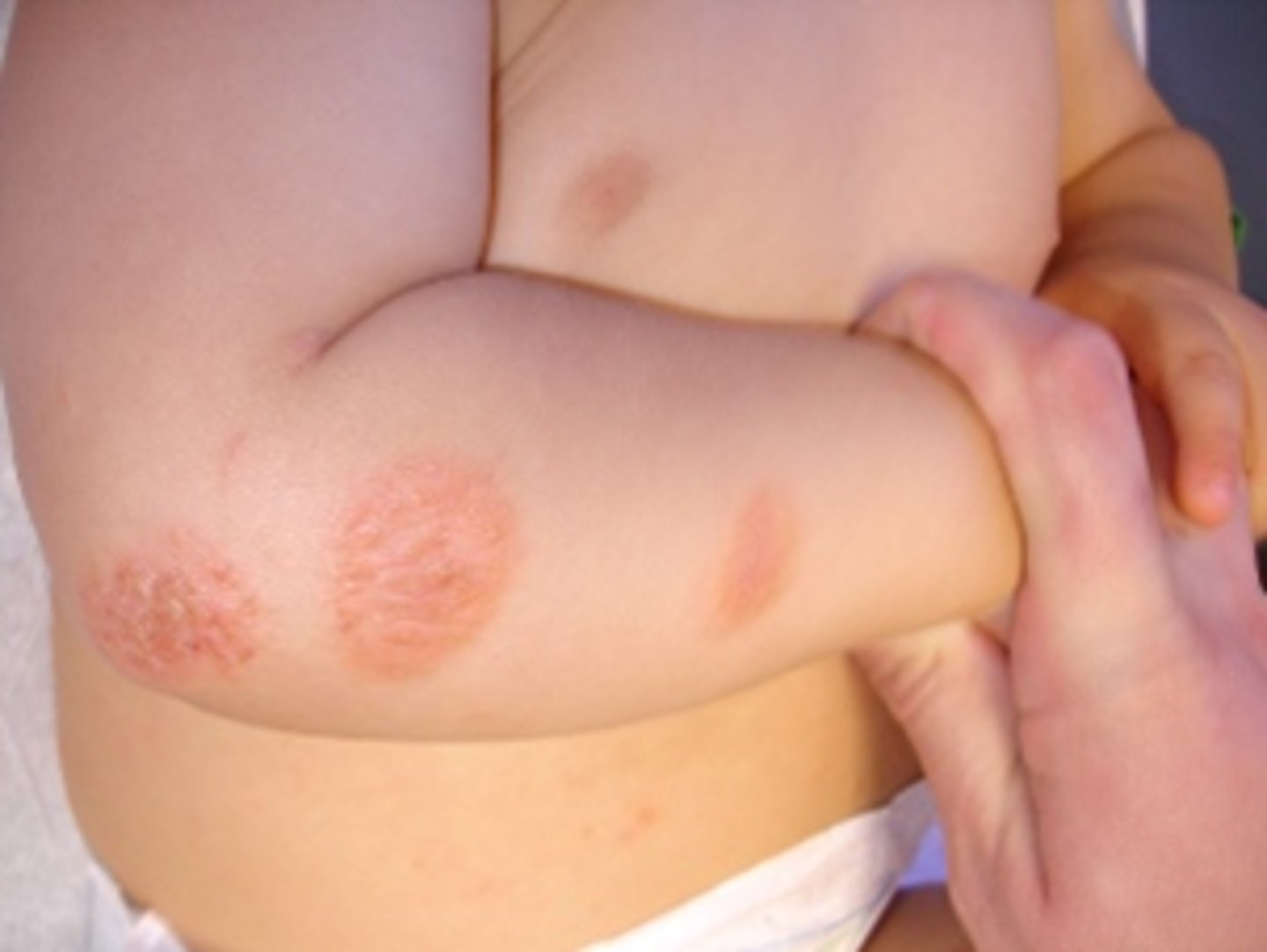
sharply defined erythematous, edematous coin-shaped crusted patches on the dorsal of the hands/feet and extensor surfaces (knees, elbows)
nummular (discoid) eczema
tx for eczema that is alternative to topical steroids and DO NOT cause skin atrophy
topical calcineurin inhibitors → pimecrolimus, tacrolimus
irritant vs allergic contact dermatitis
irritant (MC type) → non-immunologic reaction (immediate)
allergic → type 4 hypersensitivity reaction (delayed)
MCC of allergic contact derm
nickel MC worldwide
poison ivy is also a big cause
erythematous papules or vesicles in a linear or geometric pattern + localized pruritus, stinging & burning
+/- lichenification
contact dermatitis → patch testing to identify etio
lichenification seen in chronic cases
secondary infections associated with diaper dermatitis
- candidiasis
- impetigo
- HSV → child sexual abuse
beefy red plaques +/- maceration or erosion in the groin area, involving the inguinal folds w papular satellite lesions
cutaneous candidiasis (secondary infection from diaper rash)
**regular diaper dermatitis SPARES skin folds
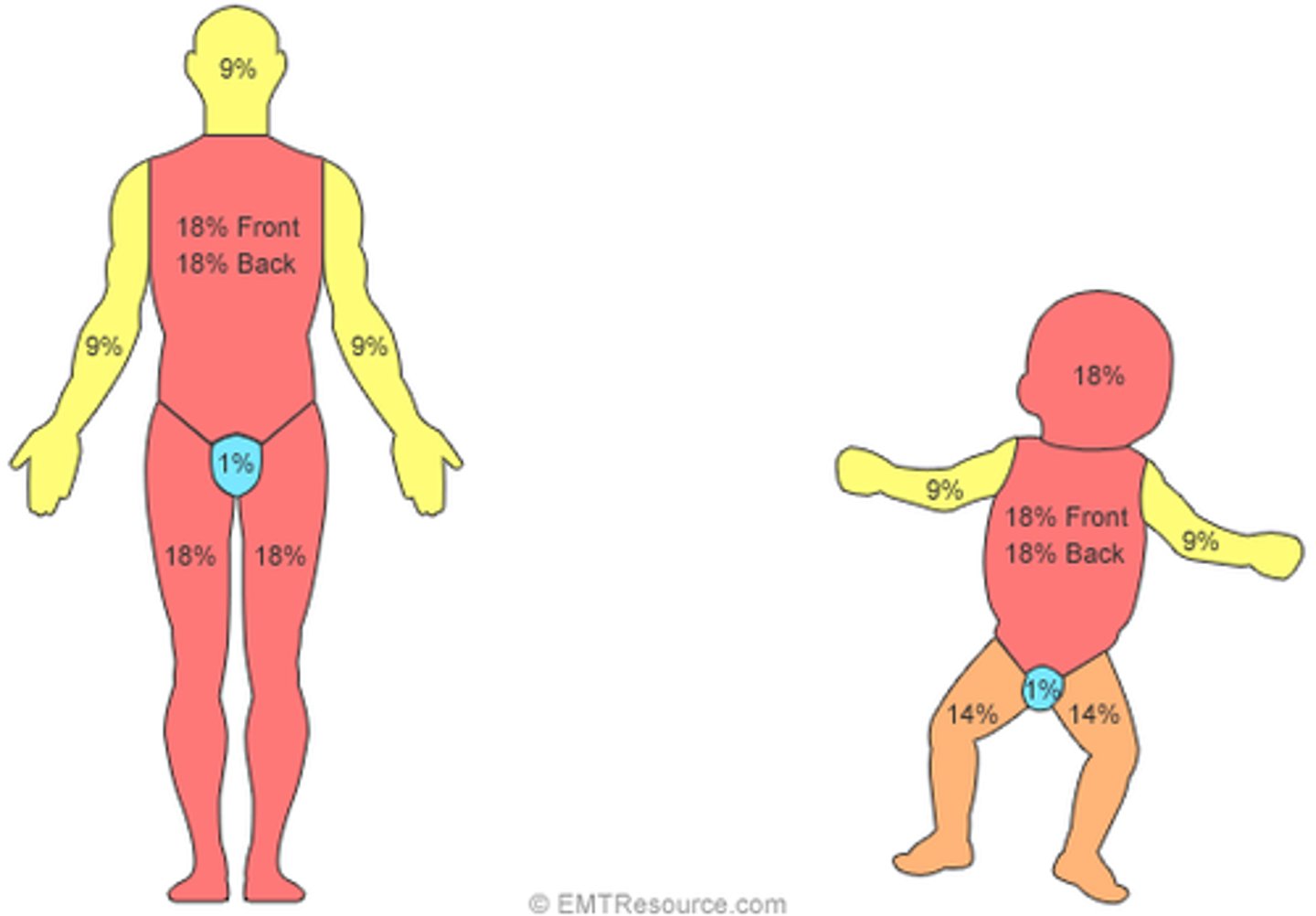
most accurate method for estimating TBSA
Lund-Browder
degree of burn:
- confined to epidermis
- red, DRY
- painful
- blanches w pressure
superficial (1st degree) → do not calculate TBSA%
degree of burn:
- epidermis + papillary dermis
- pink-red; weeping/MOIST
- BLISTERING
- painful; INTACT cap refill
- blanches w pressure
superficial partial-thickness (2nd degree) → may heal with pigment changes
degree of burn:
- epidermis + reticular dermis
- mottled color variation from cheesy white to red
- WET or WAXY
- BLISTERING
- pain ONLY w pressure; ABSENT cap refill
- does NOT blanch w pressure
deep partial-thickness (2nd degree) → heals w hypertrophic scarring
degree of burn:
- epidermis + dermis + SQ
- waxy white to leathery gray to charred/black
- DRY, inelastic
- NO BLISTERING
- lack of sensation (painless)
- does NOT blanch w pressure
full-thickness (3rd degree) → requires surgery for healing
degree of burn:
- epidermis + dermis + SQ + fascia/muscle/bone
- black, CHARRED, dry
- no blistering
- no sensation, no cap refill
- does not blanch w pressure
4th degree → requires surgery
what BSA in children warrants fluid resuscitation?
>10% BSA → LR via 2 large bore
*can add 5% dextrose for children < 5 y/o or < 20 kg to prevent hypoglycemia
Parkland formula for children
3 mL x TBSA% x wt (kg)
***adults is 4 mL
4-2-1 rule for maintenance fluids
4 mL for first 10kg + 2 mL for next 10kg + 1 mL for each remaining kg
MC lab abnormality seen in burns
hyperkalemia
criteria for burn center admission
- > 10% BSA or ANY deep partial/full-thickness burns
- burns to hands, feet, face, genitalia
- chemical, electrical or inhalation injury
- circumferential burns
- underlying comorbidity
- abuse
cutaneous drug reaction types
type 1 → IgE mediated; urticaria, angioedema; immediate
type 2 → antibody-mediated, cytotoxic
type 3 → antibody-antigen complex; vasculitis, serum sickness
type 4 → delayed cell-mediated; erythema multiforme, ACD
type 5 → non-immunologic; genetic incapability to detox meds (anticonvulsants, sulfa)
MC drugs assoc w an exanthematous drug eruption
abx → aminopenicillins, sulfonamides, Bactrim
anticonvulsants → carbamazepine
CCBs
NSAIDs
causes morbilliform rash primarily on trunk/proximal extremities after drug initiation; NO mucosal involvement
type IV hypersensitivity rxn
mast-cell mediated vs bradykinin-mediated angioedema
mast cell → has assoc allergic sxs (flushing, pruritus, urticaria, etc)
- d/t histamine release
bradykinin → NO associated allergic sxs
- hereditary deficiency or ACE-induced
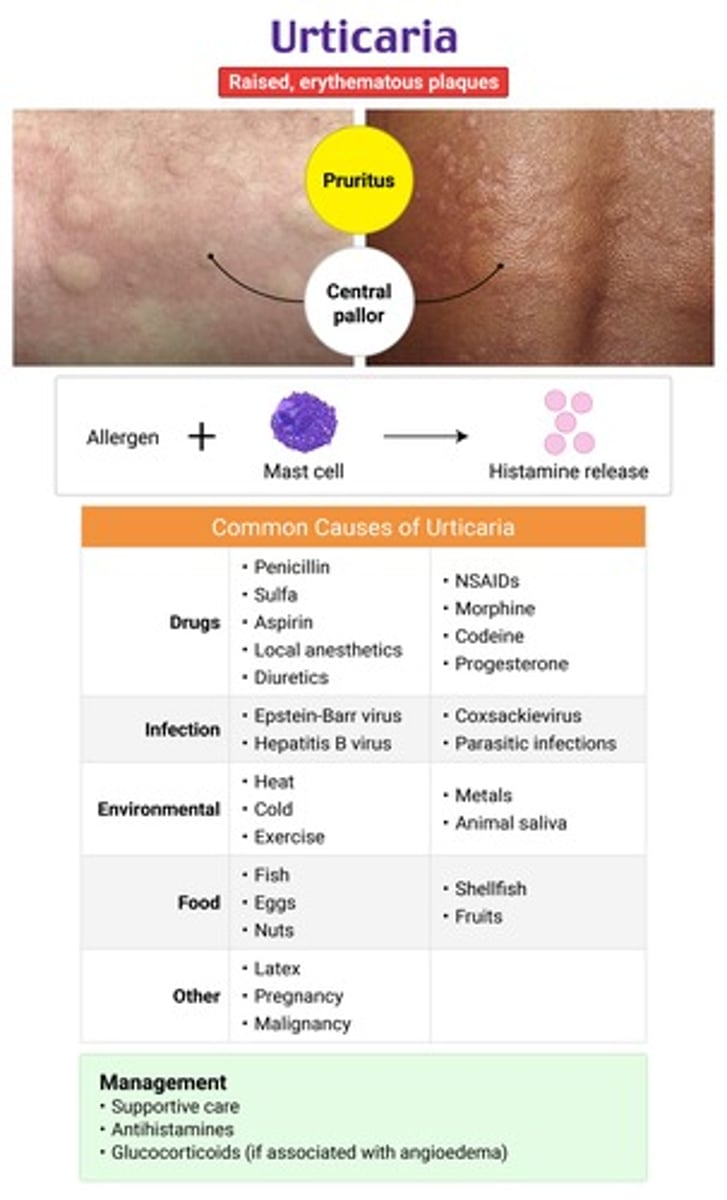
edema of the superficial layers of the skin → sudden onset transient well-circumscribed hives or wheals with central pallor
urticaria → lesions are blanchable
histamine release from mast cells & basophils in dermis = ↑ vascular permeability
MCC of erythema multiforme
HSV
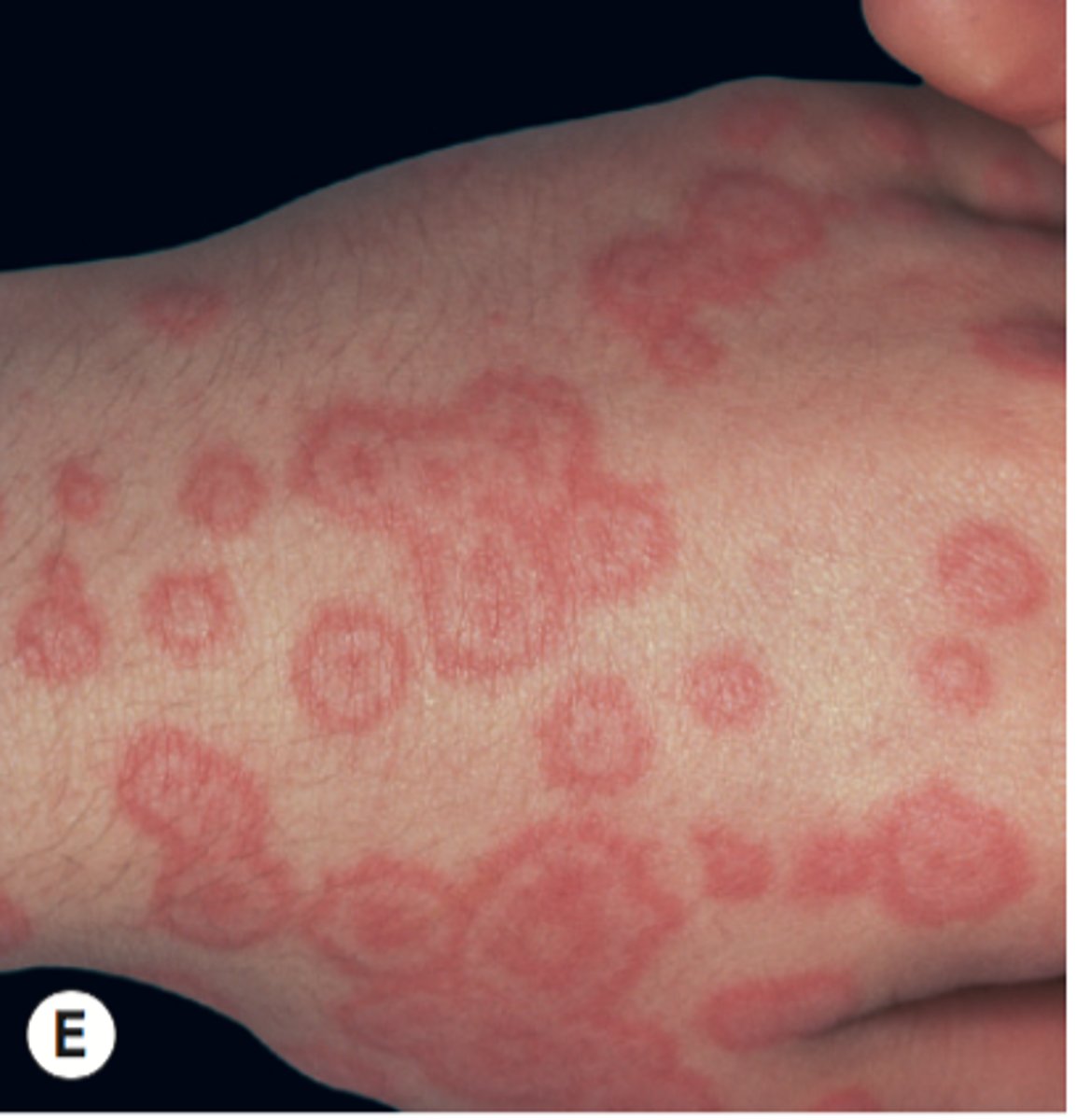
target lesions MC on extremities (hands/feet) with 3 zones → dusty central blister, ring of pallor and surrounding peripheral ring of erythema
(-) Nikolsky sign
erythema multiforme
EM minor → mild/no mucosal involvement; no system sxs
EM major → widespread, severe mucosal involvement + systemic sxs (fever, arthralgia)
both erythema multiforme and SJS/TEN have target-like lesions, what differentiates them?
EM → - Nikolsky; +/- mucous membrane involvement
SJS/TEN → + Nikolsky; always has mucous membrane involvement
**SJS/TEN can also have a flu-like prodrome
SJS < 10% BSA
TEN > 30% BSA
prodrome: high fever + 3Cs (cough, coryza, conjunctivitis)
morbilliform dark brick red rash starting at the hairline
small pale white/blue papules w a red base on the buccal mucosa
rubeola (1st disease) → koplik spot pathognomonic
*etio = measles virus from paramyxovirus
give vit A for young/severely malnourished children to ↓ risk of complications/death
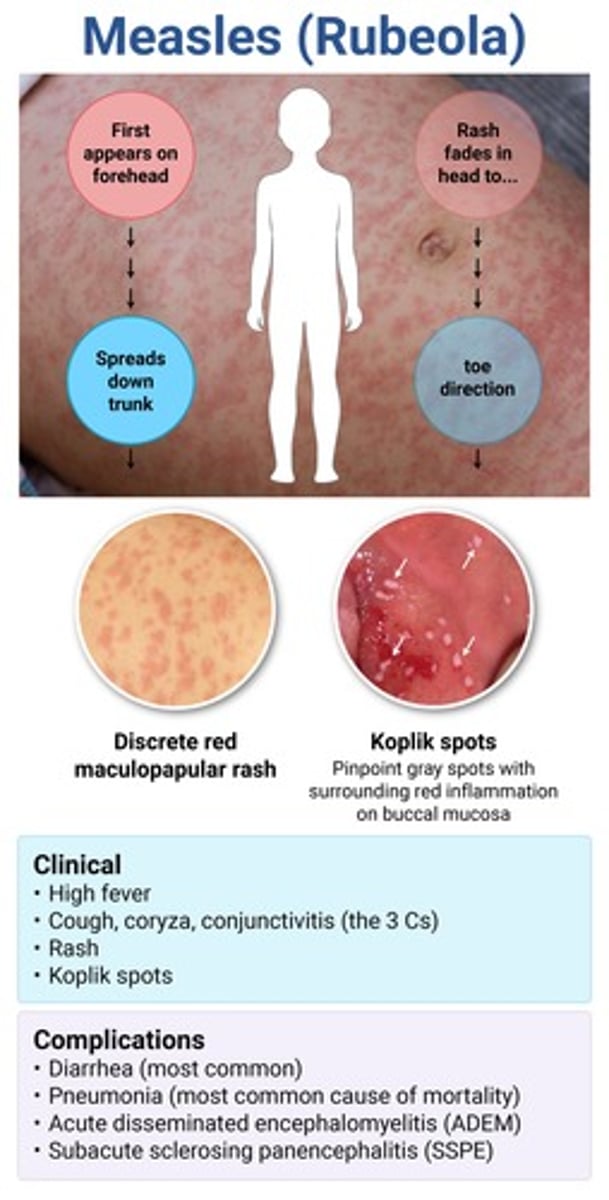
complications of rubeola
- severe diarrhea → MC
- pneumonia → MCC of measles-related death
- AOM, conjunctivitis
- sclerosing panencephalitis
- diffuse erythema (resembling a sunburn) that blanches with pressure + small papular elevations giving a sandpaper texture → desquamation
- red tongue with enlarged papillae (strawberry tongue)
- linear petechial lesions in skin folds (pastia lines)
scarlet fever → GAS type IV hypersensitivity rxn
typically occurs w/in 1-2 days of strep infxn
tx = PCN or amox (preferred in kids)
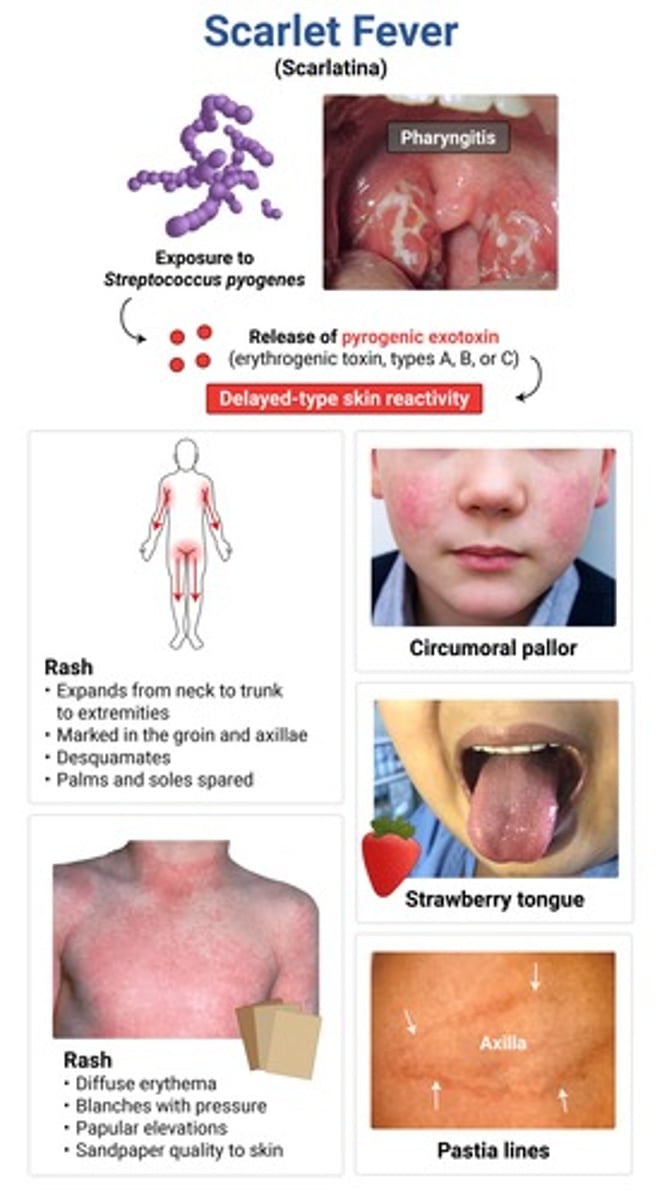
complications of scarlet fever
rheumatic fever and post-strep glomerulonephritis
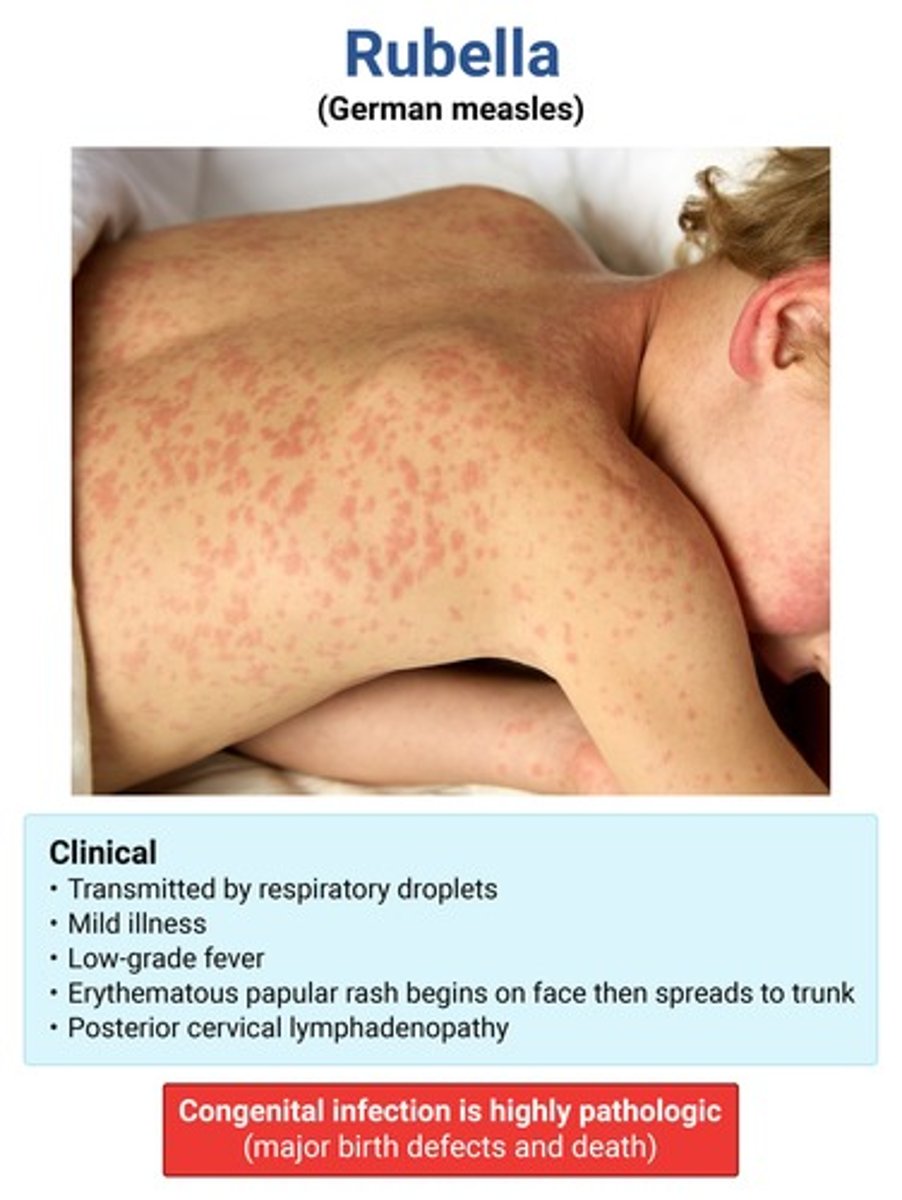
single phase lasting 3 days (NO PRODROME) → low-grade fever, postauricular/post-cervical LAD
arthritis/arthralgias → teens/adult women
light red/pink non confluent rash starting on face & generalizes w/in 24 hrs
pinpoint red macules & petechiae on the soft palate & uvula
rubella (aka "3 day measles") → forchheimer spots
*etio = togavirus family → MC in African regions
TERATOGENIC IN 1ST TRIMESTER!!!
patho of erythema infectiosum
parvo B19 → infects & destroys reticulocytes = transient halt in erythropoiesis
leads to aplastic crisis in sickle cell, G6PD, IDA, hereditary blood d/o pts → do NAAT & give RBC transfusion
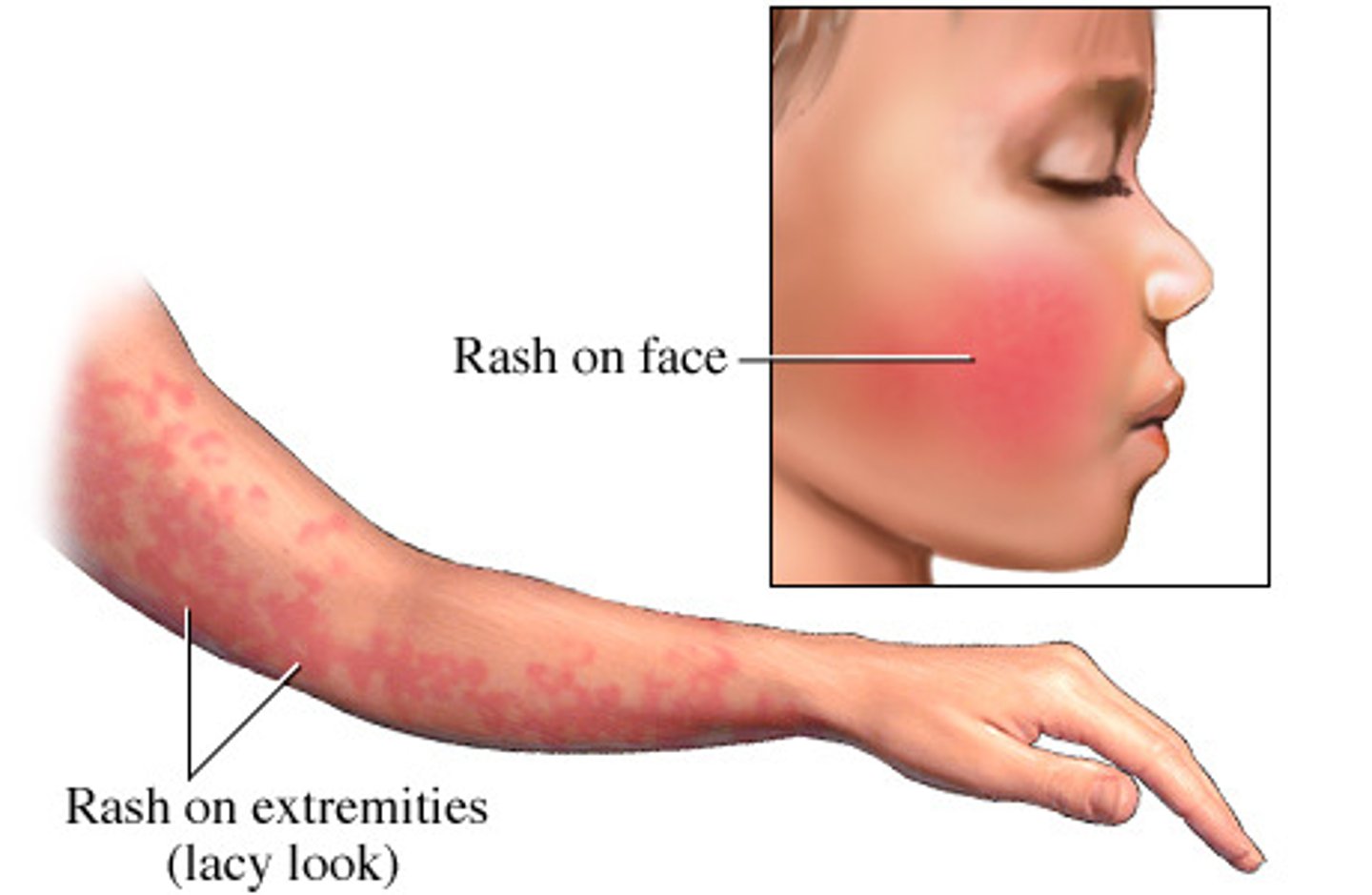
erythematous malar rash w circumoral pallor → develops into lacy reticular blanching rash on trunk/ext sparing palms/soles
symmetric arthlagias/arthritis in small joints common in older children/adults
erythema infectiosum (5th disease) → slapped cheek
can cause hydrops fetalis/fetal demise if infected during pregnancy
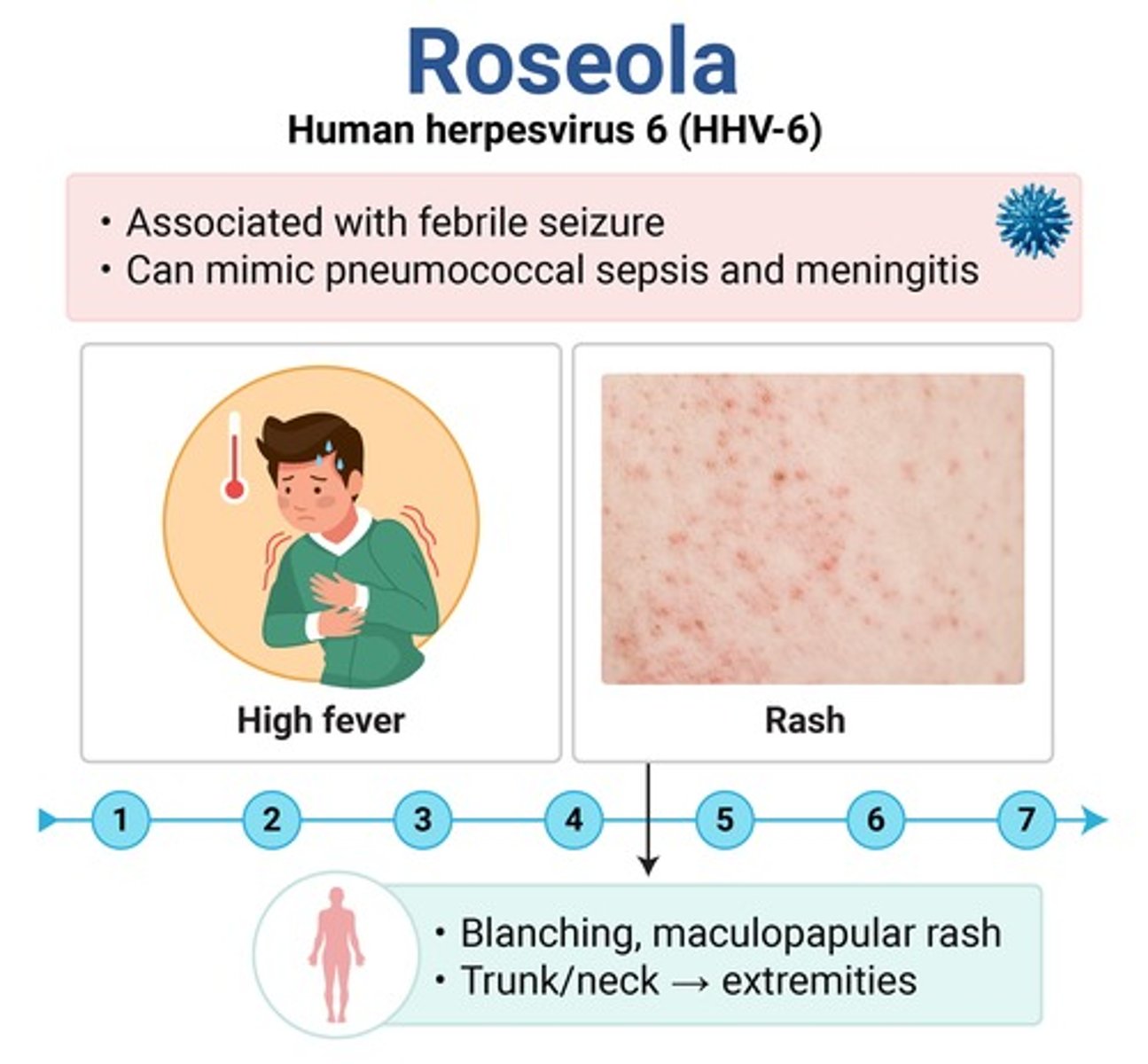
~3 days of HIGH fever (> 104F) in an otherwise healthy appearing child
fever resolves → rash starting on trunk/neck
Nagayama spots → red papules/ulcers on the soft palate & uvula
roseola (HHV-6) → only exanthem that starts on the trunk
major cause of febrile seizures!!
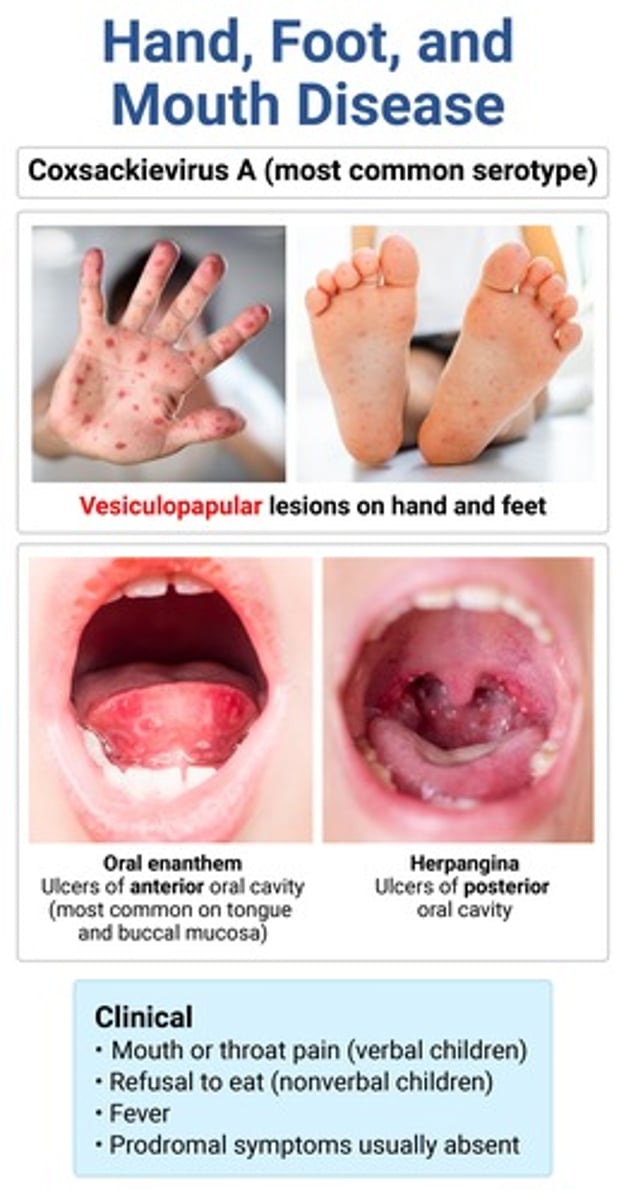
etio of HFMD
coxsackie type A16 → MC in summer months; fecal-oral transmission
prodrome: mild URI sxs, mouth/throat pain, ↓ or no appetite/refusal to eat
enanthem: small red macules → vesicles → ulcers w/ gray base & erythematous on buccal mucosa & tongue
exanthem: gray-yellow nonpruritic nontender vesiculopapular lesions on distal extremities
HFMD → typically resolves in 1 wk
complications of HFMD
aseptic (aka viral) meningitis
GBS
type A → herpangina
type B → myocarditis, pericarditis
HFMD vs herpangia
HFMD → ulcers of anterior oral cavity (buccal mucosa, tongue)
*mild URI sxs, assoc skin lesions on hands/feet
herpangina → ulcers of posterior oral cavity (soft palate, uvula, tonsils)
*sudden onset HIGH fever, no skin lesions
etio of mumps
paramyxovirus → MC in unvaxxed (2-9y), crowded settings (college, schools), boys > girls
~48 hrs of low-grade fever, HA, otalgia, malaise then U/L (possibly B/L) parotitis with facial edema that obscures the angle of the mandible
stensen duct orifice enlarged, red & edematous
mumps → isolate for 5 days!!
↑ amylase, leukopenia on labs
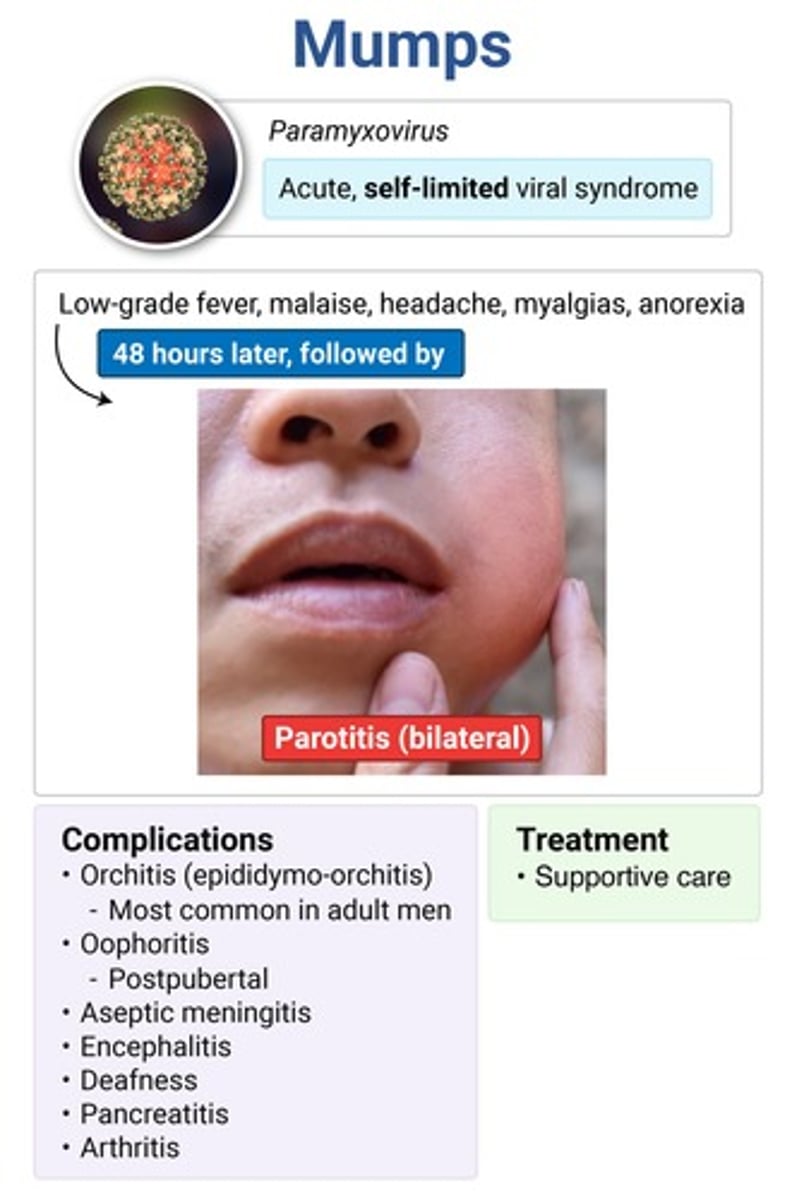
complications of mumps
- orchitis → MC in adult men
- oophoritis → post pubertal females
- encephalitis → incidence ↓ with vaccine
- acute pancreatitis → MCC of pancreatitis in kids
- deafness
URI sxs + pruritic asynchronous maculopapular rash appearing in successive crops that form vesicles & eventually crust over
rash starts on face → spreads caudally
varicella (HHV-3) → confirm w PCR
antivirals if >13 y/o, unvaxxed or immunocompromised (< 13 is supportive)
VZIG if high-risk
complications of varicella
bacterial superinfection → MC in kids
pneumonia → MC in adults
encephalitis
reye syndrome → if use of aspirin
MC bacterial skin infection in children
impetigo → highest incidence 2-6y; HIGHLY contagious
pruritic, nontender vesicles → dry with a honey-colored crust
occur at sites of superficial skin trauma & MC around nose/mouth
non-bullous impetigo (MC type) → S. aureus, GAS
vesicles rapidly enlarging to flaccid bullae with sharp margins & no surrounding edema → rupture and leave varnish-like crust
MC occurs on trunk
**associated fever & diarrhea
bullous impetigo → S. aureus; seen in NB & young kids
punched out ulcers with yellow crusts & violaceous margins
aka deep form of impetigo
ecthyma → GAS; heals w scarring
complications of impetigo
cellulitis (MC)
post-strep GN
***DOES NOT lead to rheumatic fever!!
intense itching esp occipital area + papular urticaria
white, oval-shaped egg capsules at base of hair shafts
pediculosis capitis (head lice) → outbreaks MC in warm & humid weather
permethrin 1st line
6Ps: purple, polygonal, planar, pruritic, papules & plaques
(+) koebner's phenomenon
Wickham striae: fine gray-white lines on skin lesions or oral mucosa
biopsy → saw-tooth lymphocyte infiltration, hypergranulosis, hyperkeratosis, degeneration of basal cell layer
lichen planus → MC involves volar (flexor) surfaces of wrist & ankles
↑ incidence assoc w HCV infection, meds (thiazides, sulfa, penicillamine), lymphoma
Herald patch followed by smaller, very pruritic round papules w collarette scaling at the edges & central clearing
oriented along the skin cleavage lines on the trunk & proximal extremities
commonly follows a viral infection
pityriasis rosea → get RPR in YAs to r/o syphilis
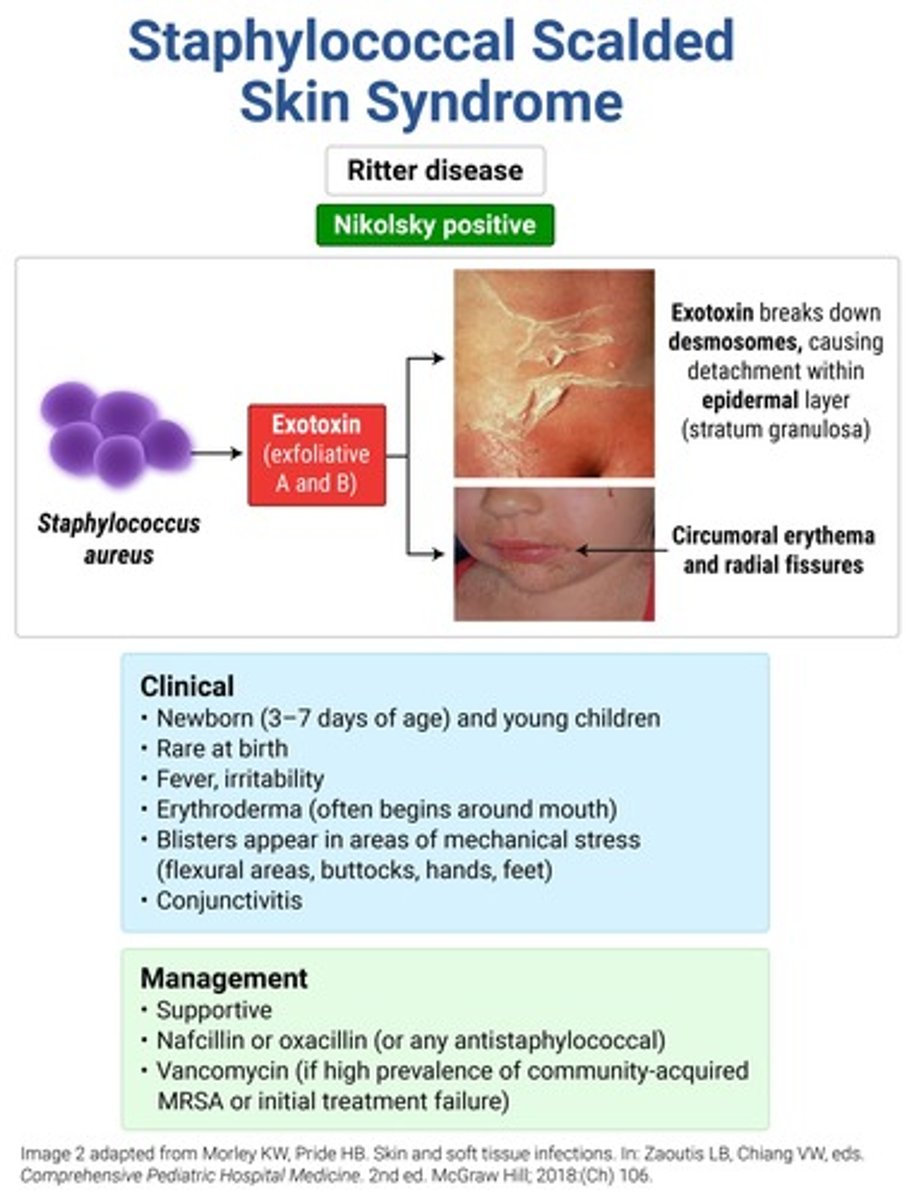
PAINFUL diffuse cutaneous blanching erythroderma that is more accentuated in skin folds → sterile, flaccid bullae in areas of mechanical stress with a (+) Nikolsky sign → sheet-like desquamation and thick perioral crusting (resembling oatmeal)
**mucous membranes NOT involved
SSSS (Ritter disease) → MC < 5y
oatmeal = "SSSS sad face"
tx = nafcillin or oxacillin (vanco if MRSA); steroids are CI!!
diffuse red maculopapular rash with desquamation of the palms & soles
toxic appearing
TSS → admit, IVFs & abx
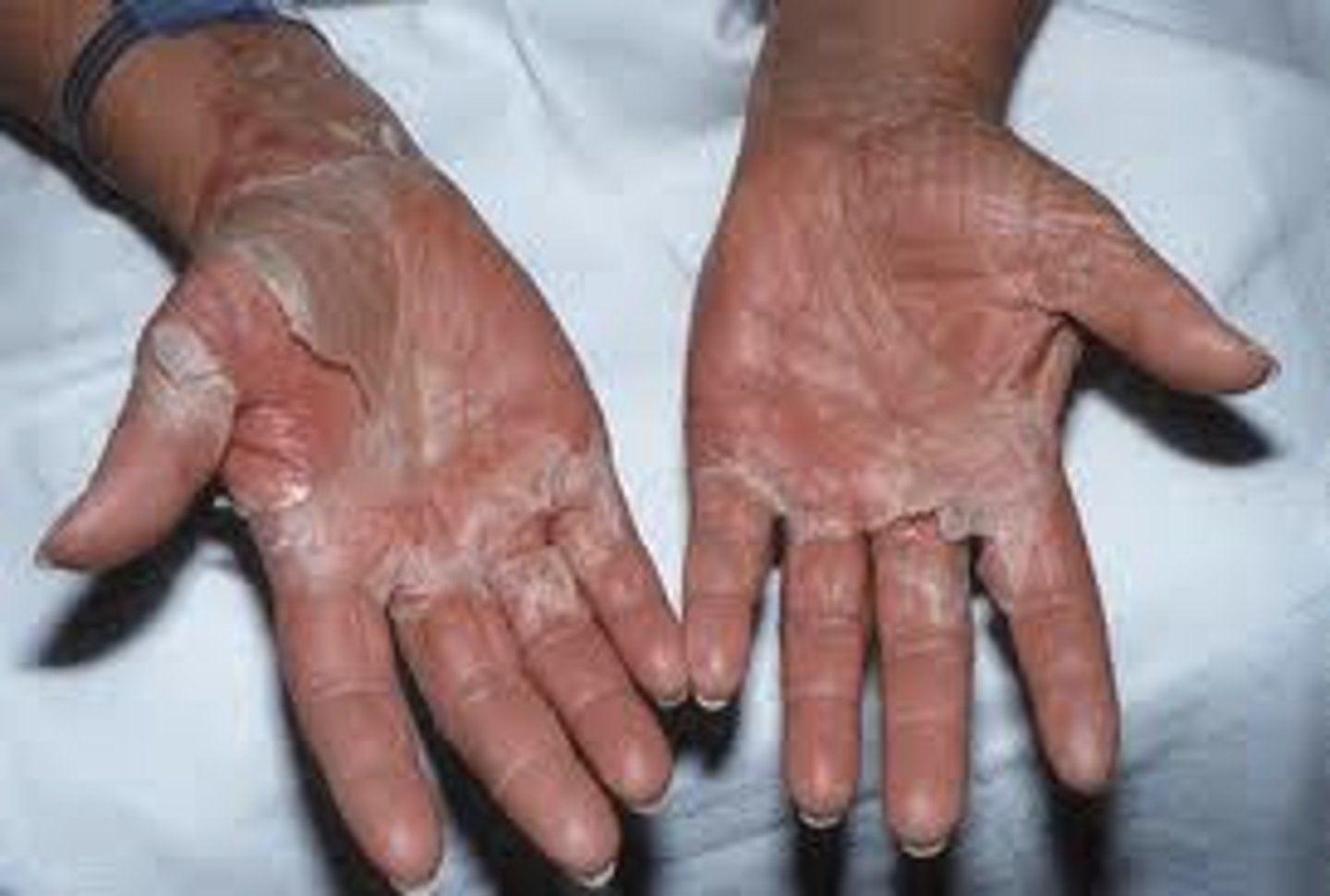
severe pruritus worse at night or after a hot shower/bath
serpiginous burrows in intertriginous zones
erythematous papules +/- excoriations
scabies → permethrin (> 2 mo); sulfur (< 2 mo)
- patches of alopecia on the scalp w black dots (distal broken hair shafts)
- gray scaly patches of hair loss
- kerion: painful edematous plaque w pustules & thick crusting
- favus: cup-shaped yellow crusts
tinea capitis → T. tonsurans; MC in prepubescent children
tx = PO griseofulvin
*ADRs: hepatitis, GI upset, HA, disulfiram rxn
MC dermatophyte infection
tinea pedis → T. rubrum; MC in teens & young males
interdigital → MC type
hyperkeratotic → soles/lateral foot surfaces; "moccasin" pattern
annular patches/plaques & diffuse erythema to inner thighs or groin w sharply demarcated raised border
spares scrotum
ținea cruris (jock itch) → T. rubrum; tinea pedis may be source of infxn
asymmetrically distributed pruritic red scaly annuals plaques/patches w central clearing & well-defined raised borders
often have h/o exposure to pet with same infection
tinea corporis → T. rubrum
segmented hyphae on KOH; cx definitive
tx for tinea infections
capitis → PO griseofulvin (alt terbinafine)
pedis, cruris, corporis → topical azoles (PO if extensive)
hypo- or hyper pigmented well-demarcated round macules w fine scaling on upper trunk, neck & proximal extremities
KOH: hyphae & spores (spagetti and meatballs)
woods lamp: yellow-green fluorescence
tinea versicolor → Malasssezia furfur
topical selenium or azoles 1st line
MC opportunistic infection
Candidiasis → C. albicans
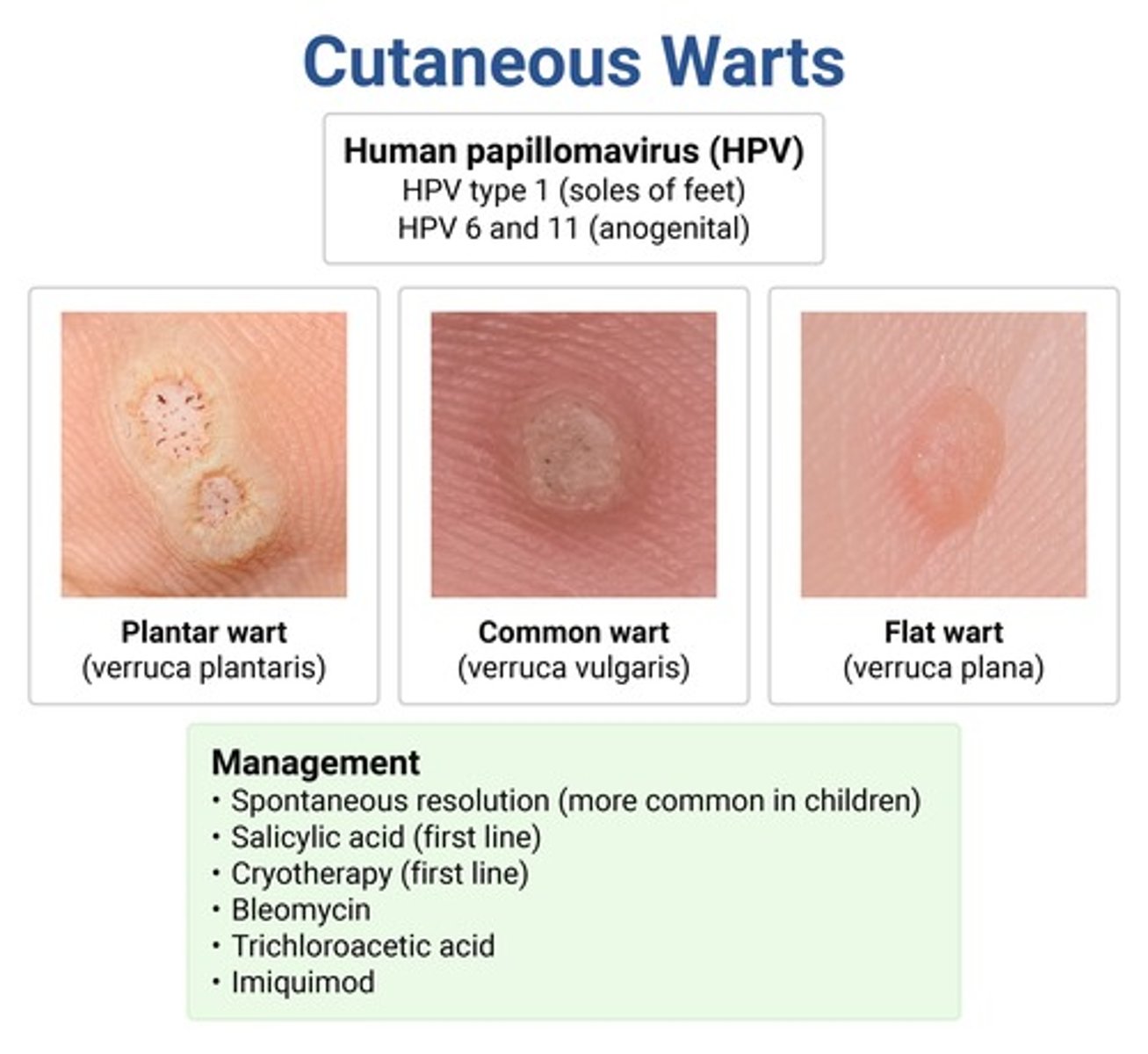
types of warts
plantar → painful, hyperkeratotic papules w central depression on bottom of foot; HPV 1
common (verruca vulgaris) → skin-colored papillomatous papules; distorts skin lines; HPV 2 & 4
flat (verruca plana) → skin-colored papules w smooth surface
anogenital (condyloma) → cauliflower-like; HPV 6 & 11
**HPV vax only protects against anogenital HPV types, not any of the others
multiple blotchy red macules & papules that rapidly progress to yellow-white pustules on the trunk & proximal extremities
typically seen w/in first 72hrs of life; MC in fat babies with higher gestational age (>40wks)
Wright-stain smear → numerous eosinophils
erythema toxicum neonatorum → resolves spontaneously

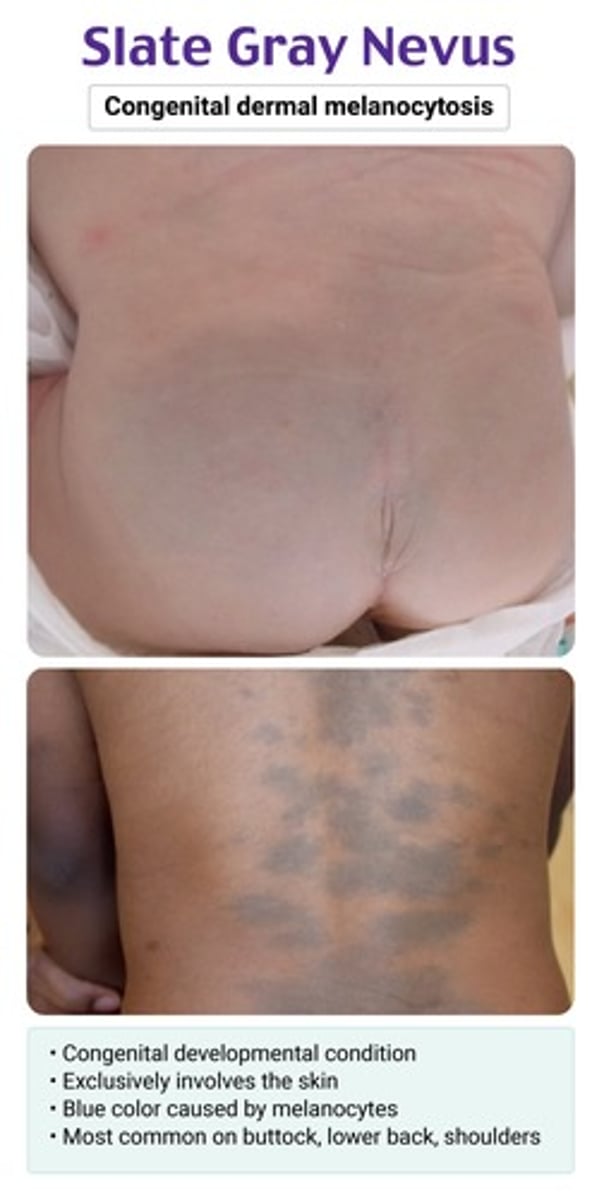
irregularly shaped bluish-gray macule on the sacrococcygeal area/butt/shoulders
usually found at birth
slate gray nevus (aka congenital dermal melanocytosis) → benign; can disappear in a few yrs
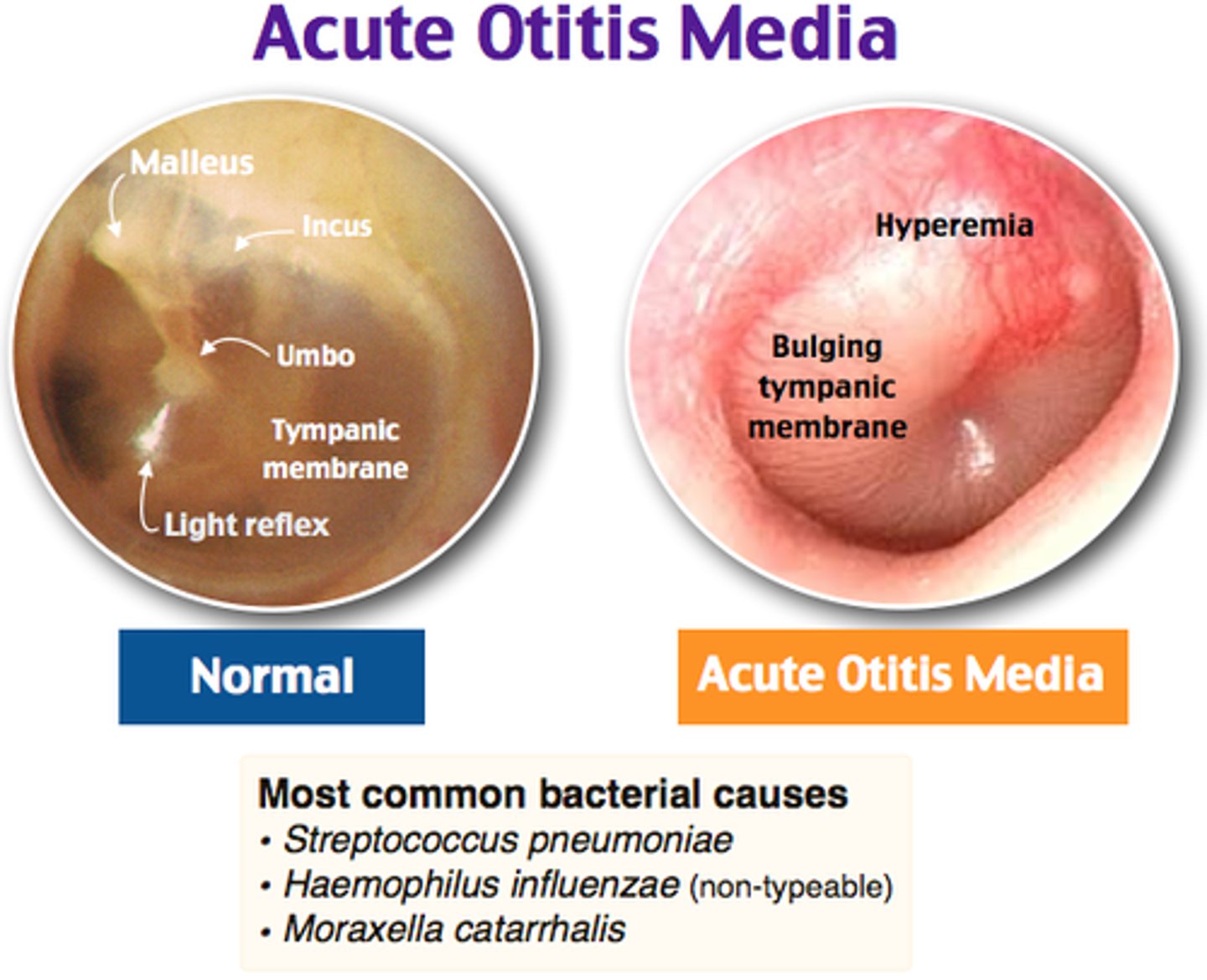
bacterial infection of middle ear, temporal bone & mastoid air cells commonly preceded by a viral URI
acute otitis media (AOM) → peak age 6-24 months (d/t more short/horizontal E tube)
RFs: daycare, bottle fed, 2nd hand smoke exposure
**being breastfed is a protective factor
etios of AOM
S. pneumo (MC), H. flu, M. catarrhalis
less common in kids → GAS (most likely to cause TM perforation)
rapid onset otalgia, ear tugging/rubbing, low-grade fever
conductive hearing loss in affected ear
bulging red TM, loss of landmarks, ↓ TM mobility on pneumatic otoscopy
AOM → amox or augmentin
comps: mastoiditis (MC), bullous myringitis, TM perforation
pain, erythema & pruritus in ear canal; ear pressure/fullness; malodorous otorrhea
+/- hearing loss d/t debris & discharge
PE: pain with traction/palpation of tragus or pinna, canal may be edematous & blocking view of TM
normal TM mobility on pneumatic otoscopy
otitis externa ("swimmer's ear") → pseudomonas MCC; S. aureus (digital trauma)
if fungal cause → moist, wet appearance
pt will have h/o water immersion (swimming), mechanical trauma (Q-tips), occlusive devices (hearing air, ear plugs, headphones)
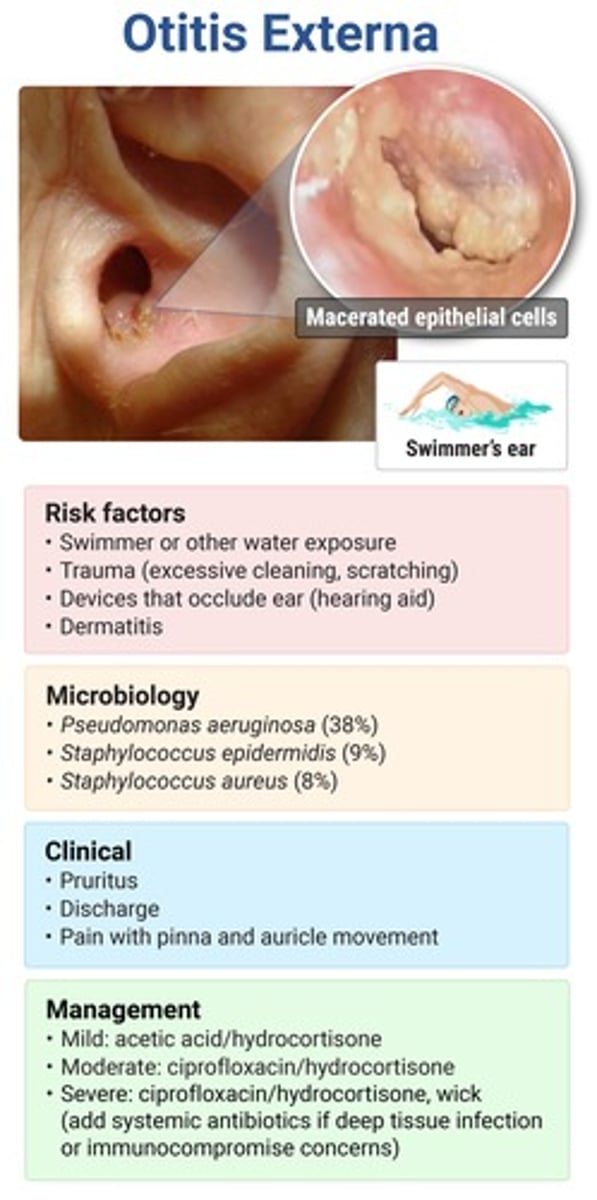
exquisite tenderness & swelling of external ear structures; pain worse @ night → radiates to TMJ (pain w chewing)
persistent purulent otorrhea unresponsive to treatment
macerated granulation tissue at bony cartilaginous junction of ear canal
CN involvement → CN 6, 7, 9
malignant (necrotizing) otitis externa → AOE sxs + CN involvement from osteomyelitis of skull base
MCC pseudomonas
complication of otitis externa seen in immunocompromised pts (DM, malignancy, steroids, HIV)
complication of untreated AOM → MC in children < 2y
deep otalgia (worse at night), tugging/pulling ear, fever, lethargy
fussiness, +/- CN palsies
PE: bulging red TM, erythema/tenderness posterior to ear, forward protrusion of ear, narrowed auditory canal
mastoiditis → confirm w CT w contrast
same bugs as AOM → S. pneumo (MC), S. pyogenes, H. flu, M. cat
acute otalgia & conductive hearing loss → sudden pain relief w bloody otorrhea
+/- transient tinnitus, vertigo
MC d/t penetrating or noise trauma, barotrauma or otitis media
TM perforation → MC at pars tensa; DO NOT perform pneumatic otoscopy!!
comp: cholesteatoma
*sudden pain relief is a sign that TM has ruptured (release of pressure)
MCCs of conductive & sensorineural hearing loss
conductive → anything that ↓ transmission of sound from environment to cochlea
- otitis media, cerumen impaction, cholesteatoma, TM perf
SN → disruption of sound transmission after cochlea
- presbycusis (MC), noise-induced, drug-induced, rubella (MC congenital cause)
ototoxic drugs
loops, vanco, aminoglycosides, macrolides, ASA, NSAIDs, anti-malarials, chemo drugs, PDE5i
NB testing for hearing loss
auditory brainstem response or otoacoustic emissions
**all infants should have hearing screened by 1 month
conductive vs SNHL weber & rinne
conductive → weber: lateralizes to affected ear; rinne BC>AC
SN → weber: lateralizes to good ear; rinne: AC>BC
what is the ONLY surgical treatment for SNHL?
cochlear implants
MCC of acute pharyngitis
VIRAL → adenovirus
consider fungal in pts using inhaled steroids
cough, hoarseness, rhinorrhea, coryza, conjunctivitis, diarrhea
sore throat worse w swallowing or phonation + anterior stomatitis (ulcers on soft palate/tonsils
acute viral pharyngitis
these sxs suggest viral etio → no cough suggests bacterial
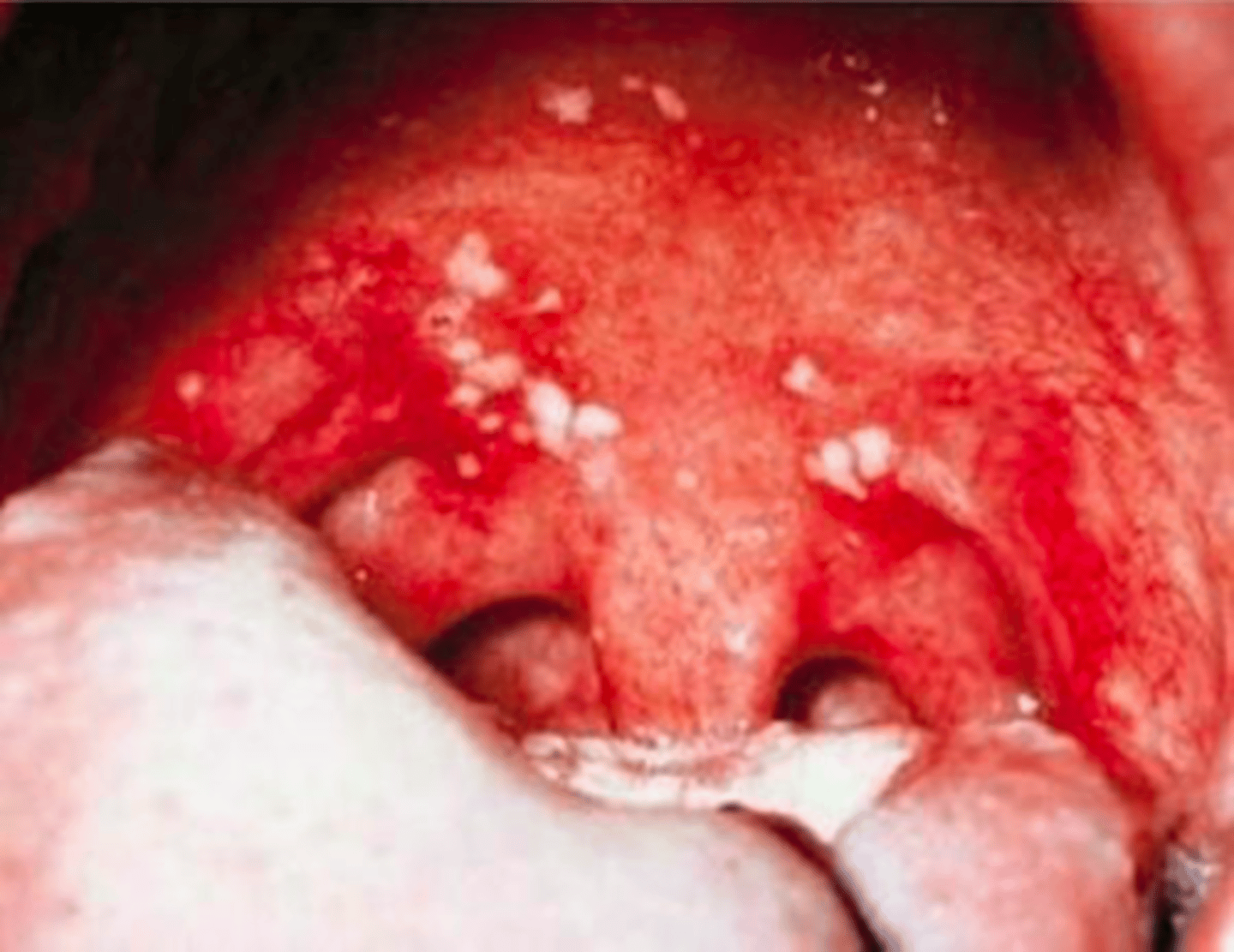
MCC of bacterial pharyngitis
GABHS → can lead to rheumatic fever if untreated
consider gonorrhea if sexually active & non-resolving pharyngitis
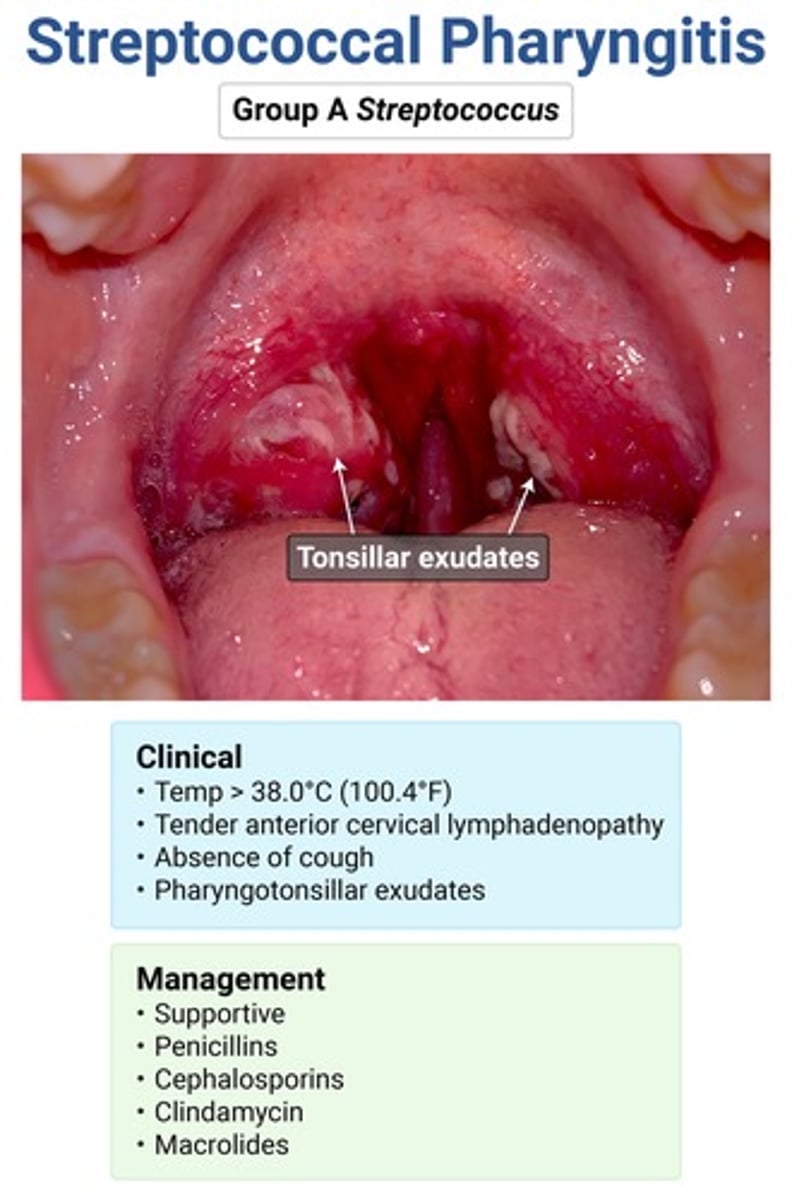
abrupt onset high fever, SEVERE sore throat + exudates
NO COUGH
scarlatiniform rash
anterior cervical LAD
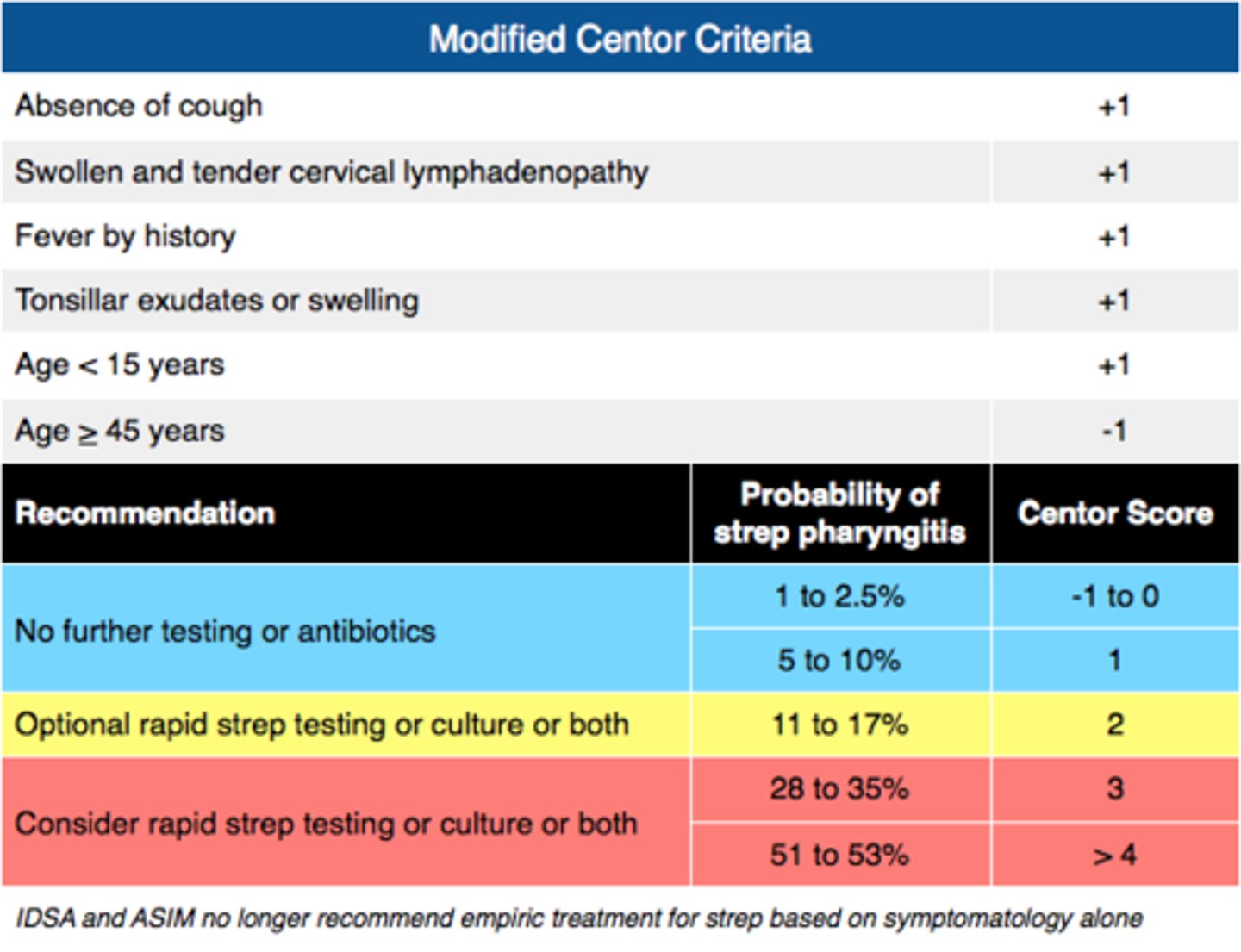
strep pharyngitis → use Centor criteria to determine need for testing (need 3 out of 4 to do rapid strep)
complications of strep pharyngitis
acute rheumatic fever → prevented w abx
severe pharyngitis → give IM dexamethasone
post-strep GN
peritonsillar abscess
PANDAS → ped autoimmune neuropsych d/o assoc w strep
MCC of chronic rhinosinusitis
S. aureus
chronic = sxs > 12 wks
*get CT of sinuses & refer for allergy testing
nasal congestion, CLEAR rhinorrhea, hyposmia
HA, cough, malaise
maxillary tooth discomfort
red, engorged nasal mucosa
Eustachian tube dysfunction → ear pain/fullness/pressure, HL, tinnitus
SXS LAST < 10 DAYS!!!
acute viral rhinosinusitis → rhinovirus MCC (common cold)
SXS PRESENT > 10 DAYS
purulent yellow-green nasal d/c
facial pain/pressure worse when bending down/leaning forward
fever, HA, halitosis, cough
sinus TTP → maxillary (MC) > ethmoid > frontal > sphenoid
biphasic pattern ("double worsening") → sxs initially improve but then worsen ~5-6d later
acute bacterial rhinosinusitis → MC from viral URI (S. pneumo)
**maxillary tenderness = referred dental pain
samter's triad
asthma + allergic rhinitis + ASA/NSAID sensitivity
types of rhinitis
allergic (MC type) → IgE-mediated mast cell histamine release d/t allergens
infectious → rhinovirus MC (common cold)
vasomotor → nonallergic & noninfectious dilation of blood vessels d/t temp changes, smells, humidity
paroxysms of sneezing, nasal congestion & itching
clear watery rhinorrhea
allergic shiner → bluish discoloration around eyes
Dennie-Morgan lines → accentuated lower eyelid lines
salute sign → transverse nasal bridge crease
PE: pale blue edematous boggy turbinates, nasal polyps, cobblestone conjunctival mucosa
allergic rhinitis → MCC of nasal polyps
rhinitis sxs + erythematous ("beefy red") turbinates on PE
viral rhinitis (common cold)
what med can be used for allergic rhinitis and asthma?
leukotriene receptor antagonists → montelukast
anterior vs posterior epistaxis
anterior → Kiesselbach's plexus; MC d/t trauma (nose picking); bleeding usually only in one nare
posterior → sphenopalatine artery (Woodruff's plexus); MC in older pts w HTN; bleeding in both nares & posterior pharynx
painless thick mucopurulent eye discharge
LACK of itching
diffuse conjunctival erythema w no ciliary injection
bacterial conjunctivitis → S. pneumo & H. flu MC in children
S.aureus MC in adults