SIO Life in the Oceans Final Flashcards
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Marine life, marine biology, solutions, the ocean and us.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What is the vital statistic about sea food consumption we learned in class?
“Seafood represents only about 1% of the food consumed each year, but represents about 30% of total animal protein consumed.”
What are the four methods of fishing we learned about in class?
Gill Nets (that look like a large filter feeder)
Purse seine (that look like a purse and are very large)
Long Line (Only method on the surface and bottom of the ocean)
Trawls (that look like a limp hot air balloon
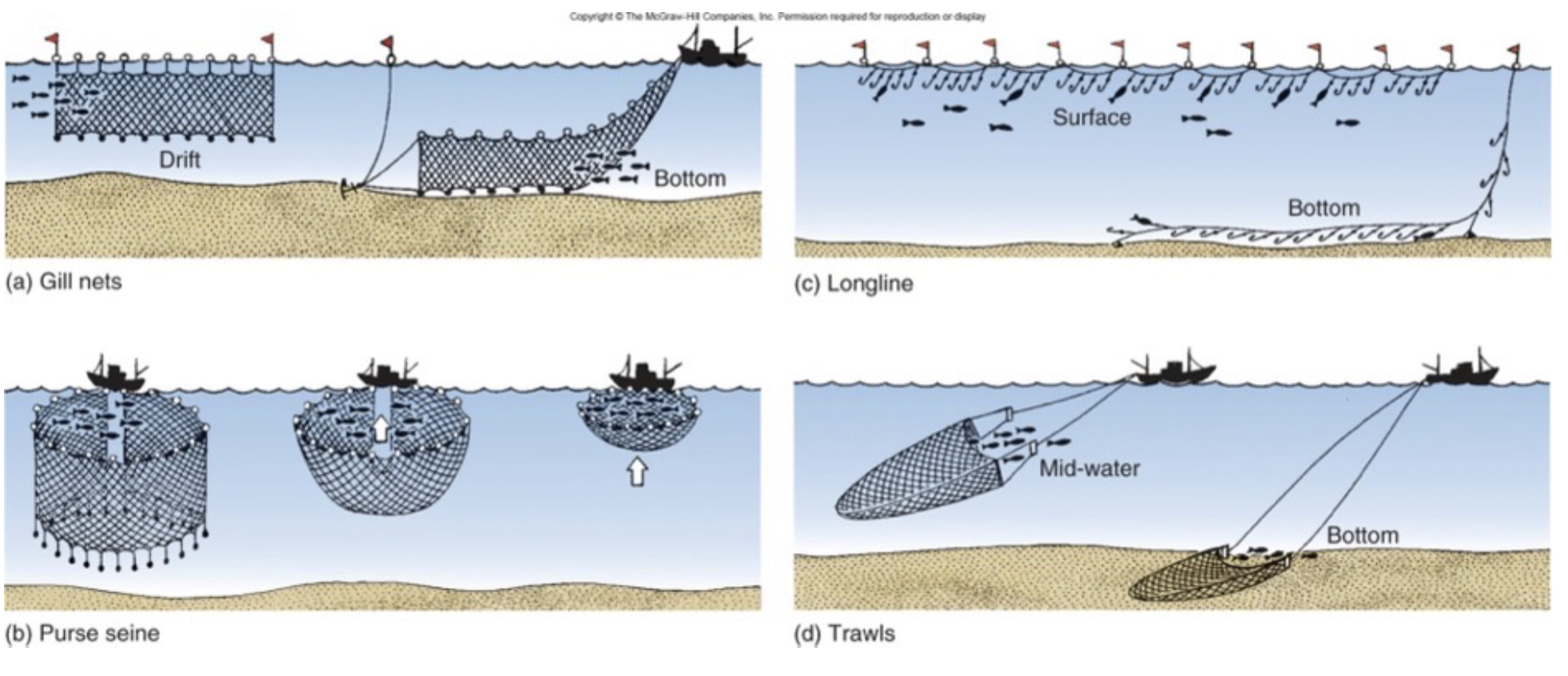
What defines the collapse of a fishery?
If numbers fall to 10% of historic highs.
Meaning that there isn’t enough biomass to sustain the life of that organism. Therefore the species can no longer reproduce.
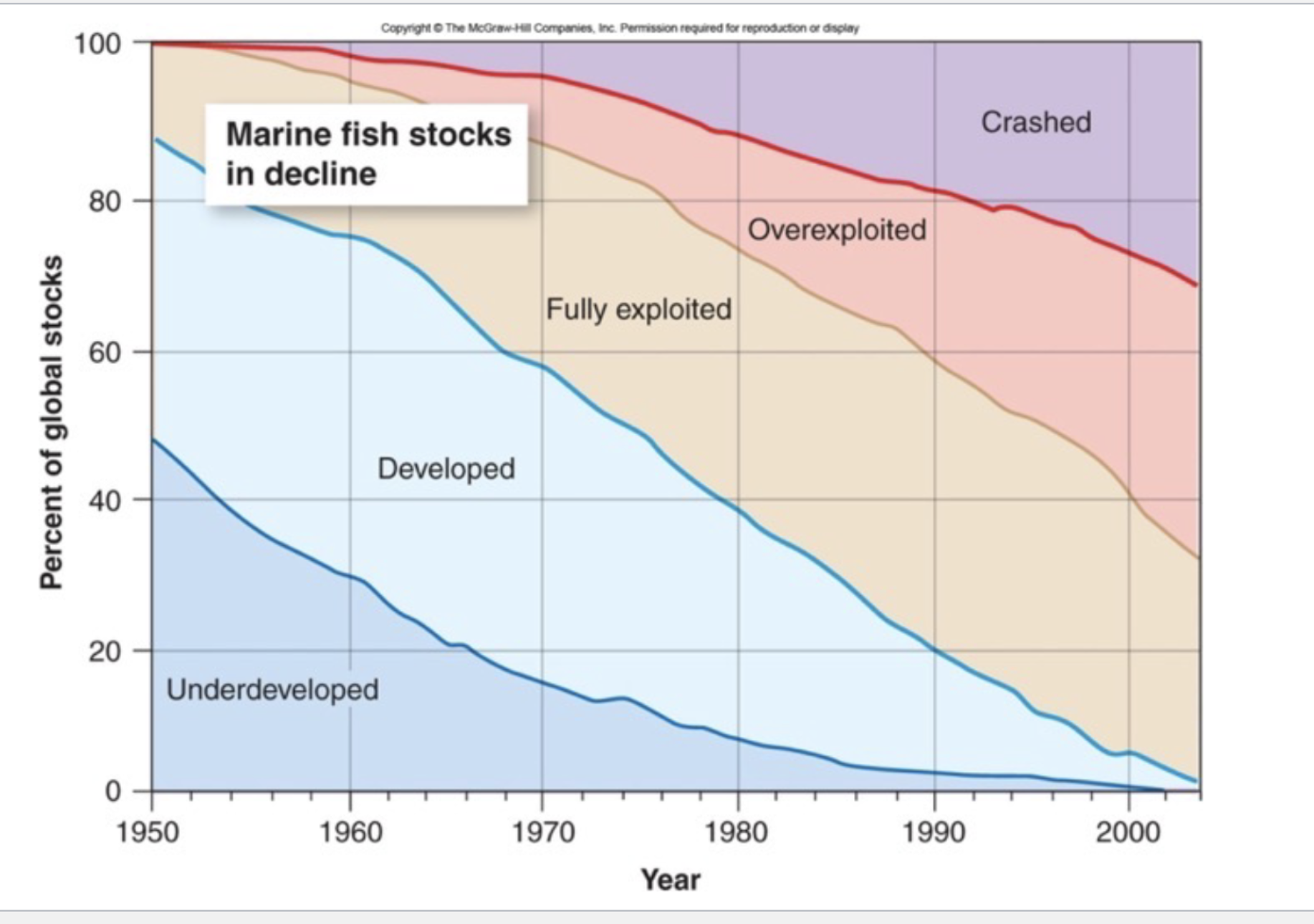
Is fishing sustainable?
Yes, fishing can most definitely be a sustainable food source, but only if we make some changes to how we fish and treat these ecosystems right.
What are some challenges to fisheries?
Habitat destruction: critical breeding grounds like seagrass beds, estuaries, and mangroves are destroyed each year. Trawls damage the ocean floor, detrimental to demersal species.
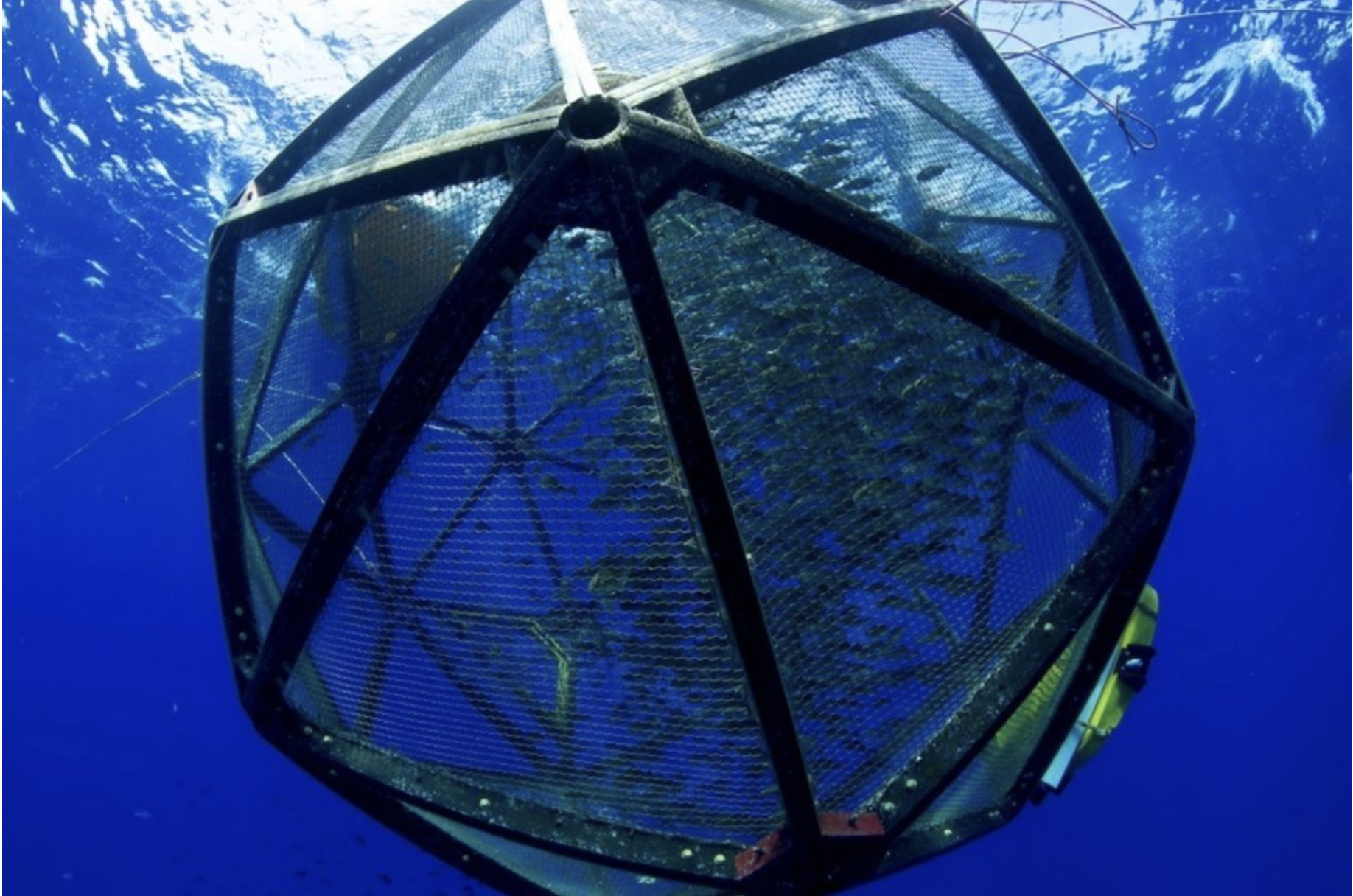

What is aquaculture?
The application of farming techniques to the growth and harvesting of aquatic organisms
What is Mariculture?
Applies specifically to marine organisms! Marine organisms such as shrimp, salmon, and seaweed has risen three-fold since 1990
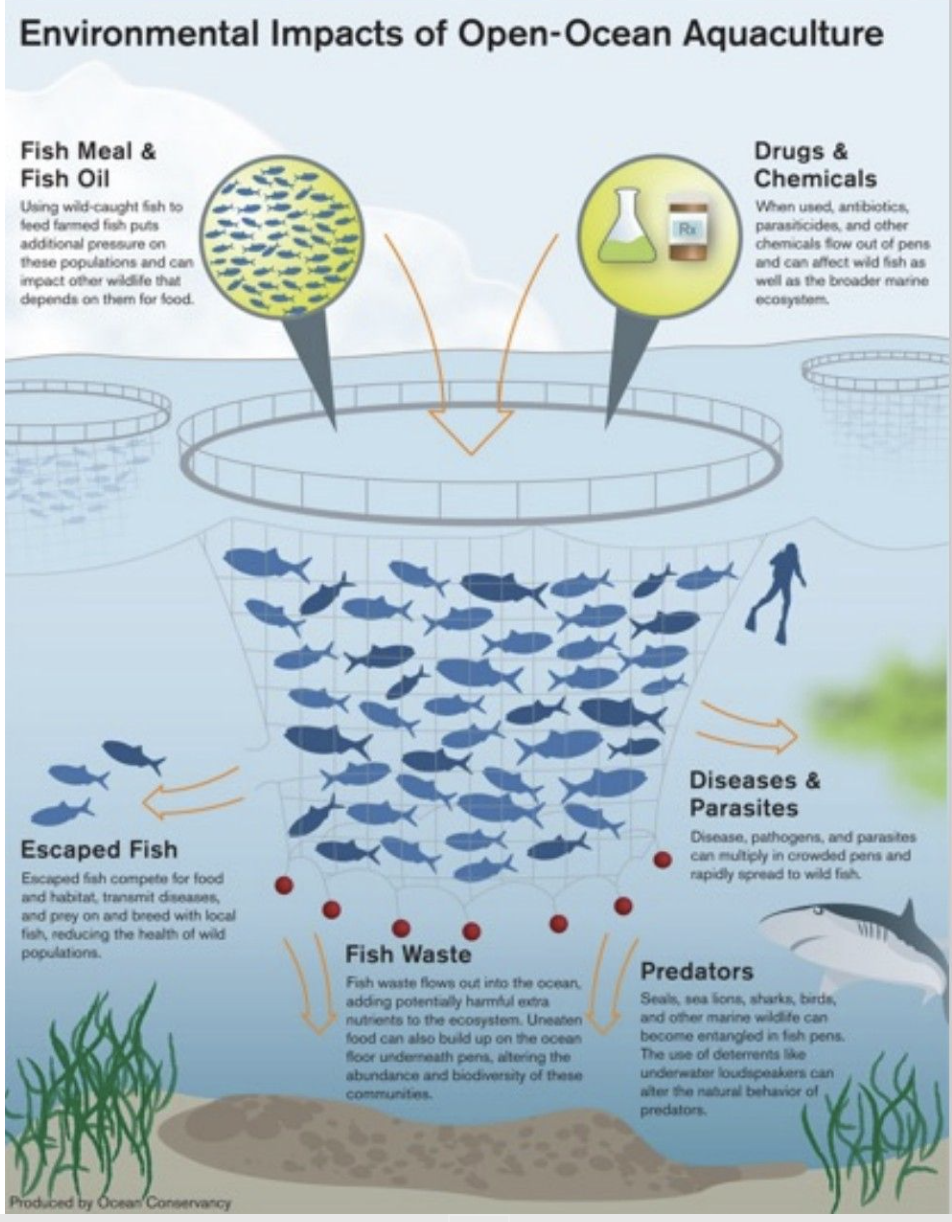
What are some Challenges with Aquaculture?
Disease and parasites
Difficult maintaining water quality
If farmed species escape, they may breed with wild stocks
Pollution
Estuarine communities may be destroyed to create farms
What kind of resources does the ocean provide for humans?
Oxygen, sodium chloride, food, nutrients, and many more!
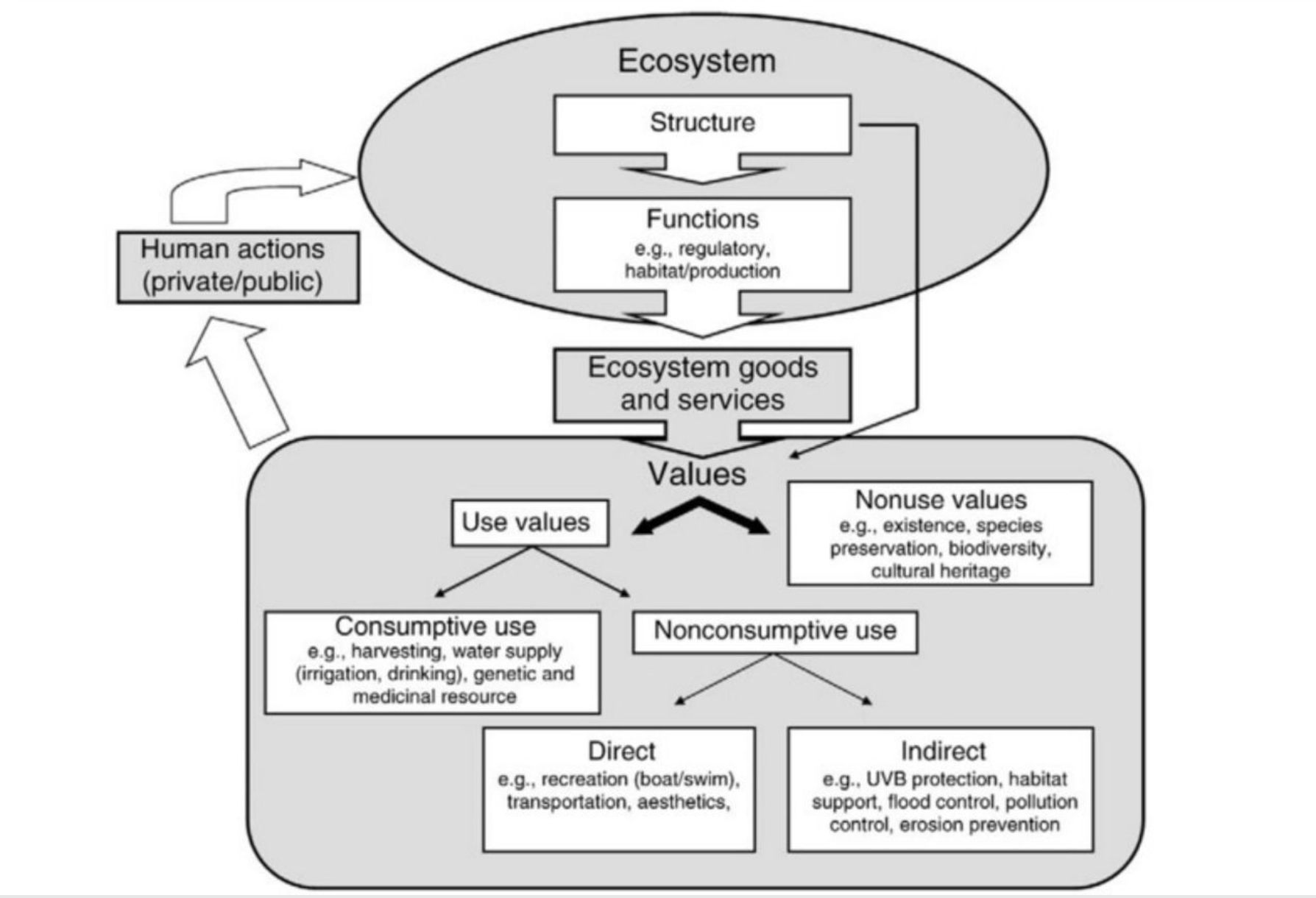
What does this photo demonstrate?
How ecosystems provide us humans with goods and services. There are Direct and indirect values. Check out decktoys for practice with this!
What are marine resources utilized for?
Food (fish, which are about 90% of worldwide harvest), Materials (Salt, Oil and Gas, Sand and gravel for the construction industry, freshwater via desalination process)
What is one vital resource the ocean provides that is two elements?
Sodium Chloride
What does sodium chloride provide for humans?
Food industry, medicine, and agriculture.
(Oil and gas exploration, textiles, paper industry, bleaching chemical, rubber manufacture, highways constructions, plastic industry, food industry, medicine, agriculture)

Why are transportation and shipping so important?
The oceans are what provide us with incredible worldwide shipping. However, Transportation and shipping have a big impact on our CO2 emissions, similar to our food production.
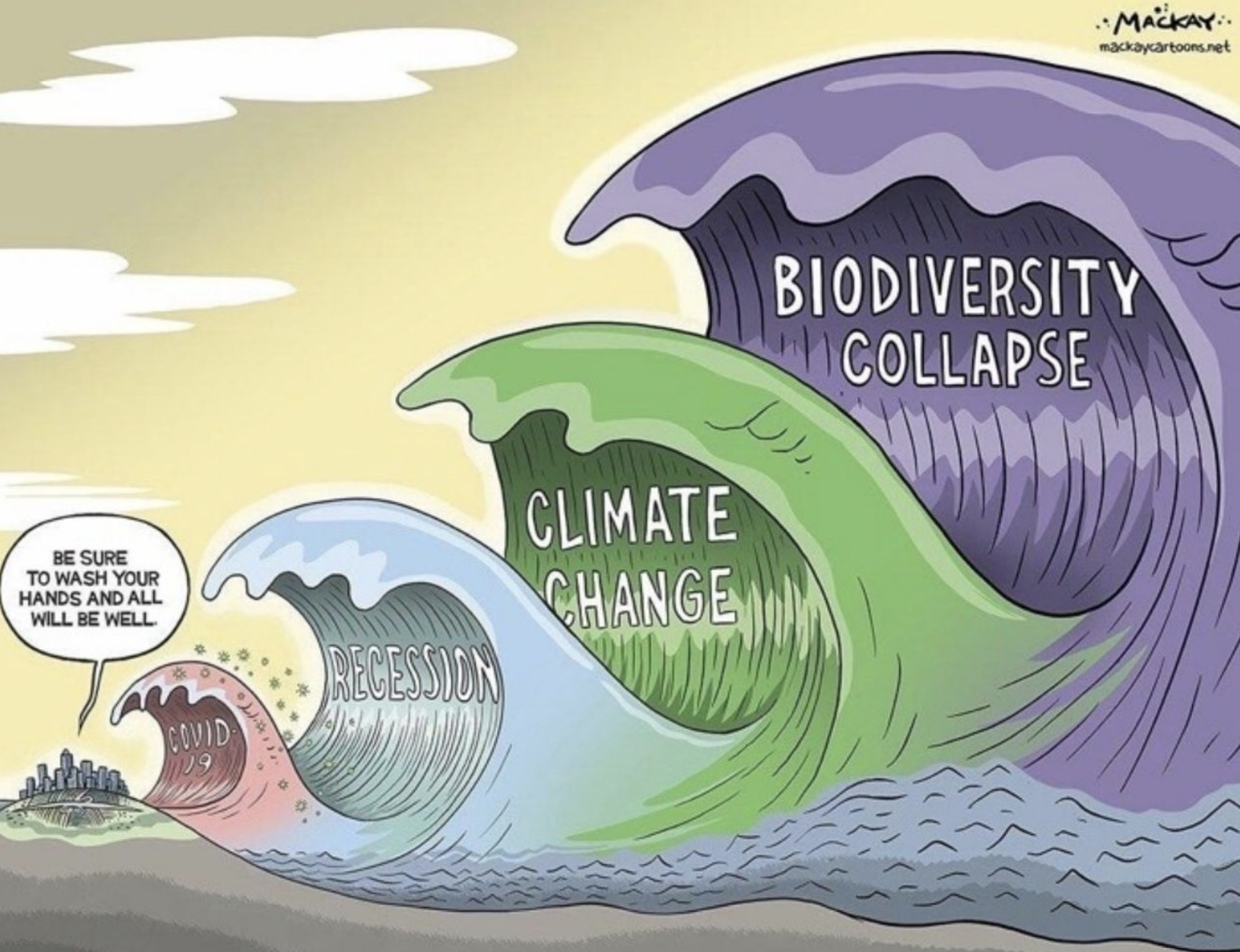
How do humans cause biodiversity collapse?
Modification and Destruction of Habitats
Threatened and Endangered species
Shifting baselines
Pollution
Why is biodiversity important?
Biodiversity=Stability
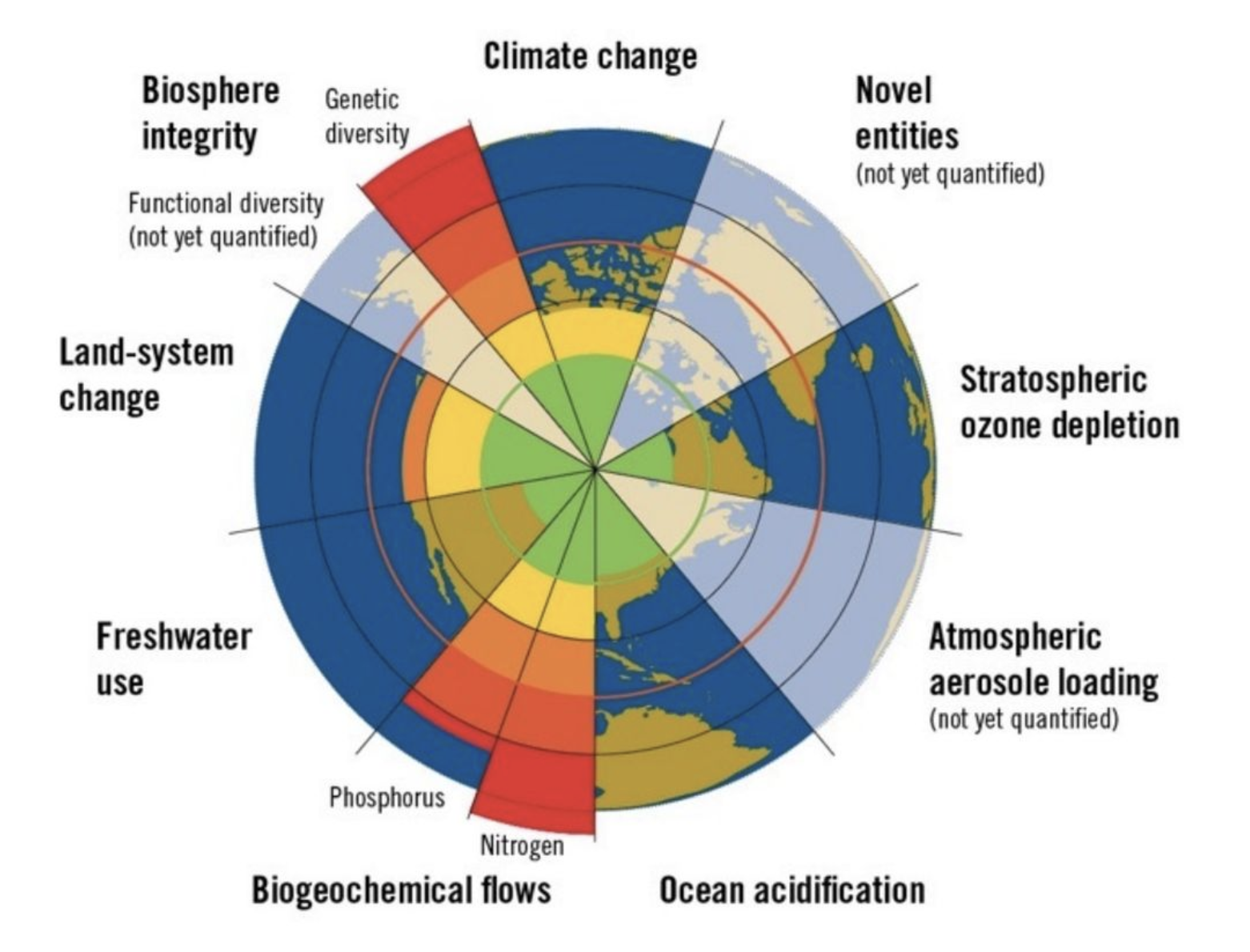
What are Planetary Boundaries?
They are the safe limits for human activities on Earth. Such as freshwater use, genetic diversity, climate change, Biogeochemical flows (nitrogen and phosphorus), and Ocean Acidification.
What is happening to our Coral Reefs?
¼ of our coral reefs have been lost or are at risk, while 1/3 face extinction.
Corals are lost due to aquarium trade and sold as souvenirs
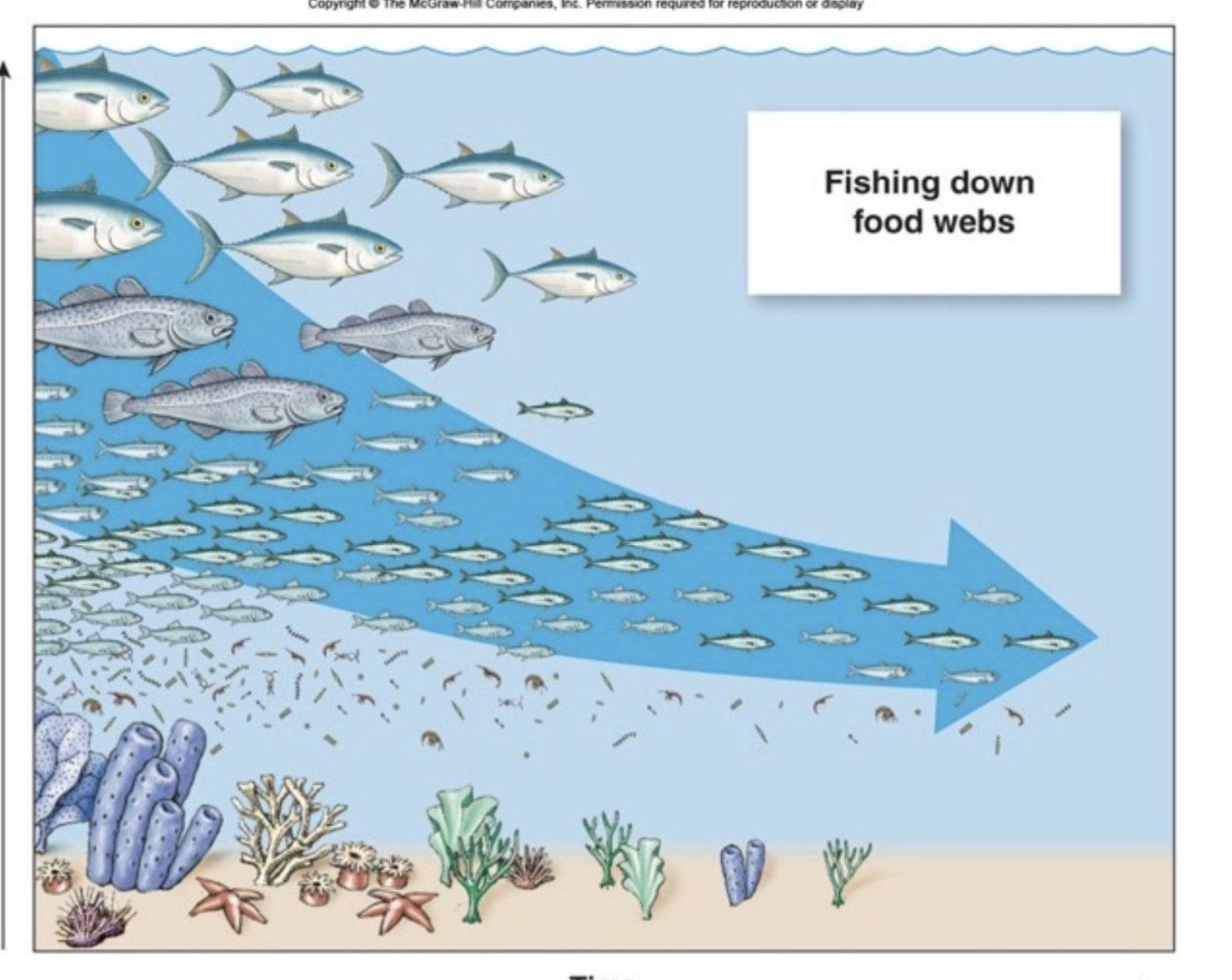
What does “fishing down” food webs mean?
It signifies how humans have hunted all of the large predators, and now we see fewer of them/ they are smaller.
Many species of fish have adapted to grow rapidly and reduce size so that they can reproduce.
This creates threatened and Endangered species because if they can’t adapt, then they go extinct.

What is the concept of “Shifting Baselines”?
In short, it is when what looks like a healthy ecosystem to us may not look like a healthy ecosystem to the generation before us.
Getting to the big idea of what “Pristine Seas” are since we haven’t seen them.
What are the four major sources of pollution we learned about in class?
Fertilizers
Sewage
Oil
Persistent Toxic Substances
Most pollutants come from land-based substances.
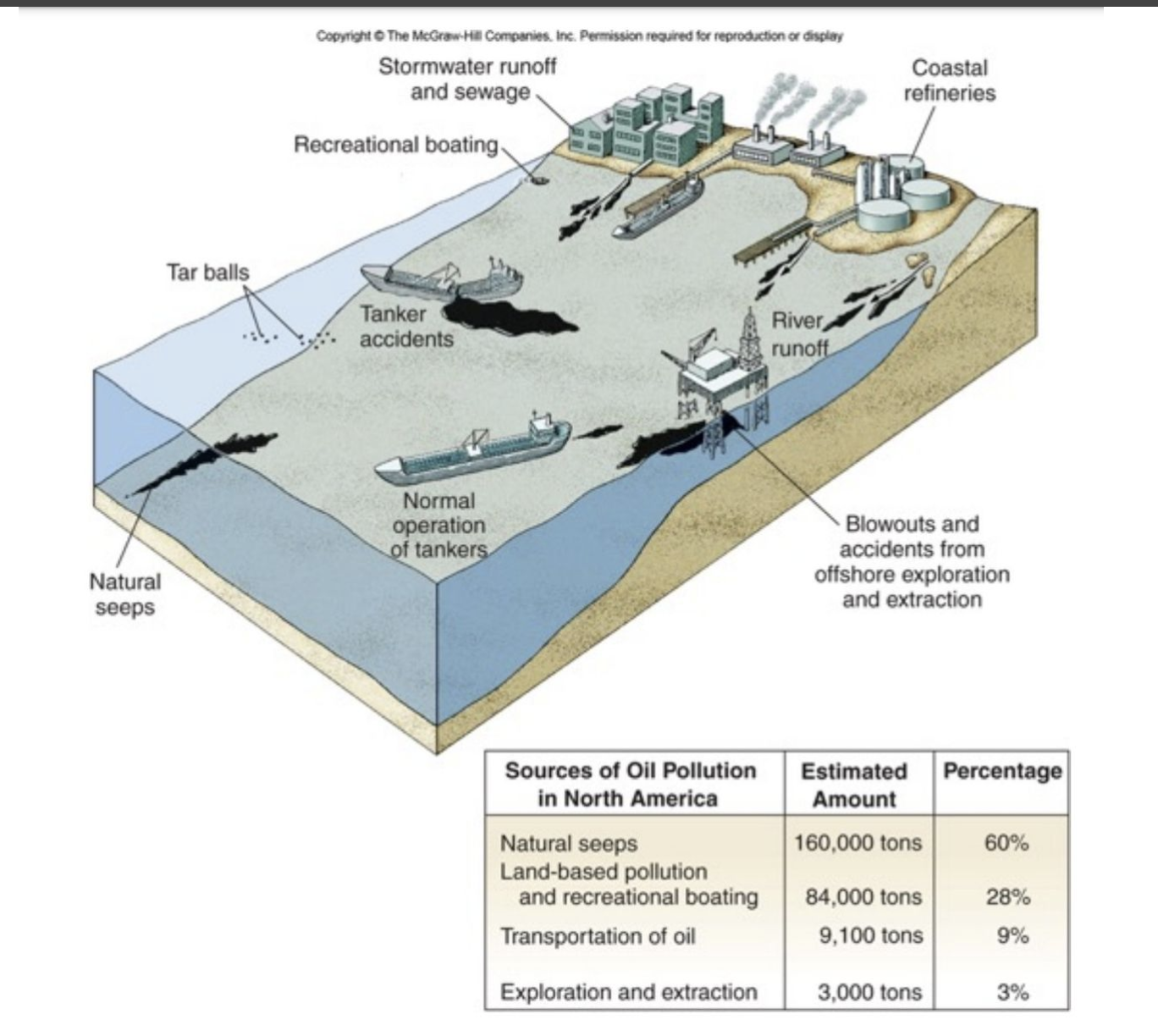
What is pollution?
Human introduction of substance that reduces the quality of the environment
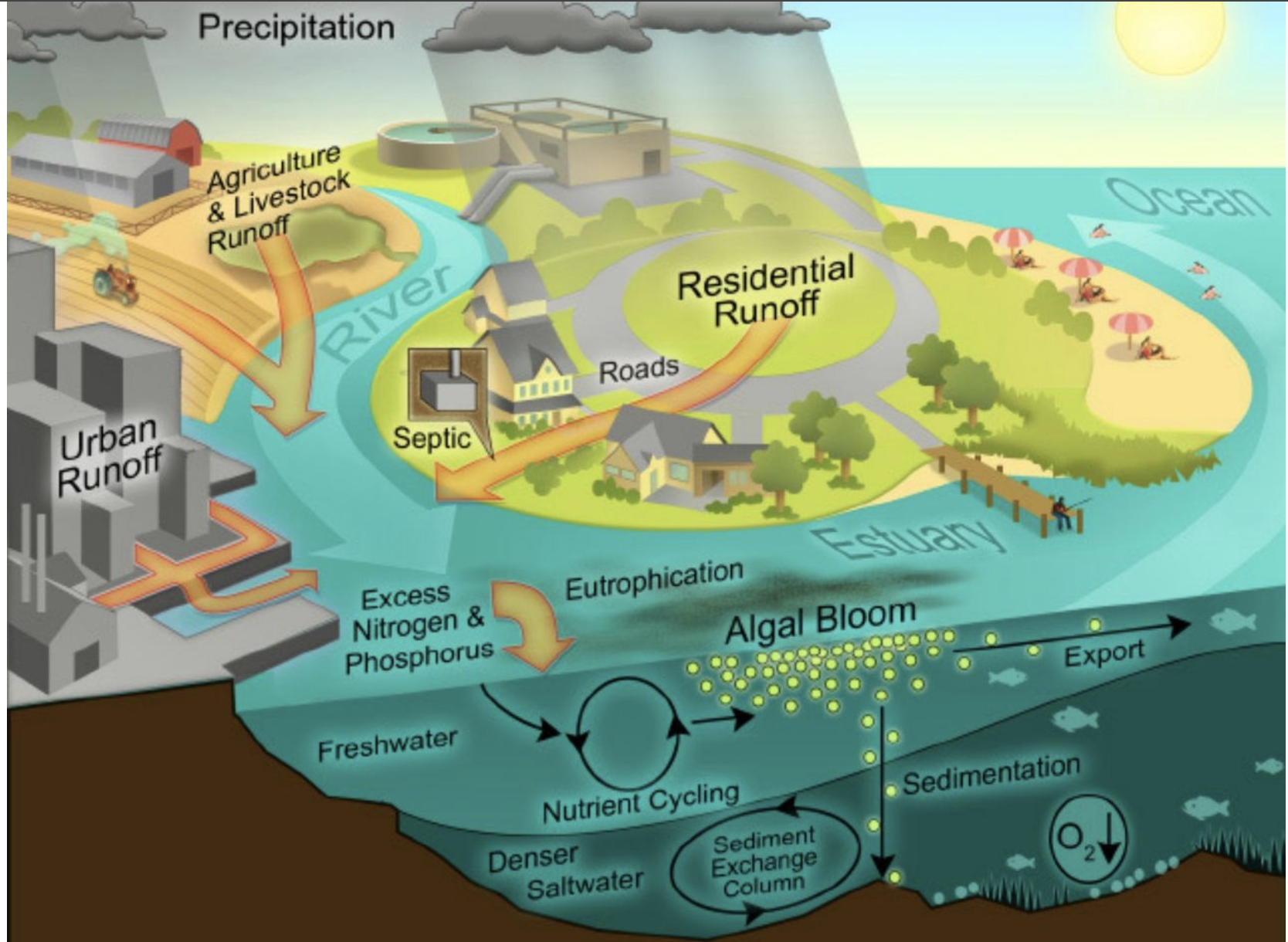
How do fertilizers and sewage pollute the ocean?
Fertilizers and sewage…
Wash into streams/rivers
Causes blooms of phytoplankton (eutrophification)
Blooms reduce the amount of light available
After bloom: anoxic conditions from decomposition
Which causes DEAD ZONES!
What is Etrophification?
The introduction of too many nutrients causes algal blooms, which out complete the natural status of other photosynthetic organisms. Reducing light causes anoxic conditions.
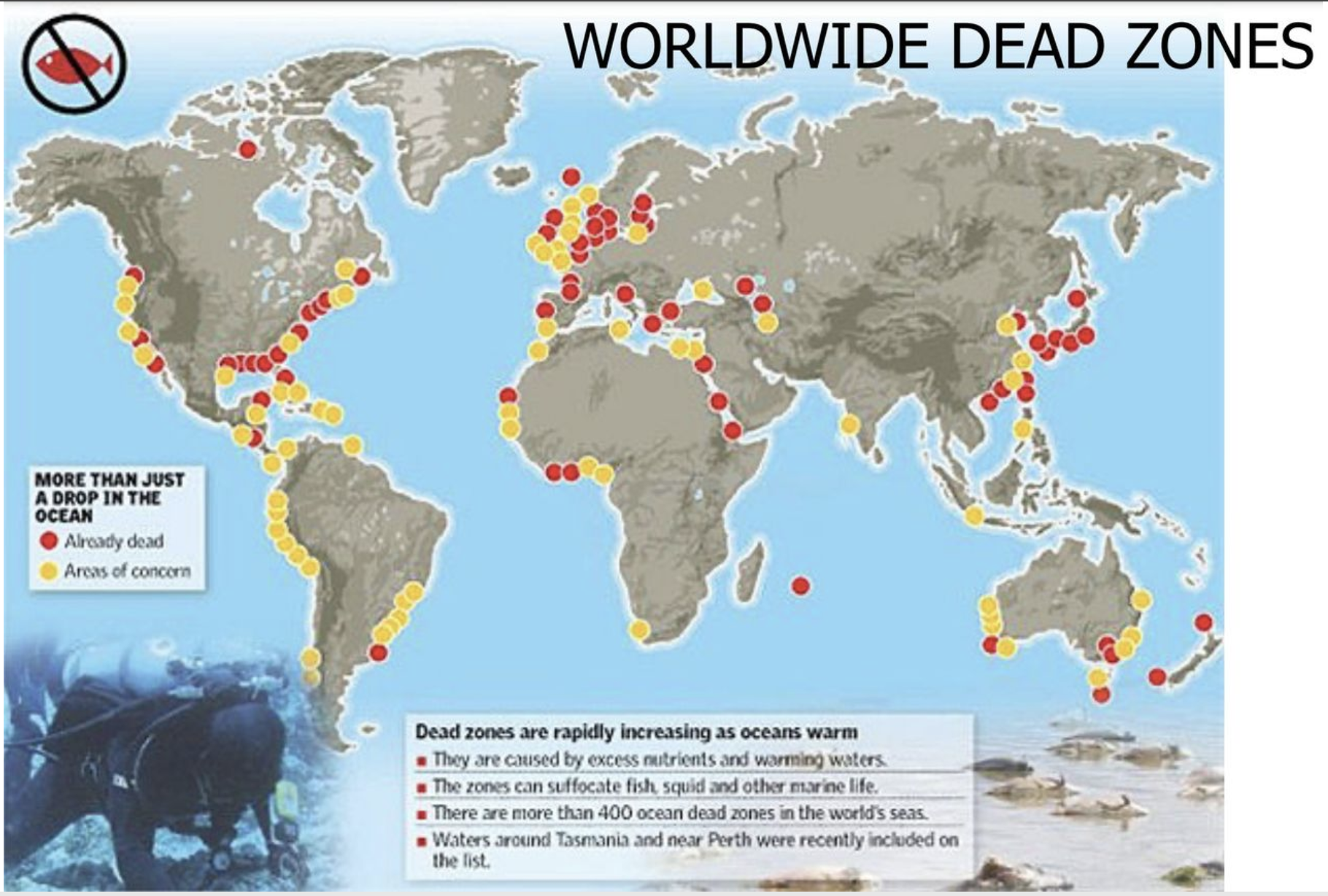
What are Worldwide Dead Zones?
Anoxic zones that can suffocate marine life.
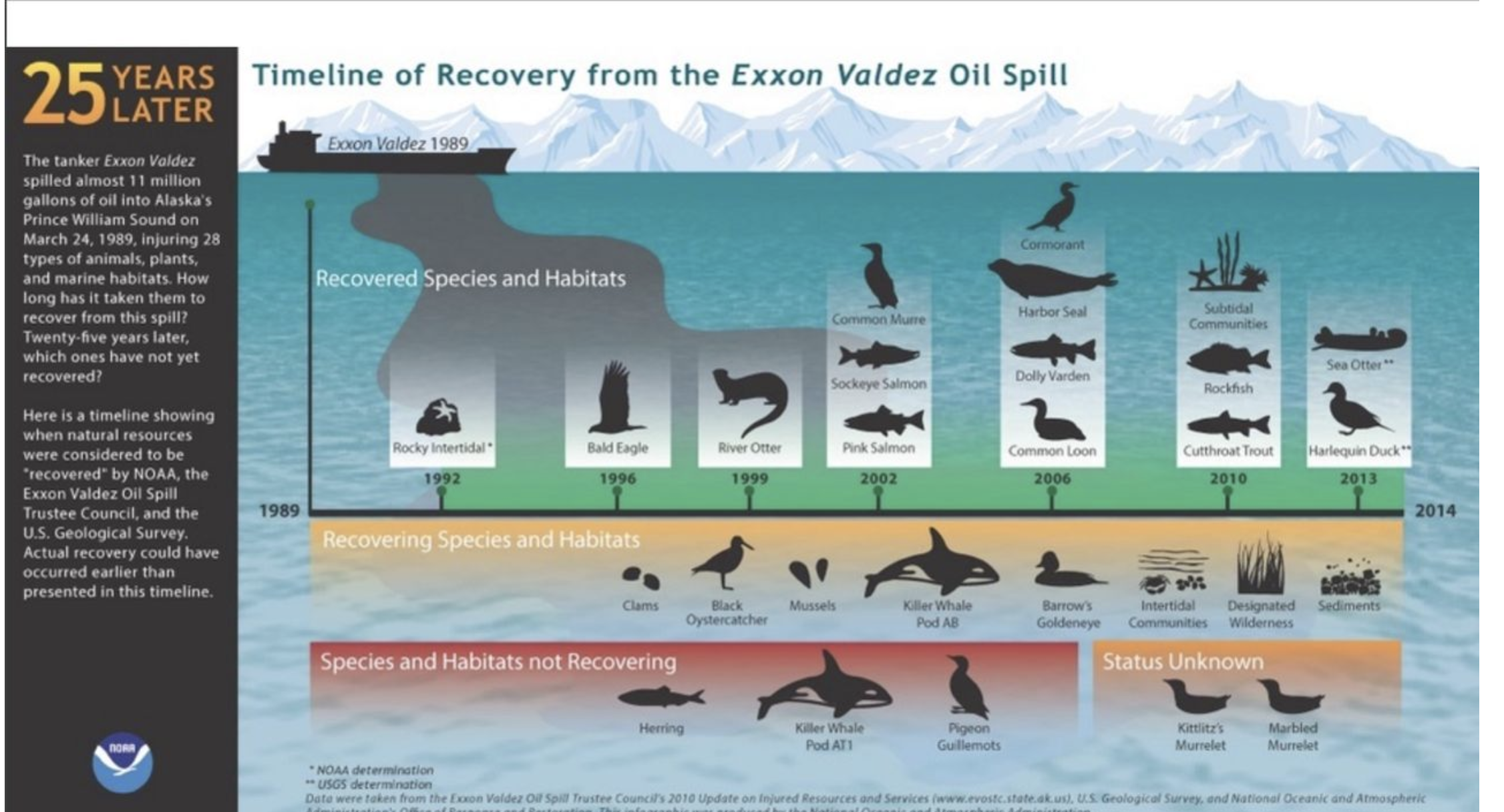
How does oil pollute the ocean?
Large oil spills can impact species and habitats for a long time. In class, we talked about the Exxon Valdez Oil Spill and how even after 25 years, many species and habitats were still not recovering.
How do Persistent Toxic Substances pollute the ocean?
I.e. chlorinated hydrocarbons, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB’s), and heavy metals
– Can concentrate up food chain: biological magnification
– As predators eat more prey, continue to accumulate in tissues
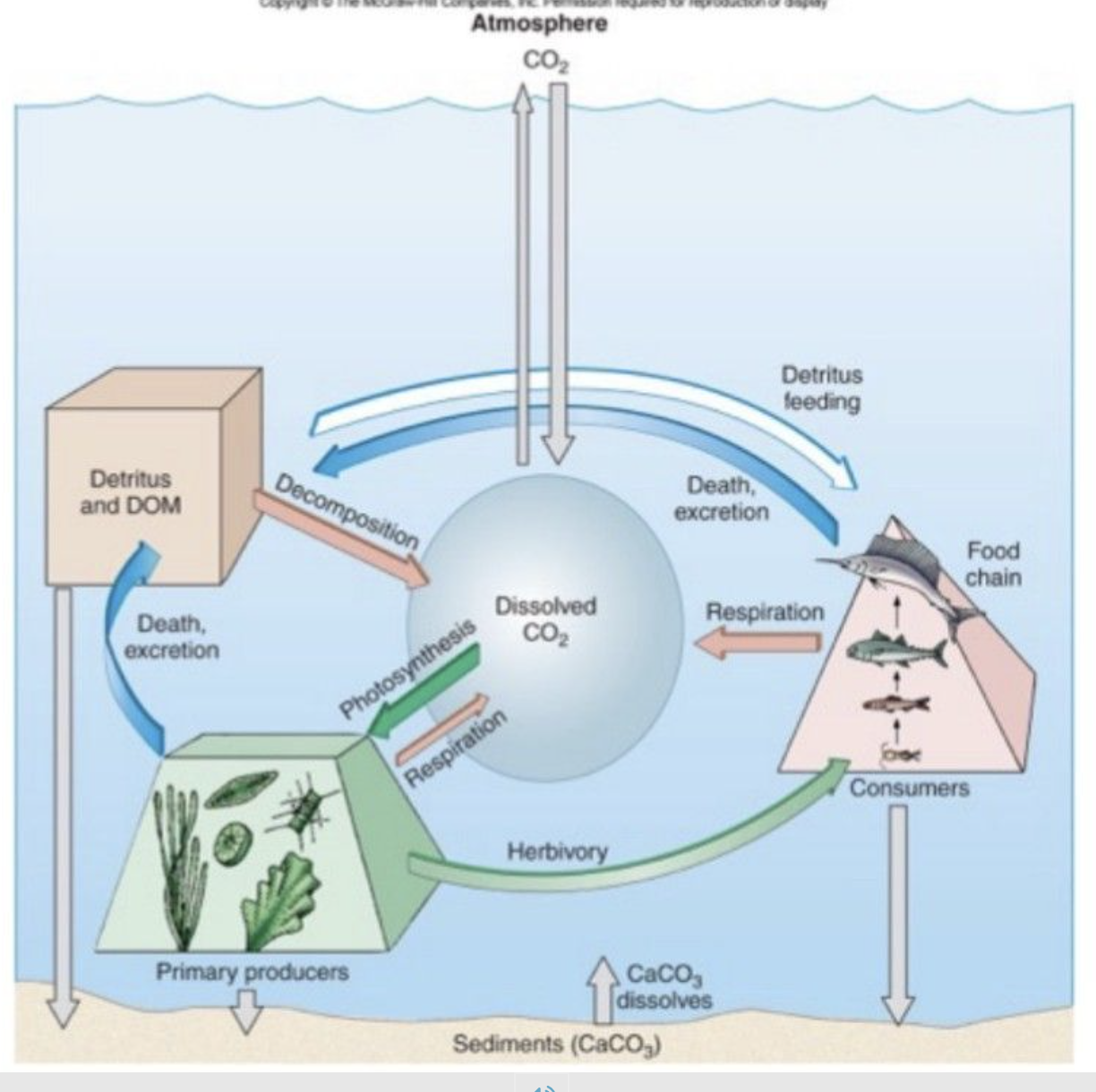
What is the carbon cycle and what have humans done to impact it?
The carbon cycle is what maintains carbon and cycles it through the environment.
Humans have destabilized this system because we have been overloading this cycle with too much carbon.
Scientists believe that our idea of the carbon cycle has changed because of all of our carbon emissions putting pressure on this delicate cycle.
What is the Greenhouse effect?
Warming of the Earth’s atmosphere due to an increase of greenhouse gases.
Human activities have intensified this natural phenomenon
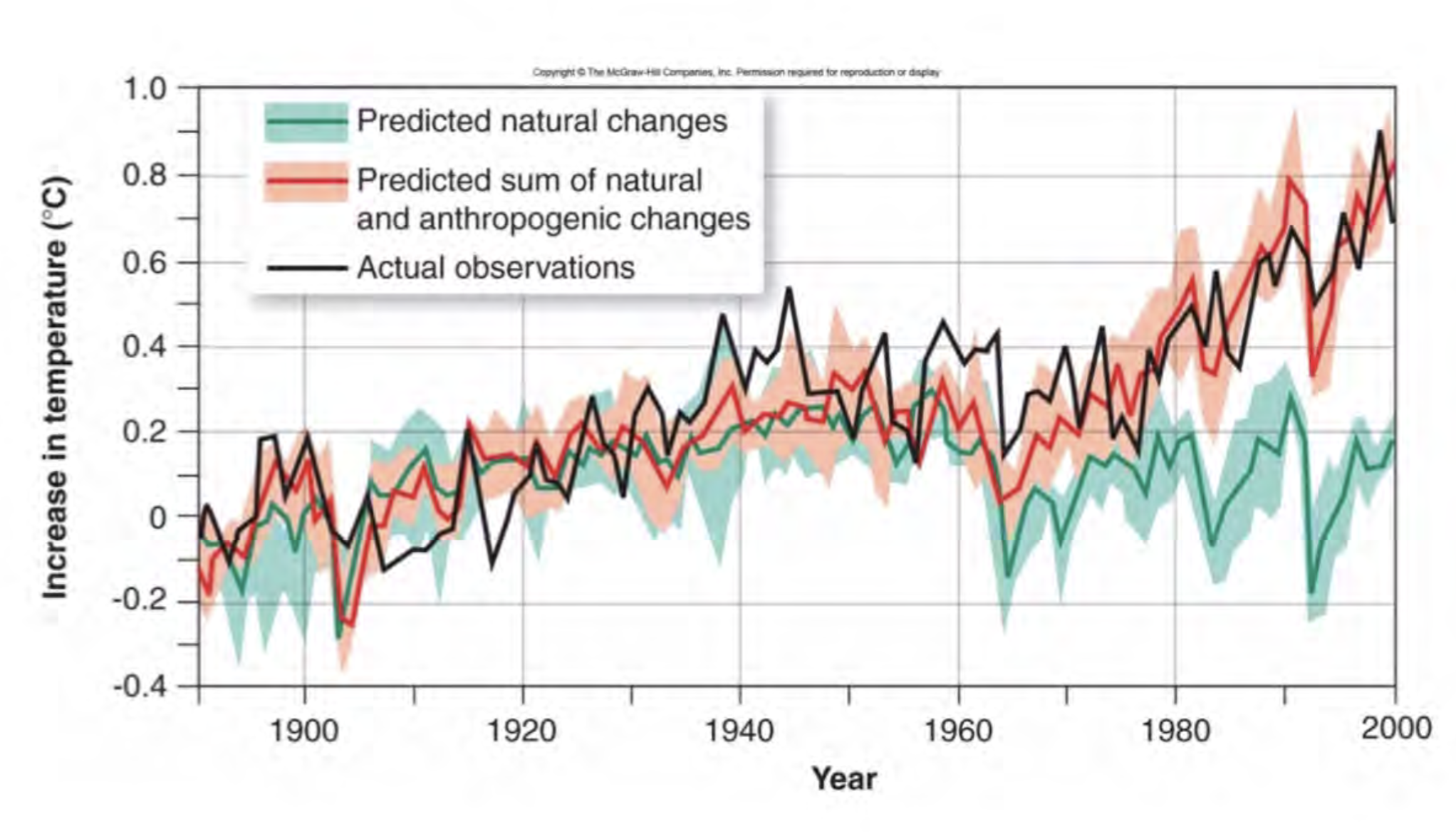
What are greenhouse gases?
water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone
What is NOT a greenhouse gas?
Oxygen, for example!
“Nitrogen isn’t a greenhouse gas. If you see something that is an element on its own, it’s probably not a greenhouse gas, but when you start combining elements, that’s where you get greenhouse gases.” - Jamee
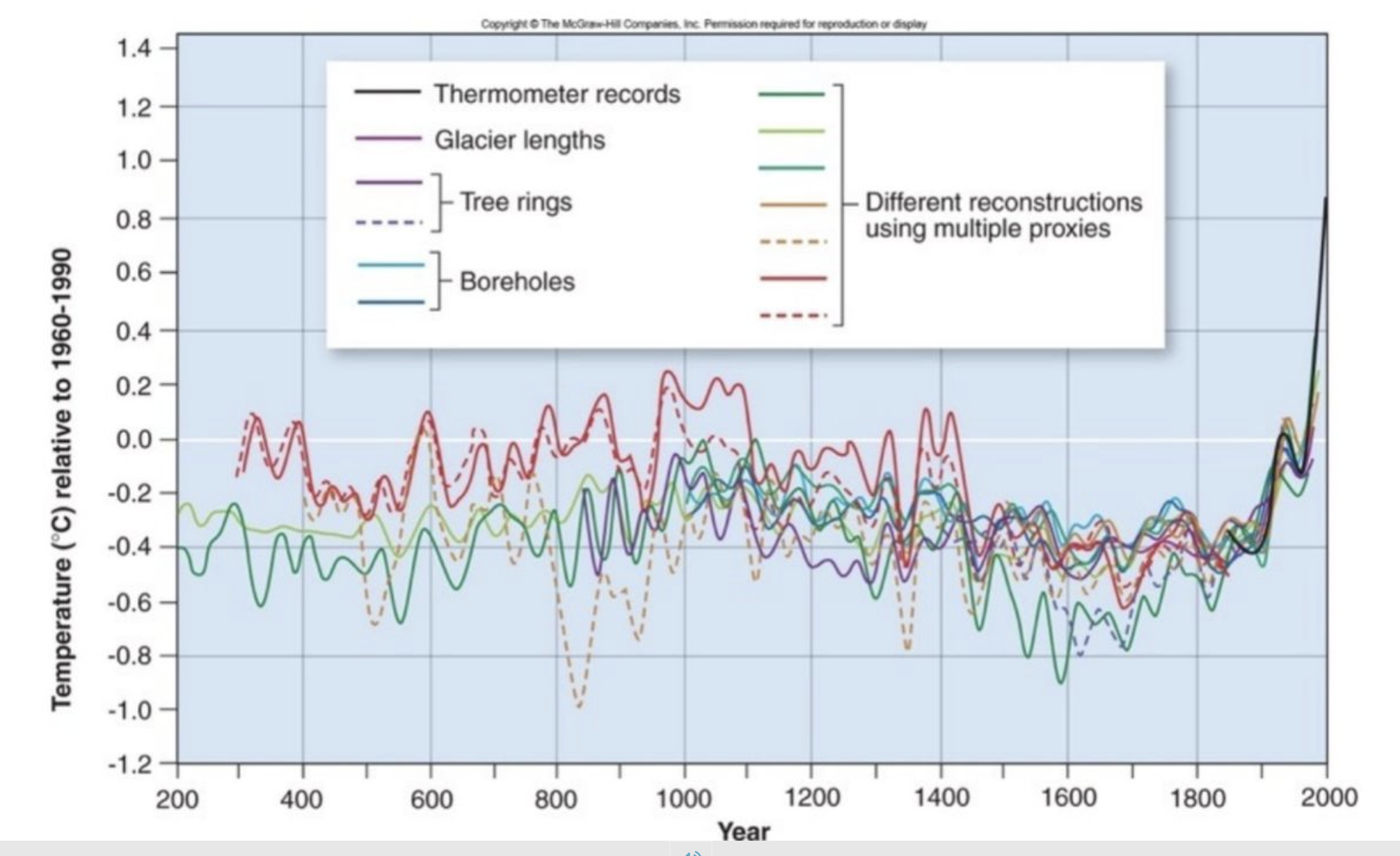
How can we measure historic temperature?
There are four ways we measure temperature 1. Thermometer records
Glacier lengths
Tree rings
Bore holes
Temperature through the years ebbs and flows until the Industrial Revolution and onward.
CO2 Levels are now over what ppm?
400 ppm
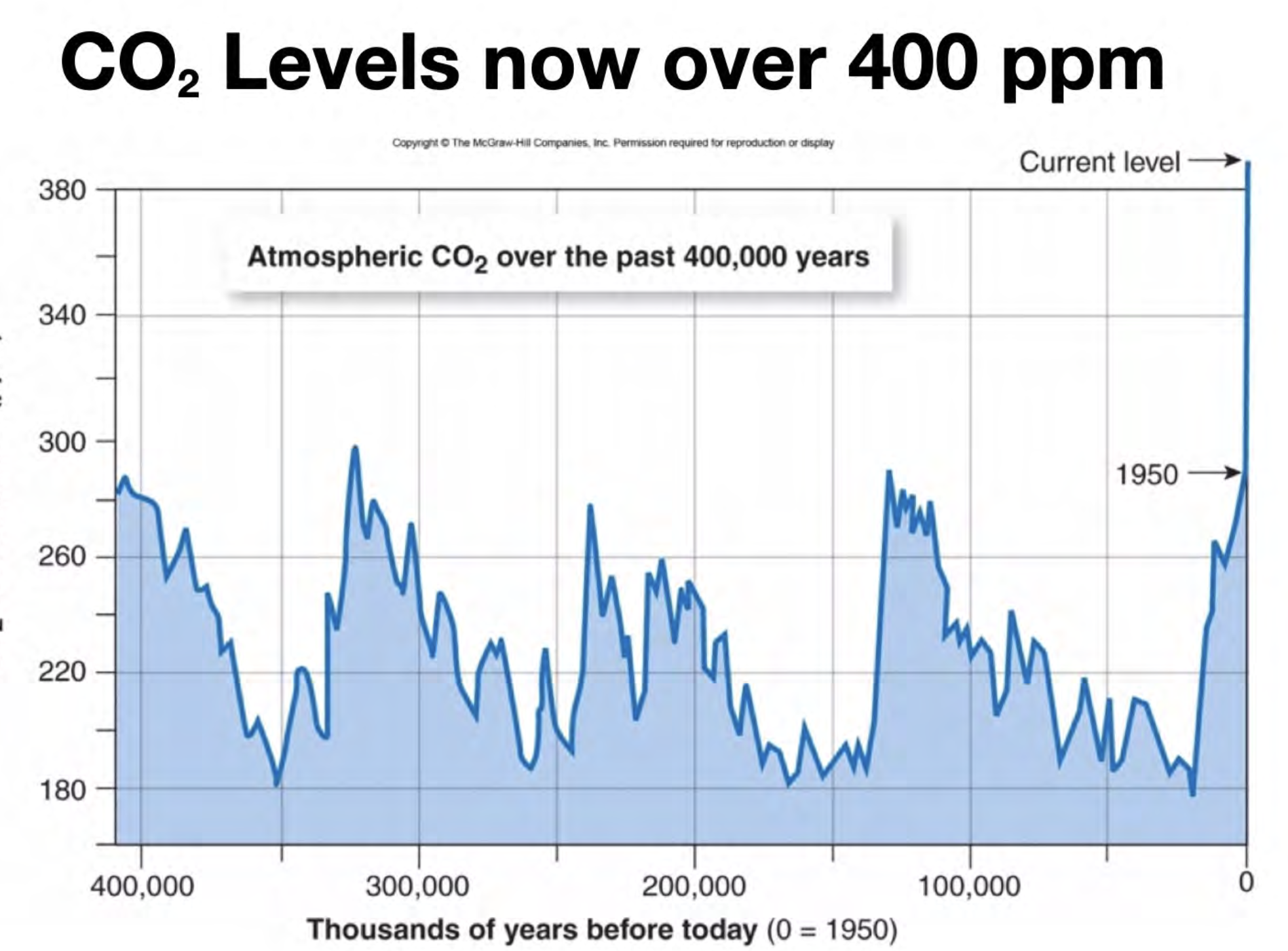
What are the consequences of a warmer Earth?
START HERE :)
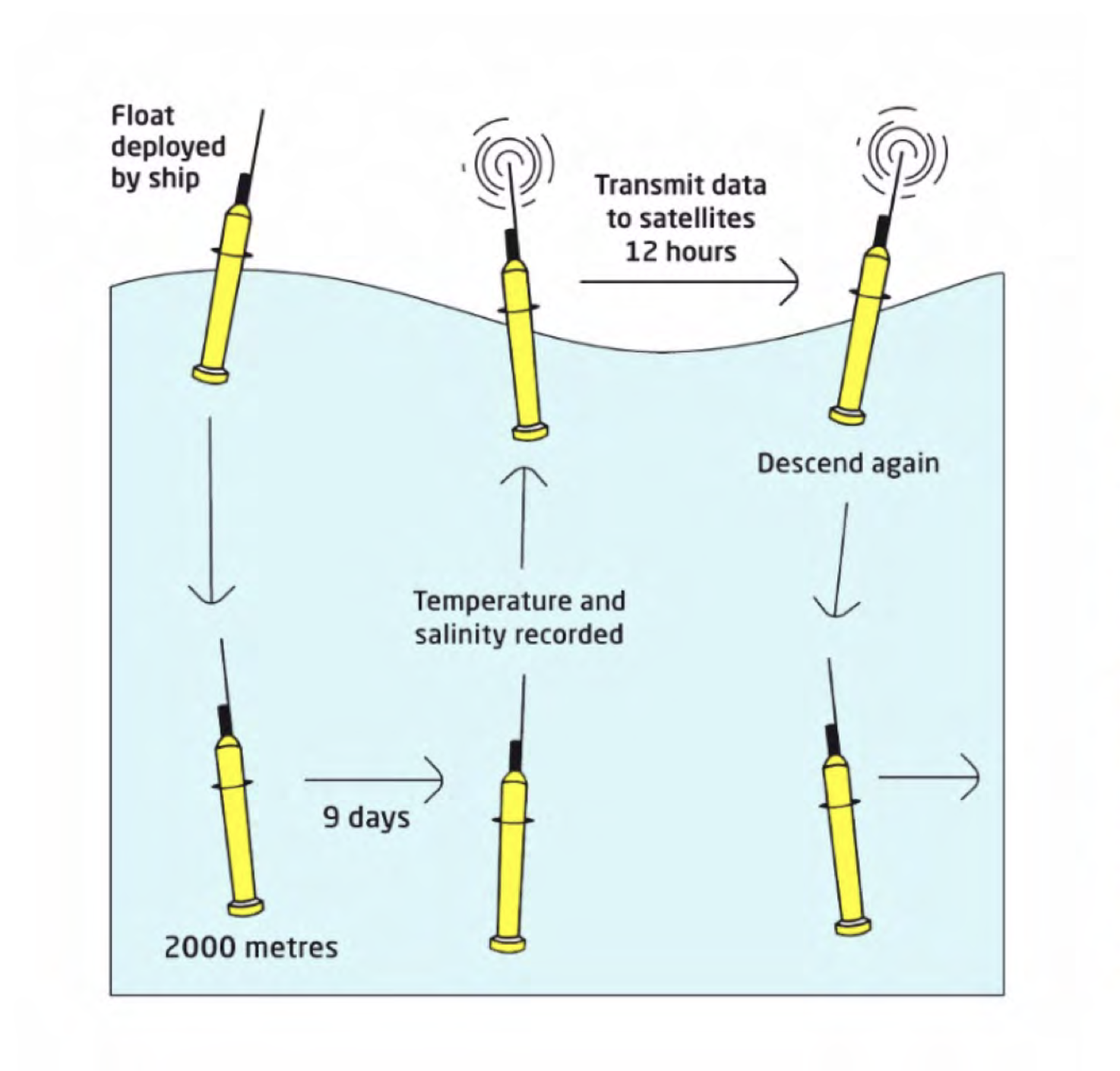
What are Argo Floats?
They are like little robots!
Can measure temperature and salinity of the sea water
Sink down to 2000 meters, come back up, and provide data, then sink back down and repeat!