AALSO Water Quality Level 1
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Define "absorption spectroscopy"
An analytical method that uses the wavelength dependent absorption characteristics of materials to identify and quantify specific substances
Define "accuracy"
The degree of agreement between the experimental result and the true value
Define "administrative controls"
Changes in work procedures with the goal of reducing the duration, frequency, and severity of exposure to hazardous chemicals or situations
Define "alkalinity" (water quality definition)
A measure of water's resistance to changes in pH or its buffering capacity
What does AOB stand for?
Ammonia oxidizing bacteria
Define "ammonia oxidizing bacteria"
Nitrifying bacteria that promote oxidation of ammonia into nitrite
What does AOD stand for?
Applied ozone dose
Define "applied ozone dose"
The quantity of ozone applied for a given flow, or the required ozone production rate
Define "DPD Method"
A method of measuring the chlorine residual in water
Define "engineering controls"
Methods that are built into the design of a plant, equipment, or process to minimize the hazard
What does GHS stand for?
Globally Harmonized System
Define "Globally Harmonized System"
An international system of classification and labelling of chemicals
Define "Laboratory Fortified Blank"
a sample of reagent water to which known quantities of the method analytes are added in the lab. analyzed like a sample
Define "Laboratory fortified matrix"
a sample of an environmental sample to which known quantities of the method analytes are added in the lab. analyzed like a sample
Define "Laboratory fortified matrix duplicate"
A duplicate of the matrix spike also used to assess the precision and bias of a method in a given sample matrix
Define "Matrix" (water quality definition)
The components of a sample other than the analyte of interest
Define "Matrix duplicate"
A split sample used to assess the precision of a method in a given sample matrix
What does MPN stand for?
Most Probable Number
What is MPN used for?
Quantifying an estimated concentration of bacteria
Define "New Tank Syndrome"
The toxic buildup of ammonia and nitrite in a new system
What causes New Tank Syndrome?
The bacteria have not reached a population level large enough to process the available ammonia or nitrite produced
What does ORP stand for?
oxidation-reduction potential
Define "Oxidation-reduction potential"
The electrical potential required to transfer electrons from one compound or element (the oxidant) to another compound or element (the reductant); in water quality, this result is the net status of all oxidation and reduction reactions in the sample being measured.
What unit is used for oxidation-reduction potential (ORP)?
millivolts
Define "oxidant"
A reactant that oxidizes or removes electrons from other reactants during a redox reaction
Define "oxidation"
A chemical reaction involving the gain of oxygen, or loss of electrons
What does a positive ORP result indicate?
An oxidizing environment
What does a negative ORP result indicate?
A reducing environment
Define "ozone" (water quality definition)
An unstable gas that is toxic to humans and has a strong odor; a strong oxidizing agent
What is the chemical composition of ozone?
O3
Define "pH"
An expression of the intensity of the basic or acidic condition of a liquid
Define "random error"
Unpredictable errors that average out, and have a varying magnitude; errors outside of one's control
Define "reagent blank"
A blank that is processed like a sample and can be used to zero or subtract out the small positive error that may arise in the reagents
What does SDS stand for?
Safety Data Sheet
Define "Safety data sheet"
A document that provides pertinent information and a profile of a particular hazardous substance or mixture
Who adopted that GHS?
The UN
What aspects are required to be on an SDS?
1) Product or chemical identifier
2) Hazards identification
3) Composition/Information on ingredients
4) First-aid measures
5) Firefighting measures
6) Accidental release measures
7) Handling and storage
8) Exposure Controls/Personal Protection
9) Physical and Chemical Properties
10) Stability and Reactivity
11) Toxicological Information
12) Other information
What aspects are recommended to be on an SDS but are not required?
1) Ecological information
2) Disposal Considerations
3) Transport Information
4) Regulatory information
What must all chemical labels include?
1) Pictogram(s)
2) Signal word
3) Hazard statements
4) Precautionary statements
5) Product identifier (ingredients)
6) Supplier contact information
7) Supplemental information
Pictogram indicating explosive

Pictogram indicating flammable

Pictogram indicating oxidizers

Pictogram indicating gas under pressure

Pictogram indicating corrosives
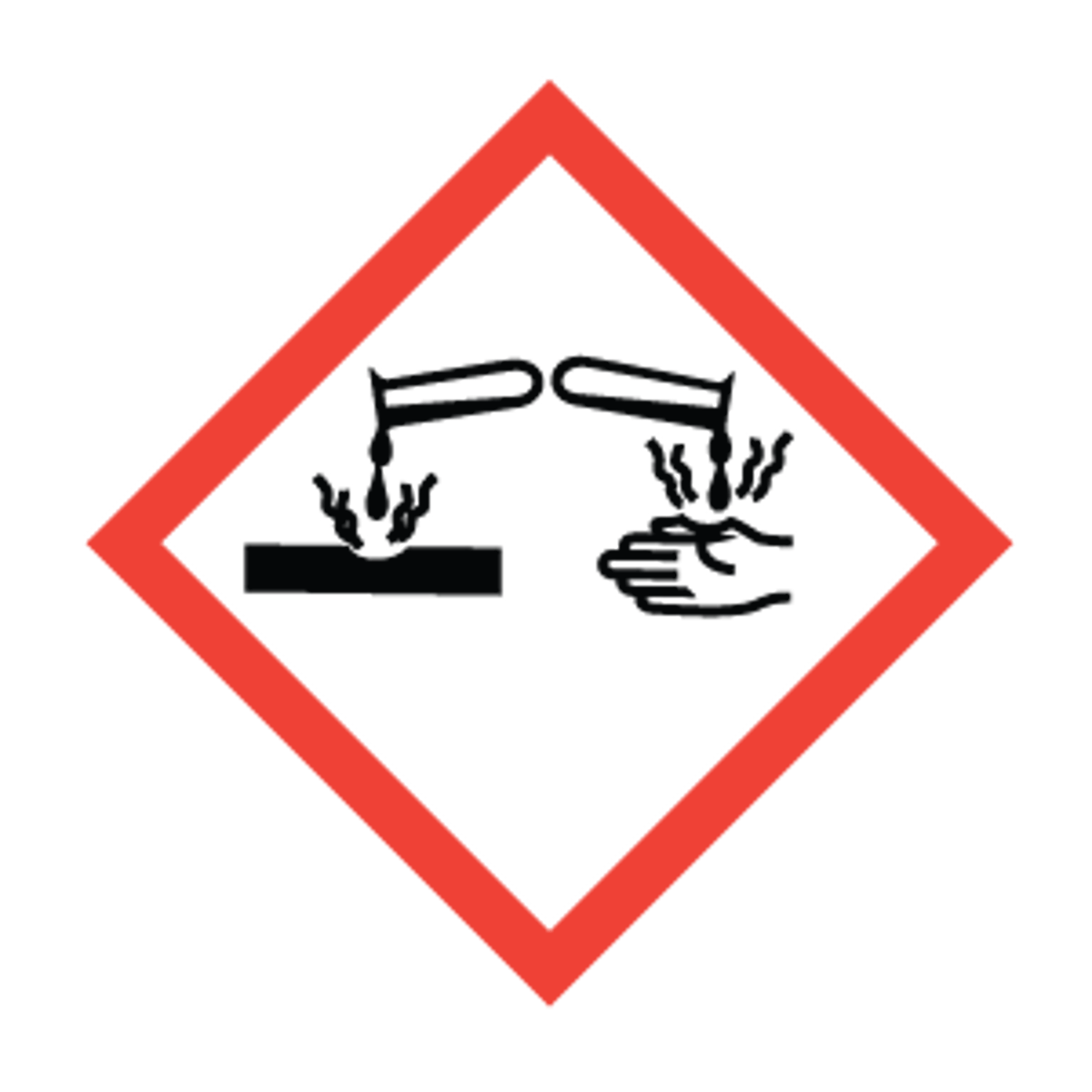
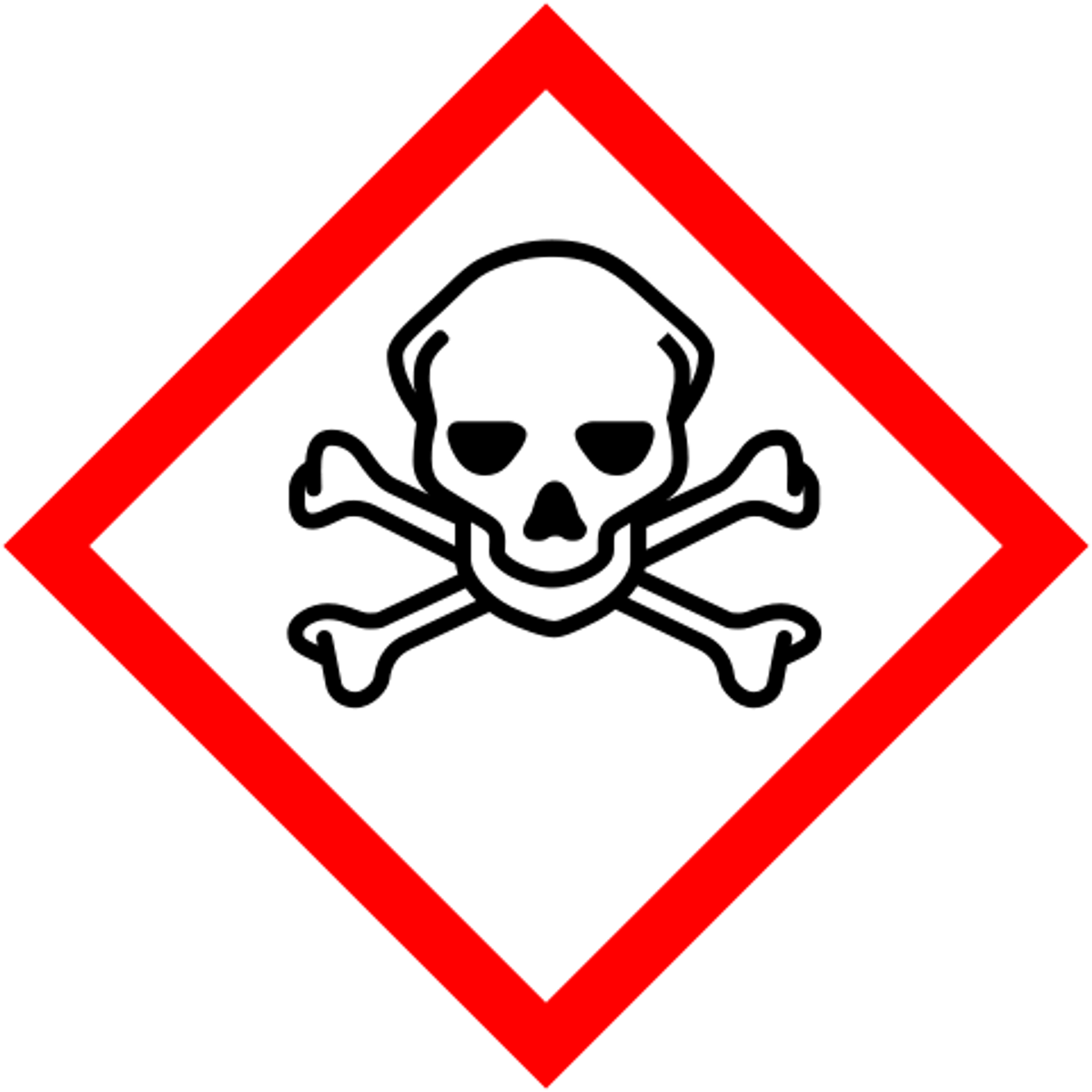
Pictogram indicating acute toxicity

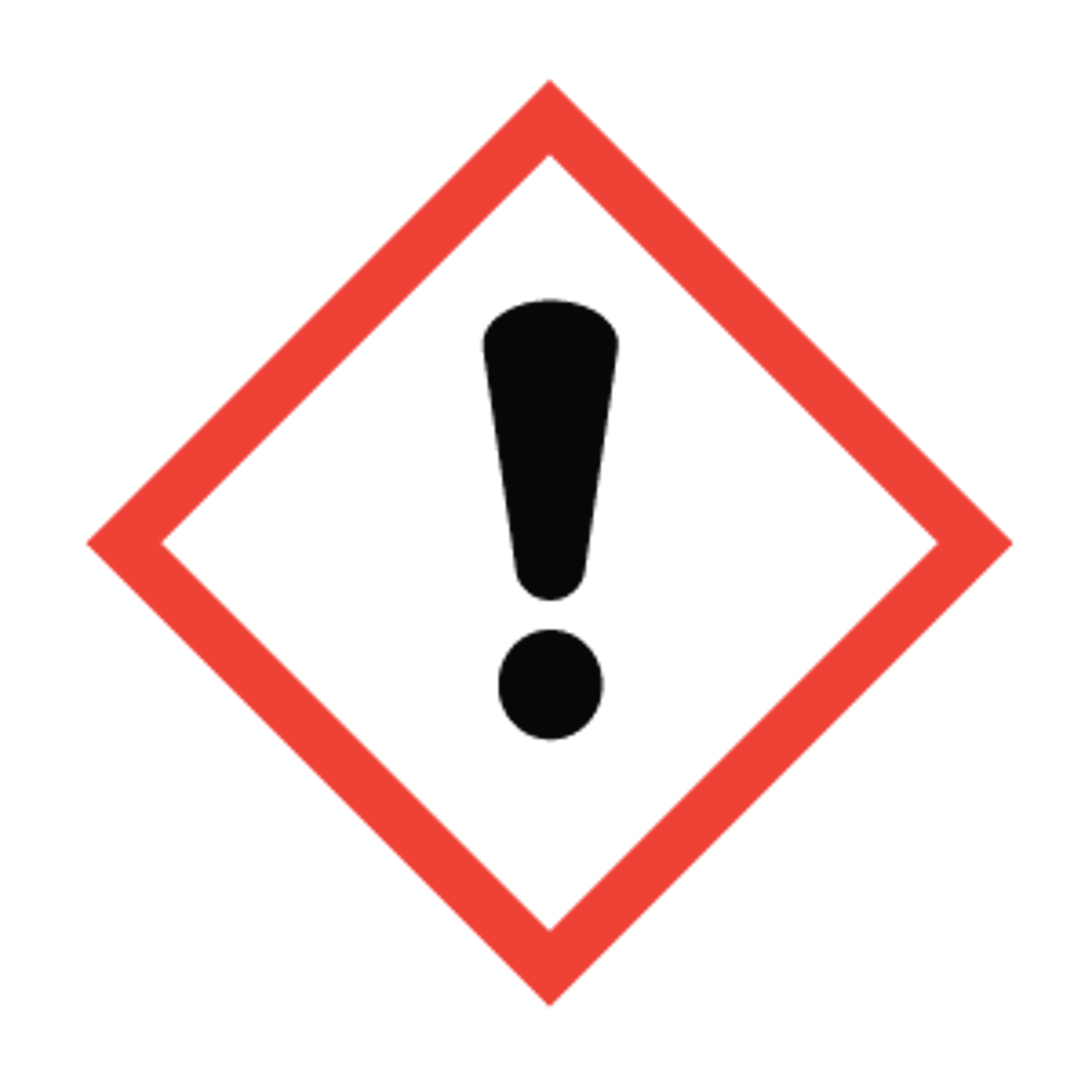
Pictogram indicating harmful irritant

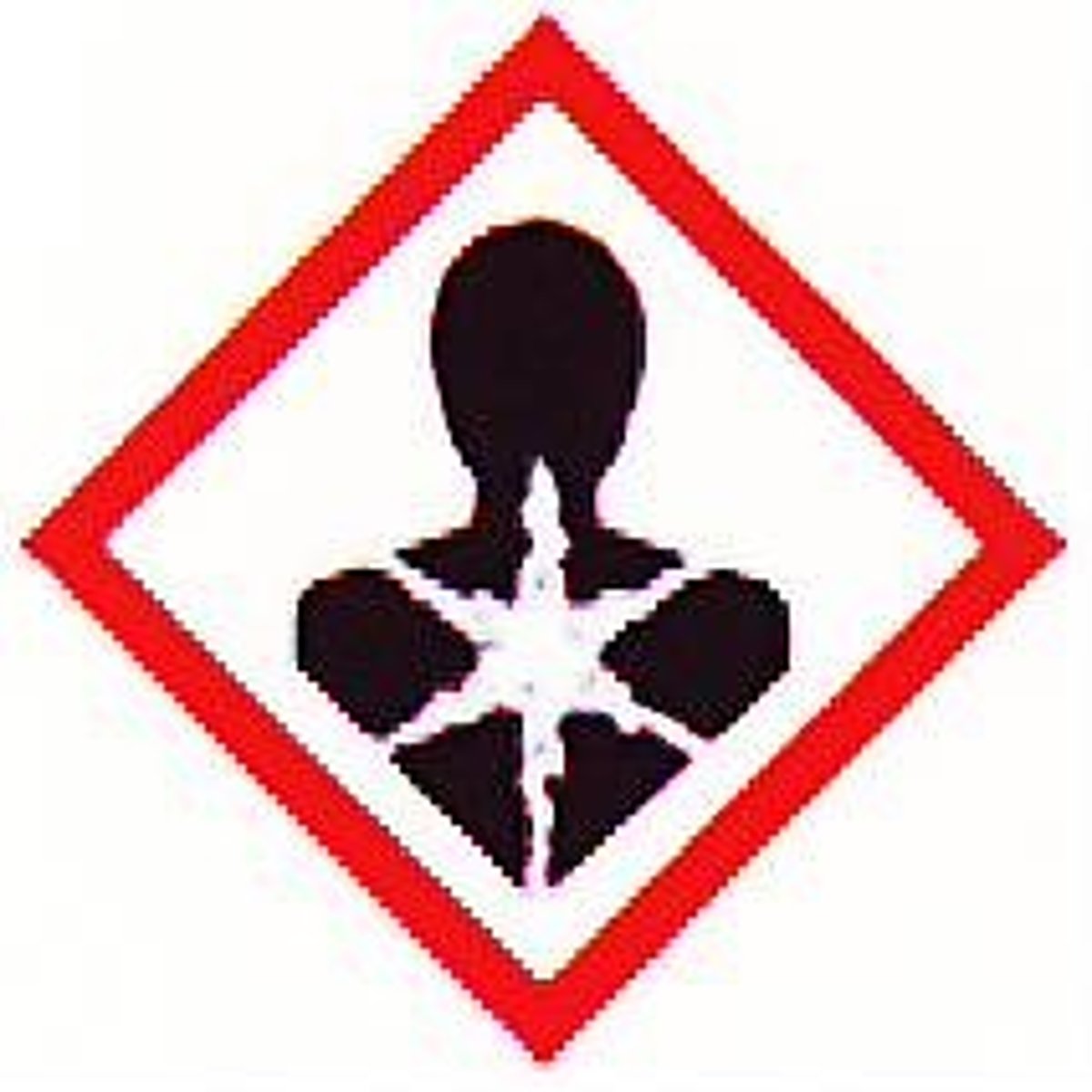
Pictogram indicating severe health hazards

Pictogram indicating environmental toxicity

When mixing acid and water, how should you combine them?
Add acid to water
Why should you not add water to acid?
The exothermic reaction may cause splashback
What are the goals of chemical clean-up?
1) Prevent spread of dusts and vapors
2) Control spread of liquids
3) Neutralize acids and bases
4) Absorb chemicals
5) Collect and contain clean-up residue
6) Discard broken class in appropriate containers
7) Decontaminate area and affected equipment
List the hierarchy of hazard controls from most effective to least effective
1) Elimination
2) Substitution
3) Engineering controls
4) Administrative controls
5) PPE
Define "spectrophotometers"
Instruments that can measure the absorbance or transmittance of a sample
What type of instrument is our Hach machine?
A spectrophotometer
Define "potentiometry"
An analytical methodology that is based on measurement of an electrochemical cell's potential
What unit is measured in potentiometry?
Millivoltes
What instrument is used for potentiometry?
Electrodes
What is another term for electrodes?
Probes
What is another term for probes?
Electrodes
What is the equation for calculating pH?
pH = -log[H+]
Define "salinity"
The measurement of salt ion concentration in water
What is the preferred unit for salinity?
parts per thousand (ppt)
What are two methods to measure salinity?
1) Refractometry
2) Conductivity
Erlenmeyer flask
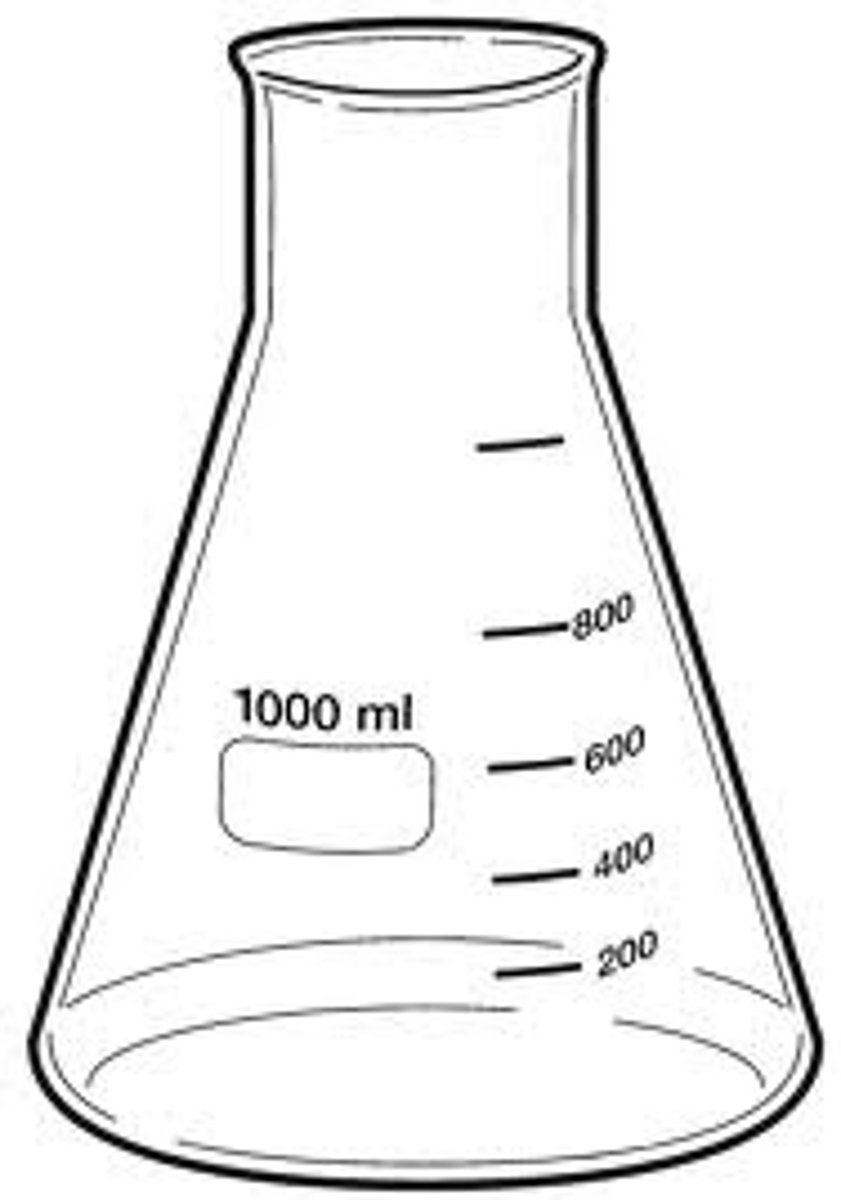
What is an Erlenmeyer flask the best glassware for?
Mixing a liquid solution on a spinner plate
Graduated cylinder

What is a graduated cylinder best used for?
Accurately measuring liquids
Volumetric flask

What is a volumetric flask used for?
An accurate measure of a fixed liquid volume; dilutions
Beaker

What is a beaker best used for?
Mixing solutions and weighing dry chemicals
What is a burette used for?
Titrations
What are the two possible endpoints for titrations?
1) Colorimetric end point
2) pH endpoint
What water quality test due we run that uses titration?
Alkalinity
Define "precision"
Indicates how closely repeated measurements agree
Define "sample blank"
A solution free of the analyte of interest
What is a sample blank used for?
Instrument calibration and zeroing out
What does LFB stand for?
Laboratory fortified blank
What is a laboratory fortified blank used for?
Used to show that sample preparation procedures do not contribute to loss of analyte
What does LFM stand for?
Laboratory fortified matrix
What is another term for laboratory fortified matrix?
Matrix spike
What is a laboratory fortified matrix used for?
Used to assess the bias of a method in a given sample matrix
Define "gross error"
Error due to human error with collection or testing
Define "systemic error"
Errors with the testing process
What are the steps of the nitrogen cycle?
1) Animals produce waste
2) Bacteria cause ammonification of waste to ammonia
3) Nitrifying bacteria and oxygen convert ammonia to nitrite
4) Nitrifying bacteria and oxygen convert nitrite to nitrate
5) Plants, denitrifying bacteria, and water changes convert nitrate to elemental nitrogen
6) Elemental nitrogen is consumed by marine life and converted to waste
Define "old tank syndrome"
An established system that is at risk for producing high levels of nitrates
What is the difference between units expressed as [Compound] and units expressed as [Compound]-N?
[Compound] uses the molecular weight of the entire compound, whereas [Compound]-N uses the molecular weight of only the nitrogen atom
What is the chemical composition of ammonium?
NH4+
What is the chemical composition of ammonia?
NH3
Which is considered the more toxic form of ammonia?
Unionized ammonia (NH3)
Which is considered the less toxic form of ammonia?
Ammonium (NH4+)
What two factors could potentially cause a decrease in alkalinity?
1) Acidic pH
2) Increased bacteria
What does CFU stand for?
colony forming unit
What does CFU measure?
Coliform bacteria and enterococci
What is the difference between CFU and MPN?
How the values were obtained
How is MPN obtained?
Through multiple tube fermentation (well trays)
How is CFU obtained?
Membrane filtration (petri dish)
What is ozone used for?
1) Point of contact sterilization
2) Pathogen control
3) Reducing organic load
4) Clarification agent
How does ozone control pathogens?
Facilitates in the rupture of microorganisms' cell walls
What color does ozone turn water?
Light blue