fetal gastrointestinal & genitourinary systems
1/241
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
242 Terms
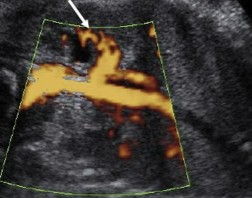
The fetus scanned on has testicular hypoplasia. When the sonographer scanned up to the kidneys, this was seen. What can be assumed here?
Unilateral renal agenesis
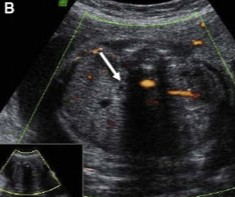
The fetus scanned on was seen with a single umbilical artery wrapped around the bladder. That prompted the sonographer to take a look at the kidneys and this was seen.
What pathology can be assumed here?
Why can this pathology happen?
Unilateral renal agenesis
The ureteral buds failed to develop
With esophageal atresia, the fetus is (1)_________ part of the esophagus or it’s (2)__________.
Missing
Underdeveloped
With esophageal atresia, will amniotic fluid pass into the intestines for absorption?
No
List the 2 US findings of esophageal atresia.
½ No fluid filled stomach
2/3 polyhydramnios
If ½ of esophageal atresia cases have no fluid in the stomach, then the other ½ can see fluid in the stomach. Why is that?
Because of TEF
Around 90% of esophageal atresia cases have what structural variation?
Distal tracheo-esophageal fistula
The TEF variation in esophageal atresia enables amniotic fluid to pass through an _________ connection between the trachea and esophagus.
Abnormal
Esophageal atresia is associated with…
________ problems
________ problems
________ problems
____________ abnormalities
Cardiac
GI
GU
Chromosomal
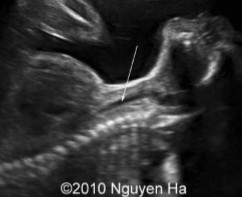
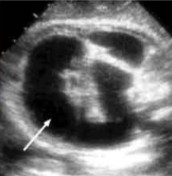
What structure is seen at the arrow?
Trachea
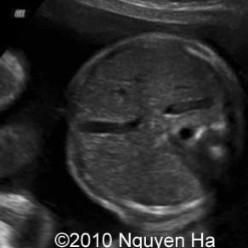
The fetus scanned on had polyhydramnios. What can be assumed here?
Esophageal atresia
Why do fetus’ with esophageal atresia have polyhydramnios?
Amniotic fluid is unable to pass into the intestines for absorption
What is the most common cause of small bowel obstruction?
Duodenal atresia
Duodenal atresia will see 2 fluid filled structures in the (1)______ abdomen that (2)_________.
Upper
Communicate
What is the most important US finding of duodenal atresia?
Double bubble
The double bubble sign for duodenal atresia will show a dilated (1)________ and (2)________ duodenum.
Stomach
Proximal
When can the double bubble sign appear for duodenal atresia?
After 24 weeks
Duodenal atresia is associated with ______hydramnios.
Poly
Duodenal atresia is associated with what 3 pathologies?
Trisomy 21
Cardiac anomalies
VACTERL complex
What does each letter of ‘VACTERL’ stand for?
Vertebral
Anal atresia
Cardiac
Trachea
Esophagus
Renal
Limb defect
Based on previous lectures, what pathology is VACTERL associated with?
Caudal regression syndrome (CRS)
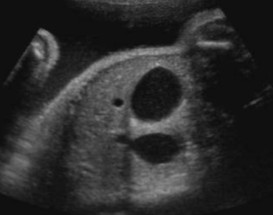
The sonographer found polyhydramnios. This was found.
What US finding is seen here?
What pathology is it seen with?
Double bubble sign
Duodenal atresia
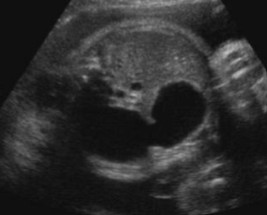
The sonographer scanned a fetus that has Trisomy 21. This was seen.
What US finding is seen here?
What pathology is it seen with?
Double bubble sign
Duodenal atresia
Intestinal atresia is the (1)________ or abnormal (2)_________ of the intestines.
Absence
Narrowing
General rule for intestinal atresia is that the more (1)_______ the obstruction, the less severe the (2)____________ will be and the later it will develop.
Distal
Polyhydramnios
If the sonographer sees multiple fluid filled loops of bowel, what pathology should be suspected?
What can this pathology lead to?
Intestinal atresia
Bowel obstruction
If bowel obstruction perforates with intestinal atresia, what 4 US findings can be seen?
Calcifications
Ascites
Polyhydramnios
Meconium peritionitis
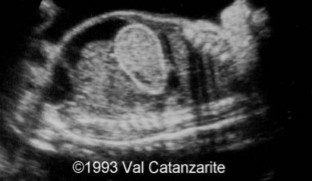
Fluid filled bowel loops were seen on US. What pathology can be asusmed here?
Intestinal atresia
What causes meconium peritonitis?
Bowel perforation
What is another term for fetal stool?
Meconium
Meconium peritonitis is when (1)_________ goes into the (2)______________ and causes (3)_________.
Meconium
Surrounding spaces
Inflammation
List 4 pathologies that meconium peritonitis can lead to.
Ascites
Fibrosis
Calcification
Cyst formation
Approximately 80-90% of meconium peritonitis cases have what US finding?
Intra-abdominal calcifications
Meconium peritonitis occurs due to bowel perforation. List 2 pathologies that can cause perforation.
Intestinal atresia
Cystic fibrosis
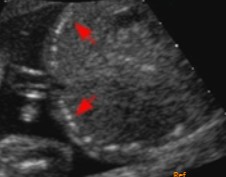
Bowel obstruction has occurred in the fetus, and this was seen on the scan.
What US finding is seen here?
What pathology is it an indication for?
Meconium cyst
Meconium peritonitis
Bowel obstruction has occurred in the fetus, and this was seen on the scan.
What US finding is seen here?
What pathology is it an indication for?
Calcification
Meconium peritonitis
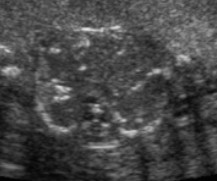
Bowel obstruction has occurred in the fetus, and this was seen on the scan.
What US finding is seen here?
What pathology is it an indication for?
Calcification
Meconium peritonitis
When fetal bowel appears hyperechoic, what structure should the sonographer compare it to?
Fetal bone
Define hyperechoic bowel.
When fetal bowel is brighter than it should be
How is hyperechoic bowel determined?
Turning off harmonics
Turning down gain
The brightness and harmonics have been turned down.
The echogenicity of the bowel and bone are the same.
What can be assumed here?
Hyperechoic bowel
The brightness and harmonics have been turned down.
The bowel disappeared before the bone.
What can be assumed here?
NOT hyperechoic bowel
Hyperechoic bowel can be associated with what 3 pathologies?
Trisomy 21
Infections
Cystic fibrosis
Despite having associations with various pathologies, can hyperechoic bowel still be considered a normal variant?
Yes
What is the most important pathology that can be associated with hyperechoic bowel?
Trisomy 21
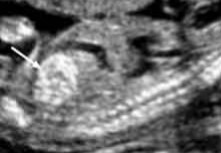
What pathology is seen at the white arrow?
Name at least 1 pathology question 1’s answer can be associated with.
Hyperechoic bowel
Trisomy 21, Infections, or cystic fibrosis
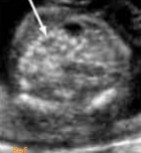
What pathology is seen if the gain were turned down and it matched the echogenicity of the fetal bone?
Name at least 1 pathology question 1’s answer can be associated with.
Hyperechoic bowel
Trisomy 21, Infections, or cystic fibrosis
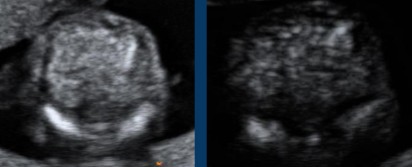
Both images were taken with the same fetus at the same area, just with different gains.
What can be assumed regarding what is seen here?
Fetus has hyperechoic bowel
Prenatal US is capable of diagnosing many anomalies of the urogenital system. What 2 systems make up the urogenital system?
Urinary
Genital
When the sonographer is scanning through the kidneys, what 2 other structures/factors should also be assessed?
Urinary bladder
Amount of amniotic fluid
What structure is considered a critical marker in the assessment of renal function?
Amniotic fluid
The fetal kidneys will begin to excrete urine after what week?
11
The fetal kidneys will not become the major contributor of fetal urine (amount of amniotic fluid volume) until __-__ weeks.
14 - 16
If there is a decrease in amniotic fluid prior to weeks 14-16, what pathologies should be suspected?
Premature ruptured of membranes (PROM)
Renal abnormalities
The observation of normal amniotic fluid volume before weeks 14-16 will not exclude the possibility of what pathology?
Renal agenesis
Renal malformations may be divided into what 2 categories?
Congenital malformation
Obstructive process
Recognition of urinary tract anomalies is important because several fetal conditions are (1)_________ with life and it is important to ensure appropriate (2)_________ management.
Incompatible
Clinical
Prognosis of any abnormalities of the urinary tract depend on _________ or _________ involvement of the kidneys as well as associated abnormalities.
Unilateral
Bilateral
What is the survival rate for fetus’ with the presence of one functioning kidney?
Excellent
Which 2 maternal factors can increase the risk for urogenital malformations?
Cocaine use
Maternal diabetes
How does unilateral renal agenesis occur?
When the ureteral buds fail to develop
If unilateral renal agenesis is suspected, the sonographer should carefully evaluate other fetal structures and the _______ area.
Pelvic
With unilateral renal agenesis, how will the one kidney appear?
What will this be termed?
Larger in size, due to compensating for the missing kidney
Compensatory hypertrophy
The missing side of unilateral renal agenesis will see what 2 US findings?
‘Lying down” adrenal gland
No renal artery
Unilateral renal agenesis will be associated with what 4 pathologies?
Single umbilical artery (SUA)
Uterine anomalies
Testicular hypoplasia
Undescended testicles
Will unilateral renal agenesis affect AFI?
No
What is the most common cause of bilateral renal agenesis?
Severe oligohydramnios
What does ‘BRA’ stand for?
Bilateral renal agenesis
Bilateral renal agenesis is a lethal disorder due to what 2 pathologies?
Renal insufficiency
Hypoplasia of lungs
Bilateral renal agenesis will exhibit what syndrome?
Potter’s syndrome
What are the 5 US findings of Potter’s Syndrome (bilateral renal agenesis)?
Flat nose
Recessed chin
Abnormal ears
Wide set eyes
Deformities of limbs (talipes)
With unilateral or bilateral agenesis, what US finding can mimic the appearance of kidneys?
‘Lying down’ of adrenal gland
When scanning for bilateral renal agenesis, how will the bladder appear?
No bladder over the course of an hour.
What arteries won’t be seen with bilateral renal agenesis?
Renal arteries
Bilateral renal agenesis will typically be seen between __-__ weeks.
16 - 28
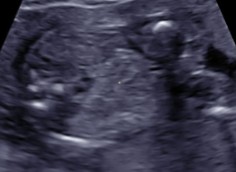
The sonographer is scanning at the level of the kidneys and does not note them. What can be assumed here?
Bilateral renal agenesis
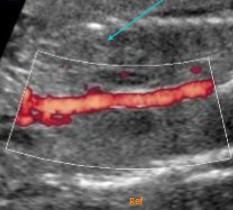
What pathology is seen here?
What syndrome can be seen with this pathology?
Bilateral renal agenesis
Potter’s syndrome
What is another term for Potter’s syndrome?
Potter’s sequence
Potter’s syndrome is caused by (1)_________ in utero due to (2)_____hydramnios.
Pressure
Oligo
Potter’s syndrome can also occur with other conditions that cause oligohydramnios. List 3 of them.
VACTERL syndrome
Blockage of the urinary tract
PROM
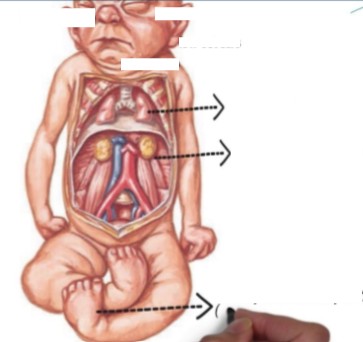
This image can be associated with what pathology?
What pathology can this condition be seen with?
Potter’s Syndrome
Bilateral Renal Agenesis
Define pulmonary hypoplasia.
Underdevelopment of the lungs
What causes the limb abnormalities of Potter’s syndrome?
Lack of fluid to move around
Bladder exstrophy can be similar to what other pathology?
Ectopia cordis
Bladder exstrophy can be ______ or _______.
Mild
Severe
How does bladder exstrophy appear on US?
What does the US appearance represent?
Small, soft tissue mass
Exposed bladder mucosa
Bladder exstrophy can be due to a (1)______ in (2)_______ abdominal wall.
Defect
Lower
Bladder exstrophy can be accompanied by other…
Abnormalities
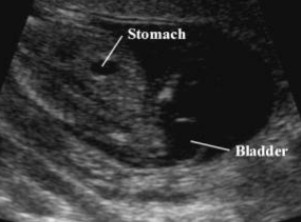
What pathology is seen here?
Bladder exstrophy
Cloacal exstrophy can only been seen in males or females?
Females
What are the 3 openings with cloacal exstrophy?
Urethra
Vagina
Rectum
With cloacal exstrophy, instead of having (1)__ separate openings, there is only (2)___ opening where urine and stool comes out.
3
1
What other pathology does cloacal exstrophy look similar to on US?
What is different?
Bladder exstrophy
Small and large intestine will be in the mass
Cloacal exstrophy is where which 2 tracts meet?
GI
GU
Cloacal exstrophy is when there is ___ opening to the outside.
1
Cloacal exstrophy will be associated with ____hydramnios.
Oligo
Cloacal exstrophy has a ____ prognosis.
Poor
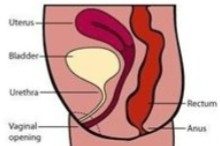
Is this image of the pelvis normal or abnormal?
If abnormal, what can be assumed here?
Normal
Normal
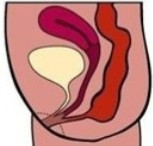
Is this image of the pelvis normal or abnormal?
If abnormal, what can be assumed here?
Abnormal
Cloacal exstrophy
What structure is responsible for helping the bladder develop?
Urachus