Lecture 15: The Reproductive System III
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
what is the perineum?
The perineum is the area between your thighs, at the bottom of the pelvis. It's where your private parts (genitals and anus) are located.
what are the two parts of the perineum?
It has two parts:
Urogenital Triangle (front): where pee and (for people with a vagina) vaginal openings are.
Anal Triangle (back): where the anus is.
RECALL: what are the hiatuses in the perineum?
Hiatuses = Openings in the Pelvic Floor
Urogenital Hiatus = Urethra and vagina
Rectal Hiatus = Rectum/anus
Your pelvic stands upright.. true or false???
FALSE!
Most people think the pelvis stands upright, but in real life, your pelvis tilts forward a bit naturally.
Points your genitals downward
Aims your anus backward
What is the perineal membrane?
The perineal membrane is ONE sheet of strong connective tissue (like a thick trampoline) that sits across the urogenital triangle. It creates two layers or "pouches":
what are the 2 pouches the membrane creates
Superficial pouch = closer to the skin
Deep pouch = deeper, closer to the inside of the body
think of like a big mac…
Top Bun = skin/external genitals
Top Filling = superficial perineal pouch
Middle Bun = perineal membrane
Another filling = deep perineal pouch
Bottom Bun = pelvic floor muscles
what is the perineal body?
The perineal body is a small but super important fibrous (strong connective tissue) structure that sits in the middle of the perineum—right between your genitals (front) and anus (back).
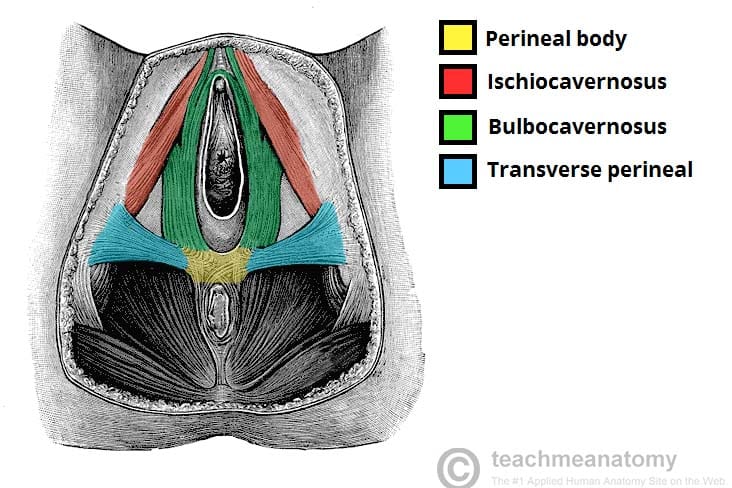
where is the perinial body in males? females?
In males: between the bulb of the penis and the anus
In females: between the vaginal opening and the anus
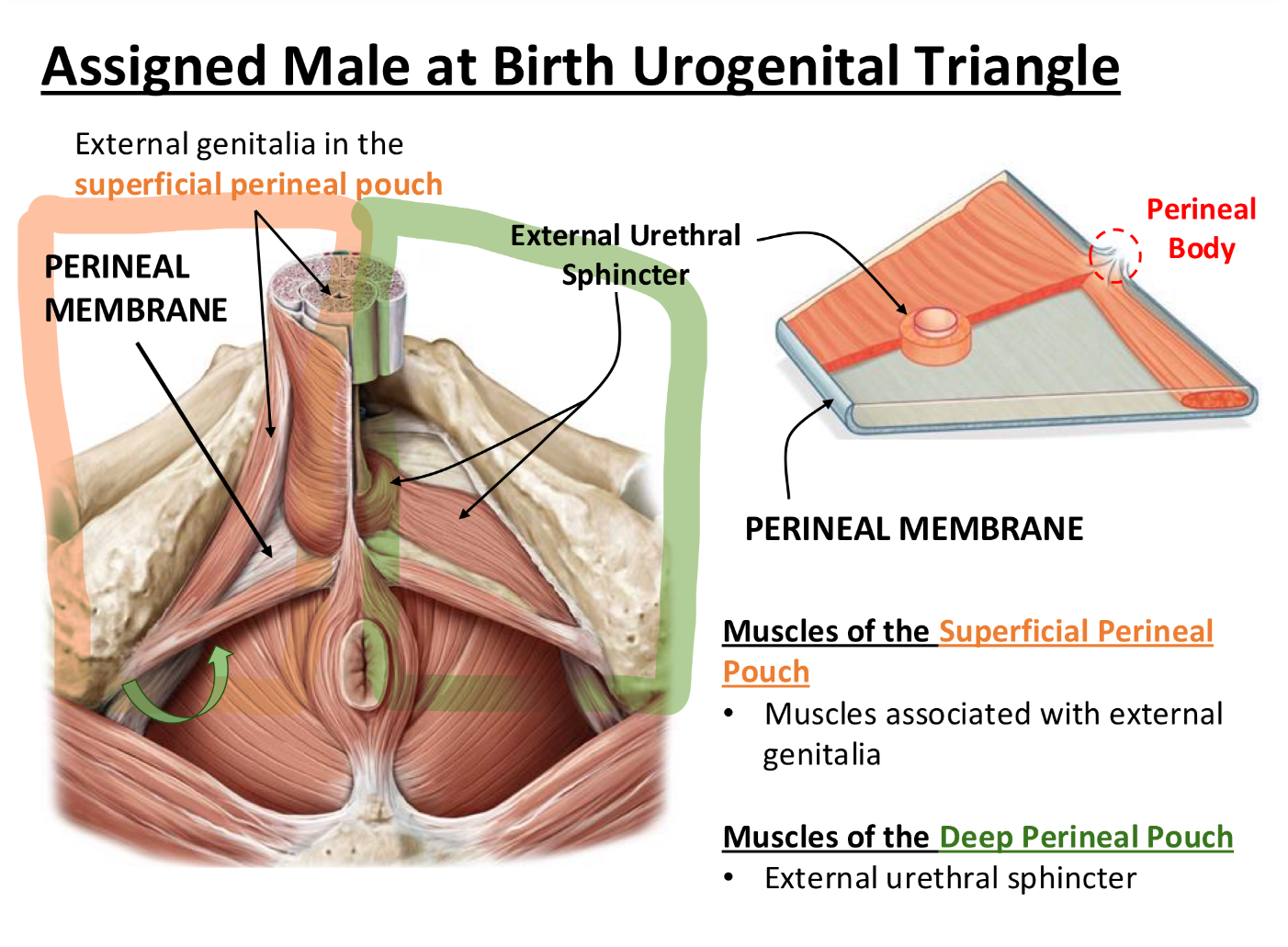
what are the contents of the superficial and deep perinal pouch in ASSIGNED MALE AT BIRTH
Superficial Perineal Pouch
Contains: Muscles of external genitalia/muscles for genital movement (like muscles that help with erection or stabilize the base of the penis).
These structures are attached to the perineal membrane for support.
Deep Perineal Pouch
Contains: External urethral sphincter, which is a circular muscle that wraps around the urethra.
This sphincter is under voluntary control (so you can “hold it in” when you need to pee).
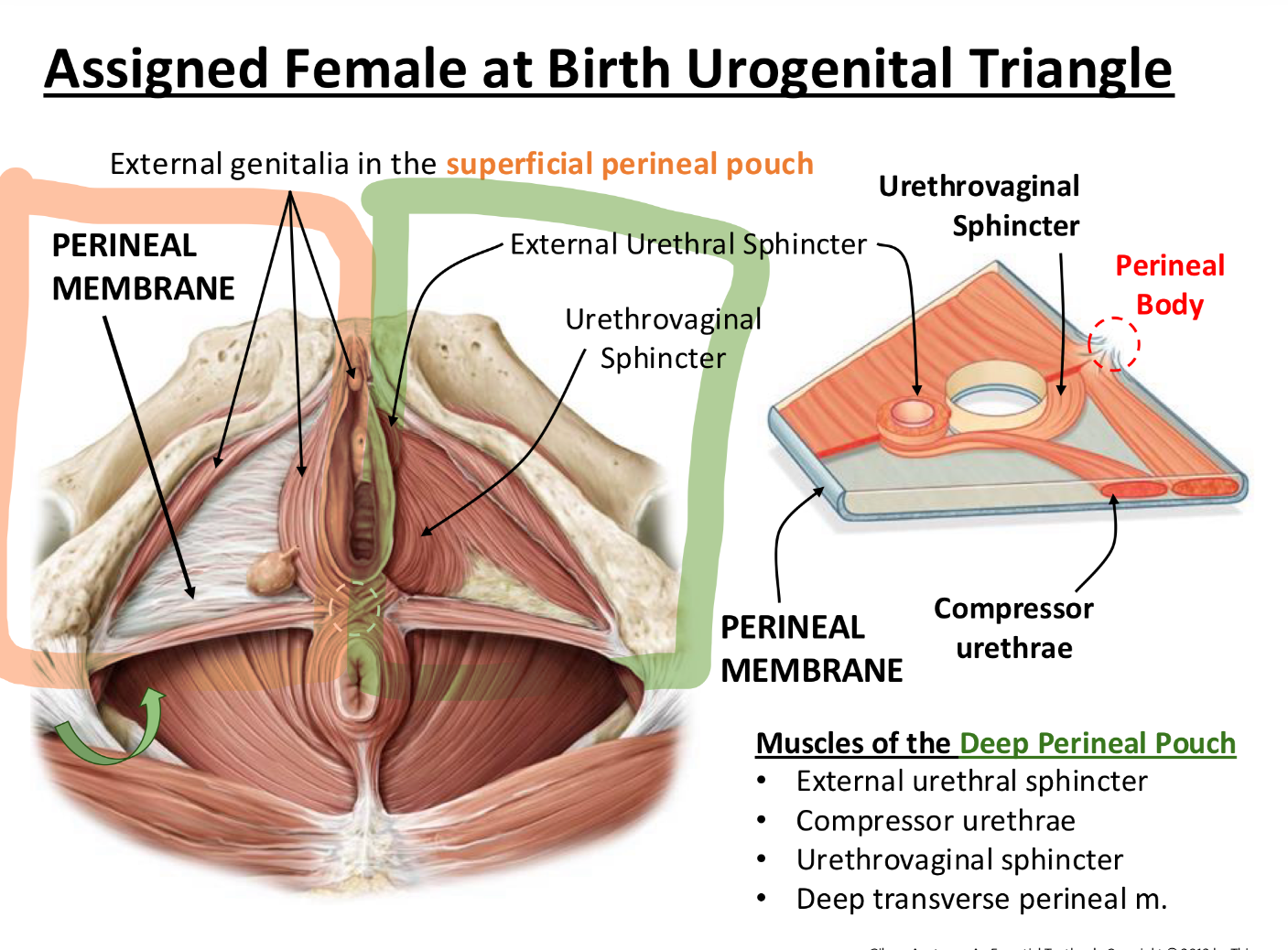
what are the contents of the superficial and deep perinal pouch in ASSIGNED FEMALE AT BIRTH
Superficial Perineal Pouch
Contains: External genitalia, like the clitoris and associated muscles (These muscles help with sexual function and stabilization of structures)
These structures are attached to the perineal membrane for support.
Deep Perineal Pouch
Contains:
External urethral sphincter – wraps around urethra to hold in pee (voluntary control!)
Compressor urethrae – squeezes the urethra from the front like a clamp
Urethrovaginal sphincter – wraps around both urethra and vagina
Deep transverse perineal muscle – supports the pelvic floor
PENIS; EXTERNAL GENITALIA - what is th penis made of? why is this beneficial?
The penis is made of special spongy tissue (erectile tissue) that can fill with blood during arousal → helps with erection.
Think of it like a sponge that soaks up blood!
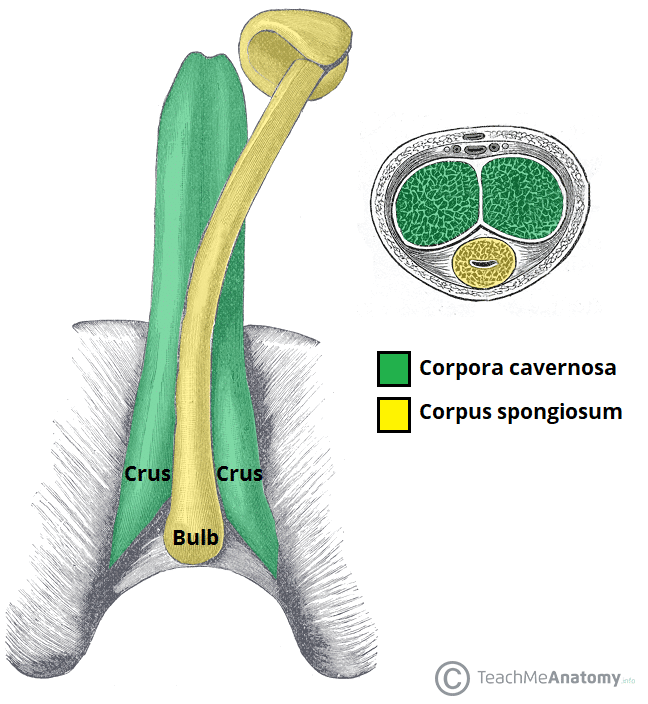
PENIS; EXTERNAL GENITALIA - what are the 3 colums of erectile tissue in the penis?
Corpus Cavernosa
Corpus Cavernosa
Corpus Spongiosum
2 eyes = Corpus Cavernosa (dorsal = top side when erect)
1 mouth = Corpus Spongiosum (ventral = bottom side, holds the urethra)
PENIS; EXTERNAL GENITALIA - what sits in the root of the penis?
Bulb of the Penis
Crura (plural of Crus)
Made of Corpus Cavernosa - one for each
PENIS; EXTERNAL GENITALIA - what muscle are associated with each of the 3 colums of erectile tissue in the penis?
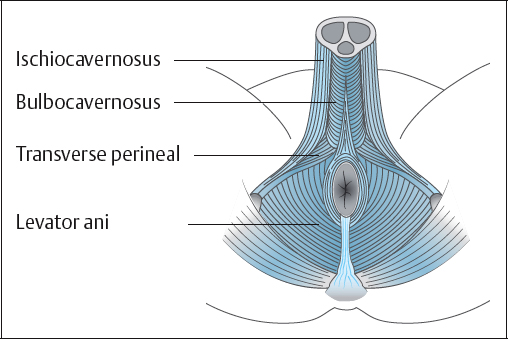
Corpus Cavernosa ~ Ischiocavernosus
Corpus Cavernosa ~ Ischiocavernosus
Corpus Spongiosum ~ Bulbospongious
VULVA; EXTERNAL GENITALIA - similar to the penis, what is the many tissue in the vulva?
The vulva is made of special spongy tissue (erectile tissue) that can fill with blood during arousal → helps with erection.
Think of it like a sponge that soaks up blood!
corpus caveronosum
corpus spongiosum
VULVA; EXTERNAL GENITALIA - where is corpus cavernosum found in the vulva
Crua and body of the clitoris
Crura of the clitoris = attaches clitoris to bones (like penis root)
Body of the clitoris = middle part
Like the penis, the clitoris can become erect when blood fills the erectile tissue.
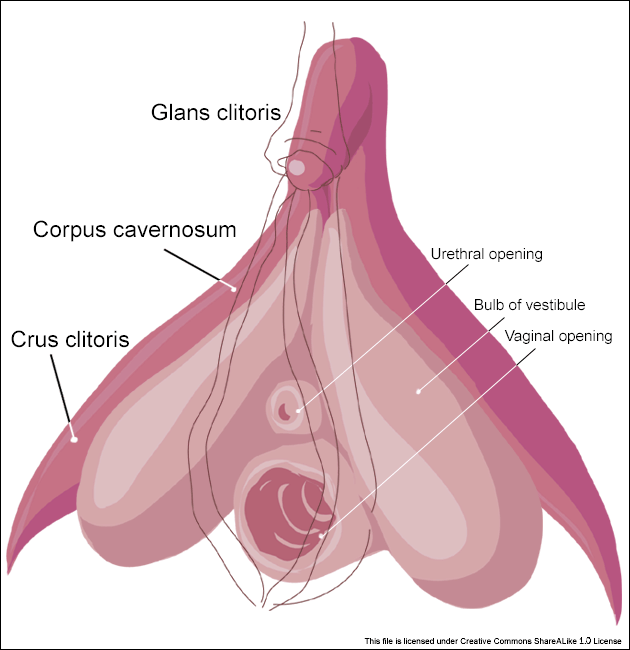
VULVA; EXTERNAL GENITALIA - where is corpus spongiosum found in the vulva
Bulbs of the Vestibule
Two sponge-like structures on either side of the vaginal opening.
Made of corpus spongiosum (same erectile tissue in penis).
Engorge with blood during arousal → help vaginal opening stretch & lubricate.

VULVA; EXTERNAL GENITALIA - what isthe tip of the vulva called
Glans of the clitoris = tip (very sensitive)
Covered by a foreskin (prepuce), like a mini hoodie!
VULVA; EXTERNAL GENITALIA - what muscle are associated with each of the 2 sets of erectile tissue in the vulva?
Corpus Cavernosa ~ Ischiocavernosus
Corpus Spongiosum ~ Bulbospongious
VULVA; EXTERNAL GENITALIA - what are 2 other features of the vulva unique to females?
Labia Majora & Labia Minora
Labia Majora = outer "lips" (skin + fat, like scrotum)
Labia Minora = inner "lips" (thinner, moist skin)
Surround and protect the vaginal and urethral openings
What are the bulbourethral glands/greater vestibular glands? what are the location differences in females + males?
Both glands provide lubrication and are involved in sexual function
In Males:
Secretes pre-ejaculate fluid
Lubricates the urethra
Neutralizes acidity in the urethra to protect sperm
Bulbourethral glands are deep in males
In females:
Secretes mucus for lubrication during sexual arousal
Greater Vestibular Glands are superficial in females!
what are the three types of innervation in the pelvis
KEY IDEA: Three Types of Innervation in the Pelvis
Somatic: Feeling (touch, pain), movement
VOLUNTARY
Autonomic - Parasympathetic: “Rest & Digest” (relaxation)
INVOLUNTARY
Autonomic - Sympathetic: “Fight or Flight” (tension)
INVOLUNTARY
how does somatic innervation work? key nerve involved?
The Star Nerve: Pudendal Nerve (S2, S3, S4)
A somatic nerve that gives you voluntary control over your pelvic muscles. Think peeing, pooping, and sexual function!
"S2, S3, S4 keep the penis off the floor"
how does autonomic (parasympathetic) innervation work? key nerve involved?
Parasympathetic (Pelvic Splanchnic Nerves ~ S2-4)
Think "peaceful" → rest, digest, relax
Relaxes sphincters - Helps you pee and poop
Contracts detrusor (bladder) muscle - Helps you urinate
Relaxes uterine muscle - During non-labor states
Vasodilation of erectile tissues - Starts erection/clitoral engorgement!
how does autonomic (sympathetic) innervation work? key nerve involved?
Sympathetic (Lumbar & Sacral Splanchnic Nerves ~ T12 - L2)
Think "stressful" → fight, hold, push
Contracts sphincters - Holds pee/poop in
Relaxes bladder (detrusor) - Prevents urination
Contracts uterus - Labor contractions or period cramps
Constricts erectile tissue - Involved in ejaculation
Now moving onto the anal triangle,,, what is the The Ischiorectal (Ischioanal) Fossa
Think of this like a fatty triangle of space around the rectum that:
Allows room for expansion when poop moves through
Contains blood vessels and nerves
what are the three stages of poopong? what muscles and nerves are involved?
Innervation to the Rectum and Anal Canal
Let’s break it down step-by-step with the 3 stages of pooping:
The Reflex Begins
When poop enters the rectum from the sigmoid colon → it stretches the wall
This triggers the defecation reflex
Muscles Get Ready
Parasympathetic nerves (pelvic splanchnic from S2–S4) tell:
The sigmoid colon & rectum to contract
The internal anal sphincter to relax
This builds pressure = the urge to poop. But you don’t always go immediately! That’s because your pudendal nerve (somatic) tells:
Puborectalis muscle and external anal sphincter to stay contracted
So you can hold it until a bathroom is nearby
Go Time!
When it’s safe to go, you relax:
Puborectalis
External anal sphincter
💩 = out