AP MACROECONOMICS FINAL MCQ
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
KEEP GOING!!!!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Expenditures Approach
Measures how much is spent in the economy.
Income Approach
Measures how much income is earned.
What does the Income Approach include:
Wages
Rent
Interest
Profit
What is the formula for Expenditure Approach?
GDP = C + I + G + (X − M)
C (Consumption) → household spending
I (Investment) → business spending (factories, machines, new homes)
G (Government) → government spending on goods/services
X − M (Net Exports) → exports minus imports
What is included in the GDP
Final goods and services
New goods
Market transactions
Legal production
What is excluded in the GDP?
Used goods
Financial transactions (stocks, bonds)
Transfer payments (Social Security, welfare)
Illegal activity
Household work (cleaning your own room)
What is Nominal GDP?
Measured using current prices
Inflation can make GDP look bigger even if output didn’t change
What is Real GDP
Adjusted for inflation
Shows true economic growth
Formula for Real GDP
Nominal GDP ÷ Price index × 100
What are the types of Unemployment?
Frictional
Structural
Cyclical
What is Frictional Unemployment?
Between jobs
Normal and healthy
What is Structural Unemployment?
Skills don’t match available jobs
Technology changes
What is Cyclical Unemployment?
Caused by recessions
Only type eliminated when economy improves
What is the Labor Force?
People working or actively looking for work
What is the Unemployment Rate?
% of labor force unemployed
What is the Labor Force Participation Rate?
% of population that is in the labor force
What is a Discouraged Worker?
Gave up looking → not counted as unemployed
What is Underemployed?
Working below skill level or part-time but want full-time
Does the Demand Shift curve move entirely?
Yes
What happens when the Demand Shifts to the Right?
More Demand
What is the result of the Demand Shifting to the Right?
Higher income (normal goods)
More consumers
Price of substitutes rises
Price of complements falls
What happens when the Supply Curve Shifts to the Right?
More Supply
What is the result of the Supply Curve shifting to the Right?
Lower costs
Better technology
Subsidies
More producers
What happens to the Curve when there is a Change in Demand/Supply?
The entire curve shifts
What happens to the curve when there is a Change in Quantity Demanded/Supplied?
There is movement along the curve
What causes a Change in Quantity Demanded/Supplied?
Caused by price change
What causes a Change in Demand/Supply?
Caused by non-price factors
What does the PPC show?
Maximum output with current resources
What does it mean when the Points in a PPC are on the Inside of the Curve?
It is inefficient (unemployment)
What does it mean when the Points in a PPC are on the Outside of the Curve?
It is impossible (right now)
What does it mean when the Points in a PPC are on the On the Curve?
It is efficient
What does an Outwards Shift of the PPC mean?
Economic growth
What does an Inward Shift of the PPC mean?
Loss of resources
What is Absolute Advantage?
Produce more with fewer resources
What is Comparative Advantage?
Lower opportunity cost
What are Gains from Trade?
Specialize in comparative advantage
Trade benefits both parties
What does it mean when the AD shifts to the Right?
More spending
What does it mean when the AD shifts to the Left?
Less spending
What does it mean when the SRAS shifts to the Right?
Lower production costs
What does it mean when the SRAS shifts to the Left?
Higher production costs
Is LRAS vertical?
Yes (it is vertical)
What causes the LRAS to Shift?
Technology
Resources
Education/productivity
During a Recessionary Gap what happens to the Short Run Aggregate Supply (SRAS) when Wages Fall?
SRAS shifts right
During an Inflationary Gap what happens when Wages Rise?
SRAS shifts left
During a Recessionary Gap is the potential GDP greater than the Output (Reap GDP)?
Yes (Output < potential GDP)
During an Inflationary Gap is the Output greater than the Potential GDP?
Yes (Output > potential GDP)
What happens to the Fiscal Policy during a Recession?
Increase government spending
Cut taxes
What happens to the Fiscal Policy during a Inflation?
Decrease government spending
Raise taxes
What are Substitute Goods?
Used instead of each other
Price ↑ of A → demand ↑ for B
What are Complementary Goods?
Used together
Price ↑ of A → demand ↓ for B
What does the CPI Measure?
Inflation
Cost of living
What are the Problems with CPI?
Substitution bias
Quality changes
New goods
What is MPC (Marginal Propensity to Consume)?
% of extra income spent
What is MPS (Marginal Propensity to Save)?
% saved
What is the formula for the Spending Multiplier?
1 ÷ (1 − MPC)
MPC + MPS = ?
1
What is Stagflation caused by?
Caused by negative supply shocks
What is Stagflation?
High inflation
High unemployment
Low growth
What is Supply Shock?
Sudden change in production costs
Shifts SRAS
Example: oil price spike
What Shifts the SRAS?
Supply Shock
What is Demand Shock?
Sudden change in AD
Caused by panic, stimulus, crashes
Supply Shocks are for Shifting what?
SRAS shifting
Demand Shocks are for Shifting what?
AD shifting
What is the Formula for GDP (Expenditures Approach)?
GDP=C+I+G+(X−M)
What is the Formula for GDP (Income Approach)?
GDP=Wages + Rent + Interest + Profit
What is the Formula for Real GDP?
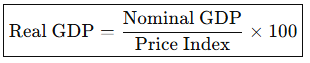
What is the Formula for Inflation Rate?
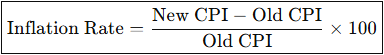
What is the Formula for Unemployment Rate?
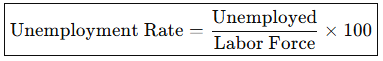
What is the Formula for Labor Force Participation Rate?
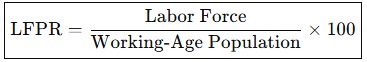
What is the Formula for Real Wage?
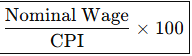
What is the Formula for Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)?
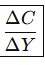
What is the Formula for Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS)?
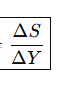
What is the Formula for MPC & MPS Relationship?
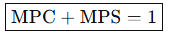
What is the Formula for Spending Multiplier?

What is the Formula for Tax Multiplier?
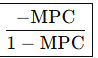
What is the Formula for Change in GDP (Spending)?

What is the Change in GDP (Taxes)?
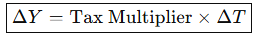
What is the Formula for Net Exports?
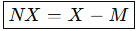
X
Exports
M
Imports
ΔC
change in consumption
ΔY
change in income
ΔS
change in savings
ΔY
change in GDP
ΔG
change in government spending
ΔT
change in taxes