Organic & Analysis
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
how does the carbon-halogen bond enthalpy influence the rate of reaction?
weaker bond enthalpy = faster rate of reaction
catalytic cracking products
aromatic hydrocarbons and motor fuels
carboxylic acid test
add Na2CO3, bubble through limewater
thermal cracking products
lots of alkenes
conditions for elimination
hot and dissolved in ethanol, concentrated
why do major products form the most?
a tertiary carbocation has more alkyl groups that stabilise the carbocation with a positive inductive effect, so they tend to form in larger quantities
conditions for fermentation
presence of yeast
anaerobic
25 - 42 degrees C
PVC uses
usually used for drain pipes. if plasticisers are added they keep the hydrocarbon chains further apart weakening the van der waals between chains making the molecule more flexible so they slide easily over each other
test for unsaturation
shake with bromine water, brown → colourless
why are addition polymers unreactive?
strong C-H and C-C bonds, is non-polar
acidified K2Cr2O7 + 1°/ 2°/ 3°
1° orange → green aldehyde R−CH=O group. excess dichromate + heat under reflux → carboxylic acid
2° orange → green ketone C=O group
3° no change
aldehydes orange → green
Tollen’s test
1° + K2Cr2O7 → aldehyde
aldehyde + Tollen’s colourless → silver mirror
Fehling’s test
1° + K2CrO7 → aldehyde
aldehyde + Fehling’s blue → brick red
ethene → ethanol catalyst?
hot sulfuric acid
are alcohols soluble?
shorter chain alcohols are because the H bonding dominates, longer chain alcohols aren’t because the non-polar chain dominates
molecular ion definition
the molecule with a single positive charge
more vibrations → ?
more IR absorbed → warmer earth (more is remitted)
nucleophilic substitution conditions
warm, aqueous, (excess ammonia)
electrophilic addition conditions
warm, aqueous, ethanol
OH peak
narrower and rounder for alcohols, broader in carboxylic acids
N—H peak
quite a shallow peak, near OH peak. NH2 will fork due to 2 NH bonds having slightly different wavenumber
C=O peak
very sharp peak near 1730
structural isomerism
same molecular different structural formula
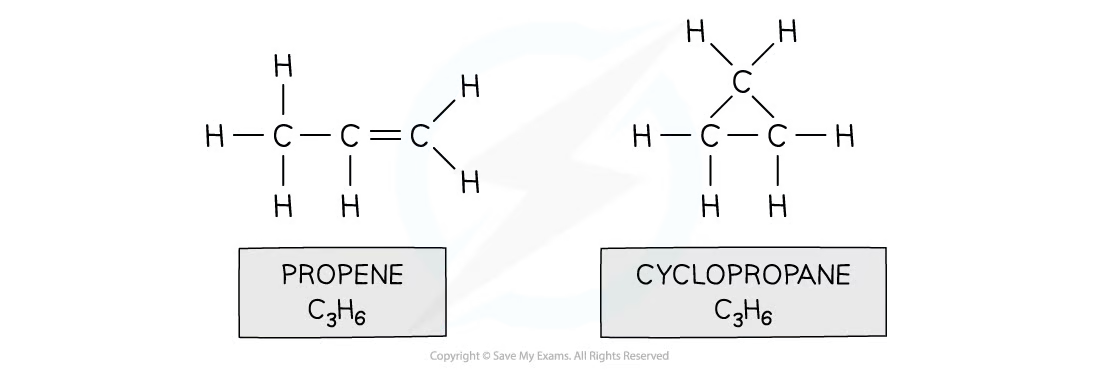
chain isomerism
same molecular formula different longest chain length due to branching
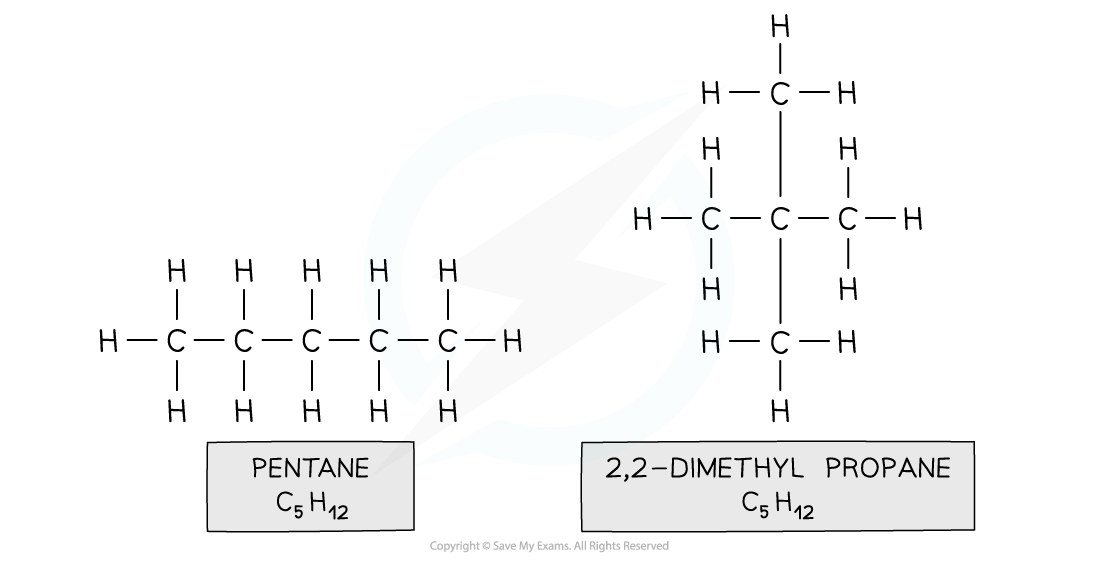
positional isomerism
different position of a functional group on each isomer
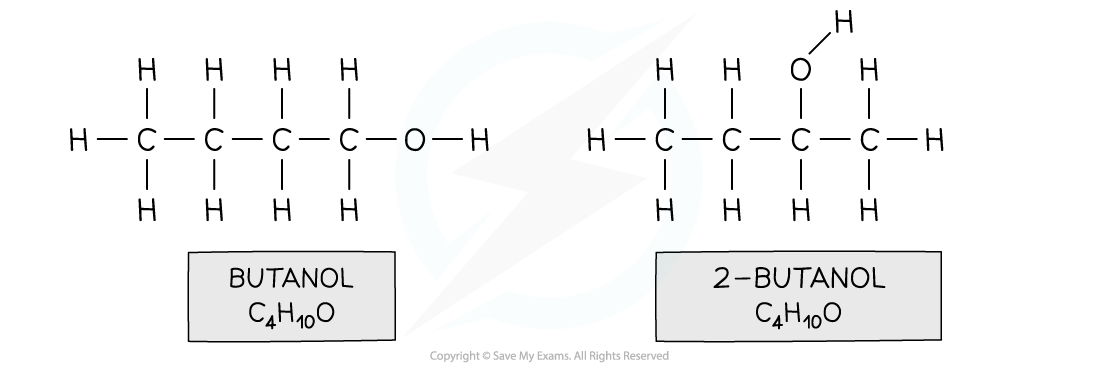
functional group isomerism
same molecular formula different functional group

stereoisomerism
same molecular formula different arrangement of atoms in space