Blood Vessels
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Blood flow
Heart to arteries to arterioles to blood capillaries to venues to veins
How do red blood cells travel in capillaries?
Single file line
Capillaries
Structure: Thin walls
Function: Gas exchange
Capillary beds
Network of interconnected capillaries
What exists in the middle of blood vessels?
Lumen
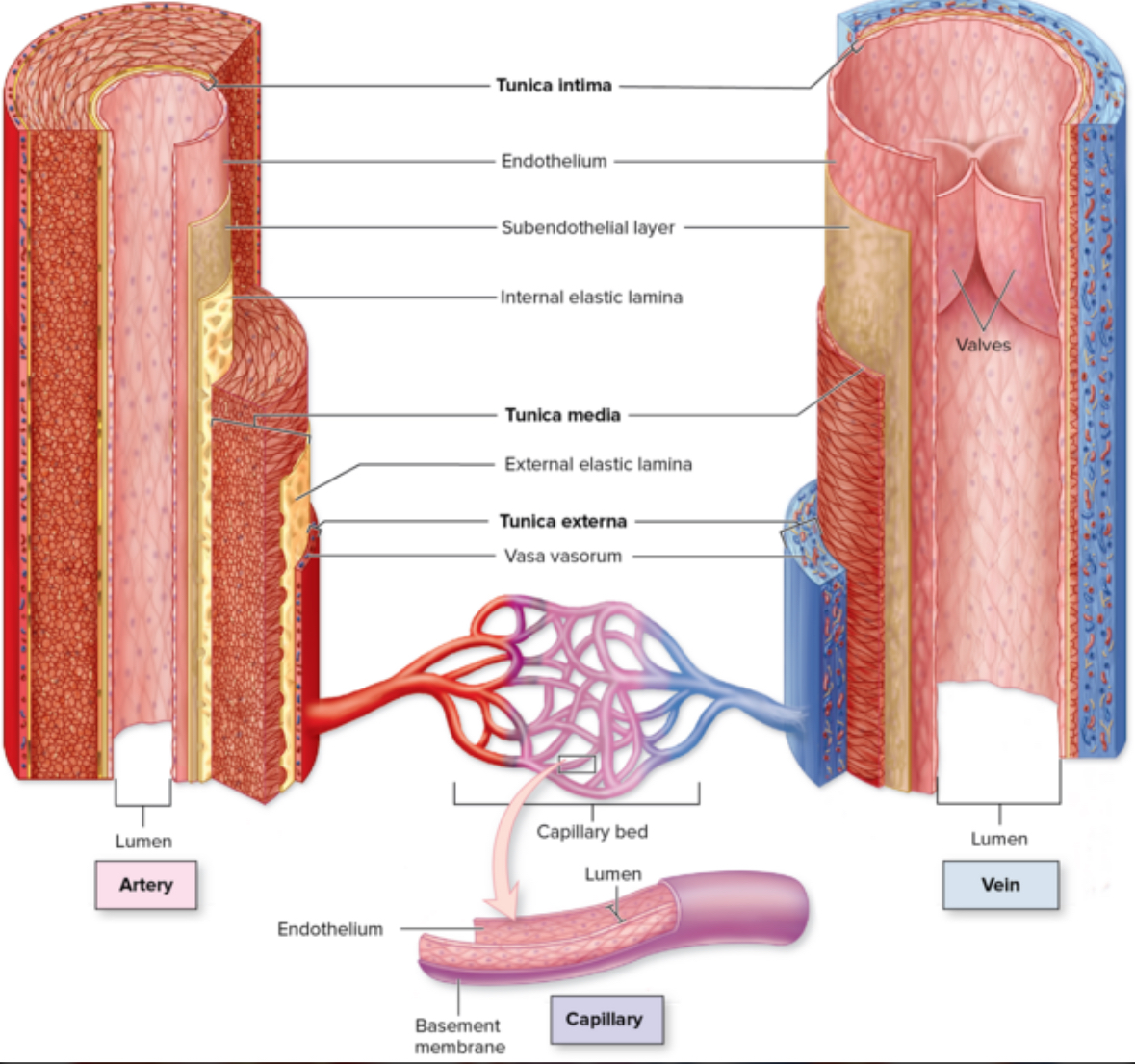
3 layers of vessels
Tunica intima
Tunica media
Tunica externa
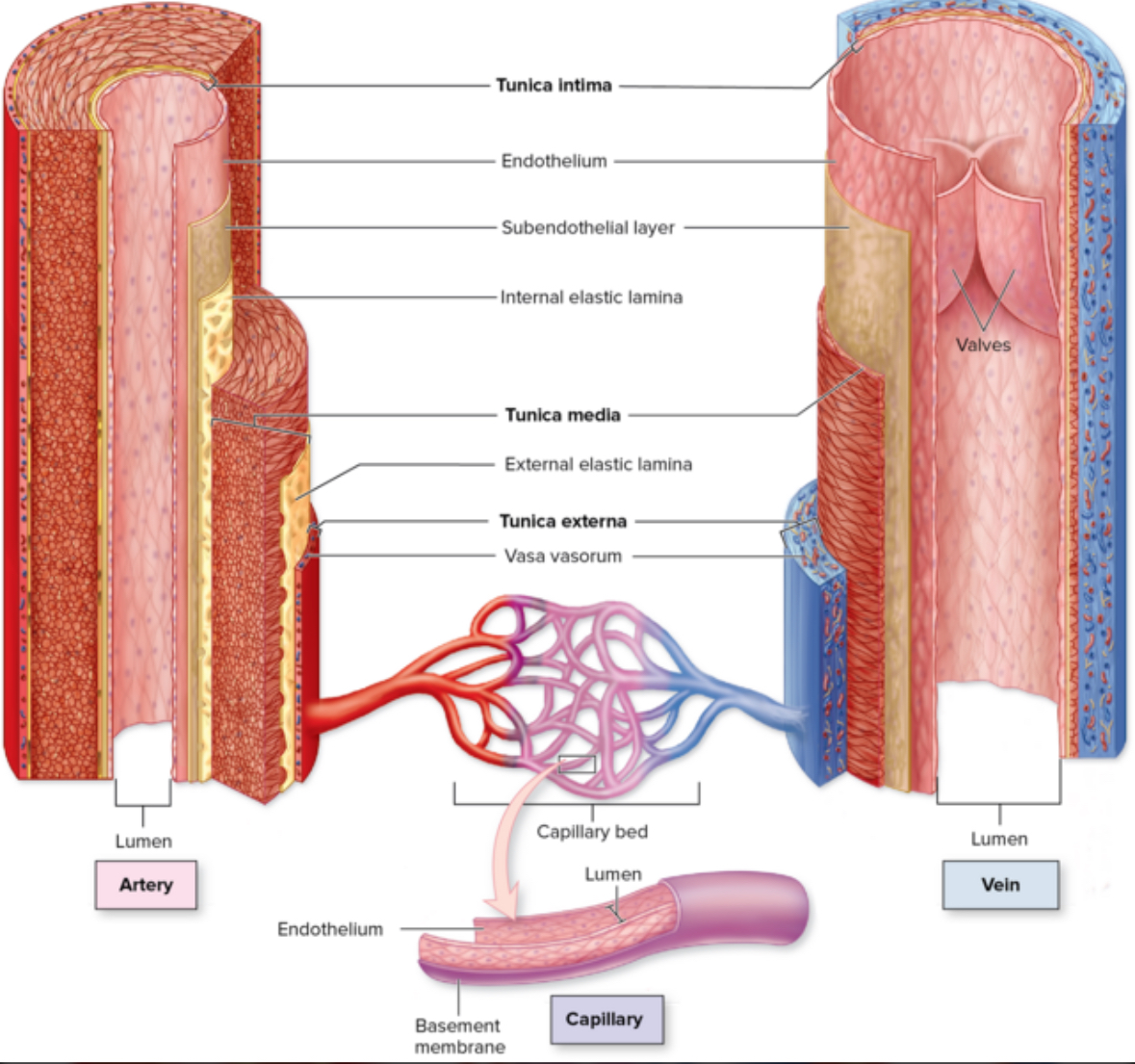
Turnica intima
Structure:
4 sublayers:
Endothelium
Basement membrane
Subendothelial layer
Internal elastic lamina
Location: closest to lumen. Inner most layer.
Endothelium
Structure: simple squamous ET
Function: secrete vasodilators and vasoconstrictors
Basement membrane
Function: connect endothelium layer to subendothelial layer
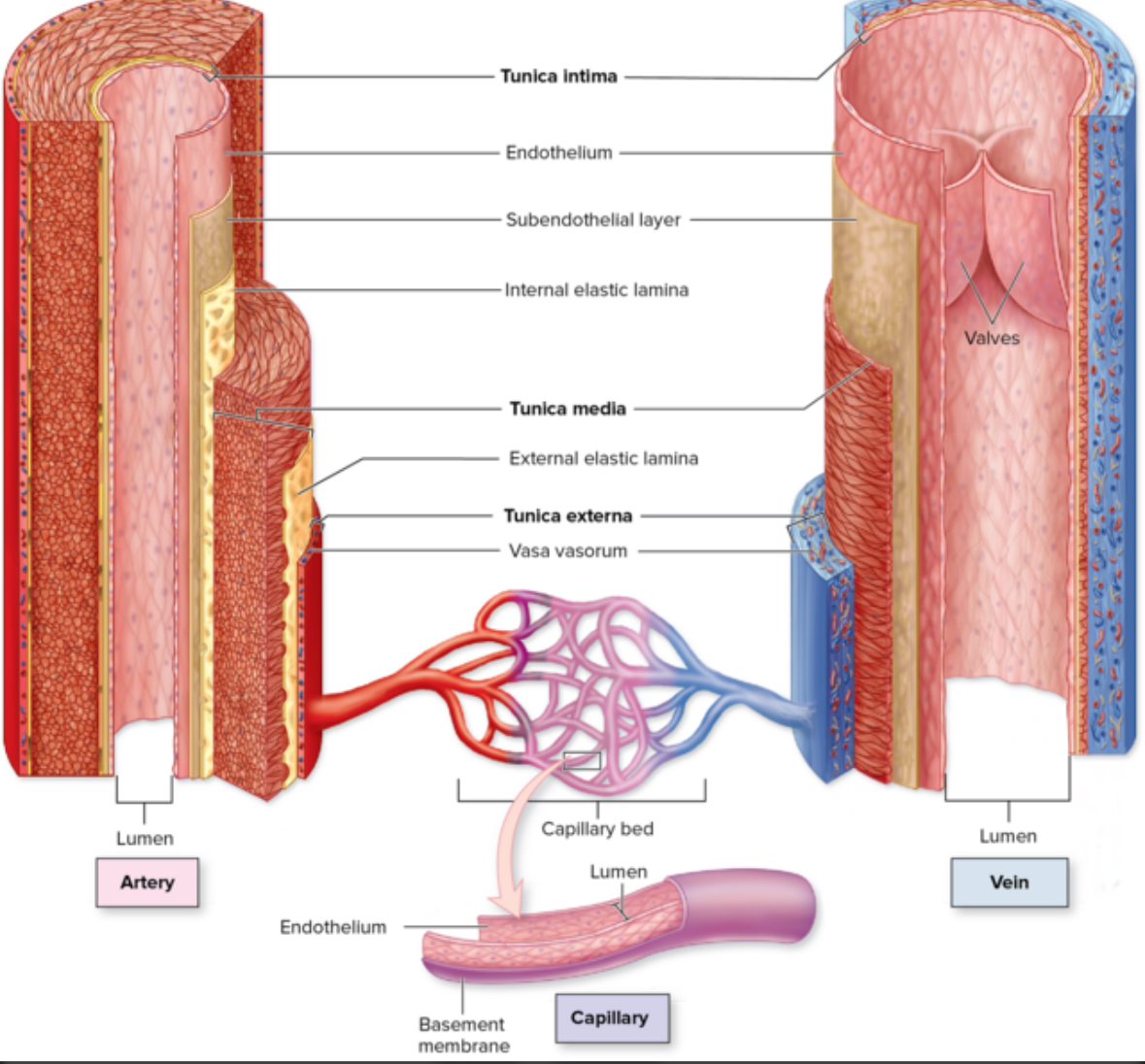
Subendothelial layer
Structure: areolar CT
Location: turnica intima layer between the basement membrane and the internal elastic lamina
Function: metabolic support
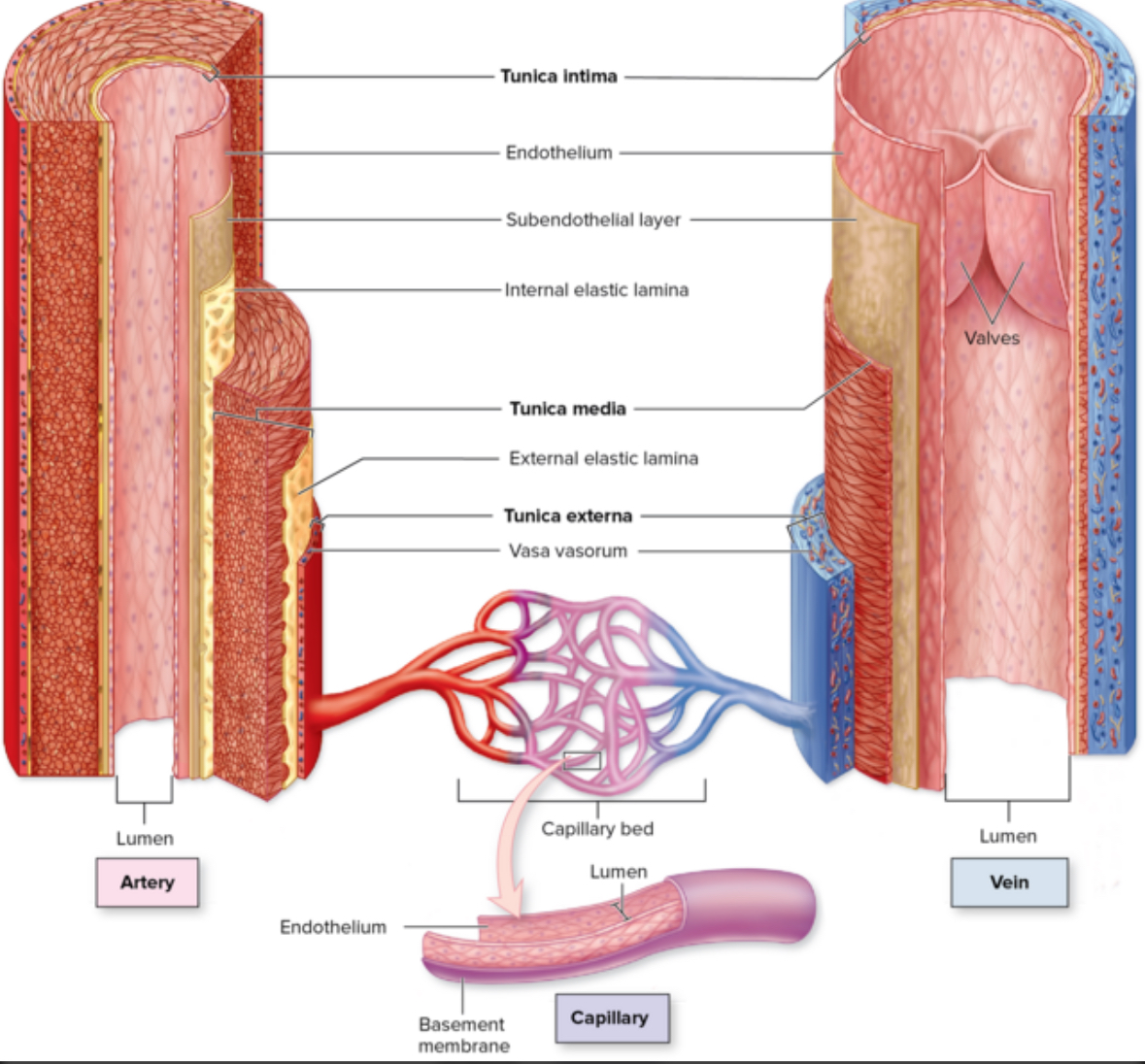
Internal elastic laminate
Structure: looks like Swiss cheese. Elastic fibers
Location: most superficial layer in the trunica intima layer
Function: contributes to elasticity of blood vessel. Stretch and recoil.
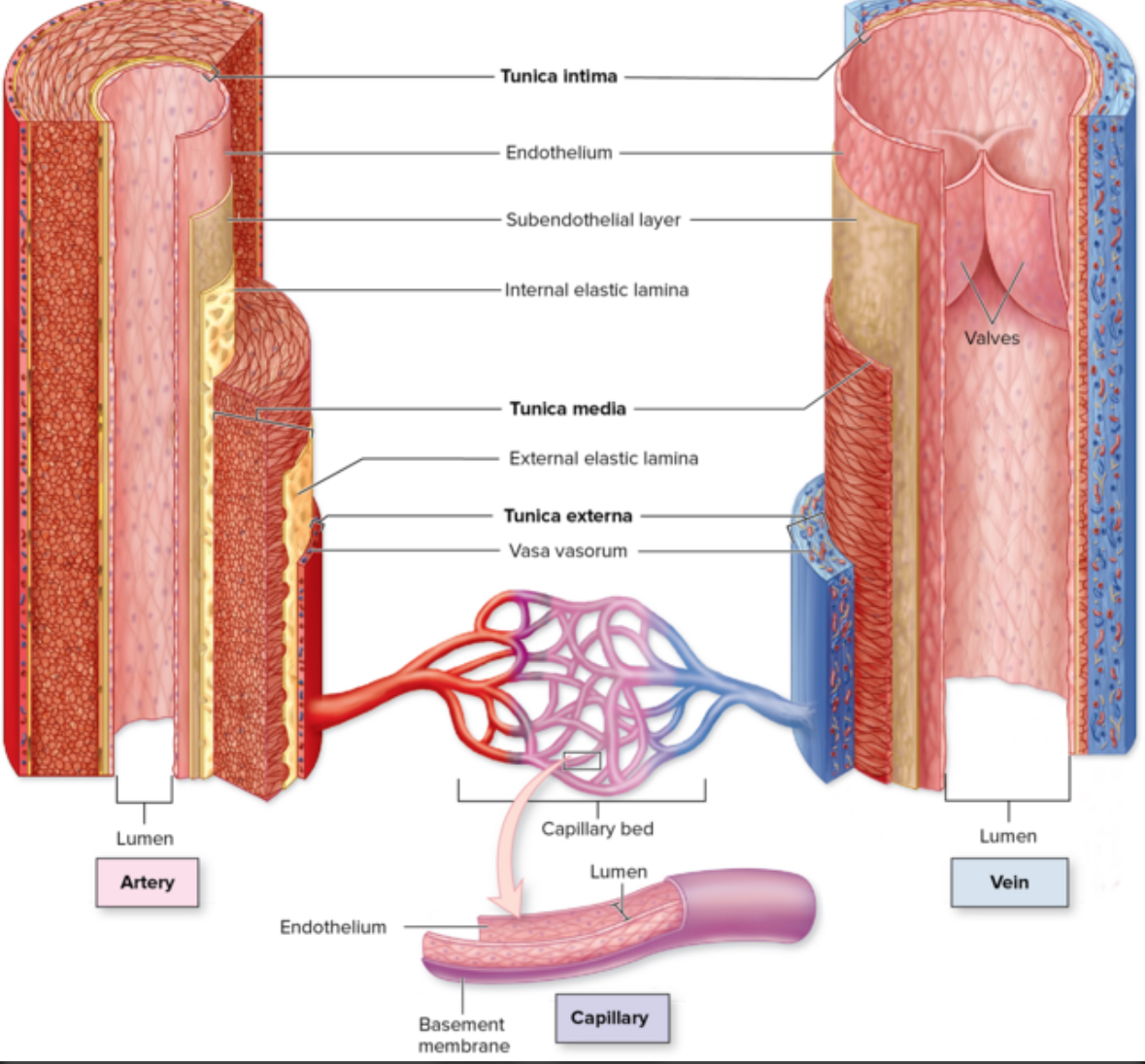
Turnica media
Structure: smooth muscle tissue
Location: middle layer of blood vessel
Function: vasoconstriction and vasodilation. Sphincter.
External elastic lamina
Structure: elastic fibers
Location: the layer between the turnica media and turnica externa
Function: provides elasticity, stretch, and recoil
Turnica externa
Structure: areolar connective tissue and dense irregular connective tissue
Location: most superficial layer of blood vessels
Function: metabolic and structural support, and anchor blood vessels to surrounding tissues and organs
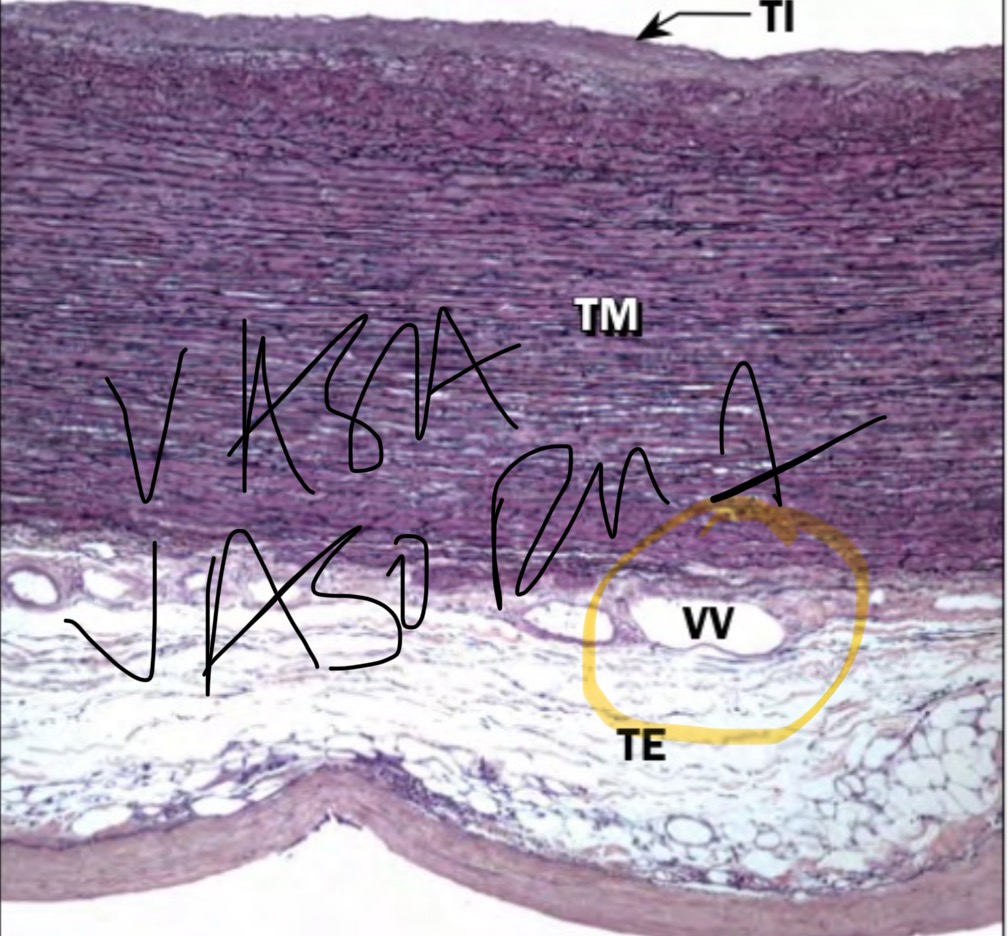
Vasa vasorum
Structure: blood vessels, capillaries
Location: found in the turnica externa layer
Function: provide metabolic support to large blood vessels
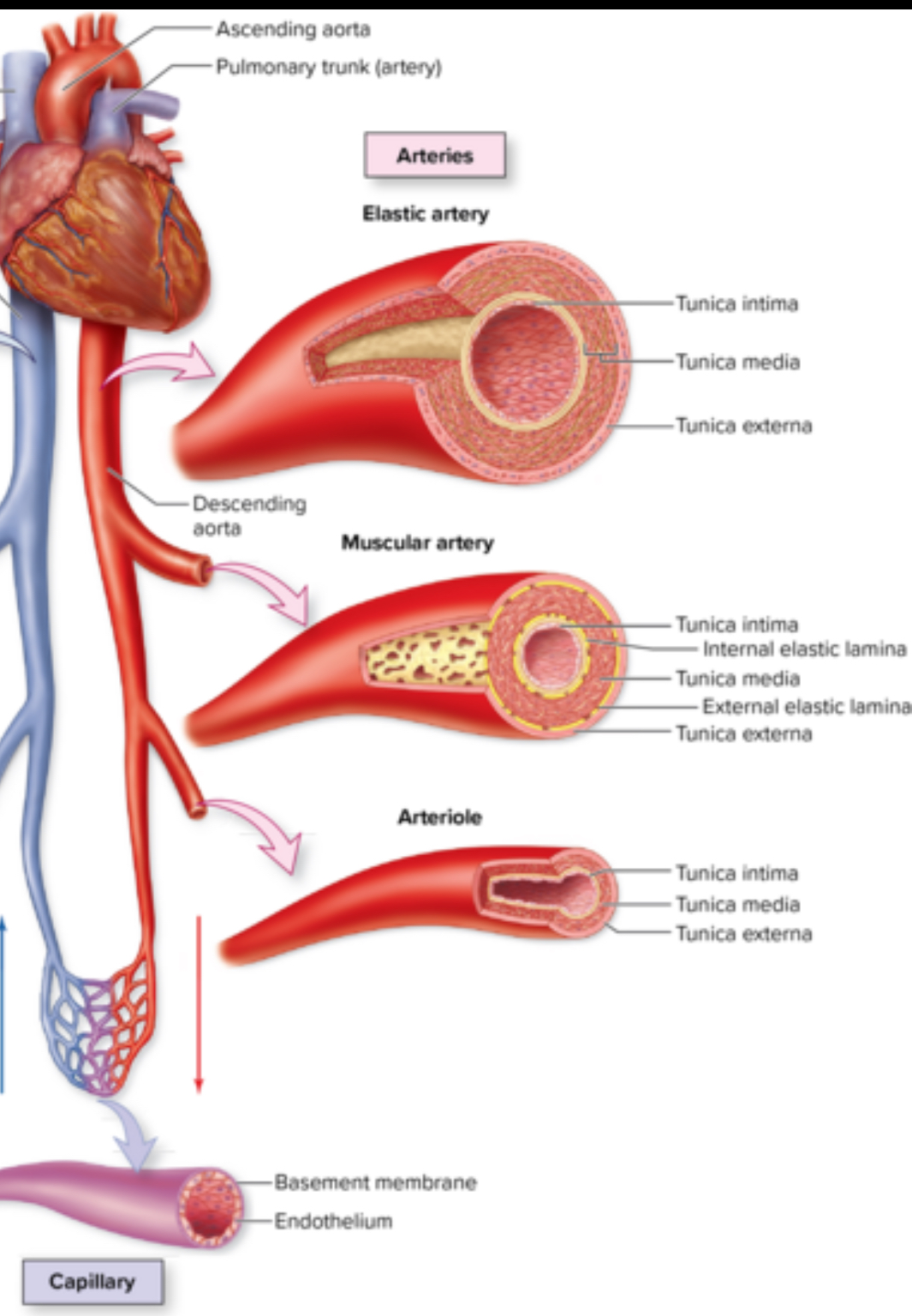
2 types of arteries
Elastic arteries
Muscular arteries
Elastic artery
Structure: lots of elastic fibers especially in tunica media. Largest arteries. AKA conducting arteries. Able to withstand strong pulsations of ejected blood
Location: aorta, pulmonary, brachiocephalic
Function: conduct blood away from the heart to smaller muscular arteries
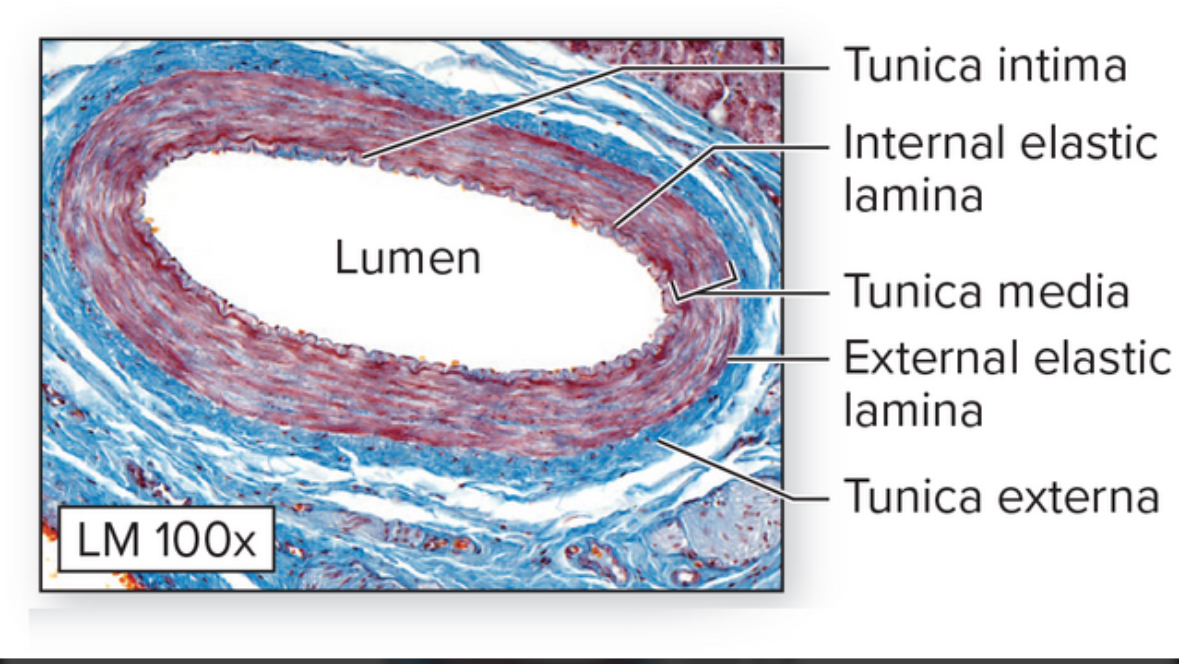
Muscular arteries
Structure: AKA distributing arteries. Thicker tunica media composed of smooth muscle tissue
Location: brachial, anterior tibial, coronary, and inferior mesenteric arteries
Function: most effective vasoconstriction and vasodilation
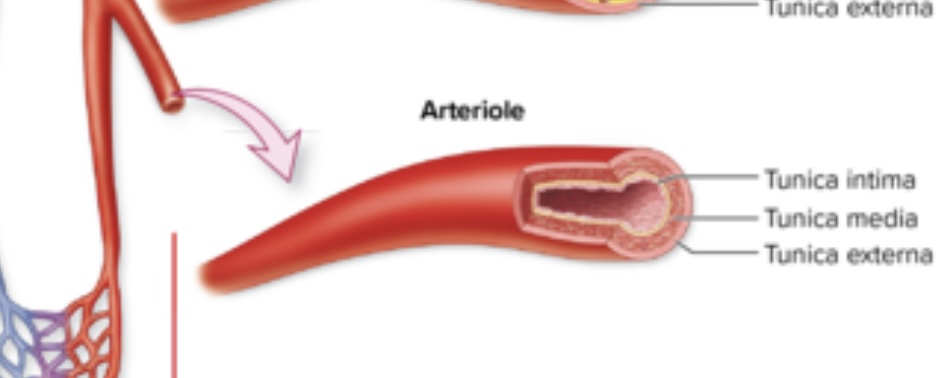
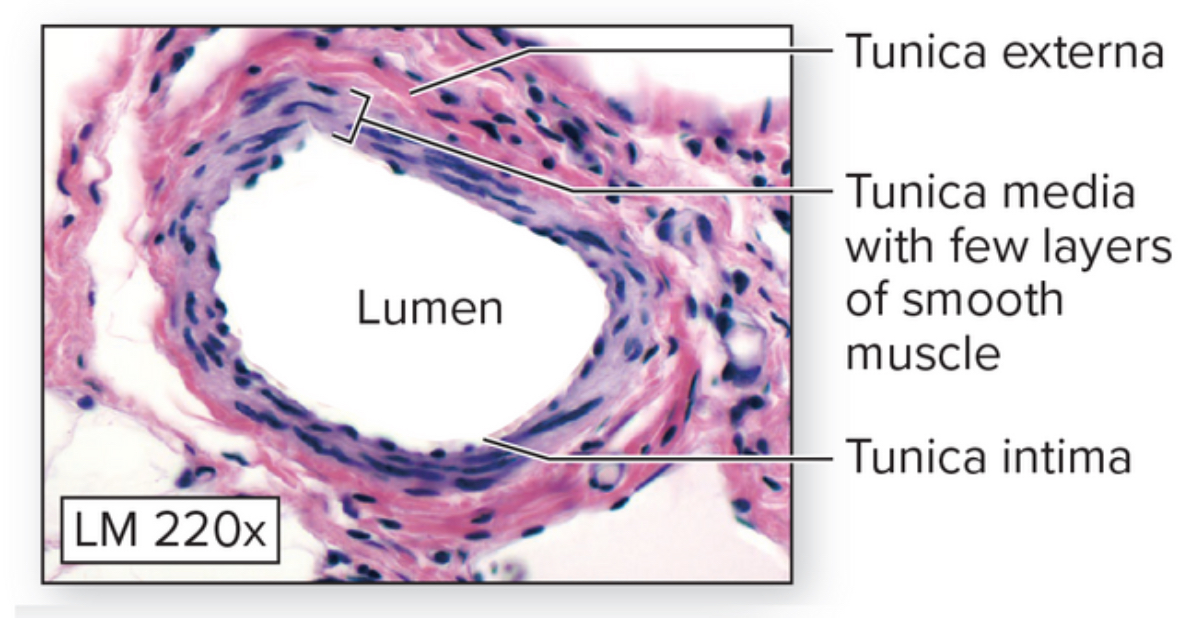
Arterioles
Structure: Smallest arteries. Lack elastic laminae. Well innervated. Sympathetic innervation controls vasoconstriction.
Location: throughout the body
Function: control blood flow
How do arterioles contribute to blood flow during exercise?
Arterioles dilate in the active skeletal muscles and constrict in less active and nonessential organs such as the digestive organs
Venules
Structure: No elastic laminae. Larger lumen and thinner walls than arterioles. Porous. Some have valves..
Location: throughout the body
Function: store more blood
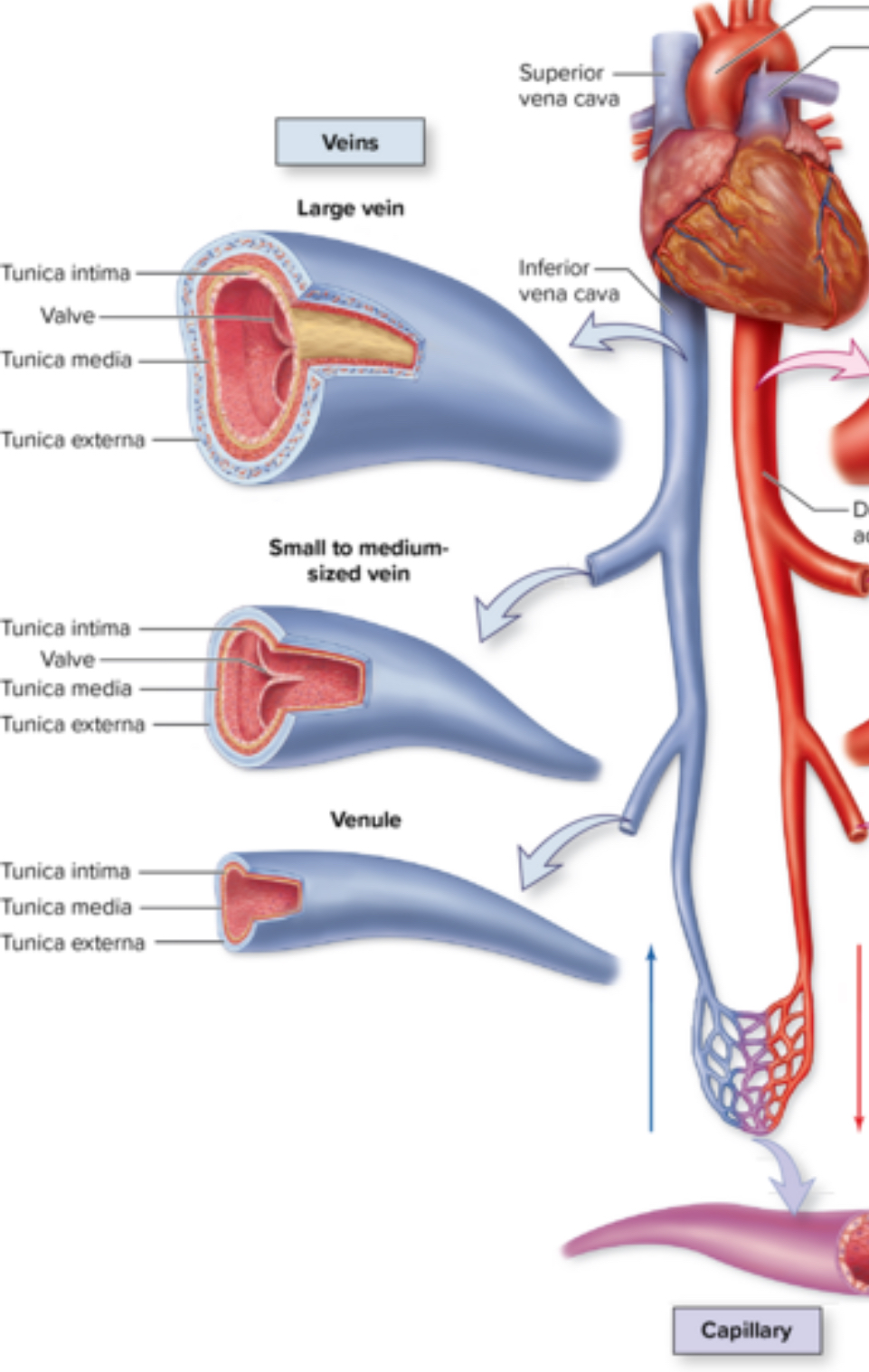
Veins
Structure: larger lumen. Store more blood. Thinner walls. Blood pressure is reduced.
Location: throughout the body
Function: drain capillaries and return blood to the heart
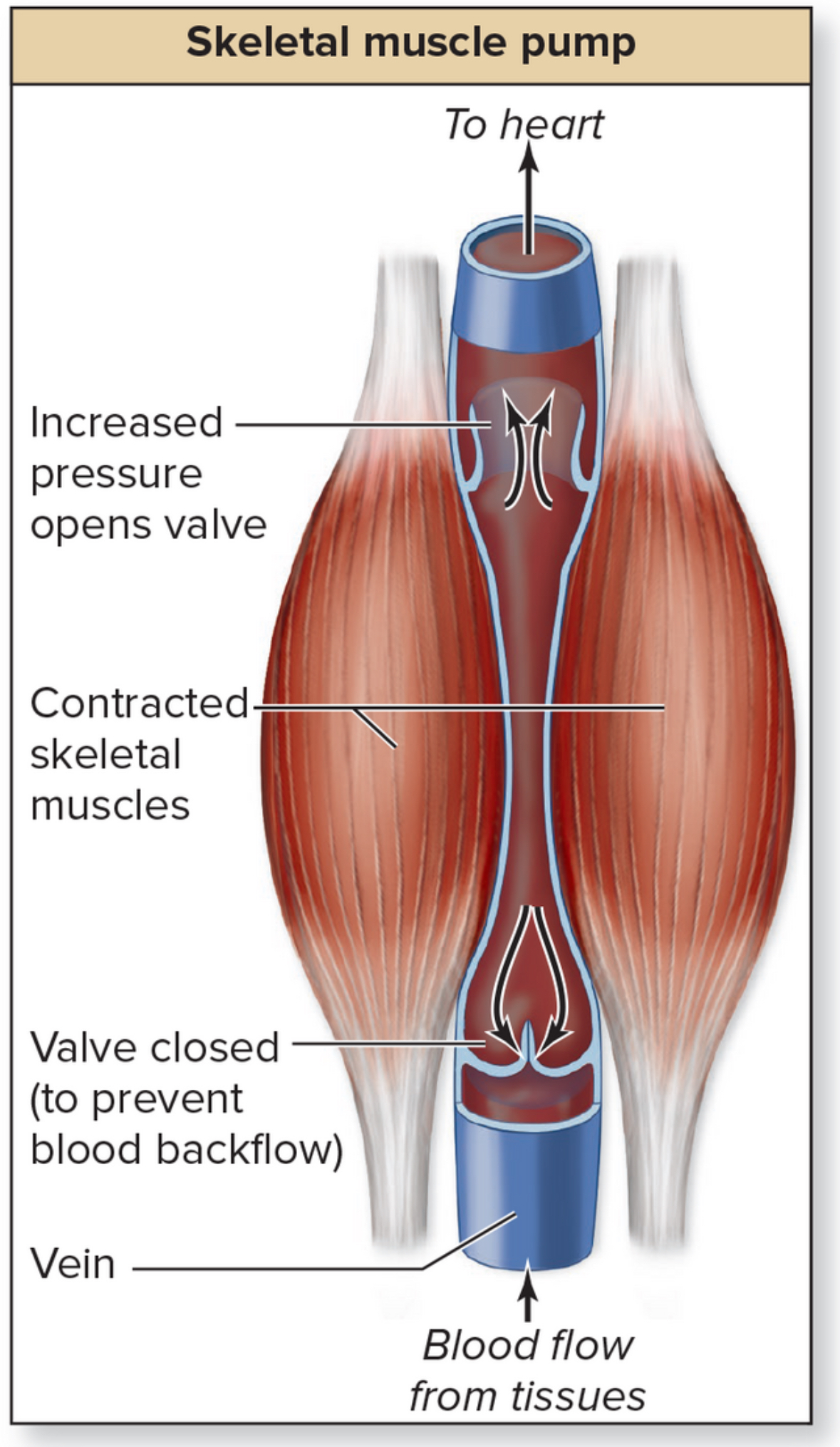
Venous valves
Structure: composed of tunica intima and strengthened by elastic and collagen fibers. Fold to create semilunar valve leaflets. As muscle contracts, blood is squeezed up the vein
Location: inside veins. More prominent in lower limbs because blood is farther from the heart and close to the ground
Function: maintain one way blood flow. Unidirectional.
What happens when valves fail?
Blood pools and dilates.
Varicose veins
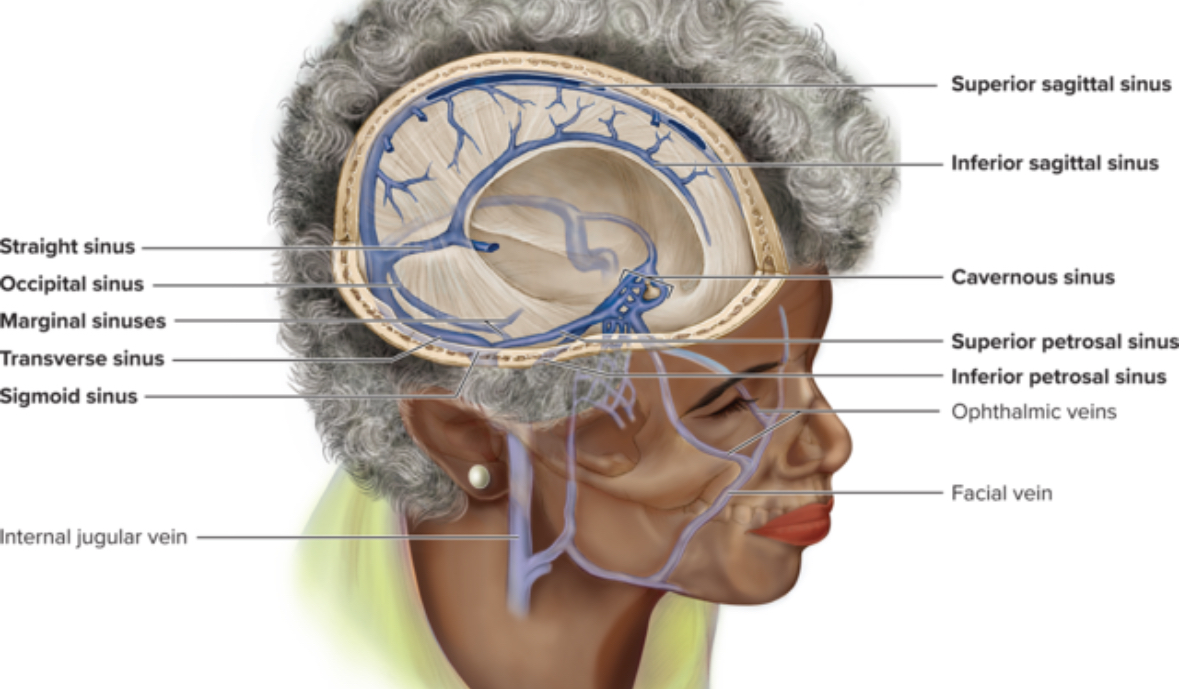
Venous sinuses
Structure: lack tunica media layer. Not capable of vasoconstriction or validity. Irregular lumen
Location: cranial cavity. Coronary sinus, superior sagittal sinus
Function: drain deoxygenated blood from the brain
Capillaries
Structure: smallest blood vessel. Erythrocytes must travel single file inside. Very thin. Composed of tunica intima only with 2 sublayers, endothelium and basement membrane. Simple squamous ET. Leaky. Things can go though very fast.
Location: connect arterioles to venules
Function: gas exchange
Intercellular cleft
Gaps between cells that cause leaks
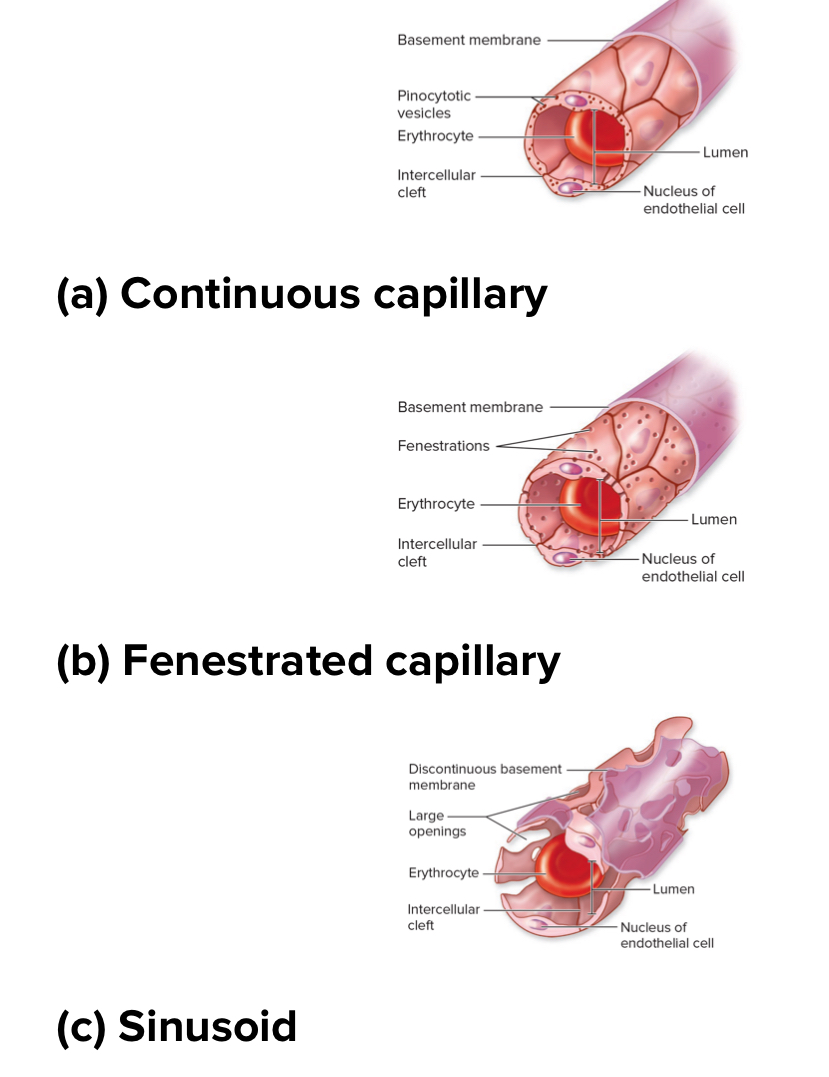
3 types of capillaries based on how leaky
Continuous capillaries
Fenestrated capillaries
Sinusoid capillaries
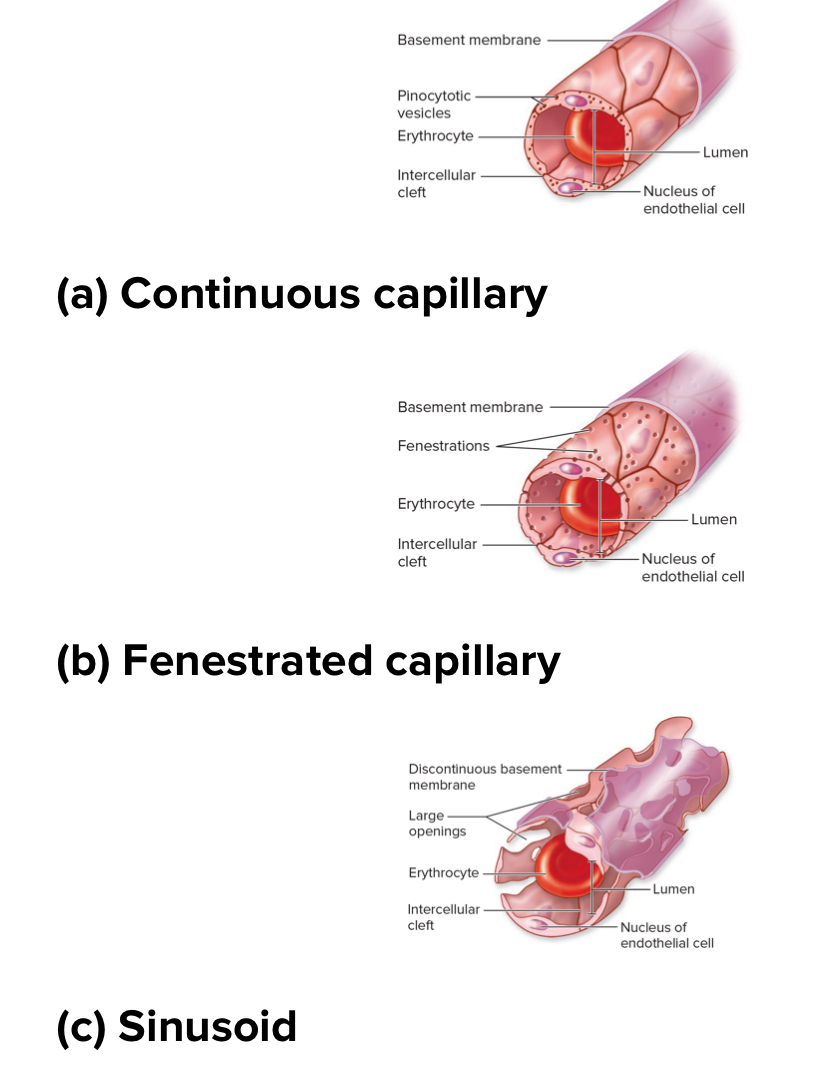
Continuous capillaries
Structure: least leaky. Basement membrane is intact. No holes or gaps. Really small intercellular clefts. Most common. Have tight junctions between cells.
Location: found in the brain. Skeletal muscle, and skin
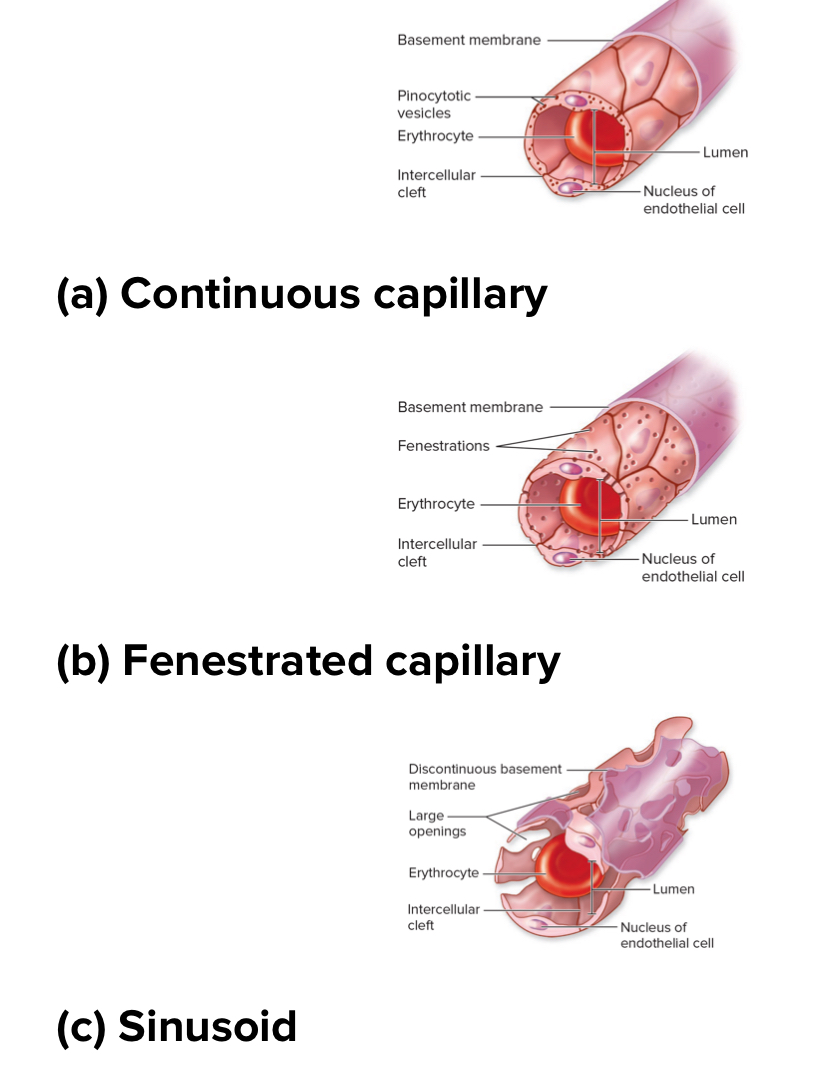
Fenestrated capillaries
Structure: middle for leakiness. Basement membrane is continuous but has fenestrations or pores within endothelial cells .
Location: kidneys, small intestine, endocrine glands
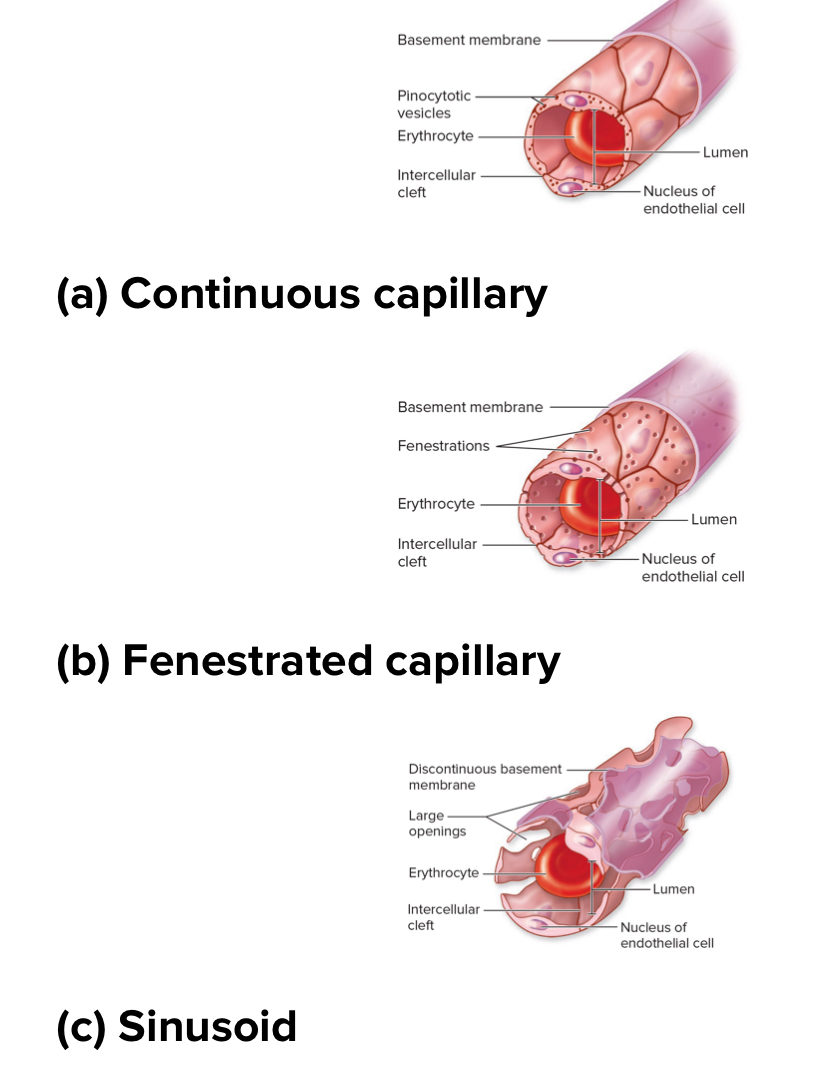
Sinusoidal capillaries
Structure: most leaky. Intercellular clefts large. Basement membrane discontinuous. Large fenestrations. Larger and wider.
Location: liver, red bone marrow, spleen
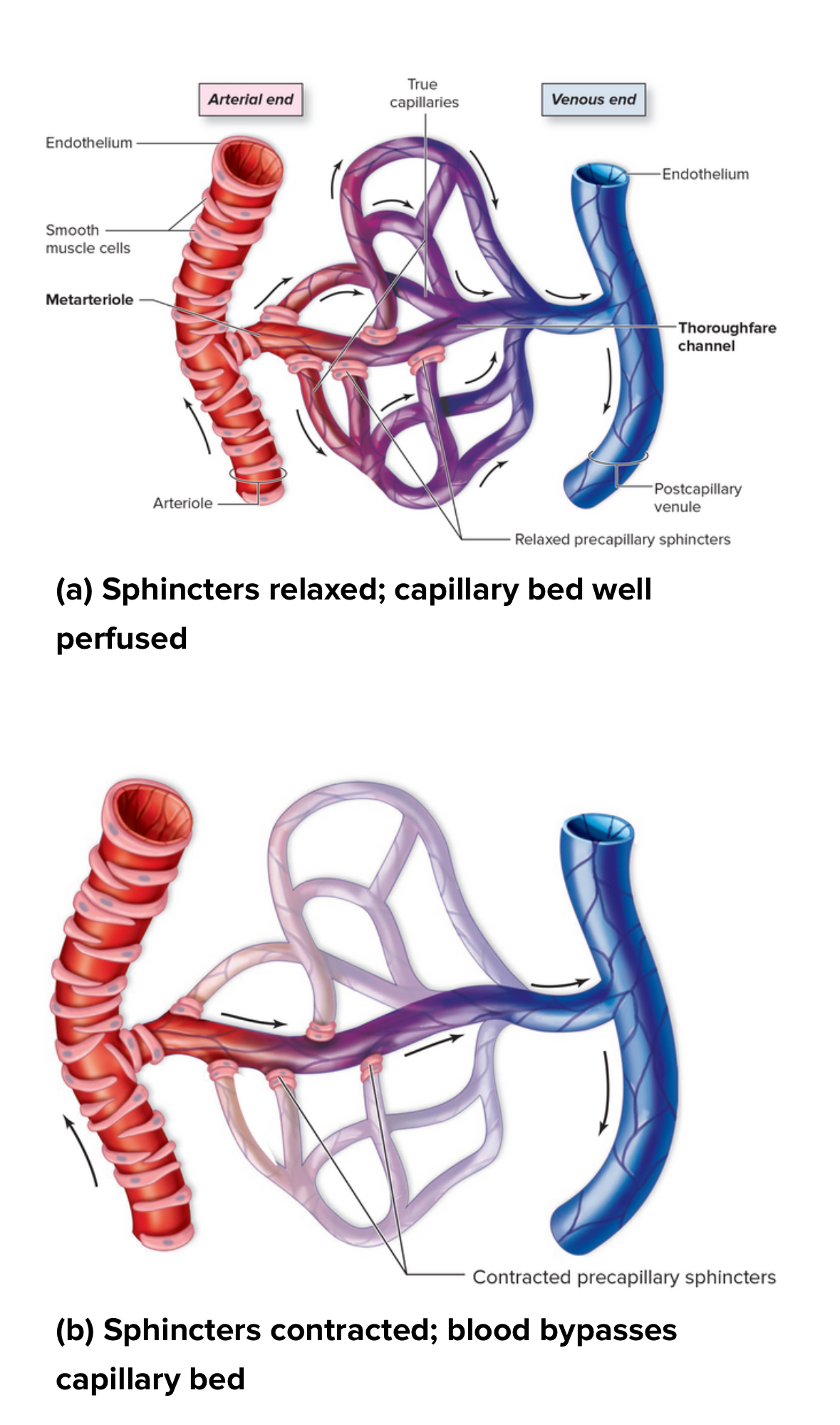
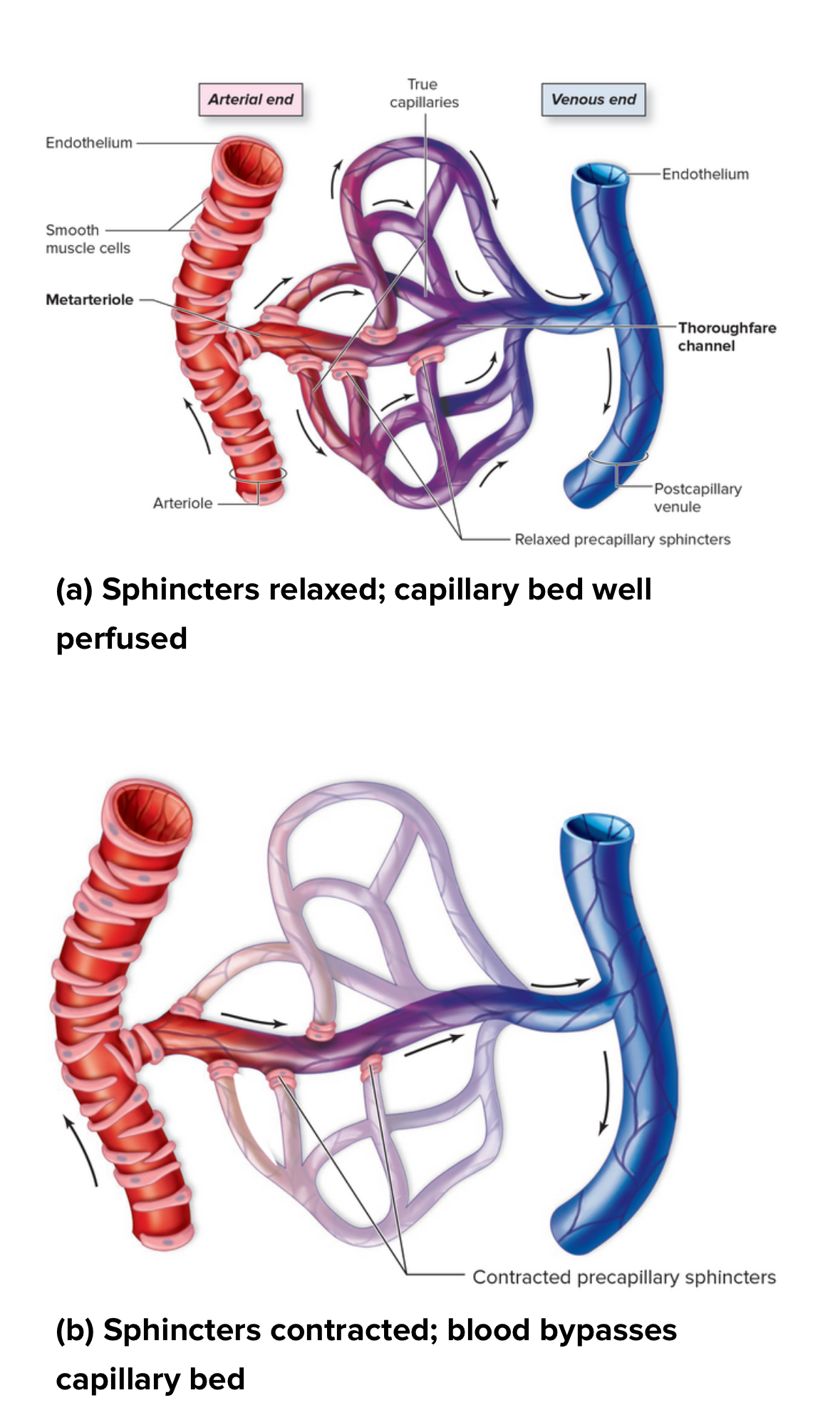
Capillary bed
Structure: Network of capillaries between an arteriolr and a Venice. May contain precapillary sphincters
Function: regulates blood flow into capillaries
Portal system
2 capillary beds between arteries and veins
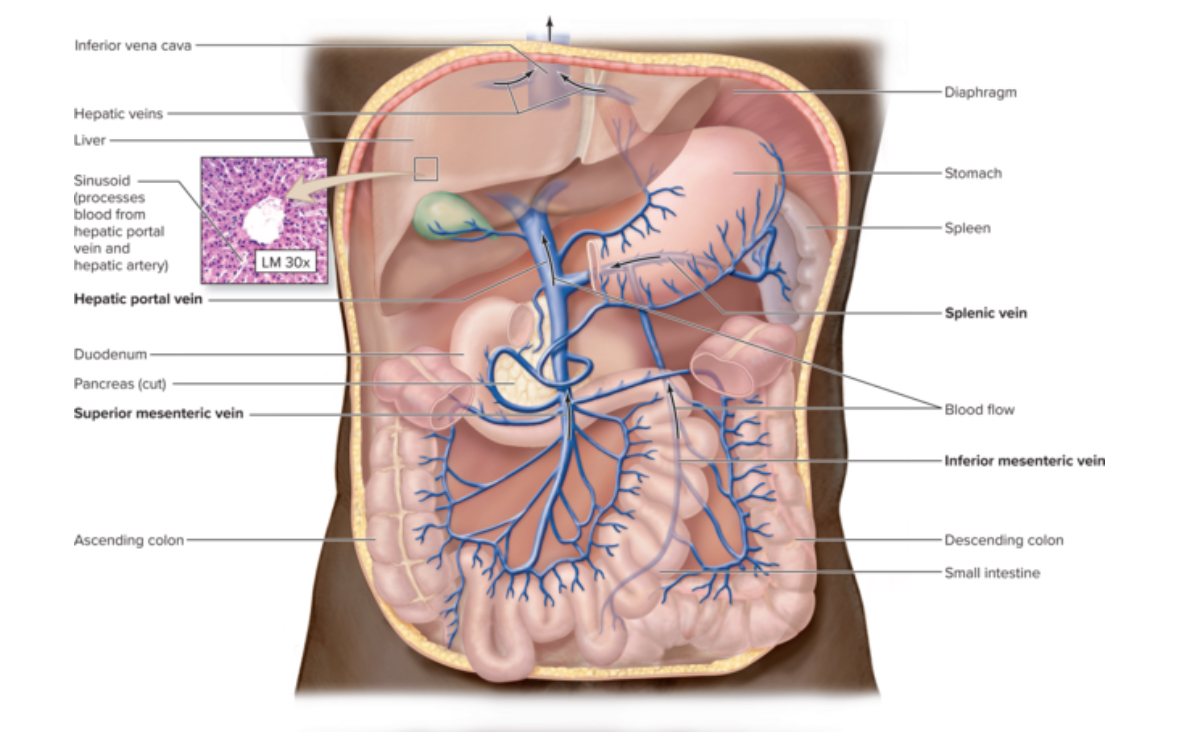
Hepatic portal system
Structure: part of the circulatory system. Main vessel is the hepatic portal vein.
Location: digestive tract
Function: nutrient processing, detoxification, bacterial clearance
What type of blood does the hepatic portal vein carry?
O2 poor dirty blood
What type of blood does the hepatic vein carry?
O2 poor clean blood
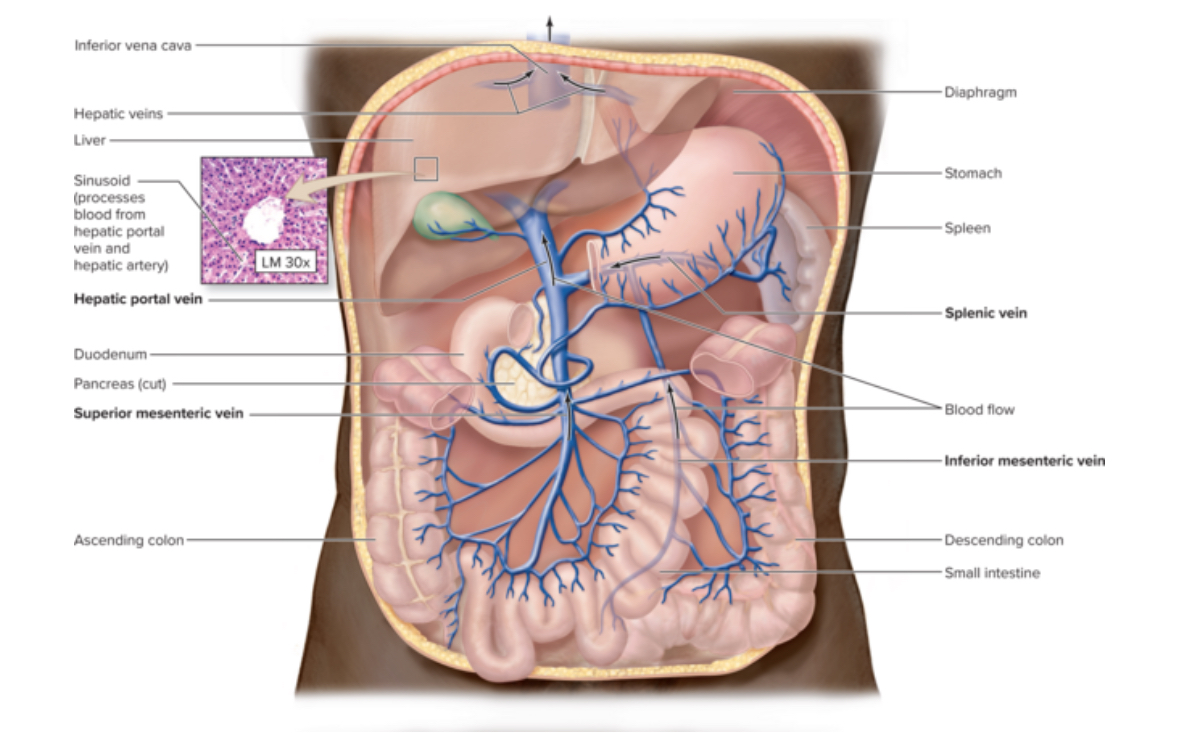
Blood flow in the Hepatic portal system
Left ventricle to aorta to hepatic artery to liver to hepatic vein to inferior vena cava to right atrium
Capillaries of digestive system
Stomach
Intestines
Pancreas
Spleen
Other option for blood flow
Left ventricle to aorta to arteries if abdominal organs to hepatic portal vein to liver to hepatic vein to inferior vena cava