LC Geography General Terms
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
1
New cards
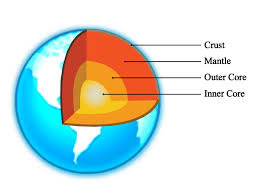
Earth's structure
inner core, outer core, mantle, crust
2
New cards
The core
centre of the earth.
inner core- solid sphere of metals under severe pressure.
outer core- completely molten due to intense heat.
inner core- solid sphere of metals under severe pressure.
outer core- completely molten due to intense heat.
3
New cards
The mantle
75% volume of the earth
4
New cards
Asthenosphere
The soft layer of the mantle on which the tectonic plates move
5
New cards
Lithosphere
A rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust.
6
New cards
Moho
boundary between crust and mantle
7
New cards
Crust
Earth's outermost layer.
8
New cards
Continental crust
The portion of the earth's crust that primarily contains granite.
SIAL
SIAL
9
New cards
Oceanic Crust
the portion of Earth's crust that is usually below the oceans.
SIMA
SIMA
10
New cards
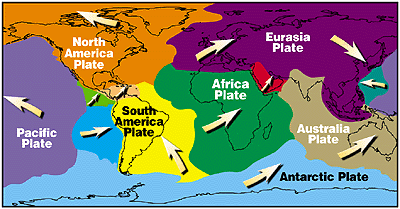
Plate tectonics
A theory stating that the earth's surface is broken into plates that move.
11
New cards
7 major plates
North American, South American, Pacific, African, Eurasian, Indo-Australian, and Antartic
12
New cards
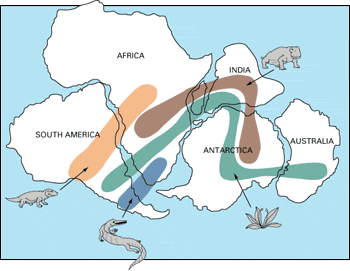
continental drift
The hypothesis that states that the continents once formed a single landmass (Pangaea), broke up, and drifted to their present locations
13
New cards
Convection Currents
Circular currents in the mantle caused by the magma being heated by the core off the Earth.
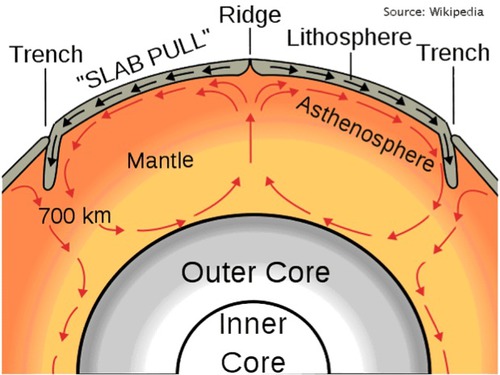
14
New cards
Mid ocean ridge
An underwater moutain chain where new ocean floor is formed
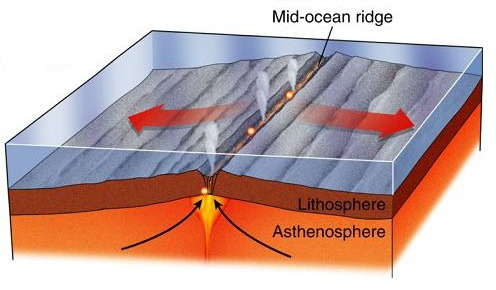
15
New cards
Sea floor spreading
The process by which molten material adds new oceanic crust to the ocean floor
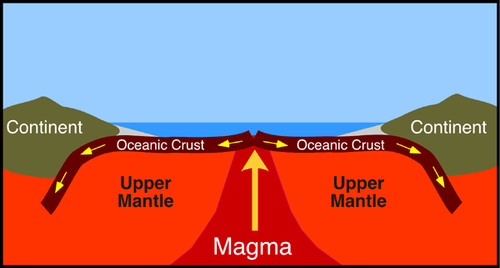
16
New cards
Subduction
When the heavier plate in a collision sinks below the lighter one back into the mantle.
17
New cards
Slab pull
the pulling of a tectonic plate as its edge subducts deep into the mantle
18
New cards
Plate separation
(divergent) (constructive)
(divergent) (constructive)
When plates move away from each other because molten magma rises to the surface.
-mid ocean ridges
-volcanic mts.
-volcanic islands ( Tenerife and Iceland)
- Rift Valley (Eastern Africa)
Eg. North American and Eurasian Plate.
-mid ocean ridges
-volcanic mts.
-volcanic islands ( Tenerife and Iceland)
- Rift Valley (Eastern Africa)
Eg. North American and Eurasian Plate.
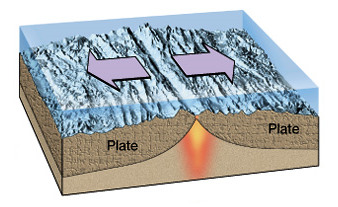
19
New cards
Plate collision (convergent) (destructive)
Oceanic to oceanic - tsunami, earthquake, trench, volcanic island (Nasca and Pacific Plate)
oceanic to continental-tsunami, earthquake, trench, fold mts,volcanic mts. (Nasca and South American Plate)
continental to continental-earthquakes and fold mountains (Himalayan Mts.) (Eurasian and Indo Australian Plate).
oceanic to continental-tsunami, earthquake, trench, fold mts,volcanic mts. (Nasca and South American Plate)
continental to continental-earthquakes and fold mountains (Himalayan Mts.) (Eurasian and Indo Australian Plate).
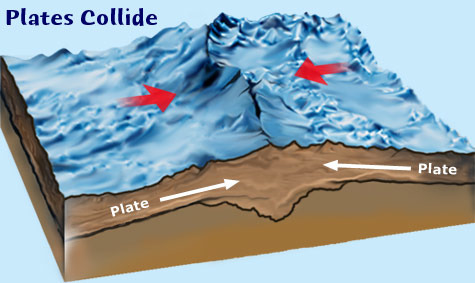
20
New cards
Passive Boundary (sliding) (transform)
Plates move laterally and the edges are rigid causing friction.
this can cause major earthquakes. ( North American and Pacific Plate)
this can cause major earthquakes. ( North American and Pacific Plate)
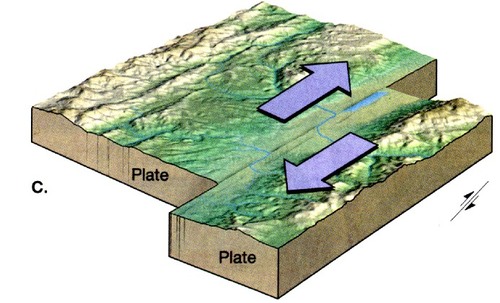
21
New cards
Fault line
place where an Earthquake originated due to a build up of pressure.
Gap between two tectonic plates or fractures in the rock caused by plate movement.
Gap between two tectonic plates or fractures in the rock caused by plate movement.
22
New cards
Focus
the point where the earthquake begins
23
New cards
Epicenter
Point on Earth's surface directly above an earthquake's focus
24
New cards
Seismic Wave
A vibration that travels through Earth carrying the energy released during an earthquake.
25
New cards
Richter scale
A scale that rates an earthquake's magnitude based on the size of its seismic waves.
26
New cards
Seismograph
A device that records ground movements (in the crust) caused by seismic waves as they move through Earth ( 1-10)
27
New cards
Mercalli scale
Visual analysis of the damage and of people's accounts . (1-12)
28
New cards
movement magnitude scale (MMS)
combines seismograph readings with the amount of rock movement recorded by strain-meters and tilt-meters.
29
New cards
Tsunami
Submarine Earthquake
30
New cards
Liquefaction
The process by which an earthquake's violent movement suddenly turns loose soil into liquid mud
31
New cards
early warning system
Alert people of seismic activity in the Pacific Ocean.
32
New cards
climate
The average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time
eg. Ireland has a cool temperate oceanic climate
eg. Ireland has a cool temperate oceanic climate
33
New cards
geomorphological region
area defined by their unique distinctive landscapes and features
eg. the Burren, Co.Clare
eg. the Burren, Co.Clare
34
New cards
administrative region
areas with political boundaries which governments divide countries into smaller sections to make easier to govern.
eg. county councils in Ireland and departments in France
eg. county councils in Ireland and departments in France
35
New cards
cultural region
an area in which a group of people share a similar culture and language
eg. The Gaeltacht (decline)
eg. The Gaeltacht (decline)
36
New cards
culture
Beliefs (religion), customs, language and traditions of a specific group of people.
37
New cards
Belgium
divided into Wallonia (South/French) and Flanders (North/Flemish-The Netherlands)
cultural divide- language line dividing the country, Brussels (headquarters of the EU) favours French speakers, language groups don't mix for marriage, education and jobs, government don't support Wallonia after the decline of the Sambre Meuse, Walloons have migrate to Flanders for work and they resent this, National Government has difficulty implementing policies to allows both regions development.
cultural divide- language line dividing the country, Brussels (headquarters of the EU) favours French speakers, language groups don't mix for marriage, education and jobs, government don't support Wallonia after the decline of the Sambre Meuse, Walloons have migrate to Flanders for work and they resent this, National Government has difficulty implementing policies to allows both regions development.
38
New cards
Northern Ireland
division of religion:
-Ulster Plantation
-Partition of Ireland
-The Troubles
-Good Friday Agreement
-Ulster Plantation
-Partition of Ireland
-The Troubles
-Good Friday Agreement
39
New cards
socio economic region
core region (GDA/Paris Basin) - highly developed area, high population density, high living standards, centre of transport/health/education/decision making.
40
New cards
peripheral region
lower living standards, low population density, lacking education/health/transport services.
41
New cards
hinterland
area around a city serviced by that city (area of influence)
42
New cards
nodal point
A place at which things converge (transport routes of air, rail, road, sea)
43
New cards
urban sprawl
uncontrolled outward spread of a city
44
New cards
conurbations
when 2 or more urban areas blend into 1 larger urban area. eg. Randstad, The Netherlands
45
New cards
primate city
when the capital is twice as big as the next city
46
New cards
industrial decline
a region that was previously heavily industrialised
47
New cards
de-industrialisation
when an area is no longer able to sustain this level of economic activity.
eg. Sambre Meuse
eg. Sambre Meuse
48
New cards
Sambre Meuse
GROWTH
- industrial development from the Industrial Revolution (1800s).
-coal and iron ore deposits were mined.
-approximately 125,000 employed.
-economic core of Belgium.
DECLINE
-1960s onwards.
-coal and iron ore deposits depleted (mines closed).
-coal was replaced by imported oil and gas.
-new integrated steel works developed along the coast of Antwerps.
EFFECTS
-mass unemployment.
-outward migration.
-high levels of industrial pollution and waste (very little inward investment).
-Flanders became the economic core region.
REVIVAL
-1980s onwards.
-Government and EU invested in the area.
-cleaning up of the landscape.
-development of new modern industrial estates.
-promotion of tourism.
-Ryanair based it's European hub in Charleroi.
-Caterpillar (CAT) have located in the Sambre Meuse also.
- industrial development from the Industrial Revolution (1800s).
-coal and iron ore deposits were mined.
-approximately 125,000 employed.
-economic core of Belgium.
DECLINE
-1960s onwards.
-coal and iron ore deposits depleted (mines closed).
-coal was replaced by imported oil and gas.
-new integrated steel works developed along the coast of Antwerps.
EFFECTS
-mass unemployment.
-outward migration.
-high levels of industrial pollution and waste (very little inward investment).
-Flanders became the economic core region.
REVIVAL
-1980s onwards.
-Government and EU invested in the area.
-cleaning up of the landscape.
-development of new modern industrial estates.
-promotion of tourism.
-Ryanair based it's European hub in Charleroi.
-Caterpillar (CAT) have located in the Sambre Meuse also.
49
New cards
Islamic World
Islam religion began in the 17th century from the teachings of the Prophet Mohammad. Muslims follow the Qu'ran. they believe in the one god of Allah and pray 5 times daily. worship at Mosques. dress in hijabs and niqabs. Ramedan. Alcohol and gambling prohibited. negative views connected to extremists acts connected to the Islamic faith.
50
New cards
Fold mountains
Areas of land which have been uplifted and are caused by bending and buckling in zones of plate collision
Eg. Himalayas and the Andes
Eg. Himalayas and the Andes
51
New cards
Anticline
A fold in rock that bends upward into an arch
block mts and Horst are its features
block mts and Horst are its features
52
New cards
Syncline
A fold in rock that bends downward to form a valley
rift valleys and grabens are it's features
rift valleys and grabens are it's features
53
New cards
Symmetrical folding
When rock bends symmetrically
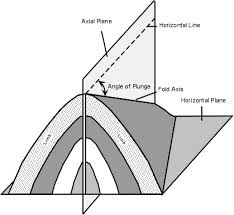
54
New cards
Asymmetrical folding
When rock folds in a diagonal form
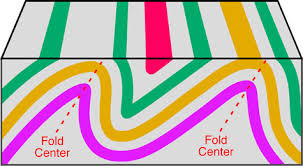
55
New cards
Overturned folding
When rock fold so much that it collocates in itself
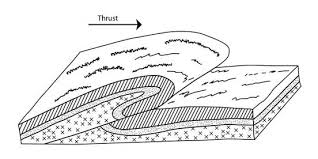
56
New cards
Caledonian Mts
450myo
rounded in appearance due to weathering and erosion.
eg. Dublin - Wicklow mts
rounded in appearance due to weathering and erosion.
eg. Dublin - Wicklow mts
57
New cards
Armorican Mts
270-250myo
less rounded in appearance due to younger age and less exposure to weathering and erosion
eg. Comeragh mts ( Waterford) and the Macgillycuddy Reeks (Kerry)
less rounded in appearance due to younger age and less exposure to weathering and erosion
eg. Comeragh mts ( Waterford) and the Macgillycuddy Reeks (Kerry)
58
New cards
Alpine Mts
60myo
highest mts of the world due to short period of exposure to weathering and erosion.
eg. Himalayas and Andes
highest mts of the world due to short period of exposure to weathering and erosion.
eg. Himalayas and Andes
59
New cards
Monocline
Caused by the localised uplifting of weaker rock which is compressed and causes a tilt in one direction
eg. Ben Bulben (Sligo)
eg. Ben Bulben (Sligo)
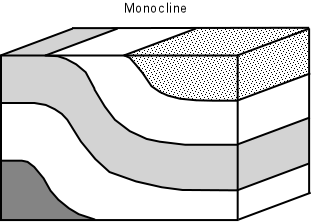
60
New cards
Doming
Caused by the localised pressure of rising magma which causes the overlying weaker rock to bulge upwards
eg. Slieve Bloom (Laois)
eg. Slieve Bloom (Laois)
61
New cards
fault
a crack in the earth's crust
62
New cards
Faulting
process of cracking that occurs when the folded land cannot be bent any further. It's when rocks are put under extreme pressure in zones where plates are separating (tension), colliding (compression) or sliding last one another (shearing).
63
New cards
Normal Fault
Fault caused by tension as plates separate
- known as a Horst and graben topography
eg. Rift Valley of East Africa
- known as a Horst and graben topography
eg. Rift Valley of East Africa
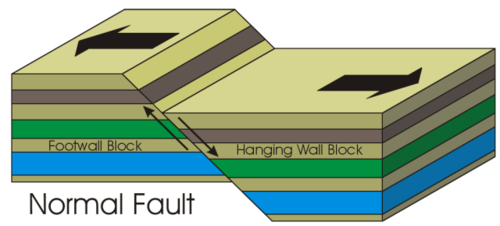
64
New cards
Reverse Fault
Fault caused by the compression when plates separate.
eg. Ox mts in Mayo
eg. Ox mts in Mayo
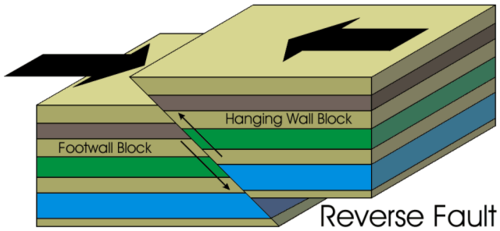
65
New cards
Transform Fault
Fault caused by the shearing if plates as they slide past each other
eg. San Andreas Fault-line in California
eg. San Andreas Fault-line in California