Basic Metabolic Panel
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
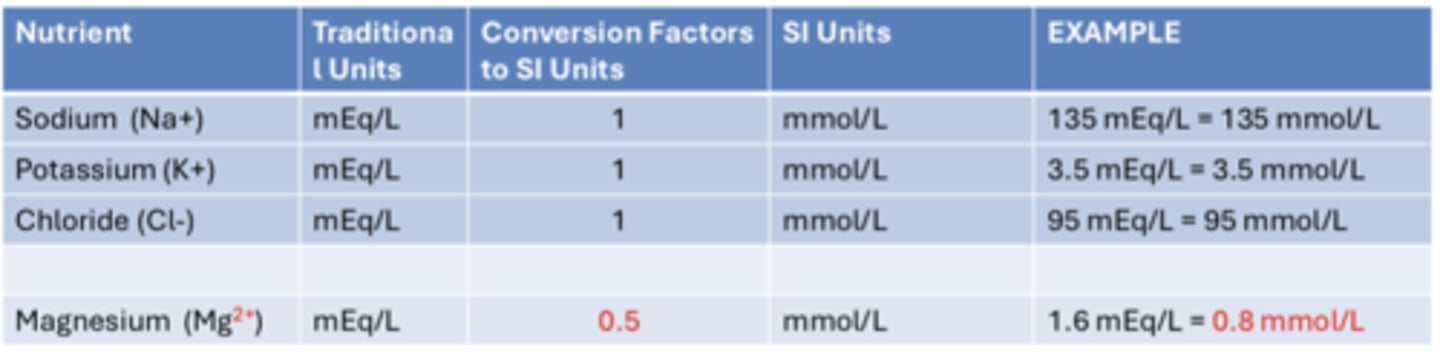
Traditional metabolic units
mEq/L, mg/dL, mcg/dL, mcg/L
International System (SI) units
mmol/L, μmol/L, nmol/L
What is a Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP)? What does it provide information on?
Provides information on the chemical balance and body metabolism (transformation of food into energy)
Electrolytes (minerals with an electric charge)
• control function of _____________ and ________________
• maintain the _____ balance of ___________
• maintain balance of __________
• control function of muscle and nerve
• maintain the pH balance (acid-base balance) of blood
• maintain balance of water
How is a BMP measured?
by a venous blood draw by a phlebotomist
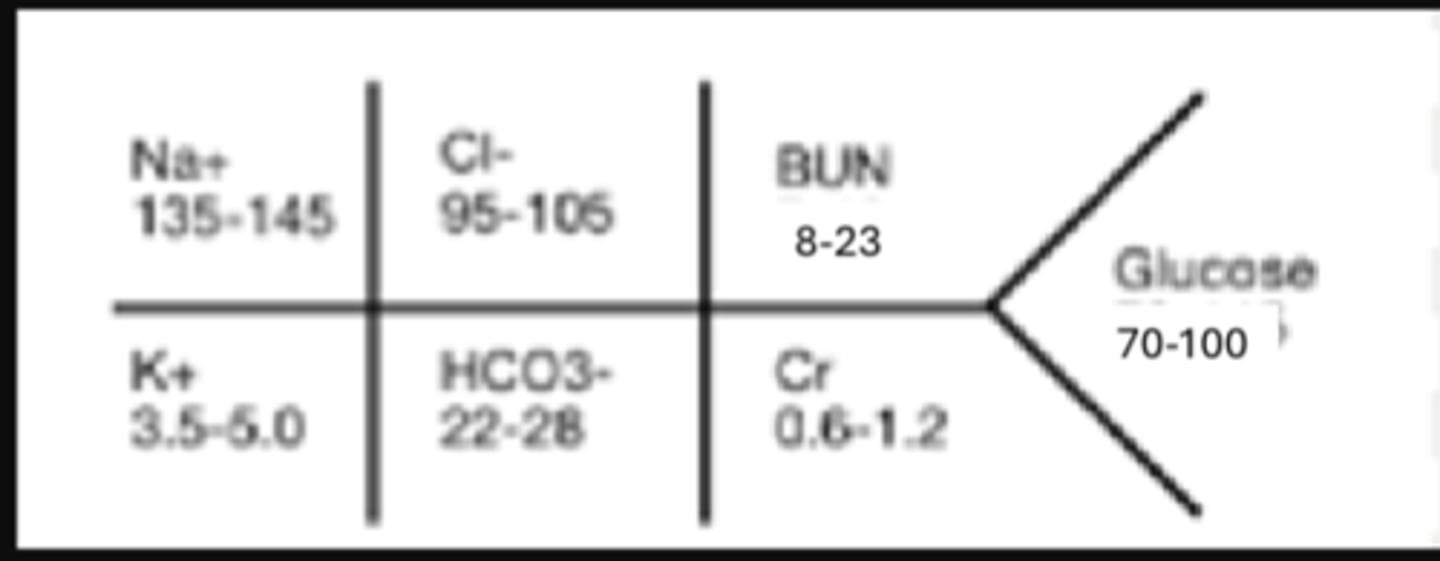
The FISHBONE for BMP
• Na+-Sodium
• K+-Potassium
• Cl- Chloride
• HCO3- Bicarbonate
• BUN-Blood Urea Nitrogen
• Cr-Creatinine
• Glucose-Glucose
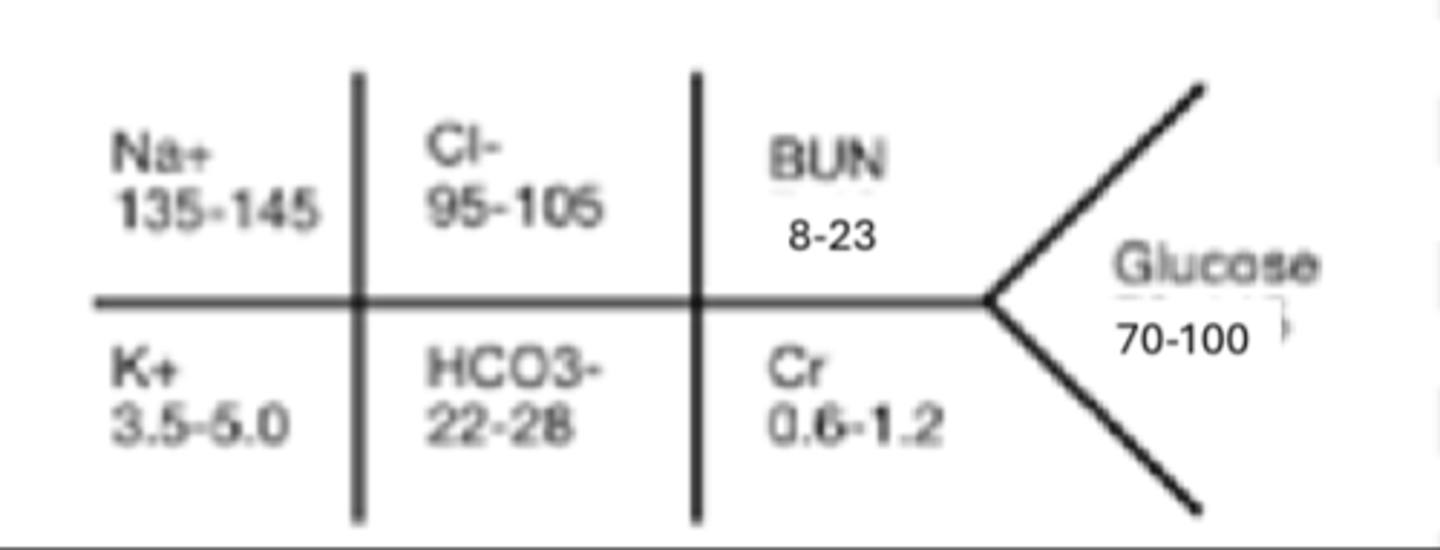
FISHBONE for BMP diagram
Normal Sodium (Na+) Range
135-145 mEq/L (135-145 mmol/L or mM)
Sodium (Na+) is crucial to......
maintain/regulate water balance and osmolality
Kidneys are the primary organ for what?
retaining and excreting sodium and water
Sodium (Na+) is the most abundant.....
- EXTRAcellular cation
- Major regulating factor for bodily fluid & water balance (HOMEOSTASIS)
Sodium (Na+) depends on a person's _________________
volume status- hypovolemia, euvolemia, hypervolemia
Hyponatremia value
- <120-125 mEq/L
- sodium depletion is more than total body water (depleted extracellular fluid)
What can cause hyponatremia?
- vomiting, diarrhea
- salt-losing nephropathy
-exercise (marathon runners-without salt replacement)
- water intoxication or excess sweating
Diluted causes of hyponatremia (5)
- SIDH-Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone
- Compromised kidney
- CHF
- cirrhosis
- neuroendocrine
What medications cause hyponatremia?
• Thiazides & Diuretics
• ACE Inhibitors, Aldosterone Antagonists, ARB
Hypernatremia value
>145-155 mEq/L
Hypernatremia causes
- dehydration
- polyuria
- hyperaldosteronism
- inadequate water intake
- excessive salt
What medications cause hypernatremia?
- steroids
- licorice
- oral contraceptives
Normal Potassium (K+) range
3.5-5.0 mEq/L (3.5-5 mmol/L)
What is the physiology of potassium (K+)?
What is it regulated by?
- excites muscle and nervous tissue (action potential)
- regulated by excretion from kidney
Potassium (K+) is the primary....
INTRAcellular cation-most abundant intracellular cation
K+ is involved with....
neuromuscular irritability
K+ also affects....
HEART rhythm-arrhythmias, affects contractions of muscle
Hypokalemia value
<3 mEq/L
Causes of hypokalemia
• Vomiting (Bulimia/Anorexia-Nervosa)
• Diarrhea chronic
• Renal Tubular acidosis Types I and II
• Hyperaldosteronism
• Cushing Syndrome
What medications cause hypokalemia?
loop diuretics
Hyperkalemia value
>6 mEq/L
Causes of hyperkalemia
• Dehydration
• Acute/Chronic Renal Failure
• Addison's Disease
• Renal tubular acidosis type IV
• Hypoaldosteronism
What medications cause hyperkalemia?
• Potassium Salt
• Potassium-Sparing diuretics (spironolactone)
• ACE Inhibitors & ARB
• NSAIDs
• Beta-Blockers
• High-dose TMP-SMX
• Verapamil
T/F: K+ and Vitamin K are the same thing
FALSE
K+ is NOT vitamin K
Normal Chloride (Cl-) range
95-105 mEq/L (95-105 mmol/L)
Chloride is partially regulated by _____________, also absorbed from ________________ and in _____________
- kidney
- small intestine (PASSIVE)
- large intestine
Chloride (Cl-) is the most abundant....
EXTRAcellular ANion
Chloride (Cl-) maintain correct ____________ of body _____, ___________ pressure, _____-______ balance
- distribution
- body water
- osmotic pressure
- acid-base balance
When chloride is lost...
alkalosis
When chloride is ingested/retained...
acidosis
Causes of hypochloremia
• Vomiting/Diarrhea
• Metabolic alkalosis
What medications cause hypochloremia?
• Laxative (Chronic)
• Diuretics
Causes of hyperchloremia
• DEHYDRATION
• Metabolic acidosis from diarrhea (loseHCO3-)
What medications cause hyperchloremia?
• Acetazolamide (Hyperchloremic acidosis)
• Androgens
• HCTZ
• Salicylate intoxication
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) or Bicarbonate (HCO3-) normal range
22-28 mEq/L
What is the purpose of CO2/HCO3-?
- ACID-BASE balance
- bicarbonate-carbonic acid buffer very important to keeping body fluid pH normal!
Critical low CO2/HCO3- value
<15 mEq/L
Critical high CO2/HCO3- value
>40 mEq/L
Normal range of Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN (not RBC))
8-23 mg/dL (2.9-8.2 mmol/L)
BUN physiology
- end product of protein metabolism excreted by the kidney
- Liver breaks down proteins your body uses to make ammonia (has N)
- Combines with carbon, hydrogen, oxygen to make UREA (waste product)
UREA goes from _______ to _______ and is filtered by __________ as a waste product in urine
- liver to kidneys
- kidney
Urea is the body's way to get rid of....
extra nitrogen
BUN is related to...
serum creatinine
Causes of decreased BUN
• Hepatic failure
• Nephrotic syndrome
• Starving & Malnourished (low protein and high carbohydrate diets)
Causes of increased BUN
• Renal failure (acute or chronic)
• Urinary tract obstruction
• Dehydration
• Increased Protein Breakdown: Shock, Fever,Burns
Medications that increase BUN
• drugs that affect kidneys
• Corticosteroids, tetracyclines
• ACEI/ARB
• NSAIDS
• Radio Contrast Dye
BUN/Cr ratio normal
normal 10:1-20:1
BUN/Cr ratio in <10:1
- What is seen? (3)
• advanced liver disease
• low protein diet/intake
• malnutrition
BUN/Cr ratio in > 20:1
- What is seen? (3)
• Dehydration
• GI bleeding
• Heart Failure
BUN/Cr ratio example
BUN: 30 mg/dL
Cr: 0.8 mg/dL
BUN/Cr= 30/0.8 = 37.5:1 <-- Increase in ratio, > 20:1
BUN/Cr ratio example
BUN: 8 mg/dL
Cr: 1.2 mg/dL
BUN/Cr= 8/1.2 = 6.7:1 <-- Decrease in ratio < 10:1
Creatinine (Cr) normal range
0.6-1.2 mg/dL (53-106 μmol/L)
Where is creatinine produced?
What is it a by-product of?
- Produced in muscle
- by-product of muscle activity
- waste product filtered and removed by kidneys
What is creatinine affected by? (4)
- age
- muscle mass
- low-protein diets
- medications
What does creatinine correlate to?
- correlates to glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
- INVERSE relationship between GFR and Cr
A 50% reduction in GFR leads to...
almost a double in Cr
Creatinine clearance is often a measure of _________, but not always
GFR
Causes of decreased Creatinine (Cr)
- reduced muscle mass
- malnourished
- aging
Causes of increased Creatinine
- Dehydration
- HF
- renal failure
- urinary tract obstruction
- nephrotoxic drugs
- hypothyroidism
Difference between creatine and creatinine
creatine is converted into creatinine
Normal range of glucose
70-100 mg/dL (3.3-5.6 mmol/L)
Glucose intake leads to what?
pancreatic production of insulin
Glucose is found in the _______________, it serves as a ___________________ for tissues. It is not excreted in the __________
- extracellular fluid
- balance of energy source
- urine
Glucose is the REASON we check...
BMP-fasting (8 hours)
Medications that can cause low glucose
insulin and medications for diabetes
Causes of severe hyperglycemia >500 mg/dL
• Diabetes mellitus
• Cushing syndrome
• Chronic pancreatitis
Medications that can increase glucose
• Corticosteroids (PREDNISONE)
• Phenytoin
• Estrogen
• Diuretics: Loop & thiazides
NON-DIABETES
FBG:
Non-FBG (Random):
A1c:
FBG: <100 mg/dl
Non-FBG (Random): <140 mg/dL
A1c: <5.7%
PREDIABETES
FBG:
Non-FBG (Random):
A1c:
FBG: 100-125 mg/dl
Non-FBG (Random): 140-199 mg/dl
A1c: 5.7-6.4%
DIABETES
FBG:
Non-FBG (Random):
A1c:
FBG: ≥ 126 mg/dl
Non-FBG (Random): ≥ 200 mg/dl*with classic symptoms of hyperglycemia (increased thirst, urination, hunger, etc.)
A1c: ≥ 6.4%
GOALS FOR PTS WITH DIABETES
FBG:
Non-FBG (1-2 hr post meal):
A1c:
FBG: 80-130 mg/dl
Non-FBG (1-2 hr post meal): <180 mg/dl
A1c: <7% or ~154 mg/dl
Level 1 hypoglycemia
<70 mg/dl and ≥ 54 mg/dl
Level 2 hypoglycemia
<54 mg/dl
Level 3 hypoglycemia
severe event characterized by altered mental and/or physical status requiring assistance for treatment, irrespective of glucose level
Symptoms of hypoglycemia
- shaky
- fast heartbeat
- sweating
- dizzy
- anxious
- hungry
- blurry vision
- weakness/fatigue
- headache
- irritable
Conversions between mEq/L to mmol/L